Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nlap Reading Information Grade 1 Standard 1
Uploaded by
adzwinjCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nlap Reading Information Grade 1 Standard 1
Uploaded by
adzwinjCopyright:
Available Formats
NEW LANGUAGE ARTS PROGRESSIONS (ESL/New Language)
Grade 1: Reading for Information 1
Common Core Anchor Standard (RI.1): Read closely to determine what the text says Main Academic Demand
explicitly and to make logical inferences from it; cite specific textual evidence when writing or Draw Inferences Using Evidence from the Text
speaking to support conclusions drawn from the text.
Common Core Grade 1 Standard (RI.1.1): Ask and answer questions about key details in a Grade Level Academic Demand
text. Inquire and Recall Key Details
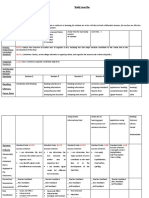
5 Levels of
Language
Entering Emerging Transitioning Expanding Commanding
Development
(Beginner) (Low Intermediate) (High Intermediate) (Advanced) (Proficient)
When acquiring a new language, using grade level texts and appropriate supports, students are able to:
Listening-Centered Listening-Centered Listening-Centered Listening-Centered Listening-Centered
Activity: Organize Activity: Organize Activity: Organize phrases Activity: Organize Activity: Organize
pretaught words and preidentified words and and sentences on a partially sentences on a –wh information on a self-
phrases on a –wh questions phrases on a –wh questions completed –wh questions questions chart to identify created –wh questions
chart to identify key details chart to identify key details chart to identify key details key details in a text, as text chart, independently, to
in a text, as text is read in a text, as text is read in a text, as text is read is read aloud in partnership, identify key details in a
aloud in partnership and/or aloud in partnership and/or aloud in partnership, small small group and/or whole text, as text is read aloud in
teacher-led small groups small groups group and/or whole class class settings partnership, small group
settings and/or whole class settings
RECEPTIVE
Oracy
Reading-Centered Reading-Centered Reading-Centered Reading-Centered Reading-Centered
and Activity: Organize Activity: Organize Activity: Organize phrases Activity: Organize Activity: Organize
Literacy pretaught words and preidentified words and and sentences on a partially sentences on a main-idea- information on a self-
Links phrases on a main-idea- phrases on a main-idea- completed main-idea-and- and-key-details chart to created main-idea-and-key-
and-key-details chart to and-key-details chart to key-details chart to identify identify multiple key details details chart, independently,
identify two or more key identify two or more key multiple key details in a in a text to identify multiple key
details in a text details in a text text details in a text
in the new and/or the home in the new and/or the home in the new and, in the new language. in the new language.
language. language. occasionally, in the home
language.
Draft NLAP Reading for Information (RI)
RI.1: RI.1.1 1
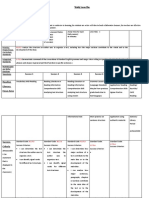
5 Levels of
Language
Entering Emerging Transitioning Expanding Commanding
Development
(Beginner) (Low Intermediate) (High Intermediate) (Advanced) (Proficient)
Speaking-Centered Speaking-Centered Speaking-Centered Speaking-Centered Speaking-Centered
Activity: Use pretaught Activity: Use preidentified Activity: Use a word bank Activity: Use the Activity: Use knowledge of
words and phrases and words and phrases and the to ask and answer questions previously completed the text, independently, to
the previously completed previously completed about key details in the text, graphic organizers to ask ask and answer questions
graphic organizers to graphic organizers to when speaking partnership, and answer questions about about key details in the text,
complete sentence starters complete sentence starters small group and/or whole key details in the text, when when speaking partnership,
that ask and answer that ask and answer class settings speaking partnership, small small group and/or whole
questions about key details questions about key details group and/or whole class class settings
in the text, when speaking in the text, when speaking settings
in partnership and/or in partnership and/or small
teacher-led small groups groups
PRODUCTIVE
Oracy
Writing-Centered Writing-Centered Writing-Centered Writing-Centered Writing-Centered
and Activity: Use pretaught Activity: Use preidentified Activity: Use a word Activity: Use the Activity: Use knowledge of
Literacy words and phrases to words and phrases to bank and the previously previously completed the text, independently, to
Links complete cloze sentences complete a cloze paragraph completed graphic graphic organizers and develop an essay that
that address key details in that addresses key details in organizers to develop a teacher-provided models to addresses key details in the
the text the text paragraph that addresses develop a short essay that text
key details in the text addresses key details in the
text
in the new and/or the home in the new and/or the home in the new and, in the new language. in the new language.
language. language. occasionally, in the home
language.
Draft NLAP Reading for Information (RI)
RI.1: RI.1.1 2
Common Core Grade 1 Standard (RI.1.1): Ask and answer questions about key details in a Grade Level Academic Demand
text. Inquire and Recall Key Details
Linguistic Demands: The following are some examples in English that may vary based on the language of instruction. In the first three levels
(entering, emerging and transitioning), students can approach these linguistic demands in the new and/or home language.
Use who, what, where, why and how question forms based on the text (Note: not • WHAT questions and answers refer to the event that took place.
all question forms have to be mastered, according to the grade level standard). • HOW question and answers refer to the sequence that leads to the main event
• WHO questions and answers target the subject(s) who were involved in an (e.g., timelines, cycles, procedures can be part of explaining the HOW of an
event. event). HOW can also be covered by WHAT, WHERE and WHEN.
• WHERE questions and answers refer to the place (or even circumstances) where
(Note: Not all question forms have to be mastered by the students.)
an event takes place.
• WHY refers to the cause/reason that triggers an event. It can be explicitly stated
in the text or it may require an inference.
Example to Address the Linguistic Demands
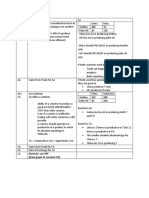
Text Excerpt Teacher Directions
Homemade Ice Cream in a Bag In small group/whole class discussion, demonstrate understanding of key details in
What you’ll need: a text by asking and answering questions to:
• Ice cubes (enough to fill each gallon-size bag about half full) • WHO/WHAT questions and answers target the subject(s) (nouns and associated
• 1 cup half and half pronouns) (bold) (e.g., ice cubes; ½ cup salt) and by asking what questions
• 1/2 cup salt (The bigger the granules, the better. Kosher or rock salt works best, (e.g., What do you need to make ice cream?).
but table salt is fine.) • WHERE questions and answers refer to the place (nouns) (italics) (e.g., gallon-
• 2 tablespoons sugar size bag; the bag, smaller bag, larger one, out) and by asking where questions
• 1/2 teaspoon vanilla extract (e.g., Where do you put the ice cream?).
• 1 pint-size ziplock bag • WHY refers to the cause/reason that triggers an event. It can be explicitly stated
• 1 gallon-size ziplock bag in the text or it may require an inference supported by a why question (e.g.,
• Your favorite mix-ins such as chocolate chips, cereal pieces, or fresh fruit. Why do you think it says “easy cleanup too?”).
• HOW question and answers refer to the sequence that lead to the main event
Instructions:
(verbs) (underline) (e.g., combine, place, take) and the sequencing words (wavy
Step 1. Combine the sugar, half and half, and vanilla extract in the pint-size bag
underline) (e.g., now, then, when) and by asking how questions (e.g., How do
and seal it tightly.
you make ice cream in a bag?).
Step 2. Place the salt and ice in the gallon-size bag, then place the sealed smaller
bag inside as well. Seal the larger bag. Now shake the bags until the mixture
hardens (about 5 minutes). Feel the small bag to determine when it’s done.
Step 3. Take the smaller bag out of the larger one, add mix-ins, and eat the ice
cream right out of the bag. Easy cleanup too!
Homemade ice cream in a bag. Retrieved from: http://spoonful.com/recipes/
homemade-ice-cream-bag
Draft NLAP Reading for Information (RI)
RI.1: RI.1.1 3
You might also like
- Lesson FrameworksDocument8 pagesLesson Frameworksh83uur hwywyeyNo ratings yet
- Evaluate: Task 4a. Proposal (Drafting of Service Learning Plan)Document3 pagesEvaluate: Task 4a. Proposal (Drafting of Service Learning Plan)cherish calachanNo ratings yet
- Informative Speech TextDocument2 pagesInformative Speech TextadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy 12Th Edition Roth Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy 12Th Edition Roth Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFgretchenmilesdxeh3100% (8)
- 4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion - WorksheetDocument12 pages4.1 Simple Harmonic Motion - Worksheetkoelia100% (1)
- Cooper Tire Warranty InformationDocument28 pagesCooper Tire Warranty InformationAbdulAziz AlGhamdiNo ratings yet
- ROM Laboratory v1.00Document548 pagesROM Laboratory v1.00Carlos Reaper Jaque OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Buwis ButilDocument2 pagesBuwis ButilHelbert Agluba PaatNo ratings yet
- HamletDocument44 pagesHamletMonica AnechiteiNo ratings yet
- Rubrics: Rubric For Concept Paper Criteria 4-Excellent 3 - Good 2 - Fair 1 - PoorDocument7 pagesRubrics: Rubric For Concept Paper Criteria 4-Excellent 3 - Good 2 - Fair 1 - PoorIvy Mie SagangNo ratings yet
- Six Scaffolding Strategies for English Language LearnersDocument31 pagesSix Scaffolding Strategies for English Language LearnersAman Gaur100% (1)
- Remedial InstructionDocument13 pagesRemedial InstructionHannieNo ratings yet
- Name: Date: Grade/Strand/Section: Subject: English 4 Instructor: Ms. Cantago PERFORMANCE TASK 1.3 - Reflection Paper Instruction(s)Document2 pagesName: Date: Grade/Strand/Section: Subject: English 4 Instructor: Ms. Cantago PERFORMANCE TASK 1.3 - Reflection Paper Instruction(s)Jorge Alfonso CabeguinNo ratings yet
- 2021-2022 P3 Upper-Int Student Course OutlineDocument10 pages2021-2022 P3 Upper-Int Student Course OutlineEyNo ratings yet
- 04 - Teacher + Student Rubric - Walk in Someone Else's ShoesDocument2 pages04 - Teacher + Student Rubric - Walk in Someone Else's Shoeslawrence_holbrookNo ratings yet
- Note-Making Skill / Dictation: By: Honey HmingDocument13 pagesNote-Making Skill / Dictation: By: Honey HmingHannieNo ratings yet
- 04 - Teacher + Student Rubric - Walk in Someone Else's ShoesDocument2 pages04 - Teacher + Student Rubric - Walk in Someone Else's Shoeslawrence_holbrookNo ratings yet
- English Gr.7 LP Wk.23.JanDocument8 pagesEnglish Gr.7 LP Wk.23.JanOgechi ElekwaNo ratings yet
- Study Skills and Strategies SSS3 Action PlanDocument3 pagesStudy Skills and Strategies SSS3 Action Planapi-358944838No ratings yet
- Year 3 Handout Day 1-5Document130 pagesYear 3 Handout Day 1-5ramanadeviNo ratings yet
- Year 3 Handout Day 1-5 PDFDocument130 pagesYear 3 Handout Day 1-5 PDFdugongNo ratings yet
- English Gr.7 LP Wk16.JanDocument9 pagesEnglish Gr.7 LP Wk16.JanOgechi ElekwaNo ratings yet
- 3.01 kl7Document4 pages3.01 kl7zansaamajlanovaNo ratings yet
- 3 English Course Pre IntermediateDocument6 pages3 English Course Pre IntermediateFernando Herrera DiazNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 DLL ENGLISH Q4 Week 8Document15 pagesGrade 2 DLL ENGLISH Q4 Week 8bidNo ratings yet
- Speaking Lesson Plan ComponentsDocument1 pageSpeaking Lesson Plan ComponentsAzri ArbaianNo ratings yet
- Components From Sow For The Development of A Lesson Plan - SpeakingDocument1 pageComponents From Sow For The Development of A Lesson Plan - SpeakingMohanah JavalanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Week 1Document9 pagesLesson Plan Week 1Ogechi ElekwaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9-English Anglo-American Literature: Prepared By: Ms. Andreata Gleen-Naie B. PaniangoDocument19 pagesGrade 9-English Anglo-American Literature: Prepared By: Ms. Andreata Gleen-Naie B. Paniango원톤면No ratings yet
- Guided Reading Assessment GridDocument5 pagesGuided Reading Assessment GridNURFARAH AFRINA BINTI ZUKRI MoeNo ratings yet
- Daily English Lesson LogDocument14 pagesDaily English Lesson LogJaneth PactoresNo ratings yet
- Tissa REPORT WRITING Rubric A211 RevisedDocument2 pagesTissa REPORT WRITING Rubric A211 RevisedNrsfqNo ratings yet
- (Arranged by Amt/Rbt) (Based On Amt/Rbt Classification) Refer To The Melc Given by DepedDocument12 pages(Arranged by Amt/Rbt) (Based On Amt/Rbt Classification) Refer To The Melc Given by DepedRogieMae Dela Cruz SantosNo ratings yet
- Gr12 EnglishJIT P1 2020Document53 pagesGr12 EnglishJIT P1 2020NhlanhlakaziNo ratings yet
- Engscimaweek 8Document10 pagesEngscimaweek 8Rica CloaNo ratings yet
- CEFR Levels and Learning Standards OverviewDocument16 pagesCEFR Levels and Learning Standards OverviewrhiyaNo ratings yet
- Odd one out statements and learning standardsDocument10 pagesOdd one out statements and learning standardsFaz FuzeNo ratings yet
- Language Lab Report 2018 19Document11 pagesLanguage Lab Report 2018 19Dimple BhatiNo ratings yet
- rz lap prof portDocument4 pagesrz lap prof portapi-503751269No ratings yet
- Core Sub EC-6 SampleDocument38 pagesCore Sub EC-6 SampleAntolio DominguezNo ratings yet
- Case Study #3: Softball Batting CageDocument2 pagesCase Study #3: Softball Batting CageSourya Mitra0% (1)
- Rubric FinalDocument2 pagesRubric Finalapi-348942329No ratings yet
- EDUU 511 Disabilities Expert Group Presentation AssignmentDocument3 pagesEDUU 511 Disabilities Expert Group Presentation AssignmentDennohNo ratings yet
- English Department Syllabus: Subject Code ING 250 Credits 3 Pre-Requisite ING 250 Year - 2020 Contact Hours 48 HoursDocument12 pagesEnglish Department Syllabus: Subject Code ING 250 Credits 3 Pre-Requisite ING 250 Year - 2020 Contact Hours 48 HoursTrung Hiếu NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Teaching Receptive Language Skills 5Document88 pagesTeaching Receptive Language Skills 5Heba AbdelazimNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Presentation RubricDocument1 pagePowerPoint Presentation RubricEA CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Summarizing: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageSummarizing: Republic of The PhilippinesAnn Raganas FonteNo ratings yet
- BG005 005 Ibraimof Internal LSA4 LPDocument13 pagesBG005 005 Ibraimof Internal LSA4 LPLiliana IbraimofNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan RubricDocument1 pageLesson Plan RubricWilma S. BentayaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Frameworks by Amir Landa (2015) .: Additions by Ben HammondDocument9 pagesLesson Frameworks by Amir Landa (2015) .: Additions by Ben HammondLuis Gerardo PérezNo ratings yet
- Vocab Mini LessonDocument4 pagesVocab Mini Lessonapi-402696363No ratings yet
- Corrective Reading (Salunayan)Document111 pagesCorrective Reading (Salunayan)MOMMY GAMERNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For Receptive Skills LessonsDocument1 pageCheat Sheet For Receptive Skills LessonsNelsonDanielEseNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet For Receptive Skills LessonsDocument1 pageCheat Sheet For Receptive Skills LessonsGabrielleNo ratings yet
- Assessing Receptive SkillsDocument22 pagesAssessing Receptive SkillsBùi Trần Bảo NgọcNo ratings yet
- Partner Conversation Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesPartner Conversation Lesson Planapi-575306719No ratings yet
- Natural Language ProcessingDocument14 pagesNatural Language ProcessingCherry FloraNo ratings yet
- BM Customer Service IGDocument224 pagesBM Customer Service IGMarcos Moreno Oliveira100% (4)
- Unit 4 MapDocument3 pagesUnit 4 Mapapi-341414616No ratings yet
- 9th-10th Info-Explan RubricDocument2 pages9th-10th Info-Explan Rubricapi-362261785No ratings yet
- Top-Down Reading ProcessDocument22 pagesTop-Down Reading ProcessMary Cris EspirituNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BussComm AWing - Hasil Rakor 04022019 - REGULERDocument10 pagesSyllabus BussComm AWing - Hasil Rakor 04022019 - REGULERIndah Dina SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesapi-552242776No ratings yet
- DLL - ENGLISH 4 - Q1 - W6 - v2Document11 pagesDLL - ENGLISH 4 - Q1 - W6 - v2Sheena Claire dela Pe?No ratings yet
- MDM VJM Y4 Transit Record - NorestrictionDocument31 pagesMDM VJM Y4 Transit Record - NorestrictionSORUPANATHAN A/L SADAYAN MoeNo ratings yet
- !1-ОШ СОР Англ.яз 7кл англ 300318Document33 pages!1-ОШ СОР Англ.яз 7кл англ 300318айназ адилетоваNo ratings yet
- Eco Test 1 Prep NotesDocument3 pagesEco Test 1 Prep NotesadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Sequence of Listening and Learning DomainsDocument1 pageSequence of Listening and Learning DomainsadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Banks' Roles, Payment Methods, Transport Risks, Trade DocumentsDocument1 pageBanks' Roles, Payment Methods, Transport Risks, Trade DocumentsadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Monroe's Motivated Sequence AttentionDocument4 pagesMonroe's Motivated Sequence AttentionadzwinjNo ratings yet
- IBM537 Chapter 1 PowerPoint LectureDocument14 pagesIBM537 Chapter 1 PowerPoint LectureadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Exporter Guide Canberra Australia 11-7-2018Document13 pagesExporter Guide Canberra Australia 11-7-2018adzwinjNo ratings yet
- DRAFTDocument5 pagesDRAFTadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Chapt 8 NotesDocument3 pagesChapt 8 NotesadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Part B Past Year Questions Ibm537Document10 pagesPart B Past Year Questions Ibm537adzwinj100% (1)
- Big Picture: Ii. Gains From International TradeDocument5 pagesBig Picture: Ii. Gains From International TradeadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Milestones - Syed QutbDocument86 pagesMilestones - Syed QutbAdeel MalikNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 Mid-Sem Break Study GuideDocument1 pageSemester 1 Mid-Sem Break Study GuideadzwinjNo ratings yet
- ECO Muet MGT420 ACC406 LAW416 Kemas Kemas: 1. Malaysian Legal System - Sources - Courts - How To MakeDocument3 pagesECO Muet MGT420 ACC406 LAW416 Kemas Kemas: 1. Malaysian Legal System - Sources - Courts - How To MakeadzwinjNo ratings yet
- Writing A Resume PDFDocument4 pagesWriting A Resume PDFadzwinjNo ratings yet
- To Be A Muslim by Fathi YakanDocument37 pagesTo Be A Muslim by Fathi Yakanabuali-almaghribi100% (2)
- Csir - CimfrDocument31 pagesCsir - Cimfrshravan kumarNo ratings yet
- Idebenone Increases Chance of StabilizationrecoverDocument5 pagesIdebenone Increases Chance of StabilizationrecoverRaluca PascalauNo ratings yet
- Knowing God Intimately Joyce Meyer Christiandiet - Com .NGDocument343 pagesKnowing God Intimately Joyce Meyer Christiandiet - Com .NGadriana mariaNo ratings yet
- 5G Americas Advanced Antenna Systems For 5G White PaperDocument59 pages5G Americas Advanced Antenna Systems For 5G White PaperArpitha HsNo ratings yet
- Catch Up Friday 011153Document3 pagesCatch Up Friday 011153Vanessa Pond100% (6)
- 1 HeterogenitasDocument46 pages1 HeterogenitasRani JuliariniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Health History SummaryDocument1 pageNursing Health History SummaryHarvey T. Dato-onNo ratings yet
- The Law of DemandDocument13 pagesThe Law of DemandAngelique MancillaNo ratings yet
- EngM6 TB WebDocument161 pagesEngM6 TB WebNong BillNo ratings yet
- Verification and Validation in Computational SimulationDocument42 pagesVerification and Validation in Computational SimulationazminalNo ratings yet
- Picture DescriptionDocument7 pagesPicture DescriptionAida Mustafina100% (3)
- Unit 1 Lesson 2 PDFDocument20 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 2 PDFKristyll ArguellesNo ratings yet
- Quantum Dot PDFDocument22 pagesQuantum Dot PDFALI ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- 2022 Consumer Trends ReportDocument29 pages2022 Consumer Trends Reportadelin litan100% (1)
- 2013 Course Structure BTech CSEDocument32 pages2013 Course Structure BTech CSEMankush JainNo ratings yet
- Cazul Cyril Burt 3Document3 pagesCazul Cyril Burt 3Cosmina MihaelaNo ratings yet
- 0000 0000 0335Document40 pages0000 0000 0335Hari SetiawanNo ratings yet
- New Life in Christ by Wilson HerreraDocument18 pagesNew Life in Christ by Wilson Herreralesantiago100% (1)
- Energy Savings White PaperDocument14 pagesEnergy Savings White PapersajuhereNo ratings yet
- CPG Prevention, Diagnosis & Management of IE PDFDocument182 pagesCPG Prevention, Diagnosis & Management of IE PDFsigitNo ratings yet
- A Closer Look at The Cosmetics Industry and The Role of Marketing TranslationDocument5 pagesA Closer Look at The Cosmetics Industry and The Role of Marketing Translationagnes meilhacNo ratings yet
- Robbins OB15GE Inppt16Document31 pagesRobbins OB15GE Inppt16Nida IsrarNo ratings yet
- Fuji Synapse PACS Quick GuideDocument1 pageFuji Synapse PACS Quick GuideM MNo ratings yet