Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q3-Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Benjamin FalletOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Q3-Lesson 3
Uploaded by
Benjamin FalletCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON
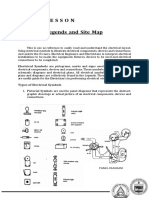
Floor Plan
A Floor Plan is a sketch of a structure showing a top view profile. It shows the
connections between rooms, spaces and other physical attributes at one layer of a
structure.
Dimensions are usually shown between the walls to project the room sizes and
wall length and width. The Scale is used to illustrate the floor plan in small details,
it means that each element in the sketch is proportional to the actual measurement.
In common practice, a 1:100M is used for residential establishment, this simply
means that the actual measurement are 100 times bigger than it is viewed on the
floor plan. So, 1cm on the floor plan is equivalent to 100cm or 1M in its actual size.
It is therefore, important to have an accurate dimension of the floor plan in
estimating bill of materials needed.
This also drawn to illustrate other details that includes fixtures like beds, sofa,
dining table, kitchen, sink, lavatory, etc.; This is also used for Electrical Layout,
which indicates lighting and power outlets and other electrical details such as:
A. Location of lighting outlets where it should be installed
B. Location of switches which will control a particular lighting fixtures
C. Types and ratings of lighting fixtures and switches
D. Location of power outlets for small appliance loads where it should be installed
E. Location of power outlets for special appliance loads where it should be
installed
F. Types and ratings of power outlets
G. Outlets that are connected to a branch circuit
H. Location of panel board, electric meter and service entrance
Basic Guidelines in Preparing Floor Plan
In planning for electrical layout the guidelines stated in the PEC is strictly
observed, hence the preference of the owner is also considered. The number of lighting
loads, convenience outlet, special purpose outlets and other electrical connections
should be promptly identified and provision for future expansion is also indicated to
avoid overloading and to avoid electrical fire incidents. It is why careful planning,
computation of loads and materials specification should be on the national electrical
code standards.
1. A lighting outlet (L.O.) should be installed in every room or area, usually it is
located at the center to provide direct lighting.
2. L.O. are connected by a line and group in such case where connection will be
the shortest.
3. A switch to control light is located near the door opening or wherever
convenient to place it.
4. A curve arrow is used to indicate the switch of a particular L.O.
5. A power outlet (C.O.) should be installed in every room or
area, usually it islocated at a wall where an appliance is
expected to be placed.
6. Limit the number of C.O. to 8 in one circuit, if there are more than 8 C.O’s
connect it in another circuit.
7. C.O. are connected by a line and group in such case where
connection will bethe shortest.
8. A weather proof type or ground fault circuit interrupter
(GFCI) type of C.O.should be used for damp or wet
location.
9. It is advisable to have 2-branch circuit for L.O. and C.O.
10. Special Purpose Outlet (S.P.O.) should be circuited
individually. S.P.O’s are airconditioning unit, electric range,
electric motors and other similar unit with a continuous
loading.
11. Panel board is centrally located in the building to make
the circuiting muchshorter, or in a place where it is easily
accessible.
12. Service entrance and electric meter generally installed
outside the building atthe property line wall or electric post
for easy access to the meter reader.
You might also like
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsFrom Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- M3 Q3 Floor PlanDocument13 pagesM3 Q3 Floor PlanJun GagatigaNo ratings yet
- A Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2From EverandA Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2No ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring PlanDocument39 pagesElectrical Wiring PlanniloNo ratings yet
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- 5 Tall Buildings AssignmentDocument7 pages5 Tall Buildings AssignmentNikitha SaramNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guide: Wiring, 8th Updated EditionFrom EverandUltimate Guide: Wiring, 8th Updated EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- New Chapter Four LastDocument36 pagesNew Chapter Four LastephremNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL Reading Electrical PlansDocument8 pagesELECTRICAL Reading Electrical PlansShereen AliNo ratings yet
- Unit2 ACU and OutletDocument9 pagesUnit2 ACU and OutletMelanie IbarretaNo ratings yet
- The First-Time Homeowner's Survival Guide: A Crash Course in Dealing with Repairs, Renovations, Property Tax Issues, and Other Potential DisastersFrom EverandThe First-Time Homeowner's Survival Guide: A Crash Course in Dealing with Repairs, Renovations, Property Tax Issues, and Other Potential DisastersRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Unit2 ACU and OutletDocument9 pagesUnit2 ACU and OutletMelanie IbarretaNo ratings yet
- B. Electrical Systems 1. Recommended Electrical Services System For Proposed Hotel and Mall Development 1.1. Electrical Supply Distribution SystemDocument10 pagesB. Electrical Systems 1. Recommended Electrical Services System For Proposed Hotel and Mall Development 1.1. Electrical Supply Distribution SystemShanaia BualNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation Design: Terminology and DefinitionsDocument27 pagesElectrical Installation Design: Terminology and DefinitionsMirkena kebede100% (1)
- Install CH 3Document66 pagesInstall CH 3Wudu YitagesuNo ratings yet
- Electrical InstallationDocument28 pagesElectrical Installationyonas abebeNo ratings yet
- BSD - M Odule 5Document38 pagesBSD - M Odule 5M MNo ratings yet
- Conduit Design GuidelinesDocument26 pagesConduit Design GuidelinesAnirudhNo ratings yet
- Wiring Guide 2020 - The Complete Indoor and Outdoor Wiring Guide Including Smart Home Wiring in 2020Document118 pagesWiring Guide 2020 - The Complete Indoor and Outdoor Wiring Guide Including Smart Home Wiring in 2020John Priester80% (5)
- 26 00 00 - Electrical General: Design & Construction Standards, Revised January 2013 26.00.00-1Document6 pages26 00 00 - Electrical General: Design & Construction Standards, Revised January 2013 26.00.00-1rediNo ratings yet
- Electrical WiringDomest 8310585Document20 pagesElectrical WiringDomest 8310585Berry KasanNo ratings yet
- Q1L6Document26 pagesQ1L6Jade Luise BernalesNo ratings yet
- (4.4) Socket Load:: Normal Sockets Have Different Ratings Which Can Be UsedDocument3 pages(4.4) Socket Load:: Normal Sockets Have Different Ratings Which Can Be UsedHassan AbdoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities Module 3Document85 pagesEngineering Utilities Module 3Neerom BaldemoroNo ratings yet
- Design Activity 2Document3 pagesDesign Activity 2MV5 ChannelNo ratings yet
- JKR GuidelinesDocument22 pagesJKR Guidelinessulphurdioxide100% (2)
- Chapter 4 - PresentationeeeeeeDocument79 pagesChapter 4 - PresentationeeeeeeyeabmotherNo ratings yet
- 5electrical Design Considerations EditedDocument40 pages5electrical Design Considerations EditedCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- EIE 414 5 Design EarthingDocument58 pagesEIE 414 5 Design Earthingakinlade ayomideNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Supplemental Floor Plan DrawingsDocument107 pagesGroup 5 - Supplemental Floor Plan DrawingsVillaquer Dominic P.No ratings yet
- Electrical Service Design 22Document1 pageElectrical Service Design 22Hell BoyNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Supplemental Floor Plan DrawingsDocument107 pagesGroup 5 - Supplemental Floor Plan DrawingsVillaquer Dominic P.No ratings yet
- El ReportDocument9 pagesEl ReportAtse MandelaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Work Procedure - Building, Testing, Checklist, SafetyDocument34 pagesElectrical Work Procedure - Building, Testing, Checklist, SafetyRITAM CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.3-3 Architectural Working DrawingsDocument6 pagesInformation Sheet 1.3-3 Architectural Working DrawingsNico C GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Loom Solar 340 Watt AC Module User Manual PDFDocument12 pagesLoom Solar 340 Watt AC Module User Manual PDFAnonymous 44uezWL0No ratings yet
- Upgrading of Electrical SystemDocument42 pagesUpgrading of Electrical SystemRafael SerranoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Basis of Design Standards GuidelinesDocument19 pagesElectrical Basis of Design Standards Guidelinesessk100% (1)
- Zufan Wallelegn Electrical ReportDocument8 pagesZufan Wallelegn Electrical ReportFitsum Tadesse100% (3)
- Slht-Tve 10 Q3 M2Document13 pagesSlht-Tve 10 Q3 M2Jecel Feb BiangosNo ratings yet
- EDECDocument41 pagesEDECsowmya G JNo ratings yet
- Student Development Programme On: Electrical Design Estimating & CostingDocument41 pagesStudent Development Programme On: Electrical Design Estimating & Costingsowmya G JNo ratings yet
- Steven - Xu - 13654872 - Case StudyDocument12 pagesSteven - Xu - 13654872 - Case Studyguanfanggei64No ratings yet
- CoordinationDocument35 pagesCoordinationkkkNo ratings yet
- Design Construction Manual2002 - 4Document1 pageDesign Construction Manual2002 - 4visanuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design ProcessDocument6 pagesElectrical Design ProcessUsha HaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design Estimation and Costing Unit 2Document10 pagesElectrical Design Estimation and Costing Unit 2srinimeha@gmail.com100% (1)
- Question # 1 M&E: 4 Year Architecture - ENGINEERING SYSTEM - Part C ExamsDocument8 pagesQuestion # 1 M&E: 4 Year Architecture - ENGINEERING SYSTEM - Part C ExamsMuhammad HammadNo ratings yet
- Wiring ProjectDocument10 pagesWiring ProjectGarion CharlesNo ratings yet
- 02 13 Section LightingSystemRev05Document33 pages02 13 Section LightingSystemRev05Sanj PandeyNo ratings yet
- PRE Electrical in Residence 2022Document19 pagesPRE Electrical in Residence 2022Maricar SsiNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications - Cable LayingDocument48 pagesTechnical Specifications - Cable LayingShkelzen GoxhajNo ratings yet
- EIM 11 - Q3 Module 2Document6 pagesEIM 11 - Q3 Module 2Wilbert EleccionNo ratings yet
- WEEK 12 - Integration of M&EDocument35 pagesWEEK 12 - Integration of M&EHazwani SaparNo ratings yet
- Select SplitDocument8 pagesSelect Splithodabele135No ratings yet
- Commercial and Residential Electrical InstallationDocument15 pagesCommercial and Residential Electrical InstallationCovid VirusNo ratings yet
- Cinema Act & Hospital LightingDocument3 pagesCinema Act & Hospital LightingBadarul MuneerNo ratings yet
- TLE 9 EIM 9 Q3 M2revDocument5 pagesTLE 9 EIM 9 Q3 M2revBenjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- M1-General Requirements For Electrical InstallationDocument4 pagesM1-General Requirements For Electrical InstallationBenjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- Q3-Lesson 4Document4 pagesQ3-Lesson 4Benjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- Facebook GuideDocument7 pagesFacebook GuideBenjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring DiagramDocument12 pagesElectrical Wiring DiagramBenjamin Fallet100% (1)
- General InstructionsDocument37 pagesGeneral InstructionsBenjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- TVL IA EP9 Week8Document4 pagesTVL IA EP9 Week8Benjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- Hand Tool BestDocument14 pagesHand Tool BestBenjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- TOS Q1 TLEICTCSS 9 - Jonalyn AmbronaDocument2 pagesTOS Q1 TLEICTCSS 9 - Jonalyn AmbronaBenjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- Access Information Using ComputerDocument7 pagesAccess Information Using ComputerBenjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Industrial Arts-Electrical Installation and Maintenance Quarter 2 - Module 1Document35 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Industrial Arts-Electrical Installation and Maintenance Quarter 2 - Module 1Benjamin Fallet100% (6)
- Basic Concepts in Electronics ServicingDocument13 pagesBasic Concepts in Electronics ServicingBenjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- TLE10 - Ia - Electronicproductsassembly&servicing - q2 - Mod1 - Servicingconsumerelectronicproducts&systems... - v3 (85 Pages)Document85 pagesTLE10 - Ia - Electronicproductsassembly&servicing - q2 - Mod1 - Servicingconsumerelectronicproducts&systems... - v3 (85 Pages)Benjamin FalletNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Curve FittingDocument19 pagesChapter 5 Curve FittingNiguse GeteNo ratings yet
- Offshore Drilling Waste Management ReviewDocument289 pagesOffshore Drilling Waste Management ReviewObande OrinyaNo ratings yet
- SCDL Organizational Behaviour Paper - 2Document9 pagesSCDL Organizational Behaviour Paper - 2Kattey Spares100% (2)
- Kaossilator Manual PDFDocument80 pagesKaossilator Manual PDFypdeaNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6011 Assessment 3 Implementing Evidence-Based PracticeDocument5 pagesNURS FPX 6011 Assessment 3 Implementing Evidence-Based PracticeEmma WatsonNo ratings yet
- Zetetic Cosmogony - by Thomas Winship, Aka RectangleDocument213 pagesZetetic Cosmogony - by Thomas Winship, Aka RectangleAristos RavmidesNo ratings yet
- Axial Leaded High Frequency Pulse CapacitorsDocument3 pagesAxial Leaded High Frequency Pulse Capacitorsgrasia77No ratings yet
- INT 213 Quiz QuestionsDocument17 pagesINT 213 Quiz QuestionsboombamNo ratings yet
- Engine Description: CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesEngine Description: Characteristicshorny69No ratings yet
- Particulate Matter in Injectables, USP Criteria - 1Document6 pagesParticulate Matter in Injectables, USP Criteria - 1SolomonNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Street Light System Using RF TransmissionDocument5 pagesIntelligent Street Light System Using RF TransmissionAbdirahman Elmi GurreNo ratings yet
- Davian Litcmore CAPE Comp Sci Unit2 Ia 2011Document80 pagesDavian Litcmore CAPE Comp Sci Unit2 Ia 2011Davian Kal'El LitchmoreNo ratings yet
- IntR 12 2013 0266Document22 pagesIntR 12 2013 0266demigoddess nixieNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of AsthmaDocument53 pagesPharmacotherapy of AsthmaStella Aprilia NurNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 09: Aim: Backtracking Ii: Implement Hamiltonian Cycle. TheoryDocument5 pagesExperiment No: 09: Aim: Backtracking Ii: Implement Hamiltonian Cycle. TheoryAbhinav aroraNo ratings yet
- Euralille - Centre International D'affaires LilleDocument20 pagesEuralille - Centre International D'affaires LilleHafiz AmirrolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Fesibility StudyDocument43 pagesChapter 2 - Fesibility StudyDaniella A. LazaroNo ratings yet
- Sephora Brand AuditDocument30 pagesSephora Brand Auditapi-294767507100% (2)
- Caterpillar Global Solutions: 50/60 HZ Switchable Genset Ipp Application (Wiring)Document19 pagesCaterpillar Global Solutions: 50/60 HZ Switchable Genset Ipp Application (Wiring)Jonathan Javier Ceballos Bonilla100% (2)
- LSI SAS Error CodesDocument36 pagesLSI SAS Error CodesThumbMcGee100% (2)
- Kinetic ReleaseNotes 2023.1.9Document102 pagesKinetic ReleaseNotes 2023.1.9Samivel KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- VTU Exam Question Paper With Solution of 18CS33 Analog and Digital Electronics March-2021-Dhanya ViswanathDocument43 pagesVTU Exam Question Paper With Solution of 18CS33 Analog and Digital Electronics March-2021-Dhanya Viswanath1DT20CS072 MANISHA POONIANo ratings yet
- C++: A General Purpose Language and LibraryDocument24 pagesC++: A General Purpose Language and LibrarySobar KhanNo ratings yet
- The Return of Population Control: Incentives, Targets, and The Backlash Against CairoDocument4 pagesThe Return of Population Control: Incentives, Targets, and The Backlash Against CairoPopulation & Development Program (PopDev)100% (1)
- 172 - Villongco v. YabutDocument2 pages172 - Villongco v. YabutPre Pacionela100% (1)
- ENM401-Speaking Examination - SVDocument4 pagesENM401-Speaking Examination - SVDinh Diem Linh (K17 CT)No ratings yet
- Curtiss Wright February2017 BulletinDocument60 pagesCurtiss Wright February2017 Bulletinal marmokaNo ratings yet
- Project On BudgetingDocument75 pagesProject On BudgetingManeha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sony VPL Ex100 SpecsDocument4 pagesSony VPL Ex100 SpecscmarquespNo ratings yet
- Keyman Insurance Lic India PolicyDocument2 pagesKeyman Insurance Lic India PolicyPriyanka KumariNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsFrom EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (242)
- Construction Process Planning and Management: An Owner's Guide to Successful ProjectsFrom EverandConstruction Process Planning and Management: An Owner's Guide to Successful ProjectsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedFrom EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignFrom EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Civil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeFrom EverandCivil Engineer's Handbook of Professional PracticeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Homeowner's DIY Guide to Electrical WiringFrom EverandThe Homeowner's DIY Guide to Electrical WiringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Building Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1From EverandBuilding Construction Technology: A Useful Guide - Part 1Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Real Life: Construction Management Guide from A-ZFrom EverandReal Life: Construction Management Guide from A-ZRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Sustainable Design and Build: Building, Energy, Roads, Bridges, Water and Sewer SystemsFrom EverandSustainable Design and Build: Building, Energy, Roads, Bridges, Water and Sewer SystemsNo ratings yet
- Welding for Beginners in Fabrication: The Essentials of the Welding CraftFrom EverandWelding for Beginners in Fabrication: The Essentials of the Welding CraftRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Estimating Construction Profitably: Developing a System for Residential EstimatingFrom EverandEstimating Construction Profitably: Developing a System for Residential EstimatingNo ratings yet
- Pile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbFrom EverandPile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Connections in Steel Structures III: Behaviour, Strength and DesignFrom EverandConnections in Steel Structures III: Behaviour, Strength and DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Post Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AFrom EverandPost Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&ANo ratings yet
- Essential Building Science: Understanding Energy and Moisture in High Performance House DesignFrom EverandEssential Building Science: Understanding Energy and Moisture in High Performance House DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Complete Guide to Building With Rocks & Stone: Stonework Projects and Techniques Explained SimplyFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Building With Rocks & Stone: Stonework Projects and Techniques Explained SimplyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideFrom Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- The Everything Woodworking Book: A Beginner's Guide To Creating Great Projects From Start To FinishFrom EverandThe Everything Woodworking Book: A Beginner's Guide To Creating Great Projects From Start To FinishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- BIM and Construction Management: Proven Tools, Methods, and WorkflowsFrom EverandBIM and Construction Management: Proven Tools, Methods, and WorkflowsNo ratings yet
- Markup & Profit: A Contractor's Guide, RevisitedFrom EverandMarkup & Profit: A Contractor's Guide, RevisitedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (11)
- The Aqua Group Guide to Procurement, Tendering and Contract AdministrationFrom EverandThe Aqua Group Guide to Procurement, Tendering and Contract AdministrationMark HackettRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)