Professional Documents
Culture Documents
U1L4 Student Guide
Uploaded by
theoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
U1L4 Student Guide
Uploaded by
theoCopyright:
Available Formats
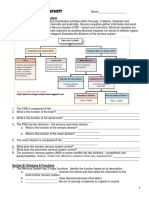
Unit 1: Introduction to the Brain
Student Guide Lesson 4
1. What are the objectives of today’s lesson?
2. What is a Neurotransmitter?
The brains c_______ m_________.
There are more than _____ kinds of neurotransmitters.
Neurotransmitters are released from n____ t_________, spread across the _________, and
attach to receptors on the t_______ _____.
3. What are the two different types of neurons?
A _____________ neuron is a neuron that _______ the neurotransmitter when an action
potential enters its axon terminal.
An _______ __________ occurs when a neuron _______ information down an axon, away
from its cell body.
A _______________ neuron is a neuron that ___________ the neurotransmitter after it has
crossed the synapse.
4. Take a few notes on the neurotransmission video:
5. What are 8 key neurotransmitters and what do they associate with?
Adrenaline; _______ or flight
Dopamine; p________
Serotonin; ________
GABA; c______
Acetylcholine; ___________
Glutamate; __________
Endorphins; e_________
U1L4 Student Guide 1
6. What does dopamine do?
Interacts with the ________ __________to organize behavior
Produces attention, stimulation, and focus to get something you want, satisfaction comes
afterward
Is associated with ___________ ____ ____________
7. What are the three parts of the brain that are involved the Reward triad?
8. What is the Rewards System?
Your reward system __________ the likelihood that an activity will have a __________
outcome.
The cortex is the d________ _________ that is responsible for e___________ ___________
and decisions made.
The amygdala assesses your e__________ _______ and evaluates the l_______ of ________.
The nucleus accumbens p___________ the r________ and r________ dopamine for you to
chase what you love and want.
9. What are some facts about the reward system?
The brain remembers w_____ and _________.
The brain _____________ behavior to a________ reward and experience a pleasurable
activity or experience again.
T______ is not really a ___________ to a teen.
The teen reward system is always on _____.
10. We know that in teens:
The influence of the a________ over the c_______ is stronger than the CORTEX over the
AMYGDALA.
Teens may know to make a better decision BUT may choose the opposite decision due to the
decision being driven by _________.
11. In Summary:
The cortex and amygdala do not have a m________ connection.
This explains why adolescents take _______ ________ than adults.
The teen brain weighs the r______ greater than the _______ and therefore drives the
decision-making process.
U1L4 Student Guide 2
12. Based on the video, take a few notes on how does the brain responds to fear?
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________
13. Why is fear useful?
It is a s_______ m_________.
The amygdala is the brain’s t______ c______.
S_____ ______ (unconscious)- amygdala prepares our body to respond to _______ and jump
starts our f_____ or f______ response.
Long path c_________ the a____________; confirmed vs. a false alarm.
A memory is created that may influence a person if a s________ s_________ occurs in the
future.
14. How can a teen strategize for informed decision-making?
Recognize and understand that the “___________ ________” affects decision-making
Practice s_________ d_____ and thinking about how to make a good decision before
a______
Ask a ________ adult for advice
Understand how you have the ability to s____-_________ and influence your decisions.
15. Triad Summary:
The brain balances p________ r_________ and threats and takes p______ a_______.
The teen brain loves to anticipate r_______.
The teen brain does not v______ ________ as accurately as the ______ brain.
U1L4 Student Guide 3
You might also like
- Rang Dale S Pharmacology Self Assessment Questions 7th PDFDocument62 pagesRang Dale S Pharmacology Self Assessment Questions 7th PDFJohita Paz100% (8)
- FAA Newcomer's Packet Online VersionDocument48 pagesFAA Newcomer's Packet Online VersionPeyton Brooke100% (3)
- Introduction to the Brain and NeurotransmittersDocument3 pagesIntroduction to the Brain and NeurotransmittersAle M0% (1)
- Schizophrenia NCMH Case StudyDocument41 pagesSchizophrenia NCMH Case StudyJohn Crisostomo89% (36)
- Brain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASSDocument15 pagesBrain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASSRenee NasserNo ratings yet
- Where Theres A Will Theres An A AnswersDocument9 pagesWhere Theres A Will Theres An A Answerssundevil2010usa4605No ratings yet
- Donald Hilton Address PornographyDocument24 pagesDonald Hilton Address Pornographyda5idnzNo ratings yet
- Neurobiological Basis of Human BehaviorDocument72 pagesNeurobiological Basis of Human Behaviorelvinegunawan0% (1)
- Your Brain On Porn Covenant EyesDocument47 pagesYour Brain On Porn Covenant EyesJose Leon AburtoNo ratings yet
- Molecular Origins of Human AttentionDocument260 pagesMolecular Origins of Human AttentionAndreea DumitrescuNo ratings yet
- U1L6 Student Guide - 2Document2 pagesU1L6 Student Guide - 2jonahNo ratings yet
- Brain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASS Private WorkbookDocument15 pagesBrain Breakthroughs MASTERCLASS Private WorkbookRida ArifNo ratings yet
- U1L8 Student Guide - 2Document5 pagesU1L8 Student Guide - 2jonahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Body Coordination: Form 4 ScienceDocument28 pagesChapter 2: Body Coordination: Form 4 ScienceSudhan NairNo ratings yet
- U1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1Document4 pagesU1L9 Student Guide (1) - 1jonahNo ratings yet
- " The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #8 ":: Longest Shortest CAN CannotDocument7 pages" The Nervous System, Part 1: Crash Course A&P #8 ":: Longest Shortest CAN CannotNargess OsmanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Elective: Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Science Elective: Nervous SystemVincqNo ratings yet
- U1L7 Student Guide (1) - 1Document4 pagesU1L7 Student Guide (1) - 1jonahNo ratings yet
- PAU1 - S2 L3 - Crash Course 3 - The Chemical Mind - QuestionsDocument3 pagesPAU1 - S2 L3 - Crash Course 3 - The Chemical Mind - QuestionsHiểu AnhNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ExplorationDocument6 pagesNervous System Explorationapi-306762527No ratings yet
- Student Guide: Unit 2: Brain Maintenance Lesson 2Document3 pagesStudent Guide: Unit 2: Brain Maintenance Lesson 2ria wuNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Concept MapDocument12 pagesNervous System Concept MapJo BrackenNo ratings yet
- 3RD Summative Exam in Science 6Document6 pages3RD Summative Exam in Science 6Maricris Palermo SancioNo ratings yet
- NegOr Q4 MAPEH7 Module4b v2Document13 pagesNegOr Q4 MAPEH7 Module4b v2Jayvee PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Managing Stress and Anxiety Through Positive Coping StrategiesDocument4 pagesManaging Stress and Anxiety Through Positive Coping StrategiesTarash JainNo ratings yet
- I. Give What Asked in The Following Questions Then Write The Letter of Your Answer To The Space Provided. (15 PTS.)Document2 pagesI. Give What Asked in The Following Questions Then Write The Letter of Your Answer To The Space Provided. (15 PTS.)John VencintNo ratings yet
- science6nerveDocument1 pagescience6nerveIvan joseph MarianoNo ratings yet
- Prelim PsychologyDocument3 pagesPrelim PsychologyRamon Jr. MontesorNo ratings yet
- Listening Test Unit 6 - 4STWDocument2 pagesListening Test Unit 6 - 4STWShanna DegraeveNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On DevelopmentDocument11 pagesWorksheet On Developmentjerden14233No ratings yet
- MAPEH 7 - HEALTH - ASSESSMENT EditedDocument2 pagesMAPEH 7 - HEALTH - ASSESSMENT EditedBeverly Rivera RositaNo ratings yet
- How To Become A Super Learner: Impress Your FriendsDocument11 pagesHow To Become A Super Learner: Impress Your Friendsciuciu.oxanaNo ratings yet
- SEMI Detailed LP - q2Document3 pagesSEMI Detailed LP - q2Harold DagoocNo ratings yet
- Module Objectives: When Psychologists Perform Research They Begin by Asking Questions Through Critical ThinkingDocument9 pagesModule Objectives: When Psychologists Perform Research They Begin by Asking Questions Through Critical ThinkingCarolina ArtigasNo ratings yet
- Nervous System QuizDocument1 pageNervous System QuizHolly May MontejoNo ratings yet
- U2L9 Student Guide - 1Document3 pagesU2L9 Student Guide - 1MuhayminNo ratings yet
- Week 6 PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT LAS G11Document3 pagesWeek 6 PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT LAS G11elainevidalrodriguezNo ratings yet
- M3L1 Enrichment Activity Cell Defense WorksheetDocument3 pagesM3L1 Enrichment Activity Cell Defense WorksheetHannah Althea Hijan JocsonNo ratings yet
- 10th Grade Science Exam ReviewDocument2 pages10th Grade Science Exam ReviewNawal Hayyah AmerNo ratings yet
- Ameba Sisters Worksheet (1)Document2 pagesAmeba Sisters Worksheet (1)Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ESSENTIAL QUESTIONSDocument8 pagesNervous System ESSENTIAL QUESTIONSAmanuelNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Answer Sheet Q2M3Document2 pagesGrade 7 Answer Sheet Q2M3Marian Alexis FernandezNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.2.3.ReactionTimeDocument5 pagesActivity 2.2.3.ReactionTimeAnahi ByersNo ratings yet
- Science Modul F2 Chapter 1 The World Through Our SenseDocument9 pagesScience Modul F2 Chapter 1 The World Through Our SensePua LingsiewNo ratings yet
- Gr2 Wk15 Scientific MethodDocument2 pagesGr2 Wk15 Scientific MethodAnn Gee Yeap50% (2)
- Human Body Focused Notes 2023 (2)Document9 pagesHuman Body Focused Notes 2023 (2)pickles.squad11No ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1.5: (Module 4) Thinking Outside The Box Our Family Destress Reinforcement InstructionDocument2 pagesACTIVITY 1.5: (Module 4) Thinking Outside The Box Our Family Destress Reinforcement InstructionJesel QuerobinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesLesson 4 Nervous SystemMohammad FalkayNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notetaking Template 08Document6 pagesCornell Notetaking Template 08api-570399600No ratings yet
- English 8 - Q4 - Las 1 RTPDocument4 pagesEnglish 8 - Q4 - Las 1 RTPMonica PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Formative Exam InsightsDocument4 pagesFormative Exam Insightsvenus caalemNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReviewDocument6 pagesNervous System ReviewJeff LouisNo ratings yet
- Robert Harper Student - Heritagehs - U3l4 Student GuideDocument7 pagesRobert Harper Student - Heritagehs - U3l4 Student Guideapi-536822799100% (1)
- Personal Development-Worksheet No. 5Document4 pagesPersonal Development-Worksheet No. 5Angelica QuinionesNo ratings yet
- Personal Development-Worksheet No. 5Document4 pagesPersonal Development-Worksheet No. 5Angelica QuinionesNo ratings yet
- Health: Quarter 4 - Module 1: The Nature of The Common Non-Communicable DiseasesDocument28 pagesHealth: Quarter 4 - Module 1: The Nature of The Common Non-Communicable Diseaseskiahjessie100% (1)
- 5PERDEVDocument23 pages5PERDEVSynergyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Language Quiz: Part A Key VocabularyDocument2 pagesUnit 5 Language Quiz: Part A Key VocabularyaLeKs GaRcíANo ratings yet
- Study Guide Unit 3 Psychology-2Document4 pagesStudy Guide Unit 3 Psychology-2api-726122866No ratings yet
- Mamalintao, Jahnuel S.-Module 1 Activity 1Document3 pagesMamalintao, Jahnuel S.-Module 1 Activity 1Jahnuel MamalintaoNo ratings yet
- Cell Defense WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Defense WorksheetChen Chen Deinla0% (2)
- Final Exam 2Document2 pagesFinal Exam 2Nathalie MolinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Reading and Writing AssignmentDocument3 pagesChapter 10 - Reading and Writing Assignmentteemo no JutsuNo ratings yet
- U4L2 Student Guide - 1Document5 pagesU4L2 Student Guide - 1MuhayminNo ratings yet
- Practice SheetDocument2 pagesPractice Sheetperousama2020No ratings yet
- Psychology for Allied Health & Healthcare Professionals: Essential PrinciplesFrom EverandPsychology for Allied Health & Healthcare Professionals: Essential PrinciplesNo ratings yet
- Project Exploring AustraliaDocument7 pagesProject Exploring AustraliatheoNo ratings yet
- Shark TankDocument2 pagesShark TanktheoNo ratings yet
- U1L2 - Student - Paynee Football Video Discussion QuestionsDocument2 pagesU1L2 - Student - Paynee Football Video Discussion QuestionstheoNo ratings yet
- Starting a Small Business PlanDocument1 pageStarting a Small Business PlantheoNo ratings yet
- Why Is Tourette's Syndrome More Common in Men Than in Women? PROPOSAL PRESENTATIONDocument15 pagesWhy Is Tourette's Syndrome More Common in Men Than in Women? PROPOSAL PRESENTATIONCharlene RiveraNo ratings yet
- Dopamine in ParkinsonsDocument2 pagesDopamine in ParkinsonsRanjitNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Love: Lust, Attraction and AttachmentDocument7 pagesThe Chemistry of Love: Lust, Attraction and AttachmentRodel Remotigue AleNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic Nervous System Anatomy and PropertiesDocument90 pagesSympathetic Nervous System Anatomy and PropertiesayaelsaiedNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Chapter 14Document52 pagesAbnormal Psychology Chapter 14Summer Lee100% (1)
- Dopamine and Love MDocument2 pagesDopamine and Love MYana PopovaNo ratings yet
- 2018 10 14-Digital-Cocaine - Edited PDFDocument2 pages2018 10 14-Digital-Cocaine - Edited PDFDarrel50% (2)
- Drug Book On EmergencyDocument21 pagesDrug Book On EmergencyDimpal Choudhary100% (4)
- Dr. Daniel H. Bessesen: The Biology of ObesityDocument58 pagesDr. Daniel H. Bessesen: The Biology of ObesityNational Press FoundationNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in ParkinsonismDocument16 pagesDrugs Used in ParkinsonismShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Science Behind HugDocument4 pagesScience Behind HugNirav HiinguNo ratings yet
- Addiction and Self-Control - Perspectives From Philosophy, Psychology, and Neuroscience (2013) PDFDocument289 pagesAddiction and Self-Control - Perspectives From Philosophy, Psychology, and Neuroscience (2013) PDFRichardNo ratings yet
- Up Clinical PharmacyDocument14 pagesUp Clinical Pharmacyyhaky.21No ratings yet
- Levodopa/carbidopa and Entacapone in The Treatment of Parkinson's Disease: Efficacy, Safety and Patient PreferenceDocument11 pagesLevodopa/carbidopa and Entacapone in The Treatment of Parkinson's Disease: Efficacy, Safety and Patient PreferenceSherlyy Kristiani.SNo ratings yet
- PL1101E Unit 6 Notes – Consciousness & Drugs SummaryDocument3 pagesPL1101E Unit 6 Notes – Consciousness & Drugs SummaryMichael BNo ratings yet
- JBKMNDocument4 pagesJBKMNTri Santi GhozaliNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument4 pagesNeurotransmittersSalman Khan100% (1)
- Medicinal Plants From Farm To Pharmacy 2019 PDFDocument445 pagesMedicinal Plants From Farm To Pharmacy 2019 PDFJesús Gabriel Múnera Baloco100% (3)
- Pharma Nca1 Notes MidtermDocument8 pagesPharma Nca1 Notes MidtermAICEL A. ABILNo ratings yet
- Varcarolis Foundations of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Halter Test BankDocument25 pagesVarcarolis Foundations of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Halter Test BankRobertWilliamswmya100% (47)
- Schizophrenia HandbookDocument48 pagesSchizophrenia Handbookrazvan_dNo ratings yet
- Insights Into Pathophysiology From Medication-Induced TremorDocument10 pagesInsights Into Pathophysiology From Medication-Induced TremoradindaNo ratings yet
- All-Natural 5-Meo-Dmt Sigma Receptor 1 Agonist and Its Therapeutic Impact in Mental and Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Mitochondrial ActivationDocument22 pagesAll-Natural 5-Meo-Dmt Sigma Receptor 1 Agonist and Its Therapeutic Impact in Mental and Neurodegenerative Diseases Through Mitochondrial ActivationLex UNo ratings yet