Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Long Exam Chemistry
Long Exam Chemistry
Uploaded by
Kassie Louise FALLORINAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Long Exam Chemistry
Long Exam Chemistry
Uploaded by
Kassie Louise FALLORINACopyright:
Available Formats
Part I.
Essay
1. An experimenter used the wrong instrument in conducting measurements. What
type of error is committed here? Justify your answer. [2 points]
This is an example of a systematic error. It is because while the experimenter used
the wrong instrument, the measurements gathered are still precise but not accurate.
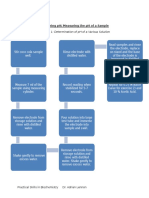
1. Describe a method through a schematic diagram to prepare 0.10 molar NaCl solution.
[2 points]
Weigh 5.844g of NaCl using
an analytical balance.
Transfer it into a beaker
Measure 1L of Distilled
water using a graduated
cylinder
Dilute the 5.844g of NaCl to
1L of Distilled Water
2. A food quality analyst is tasked to evaluate the ascorbic acid content of a commercial
orange juice. She took ten (10) measurements and found one value to be quite
different from the others. Should she reject this value? Justify your answer. [2 points]
Before rejecting the value, she should first conduct a Q-test to analyze whether the
measurement is an outlier or not. If it is an outlier, she should reject the value.
However if it is not, she should not reject the value.
3. Why is it important to use an indicator during titration? (2 pts.)
During titration, a noticeable pH change occurs near the equivalence point of acid-
base titration. Checking the pH level every time the acid or base is added, is time
consuming and is open to human error. Using an indicator to signal the end of
titration is accurate and not time consuming.
4. Cite two (2) precautionary measures when doing acid-base titration. (2 pts.)
One precautionary measure is to remove any air bubble present in the buret to
minimize error in reading the volume. Second precautionary measure when doing
acid-base titration is to continuously shake the titration flask during the addition of the
solution from the buret to ensure the solution is well-mixed.
5. Differentiate an equivalence point from an endpoint. (2 pt.)
Equivalence point signals the end of the chemical reaction, while endpoint signals the
change in pH level resulting in a color change of the indicator used where the moles
of the titrant exceeds the moles of the analyte. Endpoint occurs after the
equivalence
You might also like
- D12D380, Em-Ec96 - Esa - 02 - 586088Document2 pagesD12D380, Em-Ec96 - Esa - 02 - 586088asif basha100% (2)
- Practical Handbook of Pharmaceutical Chemistry for M.PharmFrom EverandPractical Handbook of Pharmaceutical Chemistry for M.PharmNo ratings yet
- HSC Chemistry PracticalsDocument10 pagesHSC Chemistry PracticalsRishi Máran33% (3)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 2 Practicals PDFDocument30 pagesCape Chemistry Unit 2 Practicals PDFDaniel Roopchand67% (3)
- Cadbury Dairy Milk's Advertising Campaigns in IndiaDocument35 pagesCadbury Dairy Milk's Advertising Campaigns in IndiaRohit GomesNo ratings yet
- Santrock Powerpoint Chapter 2Document32 pagesSantrock Powerpoint Chapter 2shaigest100% (1)
- Environmental Engg Lab ManualDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Engg Lab ManualAvinash DholiwalNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual of Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandPractical Manual of Analytical ChemistryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Lead Better, Start Younger: The Course DescriptionDocument4 pagesLead Better, Start Younger: The Course DescriptionBfp Rsix Maasin FireStationNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Experiment On Determination of PH: Sl. NoDocument12 pages1.0 Experiment On Determination of PH: Sl. NoJomana JomanaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Laboratory Formal ReportDocument3 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Laboratory Formal ReportAbigail MonisNo ratings yet
- PAG5.2 Student Determining Glucose Concentration - v1.0Document2 pagesPAG5.2 Student Determining Glucose Concentration - v1.0AmaniNo ratings yet
- PHE DCE606 Notes1Document14 pagesPHE DCE606 Notes1Aman PandatNo ratings yet
- Basic Lab Operations PDFDocument5 pagesBasic Lab Operations PDFErzhan OmarbekovNo ratings yet
- Self Directed Learning Sch3u Lab ManualDocument20 pagesSelf Directed Learning Sch3u Lab Manualapi-281434216No ratings yet
- Chemistry Stage 6 Year 12 Assessment Task and Marking Guidelines Titration Prac ExamDocument6 pagesChemistry Stage 6 Year 12 Assessment Task and Marking Guidelines Titration Prac ExamD Ray0% (1)
- Technical Bulletin 517 - Total Alkalinity Measurement in Natural WatersDocument4 pagesTechnical Bulletin 517 - Total Alkalinity Measurement in Natural WatersFirdaus YahyaNo ratings yet
- Nitttr Environmental Engineering and Public Health Lab ManualDocument215 pagesNitttr Environmental Engineering and Public Health Lab Manualkumsai7164% (11)
- PH, EC and TDSDocument7 pagesPH, EC and TDSBrijesh Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab Guide OBEDocument107 pagesBiochemistry Lab Guide OBEKathlyn Patricia RealNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment #1common Laboratory Operations (Part 2)Document11 pagesLaboratory Experiment #1common Laboratory Operations (Part 2)Monica RilveriaNo ratings yet
- DOC022.53.80225 10edDocument138 pagesDOC022.53.80225 10edPedro MamaniNo ratings yet
- Expt. 4 (Test For Carbohydrates)Document2 pagesExpt. 4 (Test For Carbohydrates)elizabethafrifa7No ratings yet
- Quantitative Estimation of Amino Acids by Ninhydrin: TheoryDocument11 pagesQuantitative Estimation of Amino Acids by Ninhydrin: TheoryNamrata KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Group 8 Lab Report RealDocument18 pagesGroup 8 Lab Report RealJopatrick MarananNo ratings yet
- Biochem For NSG Lab Manual 2022 EditionDocument40 pagesBiochem For NSG Lab Manual 2022 EditionJemaica A. JagolinoNo ratings yet
- Water Test Ali PPDocument7 pagesWater Test Ali PPAliNo ratings yet
- Weekly Written Report: Nature of JobDocument9 pagesWeekly Written Report: Nature of JobAngelo LazoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering LabDocument54 pagesEnvironmental Engineering LabErhom NathNo ratings yet
- Nessler Ammonia HACHDocument6 pagesNessler Ammonia HACHMesut GenişoğluNo ratings yet
- Official (Closed) / Non-Sensitive: Table 1Document4 pagesOfficial (Closed) / Non-Sensitive: Table 1John LebizNo ratings yet
- A DRAFT Chemtrac SOP - 120216Document12 pagesA DRAFT Chemtrac SOP - 120216Akin A. OkupeNo ratings yet
- Manual Cloro MerkDocument1 pageManual Cloro MerkzegoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document4 pagesExperiment 6Anton SalsaaNo ratings yet
- No 3Document12 pagesNo 3Punit Ratna ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Q2015 Physical Chemistry Measurements Laboratory Chemistry Department, Campus Monterrey Practice # 8 Distribution CoefficientDocument4 pagesQ2015 Physical Chemistry Measurements Laboratory Chemistry Department, Campus Monterrey Practice # 8 Distribution Coefficientandres_guadiana_7362100% (1)
- Teacher Resource Bank: GCE Chemistry PSA14: A2 Physical Chemistry - Determine An Equilibrium ContstantDocument8 pagesTeacher Resource Bank: GCE Chemistry PSA14: A2 Physical Chemistry - Determine An Equilibrium ContstantDzumani YamikaniNo ratings yet
- Titration Part 1Document5 pagesTitration Part 1takomolyentinNo ratings yet
- Enzyme-Technology-and-Biokinetics-Lab-Manual-BT-47L For Food LabDocument21 pagesEnzyme-Technology-and-Biokinetics-Lab-Manual-BT-47L For Food Labmasre semagnNo ratings yet
- RDEl NN IDocument2 pagesRDEl NN IOsama TaghlebiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Titration GuideDocument7 pagesChemistry Titration Guidedaniellelynch2007No ratings yet
- PP AliDocument7 pagesPP AliAliNo ratings yet
- Vitamin C (VC) Colorimetric Assay Kit: 8th Edition, Revised in February, 2018Document5 pagesVitamin C (VC) Colorimetric Assay Kit: 8th Edition, Revised in February, 2018SeftiyantiNo ratings yet
- Vitamin C (VC) Colorimetric Assay Kit: 8th Edition, Revised in February, 2018Document5 pagesVitamin C (VC) Colorimetric Assay Kit: 8th Edition, Revised in February, 2018SeftiyantiNo ratings yet
- Ascorbic Acid Titration Summer 2019 One PeriodDocument9 pagesAscorbic Acid Titration Summer 2019 One PeriodTaiga KagamiNo ratings yet
- Determination of PH Value - Ashish Arora - 0201ME16ME05Document5 pagesDetermination of PH Value - Ashish Arora - 0201ME16ME05ashishNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Analysis Laboratory Manual: Hebron University Prepared by Dr. Abdel Qader A. QawasmehDocument20 pagesPhytochemical Analysis Laboratory Manual: Hebron University Prepared by Dr. Abdel Qader A. QawasmehQOSSAY ALHROUSHNo ratings yet
- A Flowchat For Practical Skills 1Document6 pagesA Flowchat For Practical Skills 1curybooNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document3 pagesExperiment 7Ana RodriguesNo ratings yet
- BiochemlabDocument3 pagesBiochemlabMark jay LlanoNo ratings yet
- Weekly Written ReportDocument5 pagesWeekly Written ReportAngelo LazoNo ratings yet
- Lab Exp PHDocument12 pagesLab Exp PHMoeNo ratings yet
- Titration of Vinegar Lab ReportDocument8 pagesTitration of Vinegar Lab ReportIbrahim Abdulkadir JumaNo ratings yet
- DOC316.53.01219 8ed PDFDocument46 pagesDOC316.53.01219 8ed PDFRonal Urdaneta ChacinNo ratings yet
- PH of Water Extractions of Halogenated Organic Solvents and Their AdmixturesDocument2 pagesPH of Water Extractions of Halogenated Organic Solvents and Their AdmixturesShaker Qaidi100% (1)
- Bio Lab 2Document6 pagesBio Lab 2zombirificNo ratings yet
- The Amount of Acetic Acid (ML) To Neutralise Sodium-Bicarbonate Ethanoic-Acid Solution at Different Concentrations (Molar) of Acetic AcidDocument8 pagesThe Amount of Acetic Acid (ML) To Neutralise Sodium-Bicarbonate Ethanoic-Acid Solution at Different Concentrations (Molar) of Acetic AcideoqcwxhfhsedwcddmyNo ratings yet
- Amylase Quantification - StarchDocument4 pagesAmylase Quantification - StarchMuthu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Abx096002 IfuDocument3 pagesAbx096002 IfuLinh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Ujian BikarDocument4 pagesUjian BikarHana AiceNo ratings yet
- Exp 1,2,3Document13 pagesExp 1,2,3JWAN RA YA3QOBNo ratings yet
- Fat, Acidity, LR, SNF, TS, Apt, CobDocument9 pagesFat, Acidity, LR, SNF, TS, Apt, CobSahar SanwalNo ratings yet
- Doc3165301487 OjoDocument6 pagesDoc3165301487 OjoLilia Rosa Ibáñez SierrauyNo ratings yet
- Health Infographic - ExerciseDocument1 pageHealth Infographic - ExerciseKassie Louise FALLORINANo ratings yet
- Combined Script PDFDocument3 pagesCombined Script PDFKassie Louise FALLORINANo ratings yet
- Combined ScriptDocument3 pagesCombined ScriptKassie Louise FALLORINANo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Final SpeechDocument2 pages4th Quarter Final SpeechKassie Louise FALLORINANo ratings yet
- Reflection On Study HabitsDocument2 pagesReflection On Study HabitsKassie Louise FALLORINANo ratings yet
- Echoupal S PresentationDocument24 pagesEchoupal S PresentationPrabhat KumarNo ratings yet
- 9apr18 MArket PRofileDocument23 pages9apr18 MArket PRofileSinghRaviNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 BarreraDocument40 pagesActivity 1 BarreraCess RiveroNo ratings yet
- Art 29Document14 pagesArt 29lisa aureliaNo ratings yet
- FM200Document20 pagesFM200Matthew BennettNo ratings yet
- Kdidi 24621Document9 pagesKdidi 24621Abi NikilNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region XIIDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region XIINethz Flores TresbeNo ratings yet
- Committee Opinion: Preparing For Clinical Emergencies in Obstetrics and GynecologyDocument3 pagesCommittee Opinion: Preparing For Clinical Emergencies in Obstetrics and GynecologyMochammad Rizal AttamimiNo ratings yet
- Relay Iso9002: SLA XX VDC S L CDocument2 pagesRelay Iso9002: SLA XX VDC S L CMarudhasalamMarudhaNo ratings yet
- VFSS4 22012 Amerex ICE Installation Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument75 pagesVFSS4 22012 Amerex ICE Installation Operation and Maintenance ManualYAKOVNo ratings yet
- Stellant DualDocument3 pagesStellant DualAlexandra JanicNo ratings yet
- Report On Attendance: Isabela Colleges, IncDocument2 pagesReport On Attendance: Isabela Colleges, IncAnnabelle Dasalla DomingoNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Protection Corrosion Control and PreventionDocument67 pagesCathodic Protection Corrosion Control and PreventionRully KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Side Stream FiltrationDocument1 pageSide Stream FiltrationAmit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Polymers For Rheology Modification of OilsDocument24 pagesPolymers For Rheology Modification of Oilsjones32No ratings yet
- ZIM ART Guidelines 2016 - Review FinalDocument136 pagesZIM ART Guidelines 2016 - Review FinalCollen LihakaNo ratings yet
- GC University, Faisalabad Weekly Work Sheet Quality Enhancement CellDocument4 pagesGC University, Faisalabad Weekly Work Sheet Quality Enhancement CellRizwan YousafNo ratings yet
- Tugas Teknik Pengawetan Dan Emerging Processing Dalam Pengolahan PanganDocument5 pagesTugas Teknik Pengawetan Dan Emerging Processing Dalam Pengolahan PanganHasnaNo ratings yet
- Envi. Sci-BuayaDocument1 pageEnvi. Sci-BuayaRochelle MaeNo ratings yet
- Urban Education Institute COVID-19 StudyDocument17 pagesUrban Education Institute COVID-19 StudyTexas Public RadioNo ratings yet
- GE 24inch Front Load Washer: ModelsDocument99 pagesGE 24inch Front Load Washer: Modelsdan themanNo ratings yet
- 2021版MobiEye 700 H-046-007582-01 DR60使用说明书(英文)-153-200Document48 pages2021版MobiEye 700 H-046-007582-01 DR60使用说明书(英文)-153-200javo599No ratings yet
- s6 Unit 11. SolubilityDocument44 pagess6 Unit 11. Solubilityyvesmfitumukiza04No ratings yet
- Control Self Assessment (CSA) : JUNI 2020Document18 pagesControl Self Assessment (CSA) : JUNI 2020Frissca PrawithaNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice Cum Certificate of Extended Warranty RegistrationDocument2 pagesTax Invoice Cum Certificate of Extended Warranty RegistrationRavi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Drainage Condition in Water Logged Areas of Central Part in Chittagong City CorporationDocument6 pagesDrainage Condition in Water Logged Areas of Central Part in Chittagong City CorporationinventionjournalsNo ratings yet