Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sex Linked Genetics Inthnk2
Uploaded by
Leander KrowinkelOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sex Linked Genetics Inthnk2
Uploaded by
Leander KrowinkelCopyright:
Available Formats
4.3.
5 Sex Chromosomes and Sex Linkage Questions
Each person normally has one pair of sex chromosomes in each cell.
Females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome. (XY)
The X chromosome contains about 1000 genes, including the genes for haemophilia and colour
blindness. For this reason these genes are said to be sex-linked.
a. Write a definition of “sex-linkage”.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
b. Name two examples of sex-linked genetic disorders. (hint – read the introduction again)
……………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………….
c. Explain why human females can be homozygous or heterozygous for sex-linked genes,
and why males cannot.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
What is the best notation to use for these alleles of genes found on the X-chromosome?
We need to show the X chromosome or the y chromosome in the notation.
The allele must also be shown and this can be recessive or dominant.
For these reasons alleles are usually written as XN or Xn or y
-
–
(the represents the absence of an allele on the y chromosome)
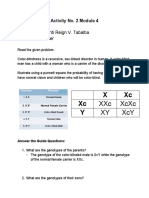
d. The allele for colour blindness (n) is recessive to the allele for normal vision (N). This
gene is carried on the X chromosome. For this reason the notation of these alleles is X n
and XN. Complete the table below to show the genotypes and phenotypes of individuals
with regard to colour blindness.
Female Male
Normal XNXN
Affected
Carrier Not possible! Why?
© David Faure, InThinking ThinkIB.net/biology adapted from a worksheet by John McMurtry
1
4.3.5 Sex Chromosomes and Sex Linkage Questions
e. In the space below, complete a punnet grid to show a cross between a male with normal
vision and a female carrier of colour-blindness.
What is the expected ratio of F1 phenotypes?
1. Haemophilia is a blood-clotting disorder that is also recessive and sex-linked.
The alleles are usually written as XH = normal clotting allele and Xh = haemophilia allele
a. State the normal function of this gene, associated with haemophilia.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
b. Describe the effects and symptoms of haemophilia.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
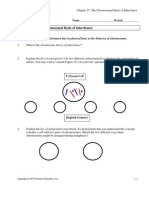
c. Use the pedigree chart to deduce all the possible genotype(s) of the named individuals.
Squares represent males, circles females. Red colouring represents haemophilia.
Leopold
Helen
Alice of Athlone
Lady May
Rupert
Bob
Britney
© David Faure, InThinking ThinkIB.net/biology adapted from a worksheet by John McMurtry
2
You might also like
- The Role of Melanin in Our Afrikan Re-Education / ReAfrikanization Process Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Document40 pagesThe Role of Melanin in Our Afrikan Re-Education / ReAfrikanization Process Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Jeffrey Greer100% (1)
- Chapter 15 Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceDocument7 pagesChapter 15 Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceJUNG LEE100% (1)
- Lab 02 Extra - Extentions To Mendelian GeneticsDocument6 pagesLab 02 Extra - Extentions To Mendelian Genetics13ucciNo ratings yet
- The Triune Brain, Hypnosis and the Evolution of ConsciousnessFrom EverandThe Triune Brain, Hypnosis and the Evolution of ConsciousnessNo ratings yet
- Endurance Exercise Performance The PhysiologyDocument10 pagesEndurance Exercise Performance The Physiologymsalungin1313No ratings yet
- Autonomic FailureDocument12 pagesAutonomic FailureAndreina AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Immunization With SARS Coronavirus Vaccines Leads To Pulmonary Immunopathology On Challenge With The SARS VirusDocument13 pagesImmunization With SARS Coronavirus Vaccines Leads To Pulmonary Immunopathology On Challenge With The SARS Virusadan_infowars88% (34)
- MicrobiologyDocument40 pagesMicrobiologyRasty Baku100% (1)
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- E148 FullDocument17 pagesE148 Fullpatricx10100% (1)
- Genetics and DNA1Document40 pagesGenetics and DNA1Joy PerezNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic ResistanceDocument32 pagesAntibiotic ResistanceEmine Alaaddinoglu100% (2)
- Sensory System SeeleyDocument63 pagesSensory System SeeleyjosephNo ratings yet
- He Ethical Brain - The Science of Our Moral DilemmasDocument209 pagesHe Ethical Brain - The Science of Our Moral Dilemmasolaidais2No ratings yet
- Theoretical Genetics: Co-Dominance & Multiple AllelesDocument2 pagesTheoretical Genetics: Co-Dominance & Multiple AllelesMARIANA BERNAL MEJIANo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Part Two Modeling Meiotic Cell Division in Drosophila Using Paper Chromosomes Lab ManualDocument3 pagesTopic 1 Part Two Modeling Meiotic Cell Division in Drosophila Using Paper Chromosomes Lab ManualKosisochukwu OkoliNo ratings yet
- Mandal Module ActivityDocument17 pagesMandal Module ActivityRalph Justin MandalNo ratings yet
- Science-9-And Filipino September-18-22Document6 pagesScience-9-And Filipino September-18-22Justine RicafortNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 5 Biology G9Document17 pagesQ1 Week 5 Biology G9Christopher MarindoqueNo ratings yet
- CH 15 HomeworkDocument5 pagesCH 15 HomeworkChristineSkorupaNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Structure and Abnormalities: HaploidDocument35 pagesChromosome Structure and Abnormalities: HaploidJonathon HartNo ratings yet
- Drosophila MelanogasterDocument10 pagesDrosophila Melanogasterraja nur aimiNo ratings yet
- Theme5Module3ReviewLecture BIO1A03Fall2023Document27 pagesTheme5Module3ReviewLecture BIO1A03Fall2023miranmaster6No ratings yet
- Honors Biology Intro To Genetics Review 2021Document4 pagesHonors Biology Intro To Genetics Review 2021Irene AntiriNo ratings yet
- Gene Segregation in DrosophilaDocument4 pagesGene Segregation in DrosophilaCorrine St. PeterNo ratings yet
- 2Document40 pages2Jason NguyenNo ratings yet
- Z (H) - II-Cell Biology-BARR BODYDocument4 pagesZ (H) - II-Cell Biology-BARR BODYMUHAMMAD SHAYANNo ratings yet
- Sex-Linked Inheritance & PedigreesDocument7 pagesSex-Linked Inheritance & PedigreesDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Sex Linkage: Characters Which Are Associate More With One GenderDocument52 pagesSex Linkage: Characters Which Are Associate More With One GenderanneNo ratings yet
- Las #2.1Document5 pagesLas #2.1Jysn EspejoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Sex Linkage/Grade 12 B Biology: - Applications 9eDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Sex Linkage/Grade 12 B Biology: - Applications 9ePutri ApriliyaniNo ratings yet
- Exercise 11: ProcedureDocument6 pagesExercise 11: ProcedureMiranda TsagueNo ratings yet
- Inheritance ProblemsDocument10 pagesInheritance ProblemsRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- XII Supplementary Material Biology (Revised) PDFDocument36 pagesXII Supplementary Material Biology (Revised) PDFlithika sri kNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Activity (Has Bonus Assignment Along With The Lab)Document7 pagesInheritance Activity (Has Bonus Assignment Along With The Lab)Leah HerbertNo ratings yet
- OEB50 Readings Probs X-LinkageDocument27 pagesOEB50 Readings Probs X-LinkageAdrian GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Melc 3 HeredityDocument37 pagesMelc 3 HeredityJENNIFER DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3d Genes of Variable ExpressivityDocument25 pagesChapter 3d Genes of Variable ExpressivityJOSHUA SALCENo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics and Punnett Squares - AnswersDocument7 pagesMendelian Genetics and Punnett Squares - AnswerskalamesuaNo ratings yet
- Q. & A. Chap 05Document14 pagesQ. & A. Chap 05umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Inheritance PatternsDocument66 pagesInheritance PatternsIftikhar Hussain RizviNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Material FOR Senior Secondary BiologyDocument12 pagesSupplementary Material FOR Senior Secondary BiologyrajNo ratings yet
- BABS2213 TutorialDocument12 pagesBABS2213 TutorialAnusia ThevendaranNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Module 3Document20 pagesGrade 9 Module 3Paul AniceteNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Rescue in Uniparental DisomyDocument12 pagesChromosome Rescue in Uniparental DisomyobiwamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceDocument7 pagesChapter 12 - Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceKasieSnowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 HeredityDocument32 pagesChapter 05 HeredityBily roriguesNo ratings yet
- Ncert Excercise Ch.5Document6 pagesNcert Excercise Ch.5Dimple DamaraNo ratings yet
- Chapters 15Document7 pagesChapters 15bakelake101No ratings yet
- Paper Pet ProjectDocument27 pagesPaper Pet Projectapi-406104878No ratings yet
- Science9 - q1 - CLAS4 - Non-mendelian-Part 2 - v5 - Edited Na - RHEA ANN NAVILLADocument12 pagesScience9 - q1 - CLAS4 - Non-mendelian-Part 2 - v5 - Edited Na - RHEA ANN NAVILLALea LaderaNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2040 Problem Set 1Document3 pagesBIOL 2040 Problem Set 1dietmug40No ratings yet
- Biology Ch. 11 Use This OneDocument66 pagesBiology Ch. 11 Use This Oneمعروف عاجلNo ratings yet
- Remediation Packet - Spring Semester 2 by Michael AcostaDocument6 pagesRemediation Packet - Spring Semester 2 by Michael AcostaFlozieNo ratings yet
- Note: HeredityDocument10 pagesNote: HeredityshishaxhanNo ratings yet
- 01sex LinkageDocument25 pages01sex LinkageRon BuenaNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal MutationDocument7 pagesChromosomal Mutationchastine daneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Notes Part IIDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Notes Part IIRida ShareefNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Fundamentals of Genetics: Short QuestionsDocument16 pagesChapter 2. Fundamentals of Genetics: Short QuestionsShouryaNo ratings yet
- SCIE Ashanti Reign Tabalba - Activity 2 Mod 4Document2 pagesSCIE Ashanti Reign Tabalba - Activity 2 Mod 4Shane TabalbaNo ratings yet
- L 15 Inheritance II - X LinkedDocument30 pagesL 15 Inheritance II - X LinkedsNo ratings yet
- RICH Mendel 1 Key PDFDocument4 pagesRICH Mendel 1 Key PDFpatson sikazweNo ratings yet
- LONG Principles of InheritanceDocument4 pagesLONG Principles of InheritanceAKM KINGNo ratings yet
- Genetics Doc 2Document2 pagesGenetics Doc 2Ssonko EdrineNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variations - Sundar - Notes - Final-.22.08.21 - Part IDocument24 pagesCH 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variations - Sundar - Notes - Final-.22.08.21 - Part Ipriyamprakash0107No ratings yet
- SM Ch04.FinalDocument19 pagesSM Ch04.Finallgraha13100% (1)
- LG 3.1 Pedigree AnalysisDocument27 pagesLG 3.1 Pedigree AnalysisAeon BeluanNo ratings yet
- Outline: The Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceDocument4 pagesOutline: The Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceGizem OsmanogluNo ratings yet
- Phases of Meiosis RDocument2 pagesPhases of Meiosis RLeander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- Keying Out Plant SpeciesDocument1 pageKeying Out Plant SpeciesLeander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- Bio HWDocument1 pageBio HWLeander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- Classification Kpcofgs Ibstyle Qns 1Document2 pagesClassification Kpcofgs Ibstyle Qns 1Leander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- Why Classify Intro Slides2Document6 pagesWhy Classify Intro Slides2Leander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Calico CatsDocument19 pagesCase Study - Calico CatsLeander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- Keying Out Plant SpeciesDocument1 pageKeying Out Plant SpeciesLeander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- Lab Chi-Squared Test Worksheet-WLDocument1 pageLab Chi-Squared Test Worksheet-WLLeander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Take Home QuizDocument3 pages1.4 Take Home QuizLeander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- True False On StakeholdersDocument2 pagesTrue False On StakeholdersLeander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Demand and SupplyDocument2 pagesDeterminants of Demand and SupplyLeander KrowinkelNo ratings yet
- Cowden Syndrome Fact SheetDocument2 pagesCowden Syndrome Fact SheetLjubomirErdoglijaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. B. Extensions of Mendelian GeneticsDocument25 pagesChapter 5. B. Extensions of Mendelian GeneticsXilca JamaimahNo ratings yet
- Celiac DiseaseDocument13 pagesCeliac DiseaseVonderNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2019Document31 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2019Faiza tasnimNo ratings yet
- Anti Age Properties of PhytoglycogenDocument2 pagesAnti Age Properties of PhytoglycogenSevres ParisNo ratings yet
- Lecture Planner - Zoology - Yakeen NEET 3.0 2024Document6 pagesLecture Planner - Zoology - Yakeen NEET 3.0 2024RyzoxbeatsNo ratings yet
- PBL - Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesPBL - Myasthenia Gravisnicdeep100% (1)
- Naas Score 2014Document40 pagesNaas Score 2014adarshNo ratings yet
- Ankita Tripathi BlogDocument5 pagesAnkita Tripathi BlogGaurav SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Vignette 1Document9 pagesClinical Vignette 1Joanne Alyssa Hernandez LascanoNo ratings yet
- The Grinding or Honing MethodDocument17 pagesThe Grinding or Honing MethodJoseph Rosales Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Principles of Animal Physiology 2nd Edition Christopher D MoyesDocument303 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Animal Physiology 2nd Edition Christopher D MoyesKathy Galloway100% (26)
- ProbabilityDocument49 pagesProbabilityKaveh ArabpourNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 TitrationDocument1 pageActivity 5 TitrationPorcha PacsayNo ratings yet
- Vivares Et Al Xenobiotica 2015Document17 pagesVivares Et Al Xenobiotica 2015klieberNo ratings yet
- Community Health Factors and Health DisparitiesDocument7 pagesCommunity Health Factors and Health Disparitiesshreeguru8No ratings yet
- Fragile X Syndrome EssayDocument4 pagesFragile X Syndrome Essayapi-338677507No ratings yet
- Rle 101Document15 pagesRle 101Fea Marielle MacapayadNo ratings yet
- Doc. AP Bio FRQ EcologyDocument5 pagesDoc. AP Bio FRQ EcologyMichael JuniorNo ratings yet
- Antraknose KedelaiDocument8 pagesAntraknose KedelaiemerensianaNo ratings yet
- Seeing Is Believing: Use of Antibodies in Immunocytochemistry and in Situ HybridizationDocument17 pagesSeeing Is Believing: Use of Antibodies in Immunocytochemistry and in Situ Hybridizationacr3656No ratings yet
- Ecologic Model of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesEcologic Model of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. SallanNo ratings yet