Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bone Anatomy
Uploaded by
Justine Kay SarmientoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bone Anatomy
Uploaded by
Justine Kay SarmientoCopyright:
Available Formats
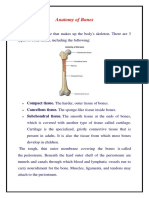
NCM116 BONE ANATOMY
BONE is living tissue that makes up the body's a shield; flat bones can also provide large areas of
skeleton. attachment for muscles.
flat bones in the skull (occipital, parietal, frontal,
FUNCTIONS OF BONE nasal, lacrimal, and vomer)
Bone provides shape and support for the body, as the thoracic cage (sternum and ribs)
well as protection for some organs. pelvis (ilium, ischium, and pubis).
Bone also serves as a storage site for minerals and
LONG BONES longer than they are wide, include the
provides the medium—marrow—for the
development and storage of blood cells femur (the longest bone in the body) as well as
relatively small bones in the fingers. Long bones
1. Compact tissue. The harder, outer tissue of bones. function to support the weight of the body and
2. Cancellous tissue. The sponge-like tissue inside facilitate movement.
bones. • Long bones are mostly located in the
appendicular skeleton and include bones in
3. Subchondral tissue. The smooth tissue at the ends the lower limbs (the tibia, fibula, femur,
of bones, which is covered with another type of metatarsals, and phalanges) and bones in
tissue called cartilage. Cartilage is the specialized, the upper limbs (the humerus, radius, ulna,
gristly connective tissue that is present in adults. It is metacarpals, and phalanges).
also the tissue from which most bones develop in
children.
SHORT BONES Located in the wrist and ankle joints,
short bones provide stability and some movement.
Periosteum tough, thin outer membrane covering
the bones
• There are 206 bones in the human skeleton, Examples of short bones
not including teeth and sesamoid bones The carpals in the wrist (scaphoid, lunate, triquetral,
(small bones found within cartilage): hamate, pisiform, capitate, trapezoid, and
• 80 axial bones. This includes the head, trapezium)
facial, hyoid, auditory, trunk, ribs, and Tarsals in the ankles (calcaneus, talus, navicular,
sternum. cuboid, lateral cuneiform, intermediate cuneiform,
• 126 appendicular bones. This includes arms, and medial cuneiform)
shoulders, wrists, hands, legs, hips, ankles,
and feet. IRREGULAR BONES vary in shape and structure and
therefore do not fit into any other category (flat,
TYPES OF BONE CELLS short, long, or sesamoid). They often have a fairly
1. Osteoblast. Found within the bone, its function is complex shape, which helps protect internal organs.
to form new bone tissue.
2. Osteoclast. A very large cell formed in bone SESAMOID BONES, bones embedded in tendons
marrow, its function is to absorb and remove These small, round bones are commonly found in
unwanted tissue. the tendons of the hands, knees, and feet. Sesamoid
3. Osteocyte. Found within the bone, its function is bones function to protect tendons from stress and
to help maintain bone as living tissue. wear. The patella, commonly referred to as the
4. Hematopoietic. Found in bone marrow, its kneecap, is an example of a sesamoid bone
function is to produce red blood cells, white blood
cells, and platelets.
TYPES OF BONE CELLS
FLAT BONES protect internal organs such as the
brain, heart, and pelvic organs. Flat bones are
somewhat flattened, and can provide protection, like
You might also like
- Brain Anatomy Function Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesBrain Anatomy Function Cheat SheetCiprian C.83% (6)
- Nclex MCN IntrapartumDocument17 pagesNclex MCN IntrapartumMary Chris C. GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Skeletal SystemDocument22 pagesChapter 5 The Skeletal SystemJUSTINE MAE MANTILLANo ratings yet
- ALVEOLAR BoneDocument72 pagesALVEOLAR BoneArchana50% (2)
- Skeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)Document10 pagesSkeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)anon_660872041No ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Femur, HumerusDocument21 pagesThe Skeletal System: Femur, HumerusLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Anatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyFrom EverandAnatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- NEET GT-5 SolutionsDocument12 pagesNEET GT-5 Solutionsabcxyz7799No ratings yet
- Biology 2nd Lab Report (Onion Cell)Document4 pagesBiology 2nd Lab Report (Onion Cell)Johanna Haludilu88% (16)
- MC1 REVIEWER (Skeletal System) - PRELIMSDocument5 pagesMC1 REVIEWER (Skeletal System) - PRELIMSFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Interaction of Skeletal and Muscular SystemDocument43 pagesInteraction of Skeletal and Muscular SystemJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021Document13 pagesAssignment 3.1: Luminang, John Chris Bsmls 1B Anaphy Nov. 18, 2021John Chris LuminangNo ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- Types of BonesDocument2 pagesTypes of BonesJess MCDNo ratings yet
- Bones Contain More Calcium Than Any Other Organ. TheDocument4 pagesBones Contain More Calcium Than Any Other Organ. Theydnic alykPNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument37 pagesBasic Anatomy and PhysiologyIndu GNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of BonesDocument6 pagesAnatomy of BonesAbdelrhman AboodaNo ratings yet
- C5 Skeletal NotesDocument10 pagesC5 Skeletal NotesJocelyn AlunanNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To The Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesIntoduction To The Skeletal SystemDenise AngelNo ratings yet
- MADAM NAHEED SHAH BioDocument10 pagesMADAM NAHEED SHAH BioAijaz bulediNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesSkeletal System Lesson PlanNicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- Chapter III SkeletalDocument26 pagesChapter III SkeletalTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Lesson Plan 2Document12 pagesSkeletal System Lesson Plan 2Trudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Christine Bas Sweet Audrey Gwen SamsonDocument39 pagesSkeletal System: Christine Bas Sweet Audrey Gwen SamsonDanielle Kate MadridNo ratings yet
- Muscloskeletal SystemDocument154 pagesMuscloskeletal SystemAbera AberaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System QuestionsDocument44 pagesSkeletal System QuestionsSritama GhoshNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: 1. Hyaline CartilagesDocument9 pagesThe Skeletal System: 1. Hyaline CartilagesRaja Nurul JannatNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesDocument90 pagesUnit 2-4 Anatomy and Human Physiology NotesAbi .JNo ratings yet
- Skeletal - System AnatomyDocument89 pagesSkeletal - System AnatomysanayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Document7 pagesUnit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Vergel CallejaNo ratings yet
- (Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFDocument7 pages(Oct 1) THE SKELETAL SYSTEM PDFBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Bones.Document20 pagesClassification of Bones.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PowerPointDocument50 pagesSkeletal System PowerPointEly QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesTopic 6 Skeletal SystemMary Ann Morillo TenederoNo ratings yet
- Skripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogDocument15 pagesSkripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogElizabetaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Medical TerminologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy Medical TerminologyNikita GosineNo ratings yet
- LEC Orthopedic NursingDocument31 pagesLEC Orthopedic NursingAlthea Franz DuoNo ratings yet
- (Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemDocument18 pages(Reading 3) The Skeletal SystemTrúc Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument27 pagesSkeletal SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesThe Skeletal SystemMatthew YoungNo ratings yet
- SkeletonDocument7 pagesSkeletonOsnovna Škola GlavatičevoNo ratings yet
- Reading Material Skeletal SystemDocument32 pagesReading Material Skeletal SystemShamel CurrayNo ratings yet
- Unit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Document78 pagesUnit Three: General Anatomy of The of Skeletal System (Osteology)Gifti DemisseNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesThe Skeletal SystemCharlie CharlesNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesThe Skeletal SystemBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MariebDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Mariebmissy23papNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument63 pagesAnatomy and Physiologykathleen.cuyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document26 pagesUnit 4sivexgamingNo ratings yet
- Types of Bones Powerpoint Ver 1Document16 pagesTypes of Bones Powerpoint Ver 1mrejcrewsNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesThe Skeletal Systemstar fireNo ratings yet
- Anatomical IntroductionDocument17 pagesAnatomical Introductionllazoozllbraa 7372No ratings yet
- Intro To Osteology (Oct 20, 2022)Document30 pagesIntro To Osteology (Oct 20, 2022)huzaifa arshadNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument13 pagesSkeletal Systemariolajose5No ratings yet
- Skeletal MusclesDocument20 pagesSkeletal MusclesDeshmukh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System PowerPointDocument46 pagesSkeletal System PowerPointLucky RiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ANAPHY Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 6 ANAPHY Skeletal Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- PE1 Movement Enhancement ModuleDocument24 pagesPE1 Movement Enhancement ModuleildefonsogarbinjrNo ratings yet
- Civil Service Examination Form No. 100 Revised September 2016Document38 pagesCivil Service Examination Form No. 100 Revised September 2016angelica valenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Bone ClassificationDocument5 pagesBone Classificationcharmcast9No ratings yet
- Bone SystemDocument11 pagesBone SystemJonathan Smith Nizama CabreraNo ratings yet
- Bones AssignmentDocument6 pagesBones AssignmentColin KennyNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure: Nursing GoalDocument3 pagesChronic Renal Failure: Nursing Goal006 shinta aprilia Ananda risnantoNo ratings yet
- Penyerapan & Asimilasi (DLP)Document2 pagesPenyerapan & Asimilasi (DLP)KomathiNo ratings yet
- Principles and Pitfalls in Coronary Vasomotor Function TestingDocument26 pagesPrinciples and Pitfalls in Coronary Vasomotor Function TestingRamón López PalopNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Enzyme Kinetics All - v2 - 3slide HandoutsDocument14 pagesWeek 2 - Enzyme Kinetics All - v2 - 3slide HandoutsFizza HussainNo ratings yet
- Viva 1Document12 pagesViva 1roseNo ratings yet
- Planilha Classificação Qualis 2017-2018 - TabelaDocument460 pagesPlanilha Classificação Qualis 2017-2018 - TabelaThiago EtcNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Cell RespDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis Cell RespKimeu BagyonNo ratings yet
- 3 Superficial Brachioradial Artery (Radial Artery)Document5 pages3 Superficial Brachioradial Artery (Radial Artery)Juan José CabezasNo ratings yet
- NOTES 3 The Stages of Cellular RespirationDocument20 pagesNOTES 3 The Stages of Cellular RespirationJillian Reyes SantosNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia 1 Lecture, BDSDocument49 pagesNeoplasia 1 Lecture, BDSHik ConnectNo ratings yet
- Aqa 8464B1H QP Nov21Document28 pagesAqa 8464B1H QP Nov21ShepardNo ratings yet
- Benedetti Placebo 2013Document40 pagesBenedetti Placebo 2013Nancy Fazzini NevenaNo ratings yet
- Lipids, Biochem, ReviewerDocument9 pagesLipids, Biochem, ReviewerKerstine Anne AndradeNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Skrlec - The Influence of Dental Implants On The Circadian Clock - ERHMDocument7 pages2022 - Skrlec - The Influence of Dental Implants On The Circadian Clock - ERHMIvana V SkrlecNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Metabolism and EnzymesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Metabolism and Enzymes绿谷出久No ratings yet
- Img 20240111 0002Document11 pagesImg 20240111 00029E EYAD AhmedNo ratings yet
- Immunity Questions and AnswersDocument12 pagesImmunity Questions and Answerskumara guruparanNo ratings yet
- Cori CycleDocument6 pagesCori CycleAina Doreen DelfinNo ratings yet
- Abdomen & Pelvis - Topical Papers 3Document5 pagesAbdomen & Pelvis - Topical Papers 3Ali Hassan SukheraNo ratings yet
- SNC 2D Biology Unit - Notes - StudentDocument33 pagesSNC 2D Biology Unit - Notes - StudentSA - 10WB 933839 The Woodlands SSNo ratings yet
- 18BTB103T - Human Physiology and Health SyllabusDocument3 pages18BTB103T - Human Physiology and Health SyllabusSounak NandyNo ratings yet
- Entamoeba HistolyticaDocument38 pagesEntamoeba HistolyticaAbdul Ghafar OrakzaiiiNo ratings yet
- Scoles Pulst SCA2-Chapter 2018Document30 pagesScoles Pulst SCA2-Chapter 2018atpNo ratings yet
- Blood PDFDocument4 pagesBlood PDFJustine May Balinggan DelmasNo ratings yet
- Unit Wise Question Bank Human Anatomy & Physiolog Class - First Year Diploma Pharmacy Unit I CellDocument5 pagesUnit Wise Question Bank Human Anatomy & Physiolog Class - First Year Diploma Pharmacy Unit I CellDhiraj DivekarNo ratings yet
- Exposure To Ambient Fine Particles Causes Abnormal Energy Metabolism and ATP Decrease in Lung TissuesDocument10 pagesExposure To Ambient Fine Particles Causes Abnormal Energy Metabolism and ATP Decrease in Lung TissuesMaria Elena Gonzalez DiazNo ratings yet