Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atmospheredfbd
Uploaded by
Fritzie Andrea Tirol0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageAsphalt is a black or brown petroleum-like material that can range from viscous liquid to glassy solid. It is obtained through the distillation of petroleum or from natural deposits. Asphalt consists mainly of hydrogen and carbon compounds along with minor amounts of nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen. Natural asphalt contains minerals while residual petroleum asphalt does not.
The atmosphere is the gas and aerosol envelope surrounding a planet that extends from its surface outward into space. Atmospheric density decreases with distance from the surface due to weaker gravitational pull. Some planets like Mercury have negligible atmospheres while others like Earth have retained theirs, which has allowed water to exist in all three phases and support life
Original Description:
Original Title
atmospheredfbd
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAsphalt is a black or brown petroleum-like material that can range from viscous liquid to glassy solid. It is obtained through the distillation of petroleum or from natural deposits. Asphalt consists mainly of hydrogen and carbon compounds along with minor amounts of nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen. Natural asphalt contains minerals while residual petroleum asphalt does not.
The atmosphere is the gas and aerosol envelope surrounding a planet that extends from its surface outward into space. Atmospheric density decreases with distance from the surface due to weaker gravitational pull. Some planets like Mercury have negligible atmospheres while others like Earth have retained theirs, which has allowed water to exist in all three phases and support life
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageAtmospheredfbd
Uploaded by
Fritzie Andrea TirolAsphalt is a black or brown petroleum-like material that can range from viscous liquid to glassy solid. It is obtained through the distillation of petroleum or from natural deposits. Asphalt consists mainly of hydrogen and carbon compounds along with minor amounts of nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen. Natural asphalt contains minerals while residual petroleum asphalt does not.
The atmosphere is the gas and aerosol envelope surrounding a planet that extends from its surface outward into space. Atmospheric density decreases with distance from the surface due to weaker gravitational pull. Some planets like Mercury have negligible atmospheres while others like Earth have retained theirs, which has allowed water to exist in all three phases and support life
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
asphalt, black or brown petroleum-like material that has a consistency varying from
viscous liquid to glassy solid. It is obtained either as a residue from
the distillation of petroleum or from natural deposits. Asphalt consists of compounds of
hydrogen and carbon with minor proportions of nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen. Natural
asphalt (also called brea), which is believed to be formed during an early stage in the
breakdown of organic marine deposits into petroleum, characteristically contains
minerals, while residual petroleum asphalt does not.
atmosphere, the gas and aerosol envelope that extends from the ocean, land, and ice-
covered surface of a planet outward into space. The density of the atmosphere decreases
outward, because the gravitational attraction of the planet, which pulls the gases and
aerosols (microscopic suspended particles of dust, soot, smoke, or chemicals) inward, is
greatest close to the surface. Atmospheres of some planetary bodies, such as Mercury,
are almost nonexistent, as the primordial atmosphere has escaped the relatively low
gravitational attraction of the planet and has been released into space. Other planets,
such as Venus, Earth, Mars, and the giant outer planets of the solar system, have
retained an atmosphere. In addition, Earth’s atmosphere has been able to
contain water in each of its three phases (solid, liquid, and gas), which has been
essential for the development of life on the planet.
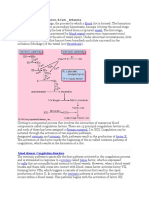
The evolution of Earth’s current atmosphere is not completely understood. It is thought
that the current atmosphere resulted from a gradual release of gases both from the
planet’s interior and from the metabolic activities of life-forms—as opposed to the
primordial atmosphere, which developed by outgassing (venting) during the original
formation of the planet. Current volcanic gaseous emissions include water vapour
(H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), carbon
monoxide (CO), chlorine (Cl), fluorine (F), and diatomic nitrogen (N2; consisting of two
atoms in a single molecule), as well as traces of other substances. Approximately 85
percent of volcanic emissions are in the form of water vapour. In contrast, carbon
dioxide is about 10 percent of the effluent.
During the early evolution of the atmosphere on Earth, water must have been able to
exist as a liquid, since the oceans have been present for at least three billion years. Given
that solar output four billion years ago was only about 60 percent of what it is
today, enhanced levels of carbon dioxide and perhaps ammonia (NH3) must have been
present in order to retard the loss of infrared radiation into space. The initial life-forms
that evolved in this environment must have been anaerobic (i.e., surviving in the
absence of oxygen). In addition, they must have been able to resist the biologically
destructive ultraviolet radiation in sunlight, which was not absorbed by a layer
of ozone as it is now.
You might also like
- R55-75N Manual Operación PDFDocument32 pagesR55-75N Manual Operación PDFJose NavasNo ratings yet
- Implementing Rules and Regulations of Chapter II - Code On SanitationDocument15 pagesImplementing Rules and Regulations of Chapter II - Code On SanitationDianne Kristine AvilaNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument9 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesJoe SellerNo ratings yet
- Gas Processing CourseDocument235 pagesGas Processing CourseIbraheem ElBakry88% (8)
- The Layers of The AtmosphereDocument54 pagesThe Layers of The AtmospheremjNo ratings yet
- L12 - Chemistry of The AtmosphereDocument40 pagesL12 - Chemistry of The AtmosphereHaneul KImNo ratings yet
- Distillation Tower DesignDocument66 pagesDistillation Tower DesignHavocFireNo ratings yet
- History of The EarthDocument40 pagesHistory of The EarthMarJenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-International Relations Theories PDFDocument47 pagesChapter 3-International Relations Theories PDFFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Seminar Presentation OnDocument27 pagesSeminar Presentation On9503599655100% (1)
- Alat Pengendali Emisi Dan Hasil Kajian CBADocument9 pagesAlat Pengendali Emisi Dan Hasil Kajian CBAAnnisa DzikriNo ratings yet
- Solubility of Chlorine in BrineDocument3 pagesSolubility of Chlorine in BrineSandro Goisis0% (1)
- Ammonia Process For FutureDocument5 pagesAmmonia Process For FutureSARFRAZ ALINo ratings yet
- Earth: Plate TectonicsDocument51 pagesEarth: Plate TectonicsAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Composition and Structure of The AtmosphereDocument47 pagesComposition and Structure of The AtmosphereJulia FlorencioNo ratings yet
- Earth Systems: Atmosphere: School of Earth Sciences SRTM University, Nanded - 431 606 Maharashtra, INDIADocument12 pagesEarth Systems: Atmosphere: School of Earth Sciences SRTM University, Nanded - 431 606 Maharashtra, INDIAMangam RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Mars Terraforming AgencyDocument3 pagesMars Terraforming Agencyraubn111No ratings yet
- Clarification NeededDocument1 pageClarification Neededsilakalantari4No ratings yet
- Composition and Structure of The AtmosphereDocument28 pagesComposition and Structure of The AtmospheredmmacarayaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Air Polllution On The AtmosphereDocument19 pagesEffects of Air Polllution On The Atmospherechristian ringorNo ratings yet
- Meteorology 1Document35 pagesMeteorology 1Lacanilao, Maureen Jaime C.No ratings yet
- Composition and Origin of The AtmosphereDocument60 pagesComposition and Origin of The AtmosphereAbhi JithNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument5 pagesEarthLime MNo ratings yet
- Protoplanet HypothesisDocument1 pageProtoplanet Hypothesiscrazysambitpanda100% (1)
- HW1 - Geological History of EarthDocument6 pagesHW1 - Geological History of EarthAna MariaNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere ChemistryDocument42 pagesAtmosphere ChemistryMelody B. MORATANo ratings yet
- Photolysis Hydrogen Escape Massive Helium Isotopic Ratios Noble Gases XenonDocument1 pagePhotolysis Hydrogen Escape Massive Helium Isotopic Ratios Noble Gases Xenonsilakalantari4No ratings yet
- Atmospheric Composition PresentationDocument23 pagesAtmospheric Composition PresentationInjeel AwanNo ratings yet
- Structure and Composition of The Earth's AtmosphereDocument3 pagesStructure and Composition of The Earth's AtmosphereIncrameezNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Meteorolgy: Air Is Tasteless, Odorless, and Invisible, Sun's EnergyDocument4 pagesEssentials of Meteorolgy: Air Is Tasteless, Odorless, and Invisible, Sun's EnergyAlexandrea ModillasNo ratings yet
- Ozone Depletion: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument23 pagesOzone Depletion: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaKrishnakant BajpaiNo ratings yet
- EARTHDocument3 pagesEARTHJane Rances PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Composition and Origin of The AtmosphereDocument71 pagesComposition and Origin of The AtmosphereGutierrez KennethNo ratings yet
- Origin of The OceansDocument6 pagesOrigin of The OceansSergio CrepaldiNo ratings yet
- La Atmósfera TerrestreDocument2 pagesLa Atmósfera TerrestreJesús Anibal CisnerosNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment in Science 2: Submitted ToDocument21 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment in Science 2: Submitted ToTrialhyn YanoNo ratings yet
- Geology Chapter 1Document14 pagesGeology Chapter 1lexay.mangadosiervoNo ratings yet
- Evolution Earth AtmosphereDocument8 pagesEvolution Earth AtmosphereMonica UrbietaNo ratings yet
- Ozone Depletion Describes Two Distinct But Related Phenomena Observed Since The Late 1970s: A SteadyDocument7 pagesOzone Depletion Describes Two Distinct But Related Phenomena Observed Since The Late 1970s: A Steadydyep31No ratings yet
- Ozone DepletionDocument24 pagesOzone DepletionKyla de Silva100% (1)
- Atmosphere - WikipediaDocument36 pagesAtmosphere - Wikipediamehdi512shah60No ratings yet
- The Origin of The Earth's Atmosphere: Still Many UncertaintiesDocument50 pagesThe Origin of The Earth's Atmosphere: Still Many UncertaintiesKarthik MadhuNo ratings yet
- Origin of Water in EarthDocument2 pagesOrigin of Water in EarthDr. Nitish Priyadarshi100% (1)
- Biogeochemical CycleDocument7 pagesBiogeochemical CycleArnel AdinoNo ratings yet
- Ozone Depletion - Chemistry ProjectDocument11 pagesOzone Depletion - Chemistry ProjectsujsamNo ratings yet
- G7 Science Q4 - Week 3 - Layers of AtmosphereDocument48 pagesG7 Science Q4 - Week 3 - Layers of Atmospherenona wayne dela peñaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentphanhaibangNo ratings yet
- Explanation TextDocument1 pageExplanation TextUlil Absor100% (2)
- Awal Evolusi AtmosferDocument16 pagesAwal Evolusi AtmosferRirin lestariNo ratings yet
- Ozone Depletion: Navigation SearchDocument22 pagesOzone Depletion: Navigation SearchNupur BhadraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 1 NotesLena RobertsNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere ReportDocument59 pagesAtmosphere Reportchadlow100% (1)
- ESE150-2 M1 HW3 VillaramaDocument6 pagesESE150-2 M1 HW3 VillaramaThortheGreayNo ratings yet
- Class 08Document17 pagesClass 08Musa al khwarizmiNo ratings yet
- Formation of Earth PowerPointDocument39 pagesFormation of Earth PowerPointAlice VermilionNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument2 pagesWaterAl Angel Chelsea TingaNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument19 pagesAtmospheremsNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument14 pagesAtmosphereCHRISTY BASILLANo ratings yet
- The Greenhouse Effect On EarthDocument43 pagesThe Greenhouse Effect On EarthsasisNo ratings yet
- Effects of Volcanic GasesDocument2 pagesEffects of Volcanic Gasesjunior.geologiaNo ratings yet
- All About EarthDocument5 pagesAll About EarthAnnalisa TealdiNo ratings yet
- Environmental ProblemsDocument13 pagesEnvironmental ProblemsShilpi RahiNo ratings yet
- Abiotic FactorsDocument37 pagesAbiotic FactorsTudor CiolanNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Volcanoes On WeatherDocument1 pageThe Impact of Volcanoes On WeatherkubashaniNo ratings yet
- Chem Pre Final and WorksheetDocument10 pagesChem Pre Final and WorksheetReyy ArbolerasNo ratings yet
- The Fourth Northern Climate Zone: Preparing for the Next Age of ManFrom EverandThe Fourth Northern Climate Zone: Preparing for the Next Age of ManNo ratings yet
- AgnosiassDocument4 pagesAgnosiassFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Sa N Anthony BurgessDocument3 pagesSa N Anthony BurgessFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- AsphaltstredDocument3 pagesAsphaltstredFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Love Happiness and Success - The Road To The FutureDocument1 pageLove Happiness and Success - The Road To The FutureFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Body Politic GeoDocument1 pageBody Politic GeoFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Chemical SymbolDocument4 pagesChemical SymbolFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- MetalDocument5 pagesMetalFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- AmalgamDocument1 pageAmalgamFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- MessageDocument1 pageMessageFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Patio ProcessDocument1 pagePatio ProcessFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Radioactive IsotopeDocument2 pagesRadioactive IsotopeFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- ResonanceDocument1 pageResonanceFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquationDocument1 pageChemical EquationFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- NeutronDocument2 pagesNeutronFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- TransmutationDocument1 pageTransmutationFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- HamomileDocument1 pageHamomileFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental DisordersDocument1 pageDiagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental DisordersFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Stockholm SyndromeDocument2 pagesStockholm SyndromeFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument2 pagesChemical KineticsFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- RoteinDocument2 pagesRoteinFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- CoagulationDocument2 pagesCoagulationFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Monarch ButterflyDocument9 pagesMonarch ButterflyFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- BrushDocument4 pagesBrushFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- EDM 204-Module 1 Unit 3Document33 pagesEDM 204-Module 1 Unit 3Fritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Painted LadyDocument1 pagePainted LadyFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Words To Inspire - 24 Powerful Moments From Recent Medical School Commencement SpeechesDocument7 pagesWords To Inspire - 24 Powerful Moments From Recent Medical School Commencement SpeechesFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Benefit Our Children and Enrich Their Educational ExperienceDocument1 pageBenefit Our Children and Enrich Their Educational ExperienceFritzie Andrea TirolNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Waste Water Treatment PlantDocument8 pagesPresentasi Waste Water Treatment Plantika yuliyani murtiharjonoNo ratings yet
- Below. Erasures Are Not AllowedDocument3 pagesBelow. Erasures Are Not AllowedChristian M. MortelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document10 pagesLecture 10AshkanNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet: Title: Refrigeration SystemDocument6 pagesLab Sheet: Title: Refrigeration SystemShan aliNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Kinetic Theory of Gases NotesDocument32 pagesClass 11 Physics Kinetic Theory of Gases NotesMath AddaNo ratings yet
- Learn About Oil and Gas SeparatorsDocument2 pagesLearn About Oil and Gas SeparatorsOlivier Whettem0% (1)
- Assignment No.1 - PE 401 - Fall 2020Document2 pagesAssignment No.1 - PE 401 - Fall 2020Dr-Adel SalemNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 Real Gases and Mixture of GasesDocument26 pagesChapter8 Real Gases and Mixture of GasesMUHAMMED FAISALNo ratings yet
- Design of Distillation ColumnDocument21 pagesDesign of Distillation Columnusmanafzal246100% (1)
- Types of Exapnsion Devices in RAC SystemsDocument4 pagesTypes of Exapnsion Devices in RAC SystemsNishit ParmarNo ratings yet
- Horizontal V-L SeparatorDocument3 pagesHorizontal V-L Separatoryamen-691904No ratings yet
- WWE - 2020 - 07 - Unit Operations - Plain Sedimentation PDFDocument48 pagesWWE - 2020 - 07 - Unit Operations - Plain Sedimentation PDFGHANTASALA VARUNNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Gauging Hydrautesting and Chemical CleaningDocument2 pagesCleaning Gauging Hydrautesting and Chemical CleaningJosephKaren LorzanoIlaganNo ratings yet
- Desalination +GF+Document31 pagesDesalination +GF+ahumadaliraNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Pneumatics SystemDocument11 pagesModule 1 Pneumatics SystemIvy Totanes TaborNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Lab ManualDocument29 pagesMass Transfer Lab ManualPrajwal ChavanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document2 pagesAssignment 5hossamkandil7No ratings yet
- c60 Cryogenic Gas Processing System (Exterran)Document4 pagesc60 Cryogenic Gas Processing System (Exterran)Martín Diego MastandreaNo ratings yet
- 06 PressureDocument9 pages06 PressureTahmedul Hasan TanvirNo ratings yet
- Answer For Final ExamDocument5 pagesAnswer For Final ExamLance OrlinoNo ratings yet
- Aset WTP PiayuDocument7 pagesAset WTP PiayuReinhard SimbolonNo ratings yet
- Group 17 NotesDocument16 pagesGroup 17 NotesChaitan TuduNo ratings yet