Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Anabolism
Uploaded by
Gievel Enoroba Lopez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views2 pagesAnabolism involves building complex molecules from simpler ones through biosynthesis, requiring energy. Examples include synthesizing proteins from amino acids and glucose into glycogen for energy storage. Photosynthesis is also an anabolic reaction that uses light energy to synthesize glucose from carbon dioxide and water, building structural materials for new cell growth and organism development through anabolic driving forces.
Original Description:
Original Title
What is Anabolism.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnabolism involves building complex molecules from simpler ones through biosynthesis, requiring energy. Examples include synthesizing proteins from amino acids and glucose into glycogen for energy storage. Photosynthesis is also an anabolic reaction that uses light energy to synthesize glucose from carbon dioxide and water, building structural materials for new cell growth and organism development through anabolic driving forces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views2 pagesWhat Is Anabolism
Uploaded by
Gievel Enoroba LopezAnabolism involves building complex molecules from simpler ones through biosynthesis, requiring energy. Examples include synthesizing proteins from amino acids and glucose into glycogen for energy storage. Photosynthesis is also an anabolic reaction that uses light energy to synthesize glucose from carbon dioxide and water, building structural materials for new cell growth and organism development through anabolic driving forces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
What is Anabolism?
Anabolic processes are building reactions. These processes use small, simple
molecules to create larger, more complex molecules, and require an input of
energy to do so. For example, single amino acids may be used to assemble
large, complex proteins. Because anabolism involves the synthesis of new
biological molecules, it is also known as biosynthesis.
The products of anabolism are often used as structural materials for the building
of new cells. Therefore, anabolism is the driving force behind the physical growth
of organisms.
Examples of Anabolic Reactions
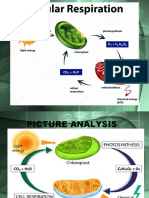
Photosynthesis
One example of an anabolic reaction is photosynthesis. This is series of
biochemical reactions that takes place in the chloroplasts of plants and involves
the synthesis of glucose from carbon dioxide gas and water molecules. Like all
anabolic reactions, photosynthesis requires an input of energy and is powered by
light energy from the sun.
Glycogen synthesis
Glycogen synthesis (AKA glycogenesis) is another example of anabolism. During
glycogen synthesis, glucose molecules are assembled into long chains of
glycogen, which are used to store energy in the liver and muscles.
You might also like
- Metabolic Concepts (Lecture 1-3)Document8 pagesMetabolic Concepts (Lecture 1-3)atifzea100% (1)
- Lec 9 Energy of LifeDocument29 pagesLec 9 Energy of LifeFahim AbidNo ratings yet
- Teachers Qualities As ProfessionalDocument5 pagesTeachers Qualities As ProfessionalGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Energy Coupling 1Document14 pagesEnergy Coupling 1Ralph jhenzel Uton100% (1)
- Metabolism and AtpDocument20 pagesMetabolism and AtpAbdul Rafay ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Catabolism Vs AnaboliismDocument3 pagesCatabolism Vs Anaboliismsnehashreemohanty39No ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument2 pagesMetabolismcheryl tayasNo ratings yet
- Bahan BBI 6 Dan 7Document1 pageBahan BBI 6 Dan 7SuciNo ratings yet
- Referat MetabolismDocument3 pagesReferat MetabolismVictor AndoniNo ratings yet
- Metabolic ProcessesDocument6 pagesMetabolic ProcessesMark Andrian PontanalNo ratings yet
- General Biology 101Document7 pagesGeneral Biology 101Czarina AsisNo ratings yet
- Plant MetabolismDocument15 pagesPlant Metabolismnegiineha2No ratings yet
- Bio Report PresentationDocument18 pagesBio Report Presentationaniqa0825No ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument4 pagesBioenergeticsMahnoor MansoorNo ratings yet
- Anabolis and CatabolismDocument6 pagesAnabolis and CatabolismUsman KhanNo ratings yet
- Microbial Physiology and GeneticsDocument3 pagesMicrobial Physiology and GeneticsYna Joy B. LigatNo ratings yet
- Coupled Reactions and Importance of Chloropyll and Other PigmentsDocument8 pagesCoupled Reactions and Importance of Chloropyll and Other PigmentsPerlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Biokimia: "Overview of Metabolic Reactions"Document20 pagesBiokimia: "Overview of Metabolic Reactions"IzzuddienNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis TheoryDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis TheoryAli Amir SufiNo ratings yet
- Plants: Photosynthesis Theory: BasicsDocument3 pagesPlants: Photosynthesis Theory: BasicsAli Amir SufiNo ratings yet
- Cellular MetabolismDocument4 pagesCellular Metabolismjanenathaneattl1No ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument51 pagesMetabolismHanna YajNo ratings yet
- Farmasi C Scanario 3Document26 pagesFarmasi C Scanario 3Pindi KogoyaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Lesson 2Document18 pagesWeek 2 Lesson 2Yury DesuNo ratings yet
- Photosenthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesPhotosenthesis and Cellular RespirationMonkey D. AilaNo ratings yet
- Module 12 PDFDocument13 pagesModule 12 PDFJohn Bernard VeloriaNo ratings yet
- 4 Bioenergetics ChecklistDocument2 pages4 Bioenergetics Checklistu19majli0No ratings yet
- Essay On PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageEssay On PhotosynthesisRameesha MalikNo ratings yet
- 2 Energy and MetabolismDocument4 pages2 Energy and MetabolismAmy SuarezNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis PathwaysDocument14 pagesBiosynthesis PathwaysLenber GarciaNo ratings yet
- What Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDocument8 pagesWhat Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDiana Jean Alo-adNo ratings yet
- The Energy of LifeDocument22 pagesThe Energy of LifeAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Biomolecules - Shobhit Nirwan-2 PDFDocument37 pagesBiomolecules - Shobhit Nirwan-2 PDFKanik100% (1)
- Biochem Cellular RespirationDocument54 pagesBiochem Cellular RespirationAila Grace PeriodicoNo ratings yet
- The Process of Obtaining and Using Energy by Living Organisms Are Best Explained by ThreeDocument2 pagesThe Process of Obtaining and Using Energy by Living Organisms Are Best Explained by ThreeemingNo ratings yet
- C) Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration (Reaction Paper)Document1 pageC) Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration (Reaction Paper)Babylyn SosaNo ratings yet
- Learning MaterialDocument7 pagesLearning MaterialPutri Dyah AstariNo ratings yet
- 9 1 PWPTPDFDocument19 pages9 1 PWPTPDFapi-262378640No ratings yet
- Biosynthetic Studies & Basic Metabolic Pathways: Prepared by Pooja H. Khanpara Asst. Professor Apip, JamnagarDocument89 pagesBiosynthetic Studies & Basic Metabolic Pathways: Prepared by Pooja H. Khanpara Asst. Professor Apip, Jamnagaranurag srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Slide 1Document1 pageSlide 1NickTheTurtleNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument51 pagesMetabolismShanna Sophia PelicanoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Week 3Document10 pagesBiochem Week 3divineNo ratings yet
- Bio Respiration Chapter SummaryDocument2 pagesBio Respiration Chapter SummaryYoussef Abdurrahman WeinmanNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Energy and MetabolismDocument29 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Energy and MetabolismClaire WeerepasNo ratings yet
- Bio ChemistryDocument16 pagesBio ChemistryAnonymous bQekGdBjKjNo ratings yet
- PhotosyntesisDocument1 pagePhotosyntesisSteven AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism: Transportation and Interaction: The Building Reactions-AnabolismDocument10 pagesMetabolism: Transportation and Interaction: The Building Reactions-AnabolismJP2001No ratings yet
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDocument9 pagesLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Micropara Transes 1.2Document4 pagesMicropara Transes 1.2Kyla Marie BadanaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration - An OverviewDocument19 pagesCellular Respiration - An Overviewapi-240096234No ratings yet
- How Animals Survive: Explain The Different Metabolic Process Involved in The Various Organ SystemDocument9 pagesHow Animals Survive: Explain The Different Metabolic Process Involved in The Various Organ SystemRoxan CampomanesNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisSai SubuNo ratings yet
- Cellular MetabolismDocument10 pagesCellular MetabolismIbrahim DukurayNo ratings yet
- Kreb's CycleDocument11 pagesKreb's Cyclemamahkelvinchidera018No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesisMina IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry IIDocument56 pagesBiochemistry IITrescia Mae EstilloreNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument8 pagesMetabolismJoel CabañasNo ratings yet
- 2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPDocument4 pages2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPTanvir KauraNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Identification of BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesIdentification of Biomoleculesmiko.mp4No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Speed or VelocityDocument17 pagesLesson 2 - Speed or VelocityGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- What Are MicrobesDocument2 pagesWhat Are MicrobesGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Thermo Combinegas Law and Ideal Gas LawDocument6 pagesThermo Combinegas Law and Ideal Gas LawGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- TTL2Document2 pagesTTL2Gievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument29 pagesTissues, Glands, and MembranesGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- RRL 5Document6 pagesRRL 5Gievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- TTL222Document5 pagesTTL222Gievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Report Microbio 1Document9 pagesReport Microbio 1Gievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- THERMODYDocument2 pagesTHERMODYGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- What Is DostDocument3 pagesWhat Is DostGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Thermody Lab 3Document3 pagesThermody Lab 3Gievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Thermody Lab 1Document3 pagesThermody Lab 1Gievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Thesis Chap. 1Document3 pagesThesis Chap. 1Gievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Significance of The StudyDocument3 pagesSignificance of The StudyGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Teaching ScienceDocument2 pagesTeaching ScienceGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument1 pageSummaryGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Script ttl2Document7 pagesScript ttl2Gievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Teaching PerformanceDocument3 pagesTeaching PerformanceGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- RINGWORMDocument3 pagesRINGWORMGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Science Innovative ProgramDocument11 pagesScience Innovative ProgramGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Thermody LabDocument1 pageThermody LabGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Responsible Person 111Document4 pagesResponsible Person 111Gievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- RRL 3Document7 pagesRRL 3Gievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument5 pagesScriptGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Responsible PersonDocument4 pagesResponsible PersonGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- RequestDocument1 pageRequestGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Module PDFDocument10 pagesModule PDFGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet
- Outline of The Wakayama Arsenic Murder CaseDocument22 pagesOutline of The Wakayama Arsenic Murder CaseGievel Enoroba LopezNo ratings yet