Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistics Formulas Excel
Uploaded by
Anderson Gabriel Pacheco SánchezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics Formulas Excel
Uploaded by
Anderson Gabriel Pacheco SánchezCopyright:
Available Formats
http://aprendeconalf.
es
Statistical formulas
Formulas
Statistics Excel function Sample Freq. table Interpretation
∑
xi ∑ The value that best represent the values of the
Mean x̄ AVERAGE(sample) xi fi
n sample (except when there are outliers).
The value in the middle of the ordered sample.
Median M e MEDIAN(sample) 50% of values of the sample are above and 50%
below it.
Mode M o MODE(sample) The most common value in the sample.
Minimum M in MIN(sample) min{xi } The minimum value of the sample.
Maximum M ax MAX(sample) max{xi } The maximum value of the sample.
25% of the values of the sample are lower or equal
First quartile Q1 QUARTILE(sample,1)
to it.
50% of the values of the sample are lower or
Second quartile Q2 QUARTILE(sample,2)
equal to it.
75% of the values of the sample are lower or equal
Third quartile Q3 QUARTILE(sample,3)
to it.
i ∗ 10% of the values of the sample are lower or
Decile i Di PERCENTILE(sample, i/10)
equal to it.
i% of the values of the sample are lower or equal
Percentile i Pi PERCENTILE(sample, i/100)
to it.
Range MAX(sample)-MIN(sample) M ax − M in M ax − M in Measures the overall spread of the sample.
Measures the spread of the 50% central values of
Interquartile Range IQR QUARTILE(sample,3)-QUARTILE(sample,1) Q3 − Q1 Q3 − Q1
∑ the sample.
(xi − x̄)2 ∑ Measures the average spread with respect to the
Variance s2 VAR.P(sample) (xi − x̄)2 fi
n mean in square units.
√ √ Measures the average spread with respect to the
Standard deviation s STDEV.P(sample) s2 s2
mean in the units of the variable.
Measures the relative spread with respect to the
s s
Coef. variation cv STDEV.P(sample)/ABS(AVERAGE(SAMPLE)) mean. It has no units. The lower the dispersion,
|x̄| |x̄|
the more representative is the mean.
∑ ( xi − x̄ )3 ∑ ( xi − x̄ )3 Measures the asymmetry of the sample distribu-
Coef. skewness g1 SKEW(sample) fi tion (g1 = 0 symmetry, g1 > 0 right-skewed, g1 < 0
s s
left-skewed).
Measures the peakness or flatness of the sample
∑ ( xi − x̄ )4 ∑ ( xi − x̄ )4 distribution compared to a normal distribution
Coef. kurtosis g2 KURT(sample) −3 fi − 3 (g2 = 0 normal kurtosis, g1 > 0 leptokurtic or
s s
peaked distribution, g1 < 0 platykurtic or flat dis-
tribution).
You might also like
- PL Engineering Corporate PresentationDocument53 pagesPL Engineering Corporate Presentationneettiyath1100% (1)
- Sample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignFrom EverandSample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignNo ratings yet
- College Statistics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCollege Statistics Cheat Sheetmaciekleja100% (2)
- E122Document5 pagesE122zudujawalo100% (1)
- Segmental Bridge Construction in Florida-A Review and PerspectiveDocument42 pagesSegmental Bridge Construction in Florida-A Review and PerspectiveTan Duy LeNo ratings yet
- Empilhadeira YALEDocument264 pagesEmpilhadeira YALEReinaldo Pimentel Sebastião75% (8)
- Calculating Sample Size To Estimate, With A Specified Tolerable Error, The Average For A Characteristic of A Lot or ProcessDocument5 pagesCalculating Sample Size To Estimate, With A Specified Tolerable Error, The Average For A Characteristic of A Lot or ProcesslkfjadfasfNo ratings yet
- Statistics Formulas ExcelDocument1 pageStatistics Formulas ExcelsalnasuNo ratings yet
- PYC3704 Past Exam QuestionsDocument143 pagesPYC3704 Past Exam QuestionsgavhumendeNo ratings yet
- Princessb3ll3 - Ap Stat TestDocument2 pagesPrincessb3ll3 - Ap Stat TestShilpa GadgilNo ratings yet
- X X X X: Statistic Symbol Population Sample DescriptionDocument3 pagesX X X X: Statistic Symbol Population Sample Descriptionwjs4572No ratings yet
- TestSummary Handout1 v01Document2 pagesTestSummary Handout1 v01KIM THUyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Measures of DispersionDocument45 pagesChapter 4 Measures of Dispersionmonicabalamurugan27No ratings yet
- Important Formulas TableDocument4 pagesImportant Formulas TableSara Beauchamp-HicksNo ratings yet
- 010 - STAT - SAMPLING Distribution of The Sample MeanDocument9 pages010 - STAT - SAMPLING Distribution of The Sample MeanGerson Tampolino Acosta100% (1)
- Application of The Paired T-TestDocument6 pagesApplication of The Paired T-TestSir BoBBYNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument21 pagesFormulasSamantha Marie RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Two Samples: Testing The Difference of Means of Two Independent SamplesDocument1 pageTwo Samples: Testing The Difference of Means of Two Independent Samplesreshma thomasNo ratings yet
- Inferencial Test PDFDocument3 pagesInferencial Test PDFfakhruldeenNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics and Analysis Course 2&3Document42 pagesBusiness Statistics and Analysis Course 2&3Mugdho HossainNo ratings yet
- Alternative Hypothesis: Central Limit TheoremDocument3 pagesAlternative Hypothesis: Central Limit TheoremEunice C. LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Sample Size To Estimate, With Specified Precision, The Average For A Characteristic of A Lot or ProcessDocument9 pagesCalculating Sample Size To Estimate, With Specified Precision, The Average For A Characteristic of A Lot or ProcessFuneral Shop NilaNo ratings yet
- Stats Lesson 6Document3 pagesStats Lesson 6VITAL, Jay Ann S.No ratings yet
- Sampling and Sampling DistributionDocument28 pagesSampling and Sampling DistributionBuetNo ratings yet
- SP ReviewerDocument4 pagesSP ReviewerMalayao, Philip Jude M.No ratings yet
- Statistics Lecture - 3Document14 pagesStatistics Lecture - 3Saraj HNo ratings yet
- STA1007S Lab 10: Confidence Intervals: October 2020Document5 pagesSTA1007S Lab 10: Confidence Intervals: October 2020mlunguNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Terms: Stat 101 Reference SheetDocument5 pagesDefinitions and Terms: Stat 101 Reference SheetChriston John Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Statistics Part 3Document4 pagesStatistics Part 3Emilia CassidyNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distributions and Central Limit Theory (SP24) ..Document48 pagesSampling Distributions and Central Limit Theory (SP24) ..mariammaged981No ratings yet
- Ch07 HandoutDocument121 pagesCh07 HandoutJack WangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Descriptive Statistics: Example 1: Making Steel RodsDocument20 pagesChapter 1: Descriptive Statistics: Example 1: Making Steel RodsCindyNo ratings yet
- Statistics 10 ReviewerDocument1 pageStatistics 10 ReviewerGeromme TudNo ratings yet
- Chapters4 5 PDFDocument96 pagesChapters4 5 PDFpicalaNo ratings yet
- MAT2001-Statistics For Engineers: Measures of VariationDocument22 pagesMAT2001-Statistics For Engineers: Measures of VariationBharghav RoyNo ratings yet
- Active Learning Task 12Document8 pagesActive Learning Task 12haptyNo ratings yet
- EstimationDocument53 pagesEstimationEyota AynalemNo ratings yet
- x=^μ= x n x x) n−1 s σ s x−μ σ se (´x) = σ n: Sample MeanDocument5 pagesx=^μ= x n x x) n−1 s σ s x−μ σ se (´x) = σ n: Sample MeanSara Beauchamp-HicksNo ratings yet
- Source: Pllnu4Dk9H04Wqyrebvzx4?Fr Yfp-T-701-S &toggle 1&cop Mss&Ei Utf8&Fp - Ip PH&P Types of Descriptive StatisticsDocument51 pagesSource: Pllnu4Dk9H04Wqyrebvzx4?Fr Yfp-T-701-S &toggle 1&cop Mss&Ei Utf8&Fp - Ip PH&P Types of Descriptive StatisticsNexBengsonNo ratings yet
- Mean, Standard Deviation, and Counting StatisticsDocument2 pagesMean, Standard Deviation, and Counting StatisticsMohamed NaeimNo ratings yet
- Module 11Document21 pagesModule 11Kashika AgarwalNo ratings yet
- x i s μ x N n: Easures OF AriabilityDocument2 pagesx i s μ x N n: Easures OF AriabilityErwin BulahaoNo ratings yet
- BUSN 2429 Chapter 14 Correlation and Single Regression ModelDocument85 pagesBUSN 2429 Chapter 14 Correlation and Single Regression ModelAwais SadaqatNo ratings yet
- Review Innovations Measures of Central Tendency FRACTILES: Percentiles, Deciles, and QuartilesDocument1 pageReview Innovations Measures of Central Tendency FRACTILES: Percentiles, Deciles, and QuartilesLemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Business Data Analytics Student 4-5Document74 pagesBusiness Data Analytics Student 4-5Siddharth KumarNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distributions & Standard Error: Lesson 7Document20 pagesSampling Distributions & Standard Error: Lesson 7Lorena TeofiloNo ratings yet
- Last Formuas of First ChapterDocument20 pagesLast Formuas of First ChapterBharghav RoyNo ratings yet
- Testing of HypothesisDocument54 pagesTesting of HypothesisKarthic SK100% (1)
- Statistics Tutorial 1Document12 pagesStatistics Tutorial 1Natalya LewisNo ratings yet
- Sample Project Report StructureDocument5 pagesSample Project Report StructureRodrigo FarruguiaNo ratings yet
- Bus. Statt. Chapter-Lecture 2+3Document43 pagesBus. Statt. Chapter-Lecture 2+3Mrz AwwalNo ratings yet
- ML Exam BHT Tough H BeeeeeeeeeDocument10 pagesML Exam BHT Tough H BeeeeeeeeeRasika DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Taylor SeriesDocument4 pagesTaylor Seriesvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- And Estimation Sampling Distributions: Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesAnd Estimation Sampling Distributions: Learning OutcomesTarek MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Assumption Checking On Linear RegressionDocument65 pagesAssumption Checking On Linear RegressionJohn San JuanNo ratings yet
- One and Two Samples Using Only An R Function: Ying-Ying ZhangDocument17 pagesOne and Two Samples Using Only An R Function: Ying-Ying ZhangeuriionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 (Part Ii)Document20 pagesChapter 5 (Part Ii)Natasha GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Module 6: Week 6: Third QuarterDocument7 pagesStatistics and Probability Module 6: Week 6: Third QuarterALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- Statistics: Dealing With Skewed DataDocument7 pagesStatistics: Dealing With Skewed DataAbhijeetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Statistical Applications in Traffic EngineeringDocument28 pagesChapter 7: Statistical Applications in Traffic EngineeringMiaNo ratings yet
- Faculty Introduction: Tkachwala@nmims - EduDocument27 pagesFaculty Introduction: Tkachwala@nmims - EduKRISHNA PRIYADARSININo ratings yet
- This Is Yet Another Function With Abundant Applications in The Industry. It Helps Us Divide The Population Into Groups. TheDocument2 pagesThis Is Yet Another Function With Abundant Applications in The Industry. It Helps Us Divide The Population Into Groups. TheAmarjeet kumarNo ratings yet
- 106 01 - MODUL FIZIK DIY TINGKATAN 4 2021-15-20-Ch2-AnsDocument3 pages106 01 - MODUL FIZIK DIY TINGKATAN 4 2021-15-20-Ch2-AnsThooi Joo WongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Research (Part 1)Document10 pagesIntroduction To Research (Part 1)ichogi kurakiNo ratings yet
- Math 10C Factors and Products Rev. F17Document2 pagesMath 10C Factors and Products Rev. F17fares mattrwdNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Material Science: ContentDocument95 pagesFundamentals of Material Science: ContentJenica Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- $RE54804Document301 pages$RE54804psmNo ratings yet
- Ovarian and Uterine Sonography in Healthy Girls Between 1 and 13 Years OldDocument6 pagesOvarian and Uterine Sonography in Healthy Girls Between 1 and 13 Years OldUsman Agus PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- A Lab Experience With Deriving Faraday's LawsDocument23 pagesA Lab Experience With Deriving Faraday's Lawsbminesrules9511950% (1)
- Introduction To Mechanical VibrationsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Mechanical VibrationsSrivatsava R.No ratings yet
- TEPEx Catalog en 2016-2017Document130 pagesTEPEx Catalog en 2016-2017rmuzeNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Tiles - SampleDocument2 pagesEstimation of Tiles - Samplejhomel garciaNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Hydrogenation of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters and Natural Oils Under Neat ConditionsDocument5 pagesHomogeneous Hydrogenation of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters and Natural Oils Under Neat ConditionsEnrique GallegosNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 One-Way Traffic LightDocument3 pagesExercise 2 One-Way Traffic LightJude Philip MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Programming Notes PDFDocument59 pagesProgramming Notes PDFJeyanth KamalNo ratings yet
- Example On Chapter 3-1Document15 pagesExample On Chapter 3-1asfawbelay2024No ratings yet
- (August 15, 2018) Diagnostic TestDocument5 pages(August 15, 2018) Diagnostic TestReyniel Layson VergaraNo ratings yet
- 1999 - Bioclimatic Zoning of Brazil - A Proposal Based in Givoni and Mahoney MethodsDocument6 pages1999 - Bioclimatic Zoning of Brazil - A Proposal Based in Givoni and Mahoney MethodsalxgoliveiraNo ratings yet
- Chem Exam 2 2012Document2 pagesChem Exam 2 2012Britanny NelsonNo ratings yet
- Niir Handbook On Paint Testing MethodsDocument6 pagesNiir Handbook On Paint Testing MethodsPardeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Seme Detailed Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesSeme Detailed Lesson PlanDianne Grace AguipoNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Power MeasurementsDocument2 pagesThree Phase Power MeasurementsNizar AlifNo ratings yet
- Owth and DevelopmentDocument21 pagesOwth and Developmentعوض الكريمNo ratings yet
- Voice Assistant NotepadDocument9 pagesVoice Assistant NotepadIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Data InterpretationDocument12 pagesData Interpretationfarhana uddinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.1 - System of Coplanar ForcesDocument35 pagesUnit 1.1 - System of Coplanar ForcesRohan100% (2)
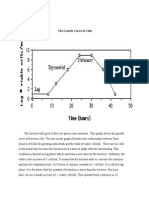
- The Growth Curve of CellsDocument3 pagesThe Growth Curve of CellsRisky KikiNo ratings yet
- Second Midterm ExamDocument11 pagesSecond Midterm Examskarleys hernandez movillaNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement For Wind TurbineDocument7 pagesGround Improvement For Wind TurbineMohammed AzarudeenNo ratings yet