Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cot Lesson Plan Math7 Polygons
Uploaded by
Myra Jane Bucag-LambusOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cot Lesson Plan Math7 Polygons
Uploaded by
Myra Jane Bucag-LambusCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
Region VII – Central Visayas
Schools Division of Bohol
BILAR NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Yanaya, Bilar, Bohol
DAILY Teacher MYRA JANE B. LAMBUS Grade Level Grade 7
LESSON Date April 3-4, 2023 Learning Area Mathematics
PLAN Monday 7:00am – 8:20am
Class Time Tuesday 8:20am – 9:40am
Quarter THIRD
COMPONENTS
Demonstrates understanding of key concepts of geometry of shapes and sizes,
Content Standards
and geometric relationships.
Performance Create models of plane figures and formulate and solve accurately authentic
Standards problems involving sides and angles of a polygon
I. LEARNING COMPETENCY/OBJECTIVES
Competency/ies Illustrates polygons: (a) convexity; (b) angles; (c) sides. (M7GE-IIIe-2)
At the end of the lesson, the learners will be able to:
a.) define polygon, identify, and illustrate different kinds of polygons
Objectives according to the number of sides;
b.) differentiate convex from non-convex (concave) polygons; and
c.) identify the parts of a polygon.
II. CONTENT POLYGONS
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. References
1. Teacher’s Guide
Jose S. Malate et al. 2014. Understanding Mathematics Grade 7. Manila: Vicarish
Publication and Trading, INC.;
2. Learner’s Materials
Soledad Jose-Dilao, Ed.D. et al. 2004. Geometry Workbook. Quezon City: Vibal
Publishing House, Inc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kTT8Do7oLMs&t=73s
3. Additional Materials
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=csbZmkMu6Uc&t=9s
from Learning
Resource https://www.dictionary.com/e/bermuda-triangle/
https://www.history.com/topics/ancient-egypt/the-egyptian-pyramids
B. Materials Learning activity sheet, images, diagrams, audio/video clips, LCD monitor,
Needed computer
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Introductory
Activity/ A. Class rules & routine
AWARENESS B. Mood setting/lesson introduction:
Let us start our class with
activity: Show to the class
different figures. Let the
students divide it into
three (3) groups according
to their forms/faces.
The teacher will provide
printed figures to the
learners for them to paste
on the board.
Guide Questions:
1.) What are your observations about the figures?
2.) Are all the figures closed?
3.) What are your bases in grouping the figures?
(The teacher presents the lesson objectives.)
Indicator 4: Managed classroom structure to engage learners, individually or in groups, in meaningful
exploration, discovery and hands-on activities within a range of physical learning environments.
BILAR NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Address: Yanaya, Bilar, Bohol
School ID: 302818
Telephone No: (038)535-9128
E-mail: bilarnhs@gmail.com
Indicator 5: Managed learner behavior constructively by applying positive and non-violent discipline to
ensure learning- focused environments.
Annotation: The teacher ensures that learners follow the safety guidelines, applying the positive and non-
violent discipline in doing all the learning tasks.
What is a polygon?
The word “polygon” comes from the two Greek words “poly”, which means
“many”, and “gon”, which means “angles”.
- A closed plane figure formed by three or more segments called sides.
- Each side intersects exactly two other sides, once at each endpoint.
- No two sides with a common endpoint are collinear.
- Each line segment is called the side of the polygon and each endpoint
where the sides meet is called the vertex of the polygon.
Indicator 2: Used a range of teaching strategies that enhance learner achievement in literacy and
numeracy skills.
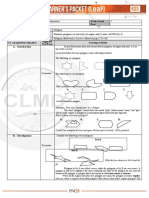
ACTIVITY:
B. ACTIVITY/Drills
Direction: Identify the following figures if it is a polygon or not
Sides of a Polygon
A polygon is classified according to the number of sides.
Number of Sides Name of a Polygon Code
3 Triangle Tri = three
4 Quadrilateral Quad = four
5 Pentagon Penta = five
6 Hexagon Hexa = six
7 Heptagon Hepta = seven
8 Octagon Octa = eight
9 Nonagon Nona = nine
10 Decagon Deca = ten
11 Undecagon Uno + deca = eleven
C. Presentation/ 12 Dodecagon Duo + deca = twelve
Discussion
n n-gon
ANALYSIS
Parts of a Polygon
Guide Questions:
1) How to name a polygon?
2) What are the vertices of the polygon?
3) What are angles of the polygon?
4) Name the sides of the polygon?
5) Give at least 2 (a) consecutive vertices; (b) consecutive angles; (c)
consecutive sides of the polygon.
6) Name all the diagonals in a polygon.
Indicator 3: Applied a range of teaching strategies to develop critical and creative thinking as well as other
higher- order thinking skills.
BILAR NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Address: Yanaya, Bilar, Bohol
School ID: 302818
Telephone No: (038)535-9128
E-mail: bilarnhs@gmail.com
Unlocking difficult terms/ Finding synonyms of the terms:
Vertices (Singular: Vertex) – a point where two or more edges meet (the corner
points)
Consecutive (Synonyms: back-to-back, continuous) – following one after the
other in order
Diagonals – a slanting straight pattern or line
Indicator 2: Used a range of teaching strategies that enhance learner achievement in literacy and
numeracy skills.
Annotation: The teacher emphasizes the usage of singular and plural to widen the learners’ literacy skills.
Convex or Concave Polygon
How to determine a convex polygon? Concave polygon?
A polygon is convex if no line that contains a side of the polygon contains a
point in the interior of the polygon.
A polygon is convex if no diagonal is in the exterior of the polygon.
To differentiate between the two types, draw its diagonals. All diagonals of a
convex polygon are inside, while a concave polygon may have a diagonal
outside.
Regular Polygon
What is a regular polygon?
A polygon is equilateral if all the sides have equal length.
A polygon is equiangular if all the angles have equal measure.
A regular polygon is both equilateral and equiangular.
BILAR NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Address: Yanaya, Bilar, Bohol
School ID: 302818
Telephone No: (038)535-9128
E-mail: bilarnhs@gmail.com
1) What is a polygon?
A closed plane figure formed by three or more segments called sides.
Each side intersects exactly two other sides, once at each endpoint. No two
sides with a common endpoint are collinear. Each line segment is called the
side of the polygon and each endpoint where the sides meet is called the
vertex of the polygon.
2) How to name a polygon?
We can name a polygon using its consecutive vertices
3) What are the parts of a polygon?
The parts of a polygon are vertices, angles, sides, consecutive sides,
consecutive vertices, consecutive angles, consecutive sides, and diagonals.
4) How to determine a convex polygon?
A polygon is convex if no line that contains a side of the polygon contains
D. ABSTRACTION/ a point in the interior of the polygon. A polygon is convex if no diagonal is in
Generalization the exterior of the polygon.
5) What is a regular polygon?
A regular polygon is both equilateral and equiangular.
6) What are the classifications of polygon according to the number of sides?
Triangle, Quadrilateral, Pentagon, Hexagon, Heptagon, Octagon, Nonagon,
Decagon, Undecagon, Dodecagon
The teacher will show a short video about polygons for enhancement.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kTT8Do7oLMs&t=73s
Indicator 3: Applied a range of teaching strategies to develop critical and creative thinking as well as
higher- order thinking skills.
Indicator 8: Selected, developed, organized and used appropriate teaching and learning resources,
including ICT, to address learning goals
Individual Oral Activity
Direction: Identify the following figures if it is polygon or not. If it is polygon,
determine whether it is convex or concave polygon. Then, classify it according
to the number of its sides.
E. APPLICATION
Group Activity
Group 1:
For academically challenged learners:
Question: What is the minimum number of non-collinear segments needed to
satisfy the definition of a polygon?
The minimum number of non-collinear segments needed to satisfy the
definition of a polygon is 3.
Group 2:
For typical learners:
Question: Can two segments form a polygon? If yes, draw the figure. If no,
explain why.
NO; because polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more
segments. Two segments cannot form a polygon.
BILAR NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Address: Yanaya, Bilar, Bohol
School ID: 302818
Telephone No: (038)535-9128
E-mail: bilarnhs@gmail.com
Group 3:
For fast learners:
Question: Can you give examples of polygon in real-life?
Some real-life examples of polygon:
rectangular-shaped screen on your laptop
television
mobile phone
a rectangular football pitch or playground
The Bermuda Triangle is a polygon with a triangle form
What is a Bermuda Triangle?
According to myth and urban
legend, the Bermuda Triangle is a
section of the North Atlantic Ocean
in which strange events
and paranormal activity occur. All
manner of bizarre and scary tales
exists about the Bermuda Triangle,
including those of alien abductions
and the underwater city of Atlantis.
The Bermuda Triangle’s spooky
reputation is due to a notable
number of ships and airplanes that
have disappeared while traveling through it.
Where is the Bermuda Triangle?
In his article, Vincent Gaddis stated that the Bermuda Triangle consisted of
an area within an imaginary triangle formed from drawing three lines across
Earth’s surface from Florida to Bermuda, Bermuda to Puerto Rico, and from
Puerto Rico back to Florida.
Polygons may also be seen in Egypt's Pyramids (triangular)
Built during a time when
Egypt was one of the richest
and most powerful
civilizations in the world, the
pyramids – especially the
Great Pyramids of Giza –
are some of the most
magnificent man-made
structures in history. Their
massive scale reflects the
unique role that the
pharaoh, or king, played in ancient Egyptian society. Though pyramids
were built from the beginning of the Old Kingdom to the close of the
Ptolemaic period in the fourth century A.D., the peak of pyramid
building began with the late third dynasty and continued until roughly
the sixth (c. 2325 B.C.). More than 4,000 years later, the Egyptian
pyramids still retain much of their majesty, providing a glimpse into the
country’s rich and glorious past.
Indicator 6: Used differentiated, developmentally appropriate learning experiences to address learners’
gender, needs, strengths, interests, and experiences.
Annotation: The teacher implements a differentiated strategy to learners with different ability levels.
Indicator 1: Applies knowledge of content within and across curriculum teaching areas.
Annotation: The teacher applies meaningful connections and inclusions of appropriate intra disciplinary
content in Mathematics and inter disciplinary content in History and real-life examples.
F. ASSESSMENT/ I. Write P if the figure is a polygon. Otherwise, write NP if not a polygon.
Evaluation
BILAR NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Address: Yanaya, Bilar, Bohol
School ID: 302818
Telephone No: (038)535-9128
E-mail: bilarnhs@gmail.com
II. State whether it is convex or concave polygon. Also, classify each polygon
according to number of sides.
III. Use the figure to answer the following questions.
1) Name the polygon.
2) How many diagonals can be drawn
from vertex S?
3) Name the diagonals can be drawn
from vertex S?
4) Is the polygon convex or concave?
5) Is it a regular polygon?
6) How many sides does it have?
7) What do you call ∠ L∧∠ E ?
8) What do you call S and T?
9) What do you call IL∧¿?
10) What do you call TE ?
Indicator 9: Designed, selected, organized and used diagnostic, formative and summative assessment
strategies consistent with curriculum requirements.
As stated by Cute Princess,
“Life is like a polygon,
Since we get different people
with different faces”.
G. Concluding
Activity
We are created by our Almighty God uniquely and according to HIS plan. We
have unique facial features, physical appearance, and even our skills, talents,
etc. Others may say that we are the same. We could not say that we are exactly
the same, maybe we have our similarities. Like the polygons that compose of
different figures/faces.
H. Assignment Competency: Derives inductively the relationship of exterior and interior angles
of a convex polygon. M7GE-IIIf-1
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation
B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation
C. Did the remedial lessons work?
No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson
D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation
E. Which of my learning strategies worked well? Why did this work?
F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor
can help me solve?
G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish
to share with other teachers?
Prepared:
MYRA JANE B. LAMBUS
Subject Teacher
Checked/Observed:
BILAR NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Address: Yanaya, Bilar, Bohol
School ID: 302818
Telephone No: (038)535-9128
E-mail: bilarnhs@gmail.com
MARLON S. JALA PhD
School Principal
BILAR NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Address: Yanaya, Bilar, Bohol
School ID: 302818
Telephone No: (038)535-9128
E-mail: bilarnhs@gmail.com
You might also like
- Week 1 DLL Math 7 q3 NEWDocument11 pagesWeek 1 DLL Math 7 q3 NEWAngela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- DLL Grade 7 Q3-Week 5-8Document14 pagesDLL Grade 7 Q3-Week 5-8Angela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- DLP Math 7 Q3 - W3 - D3Document7 pagesDLP Math 7 Q3 - W3 - D3JL Teope IcaoNo ratings yet
- Math - Grade 7 - LM. Contextualized and Localized Activities For Math. Qtr. 2Document7 pagesMath - Grade 7 - LM. Contextualized and Localized Activities For Math. Qtr. 2Edelyn PaulinioNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet Solving Problems On Real Numbers-1Document2 pagesActivity Sheet Solving Problems On Real Numbers-1Eunice Ortile100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized CotDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics 7 Contextualized CotLeizel Samson100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Math7Document4 pagesLesson Plan Math7Annie Glen LovesParamore CanilaoNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Daily Lesson Log Week2Document5 pagesMath 7 Daily Lesson Log Week2Ederlyn LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsCelyn RevillaNo ratings yet
- Circle and Its PartsDocument7 pagesCircle and Its PartsAngelen RegaroNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Mathematics 7 CMDocument3 pages3rd Quarter Mathematics 7 CMJeff LacasandileNo ratings yet
- DEMONSTRATIONlessonplanDocument6 pagesDEMONSTRATIONlessonplanLovely VillasNo ratings yet
- DLL MathDocument2 pagesDLL MathMaricel Rabang RafalNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan (DLP) : Acelo C. Badelles Sr. Memorial High School (Tipanoy National High School)Document2 pagesDaily Lesson Plan (DLP) : Acelo C. Badelles Sr. Memorial High School (Tipanoy National High School)Russhel Jon Llamas Macalisang100% (1)
- DLL Math Grade7 Quarter3 Week3Document6 pagesDLL Math Grade7 Quarter3 Week3NORIEL MABATONo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan of M8Ge-Ivc-1 (Week 3 Day 3) : LNP M MLN NQDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan of M8Ge-Ivc-1 (Week 3 Day 3) : LNP M MLN NQMjoyce A. Bruan100% (1)
- DLL Math 7 COTDocument6 pagesDLL Math 7 COTbernadeth villanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lesson Plan For MATH 7Document4 pages2nd Lesson Plan For MATH 7Joan Babao100% (1)
- DLL Math 7 March 20-24, 2023Document8 pagesDLL Math 7 March 20-24, 2023Ma Gloria Deocades FlanciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Undefined TermsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Undefined TermsJinkee F. Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 q4 Module 4 and 5 - Using Appropriate Graphs To Represent Organized Data - Dfdjnhs NewDocument23 pagesMath 7 q4 Module 4 and 5 - Using Appropriate Graphs To Represent Organized Data - Dfdjnhs NewJen TarioNo ratings yet
- Math DLLDocument4 pagesMath DLLRegine Zulita Letchejan100% (1)
- Math 7 Week 2Document18 pagesMath 7 Week 2Rey Mark RamosNo ratings yet
- Dll-Cot Multiplication of IntegersDocument7 pagesDll-Cot Multiplication of IntegersRizaneth Gay Mirar100% (1)
- DLL3 Math 7 Week 2Document3 pagesDLL3 Math 7 Week 2Angela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- Performance TaskDocument4 pagesPerformance TaskGwen MarielleNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 7 Quarter 2 Week 1Document14 pagesDLL Math 7 Quarter 2 Week 1Christine SerranoNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7: GEOMETRY: CircleDocument13 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 7: GEOMETRY: CircleBab Sita100% (1)
- COT 4th QUARTER MATH 9Document2 pagesCOT 4th QUARTER MATH 9ariel velaNo ratings yet
- DLL3 Math 7 Week 9Document3 pagesDLL3 Math 7 Week 9Angela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- G8DLL Q3W5Document3 pagesG8DLL Q3W5Mark Kiven Martinez100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log of M7Ge-Iiig-1 (Week Seven-Day One)Document3 pagesDaily Lesson Log of M7Ge-Iiig-1 (Week Seven-Day One)Zile SmithNo ratings yet
- Grade Level 7 Learning Area/ Quarter / Domain Mathematics Quarter 2 Date Section ZaraDocument5 pagesGrade Level 7 Learning Area/ Quarter / Domain Mathematics Quarter 2 Date Section ZaraJoan BabaoNo ratings yet
- DLL (Thursday 02-14-19)Document3 pagesDLL (Thursday 02-14-19)Samiracomputerstation Kuya Marvs0% (1)
- Detailedlessonplaninmath 171025142418Document7 pagesDetailedlessonplaninmath 171025142418Olive Botilo ErasmoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Undefined TermsDocument8 pagesWeek 1 Undefined TermsJo-Amver Valera ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Presentation of DataDocument5 pagesPresentation of DataAira Mae MacalingaNo ratings yet
- LAS Math 7 q4Document6 pagesLAS Math 7 q4DenNo ratings yet
- Grades 7 Daily Lesson Log: I. Objectives Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday A. Content StandardsDocument6 pagesGrades 7 Daily Lesson Log: I. Objectives Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday A. Content StandardsSHERWIN S. CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Math Grade 7 DLL Q2 W7 JANDocument4 pagesMath Grade 7 DLL Q2 W7 JANthalia alfaroNo ratings yet
- DLP For Demojul232019Document5 pagesDLP For Demojul232019Catherine SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 7 - Module 6Document4 pagesMathematics 7 - Module 6Brylle Epemar CelestialNo ratings yet
- Lesson ExemplarDocument5 pagesLesson ExemplarMsVange A LptNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2Yvone Claire BalignotaNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in Math 8Document4 pagesPerformance Task in Math 8Karen Claire Russ100% (1)
- Q3 Grade 8 Week 1Document17 pagesQ3 Grade 8 Week 1aniejeonNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document18 pagesWeek 1Lyndon B. PaguntalanNo ratings yet
- DLL - July29-31 Deductive-InductiveDocument3 pagesDLL - July29-31 Deductive-Inductiveerrol rustia100% (1)
- G8DLL - Q2W7 For CODocument4 pagesG8DLL - Q2W7 For COMark Kiven MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson PlanClaire Valdeavilla - Dudas100% (1)
- Multiply - DLLDocument2 pagesMultiply - DLLJENNICAH CYRIL REYEL100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade7 MathematicsDocument3 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade7 MathematicsAngela Mariz Penuela ForroNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Mathematics 8Document4 pagesSummative Test in Mathematics 8Garry D. DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- San Pablo Q3 M7 Week 5 MSEMontanaDocument4 pagesSan Pablo Q3 M7 Week 5 MSEMontanaPaul Marwen FernandezNo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter DLL Math 9Document2 pages2ND Quarter DLL Math 9Sakura May100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics I .Content StandardsDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics I .Content StandardsFarrah Joy Aguilar Nietes100% (1)
- MATH 7 Q1 Quarterly AssesmentDocument2 pagesMATH 7 Q1 Quarterly AssesmentGenemar Tan MarteNo ratings yet
- Q3W7 DLP CirclesDocument14 pagesQ3W7 DLP CirclesMarjuline De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 7 - Q3Document16 pagesDLL - Math 7 - Q3TITO FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- COT MATH FinalDocument5 pagesCOT MATH FinalShiela Mae Yonson100% (1)
- Aremonte Barnett - Beowulf Notetaking GuideDocument4 pagesAremonte Barnett - Beowulf Notetaking Guideapi-550410922No ratings yet
- Kingdeli Adhesive Catalogue 2020Document21 pagesKingdeli Adhesive Catalogue 2020Md Farid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Science ExperimentDocument9 pagesScience ExperimentAnil KarnawatNo ratings yet
- A Journey Thru NakshatrasDocument73 pagesA Journey Thru NakshatrasRohit Sharma83% (12)
- Accounting 121Document2 pagesAccounting 121Now OnwooNo ratings yet
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)Document3 pagesEnzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)Wael OsmanNo ratings yet
- 2020 TassapDocument4 pages2020 Tassapzhouh1998100% (1)
- MisDocument16 pagesMisMoon Kazmi100% (2)
- H. Muhammed Ka Parichay (Kannada)Document96 pagesH. Muhammed Ka Parichay (Kannada)Q.S.KhanNo ratings yet
- Letter of IntentDocument1 pageLetter of IntentReigneth VillenaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet - 04Document6 pagesTutorial Sheet - 04Tran Nguyen KhangNo ratings yet
- Technical Information: Spare Eebds Mentioned in Item 1 Are Not To Be Included in Total NumberDocument5 pagesTechnical Information: Spare Eebds Mentioned in Item 1 Are Not To Be Included in Total NumberSatbir SinghNo ratings yet
- Ebook - Atmel Avr AssemblerDocument20 pagesEbook - Atmel Avr AssemblerelfrichNo ratings yet
- IO FormativeDocument3 pagesIO Formativenb6tckkscvNo ratings yet
- Nwaneho Ozioma EstherDocument4 pagesNwaneho Ozioma EstherOziomaNo ratings yet
- 13 - Chapter 3Document22 pages13 - Chapter 3manoj varmaNo ratings yet
- 1 Crim1 - People Vs Javier - Lack of Intent To Commit So Grave A WrongDocument2 pages1 Crim1 - People Vs Javier - Lack of Intent To Commit So Grave A WrongJustin Reden BautistaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Alaa Notes PDFDocument54 pagesPediatrics Alaa Notes PDFmaimoona sulemanNo ratings yet
- Read The Text and Fill The Gaps With The Words Given BelowDocument2 pagesRead The Text and Fill The Gaps With The Words Given Belownatomasurashvili3100% (1)
- List of Telugu Films of 2005 - WikipediaDocument1 pageList of Telugu Films of 2005 - WikipediaRa RsNo ratings yet
- Amul ProjectDocument52 pagesAmul ProjectPrabuddha BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Soal Usp Bhs InggrisDocument4 pagesSoal Usp Bhs InggrisRASA RASANo ratings yet
- Gynecology Part 1Document12 pagesGynecology Part 1Subramaniam Sundaram100% (3)
- Haramaya University: R.NO Fname Lname IDDocument13 pagesHaramaya University: R.NO Fname Lname IDRamin HamzaNo ratings yet
- Crim 2 ReviewerDocument193 pagesCrim 2 ReviewerMaria Diory Rabajante100% (3)
- West Wendover Proposed OrdinanceDocument16 pagesWest Wendover Proposed OrdinanceA Safer Nevada DirectorNo ratings yet
- WH Questions WorksheetDocument1 pageWH Questions WorksheetCRISTIAN RODRIGUEZ ROJASNo ratings yet
- Improve Web-UI PerformanceDocument4 pagesImprove Web-UI Performancekenguva_tirupatiNo ratings yet
- Inesco Amc 2106735164Document3 pagesInesco Amc 2106735164spahujNo ratings yet
- Gem5 Splash2Document13 pagesGem5 Splash2Apurv SahayNo ratings yet