Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Bonds HW
Uploaded by
quinlan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
Chemical bonds hw.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageChemical Bonds HW
Uploaded by
quinlanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
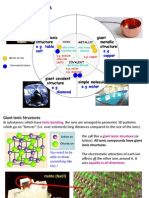
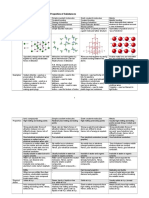
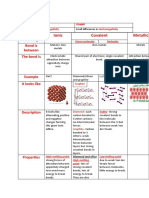
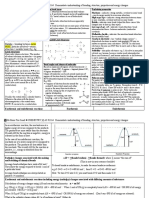
Chemical structure Property Diagram
Ionic network High melting and boiling points – strong
(eg. NaCl lattice) electrostatic bonds between particles
Poor conductors of electricity when solid – no free
moving particles
Good conductors of electricity when molten – ions
are free to move and carry charge
Good conductors of electricity when dissolved in a
solvent (eg. water) – water molecules break lattice
structure and ions are free to move and carry
charge
Covalent Extremely high melting and boiling points
network/macromolecules Hard – strong covalent bonds extending
/giant lattices throughout the lattice
(eg. diamond, silicon dioxide) Poor conductor of heat/electricity – no mobile ions
or free electrons
Most include carbon or silicon
Can occur in both elements and compounds
Covalent molecule Relatively low melting and boiling points – while
(eg. solid CO2) intramolecular forces are strong, intermolecular
dispersion forces are weak
Not hard – usually liquids or gases
Poor conductor of heat/electricity – no mobile ions
or free electrons
Can occur in both elements and compounds
Metallic High melting and boiling points – positive metal
(eg. Cu, Al) ions and sea of electrons form strong metallic
bonds
Malleable and ductile – rows of metal ions slide
over each other
Good conductors of electricity – outer shell
electrons are free and carry current
Shiny lustre – sea of electrons reflect light
You might also like
- Chemical Bonds and Lewis StructuresDocument5 pagesChemical Bonds and Lewis Structuresnicole MenesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsmartinNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDocument16 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- Chemical Bonding Structure..Document6 pagesChemical Bonding Structure..rachelNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes On StructuresDocument7 pagesChem Notes On StructuresHey thereNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Metallic Bonding: An Electrostatic Attraction Between A Lattice of Positive Ions and DelocalisedDocument1 pageChemical Bonding: Metallic Bonding: An Electrostatic Attraction Between A Lattice of Positive Ions and DelocalisedMatthew BongNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 - BondingDocument15 pages3.1.3 - BondingaprildazzleNo ratings yet
- CHM031 Module 2 ReviewerDocument10 pagesCHM031 Module 2 ReviewerrainNo ratings yet
- Summary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesSummary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesAnonymous L7ZuSkR100% (1)
- Property Explanation: Liquid StateDocument9 pagesProperty Explanation: Liquid StateNothing NameNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument16 pagesMetallic Bondingmathvin thummalaNo ratings yet
- Bonding Revision GuidesDocument1 pageBonding Revision Guidesapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Chemistry - Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesChemistry - Chemical BondingMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Structure and bonding determines physical propertiesDocument3 pagesStructure and bonding determines physical propertiesdebestieNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument1 pageStructure and BondingeohomegrownappsNo ratings yet
- Bonds ActivityDocument6 pagesBonds ActivityAna MtzNo ratings yet
- Comparison On BondsDocument7 pagesComparison On Bondseliastadele7No ratings yet
- 1 MetalsDocument39 pages1 MetalsManuel Tutacha ™No ratings yet
- Bonding Summary NotesDocument17 pagesBonding Summary NotesaleenNo ratings yet
- L05 (Bonding+Crystalline) 01Document14 pagesL05 (Bonding+Crystalline) 01amy.like.cooking.77No ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument17 pagesBonding and Structure: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyKhemou DjvickzNo ratings yet
- Elements, Compounds and AtomsDocument12 pagesElements, Compounds and Atomsananya.arumugarajanNo ratings yet
- Science Q2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience Q2 ReviewerSherra Mariel PintorNo ratings yet
- Metallic bondingDocument2 pagesMetallic bondingonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- When Atoms Meet: Chemical BondingDocument88 pagesWhen Atoms Meet: Chemical BondingWilsonNo ratings yet
- SCINOTESDocument2 pagesSCINOTESMark Beduya CuffeeNo ratings yet
- Notes On Covalent and Metallic BondingDocument8 pagesNotes On Covalent and Metallic Bondingselma samadNo ratings yet
- Anglo-Chinese School Structure of MatterDocument12 pagesAnglo-Chinese School Structure of Matterいい子No ratings yet
- Midterm Chem86 NotesDocument9 pagesMidterm Chem86 NotessujzNo ratings yet
- 2 Atomic StructureDocument43 pages2 Atomic StructureRafael ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- Bonding A LevelDocument2 pagesBonding A LevelHamzah ArabicaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDocument14 pagesLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Board NotesDocument19 pagesChemical Bonding Board NotesEmaan KhanNo ratings yet
- My FileDocument12 pagesMy FileKeeben BadoyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Study Notes Grade 10Document10 pagesChemistry Study Notes Grade 10Jynxx1387% (15)
- Covalent Bonding ReportDocument7 pagesCovalent Bonding ReportGun TnNo ratings yet
- Energy Band Structures and ConductivityDocument4 pagesEnergy Band Structures and ConductivityS.M. Abdul Mannan MahdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Properties and Applications of MetalsDocument18 pagesChapter 2: Properties and Applications of MetalsHiếu TrầnNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding NotesAyesha Awan100% (1)
- Atomic Bonding in SolidsDocument24 pagesAtomic Bonding in Solidsazad832393No ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding Properties in an Electron SeaDocument12 pagesMetallic Bonding Properties in an Electron SeailyasNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 1Document14 pagesElectrochemistry 1Warda Qasim AwanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument25 pagesChemistry NotesEbuka AnwasiNo ratings yet
- Covalent Ionic: Forms MoleculesDocument1 pageCovalent Ionic: Forms Moleculesash100% (1)
- Properties of Metals: Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesProperties of Metals: Metallic BondingNuan Ting NgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document1 pageChapter 15api-373649599No ratings yet
- Presentation On Electrical Conductors and Electrical InsulatorsDocument19 pagesPresentation On Electrical Conductors and Electrical InsulatorsAreejNo ratings yet
- Interatomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Document25 pagesInteratomic Forces: What Kind of Force Holds The Atoms Together in A Solid?Anonymous BW2VsFifi9No ratings yet
- Robot Electronics: Diode Basics and Semiconductor TheoryDocument82 pagesRobot Electronics: Diode Basics and Semiconductor TheoryCeyla Danişyan-AbuzərNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Chemical BondingQutub KhanNo ratings yet
- Forces of AttractionDocument21 pagesForces of AttractionDoveNo ratings yet
- Material Science and EngineeringDocument4 pagesMaterial Science and EngineeringErianne ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Document11 pagesCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument28 pagesMetallic BondingLysha Kana-an CarampatanaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids and SolidsDocument33 pagesProperties of Liquids and SolidsNicolette BingtanNo ratings yet
- Che 91164 AtaglanceDocument2 pagesChe 91164 AtaglanceJo StandleyNo ratings yet
- Ee 341 Course NotesDocument20 pagesEe 341 Course NotesMarvZz VillasisNo ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet