Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes About Elements
Uploaded by
Jethro ngoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes About Elements
Uploaded by
Jethro ngoCopyright:
Available Formats
Element - a substance that can't be broken down into a simpler substance - composed of one
kind of atom
from ancient to 1669 only dozen elements were known
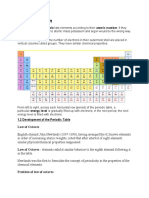
Historical development of the periodic table
1789 - Antoine-Laurent De Lavoisier, a french nobleman classified elements with similar
properties into groups
1808 - John Dalton set up a table of elements according to their relative atomic weights and
published his findings in his book A New System of Chemical Philosophy
Antoine Lavoisier - 1770-1789
- Wrote the first list of elements containing 33 elements
- Distinguished between metals and nonmetal
1828 - Jacob Berzelius improved the work of John Dalton and published a table of atomic
weights with 54 elements
1829 - Johann W. Dobreiner analyzed the existing elements and classified them into groups of
three's and called these the TRIADS
Jons Jakob Berzelius - 1828
- developed a table of atomic weights
Introduced letters to symbolize elements
1863 - Alexander-Emile De Chancourtois grouped elements in spiral order divided by vertical
lines based on increasing atomic weights.
1854 - John Newlands arranged elements in order of increasing atomic weights into groups of
eight elements. The first and the eighth elements share similar properties - The Law of Octaves
1869 - Dimitri Ivanovich Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic
mass, leaving a number of gaps reserved for undiscovered elements
1869 - Julius Lothar Meyer arranged the elements in the order of increasing atomic weights
based on the plotted values of atomic volume and atomic number
Lothar Meyer - 1869
- Compiled a periodic table of 56 elements based on the periodicity of properties such as molar
volume when arranged in order of atomic weight
Henry Mosely - 1887 -
- In 1913 through his work with X-ray spectra, he determined the actual nuclear charge(atomic
number) of the elements. He rearranged it in order of increasing the atomic number
Periodic Law - When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a
periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties
Glenn T. Seaborg - 1912-1999
After co-discovering 10 new elements, he moved 14 elements out of the main body of the
periodic table to their current location below the Lanthanide series. These became known as the
Actinide series
He is the only person to have an element named after him while still alive
"This is the greatest honor bestowed upon me-even better, I think than winning the Nobel Prize."
Periodic Table Geography
7 periods
rows of elements are called periods
18 groups/families
the elements in any group of the periodic table have similar physical and chemical properties
The main-group elements representative elements
Group 1 - Alkali metals
name alkali comes from Arabic al-Gili meaning plant ash since Na and K carbonates are major
components of the plant ashes
+1 ions never as
Group 2 - Alkaline Earth Metals
same properties similar to those of alkali but were originally found in the earth rather than in
ashes
+2
Group 13 Boron Group
all have 3 electrons on their outermost shell
Group 14 Carbon Group
There are four valence electrons in a carbon atom
Group 15 Nitrogen Group
It can have either 3 or 5 valence electrons because it can bond in the outer 2p and 2s orbitals
Group 16 The Chalcogens
All have 6 electrons on the outermost shell
all are metal except for Helonium which is always a metal
Oxygen
Group 17 Halogens
from greed halo and gen meaning salt-former
nonmetals
Group 18 Noble Gases
Don't readily combine with other elements since they all have a filled valence shell
they are complete
named inert gases until Xe and Kr were discovered
chemically stable
Transition Metals
elements in the midsection of the periodic table, groups 3-12 located in the same period tend to
have similar properties
Inner transition metals
two rows of elements set off by themselves below the main table also called rare-earth elements
Lanthanide series - rare-earth
Actinide series - radioactive (manmade)
Electric configuration
electrons are the MVP of chemistry. they're the reason atoms are able to interact with other
atoms
- complete arrangement of electrons in an atom
- the process of arranging the electrons around the nucleus of an atom
Main energy level/shells/orbitals
- where the electrons in the atoms exist
- designated by a whole number or capital letter
-KLMNOPQ
-1234567
energy level - max number of e-
1-2
2-8
3 - 18
4 - 32
5 - 50
6 - 72
7 - 98
Formula = 2(n)^2
Subshells
type - name - max e-
s - sharp - 2
p - principal - 6
d - diffuse - 10
f - fundamental - 14
Types of subshells
f - 14 electrons -7 orbital
d - 10 - 5 orbital
p - 6 - 3 orbital
s - 2 - 1 orbital
max number
s=2
p=6
d = 16
f = 14
You might also like
- History of Peiodic Table - Gen ChemDocument2 pagesHistory of Peiodic Table - Gen ChemSai Adrienne RealubitNo ratings yet
- Classification of Element and Periodicity in PropertiseDocument27 pagesClassification of Element and Periodicity in PropertiseAditya chauhanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of Elements ExplainedDocument24 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements ExplainedSidpreet SandhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document58 pagesChapter 13oninNo ratings yet
- Development of The Periodic TableDocument2 pagesDevelopment of The Periodic TableAdrian YangaNo ratings yet
- Padhle 10th - Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument21 pagesPadhle 10th - Periodic Classification of ElementsBitan DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Periodic ClassificationDocument6 pagesChapter 5 - Periodic Classificationnitin kapriNo ratings yet
- Structure of An AtomDocument16 pagesStructure of An Atomkatrina freoNo ratings yet
- CHEM Report - Periodic TableDocument3 pagesCHEM Report - Periodic TableLeah Rose Figueroa ParasNo ratings yet
- Hist. of PeriodicTableDocument30 pagesHist. of PeriodicTableRaisa Bint ZamanNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Properties and VariationsDocument23 pagesPeriodic Table Properties and VariationsvsyoiNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification NotesDocument38 pagesPeriodic Classification NotesSantosh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument47 pagesPeriodic Table of Elementsbrent tobiasNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Perodic Classification Chapter 5 NotesDocument13 pagesClass 10 Science Perodic Classification Chapter 5 NotescxsdvNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Revision NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 5 Revision NotesRaman TiwariNo ratings yet
- PT 1Document26 pagesPT 1Roronoa ZoroNo ratings yet
- X-Science (Chemistry) Dobereiner's Triads: Ebenezer Matric. Hr. Sec. SchoolDocument3 pagesX-Science (Chemistry) Dobereiner's Triads: Ebenezer Matric. Hr. Sec. Schoolr karthickNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument58 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsNevin ShajiNo ratings yet
- Development of The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesDevelopment of The Periodic Tablepanda catNo ratings yet
- International: India SchoolDocument18 pagesInternational: India SchoolAkash MondalNo ratings yet
- Development of The Periodic TableDocument8 pagesDevelopment of The Periodic TableAbigael Jhem Soriano ArtuzNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Lessons ExplainedDocument10 pagesPeriodic Table Lessons ExplainedChrisshalyn Sy PinedaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 P 1 Class 10 Sci MSBSHSE NotesDocument13 pagesCH 2 P 1 Class 10 Sci MSBSHSE NotesIrganesh MadagundiNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument3 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementshafsaNo ratings yet
- Döbereiner's Triads and Early Development of the Periodic TableDocument6 pagesDöbereiner's Triads and Early Development of the Periodic TableAndrea May IntiaNo ratings yet
- Peroidic ClassifcationDocument18 pagesPeroidic ClassifcationRoushan SinghNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument2 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsAlstroNo ratings yet
- Science Project WorkDocument16 pagesScience Project WorkSushikant Chaturvedi79% (42)
- Intrototheperiodictablepre ApDocument11 pagesIntrototheperiodictablepre ApvishakhshuklaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Priodic TableDocument11 pagesChemistry Priodic TableGada HadaNo ratings yet
- Electron Configuration and The Periodic TableDocument43 pagesElectron Configuration and The Periodic TableHanna GalatiNo ratings yet
- The History of the Periodic TableDocument16 pagesThe History of the Periodic TableMelissa MalicdemNo ratings yet
- Modern Periodic Table ExplainedDocument11 pagesModern Periodic Table ExplainedMozibor RahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument15 pagesUnit 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Propertiescpverma2811100% (1)
- Periodic ClassificationDocument60 pagesPeriodic ClassificationNidhi srivastavaNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of The Development of Periodic TableDocument2 pagesA Brief History of The Development of Periodic Tableantonetteporca100% (1)
- Chemistry Xii 1-5 InorganicDocument59 pagesChemistry Xii 1-5 InorganicSyed Mairaj Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument11 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- Attempts Made by Johann Dobereiner and Johann NewlandsDocument21 pagesAttempts Made by Johann Dobereiner and Johann NewlandsJames MahNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument38 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsLia Marlia100% (2)
- 1stch-5 Chem PartiDocument19 pages1stch-5 Chem PartiShaheen parweenNo ratings yet
- 3.classification of ElementsDocument18 pages3.classification of ElementsMUHAMMAD YASEENNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Periodic TableDocument11 pagesChemistry Periodic Tablesubhadeepdey85No ratings yet
- Elements Having The Same Number of Electrons in Their Outermost Shell Are Placed inDocument26 pagesElements Having The Same Number of Electrons in Their Outermost Shell Are Placed inMai AbdelgelilNo ratings yet
- Antoine Lavoisier (1743 - 1794) : Chapter 4: Periodic Table of Elements - HistoryDocument2 pagesAntoine Lavoisier (1743 - 1794) : Chapter 4: Periodic Table of Elements - HistoryIzzat AziziNo ratings yet
- 5.periodic Classifications of ElementsDocument5 pages5.periodic Classifications of ElementsayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4:the Periodic Table of Elements: Group 1 - Afiq Rifqal - Nicole Ho - Raihan - Bharath - Tuck HoeDocument11 pagesChapter 4:the Periodic Table of Elements: Group 1 - Afiq Rifqal - Nicole Ho - Raihan - Bharath - Tuck HoeShafeeqah FadzilNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Periodic Table PPT 2017-2018Document19 pagesPeriodic Table PPT 2017-2018api-283677111No ratings yet
- Class IX Chemistry Chapter 04Document13 pagesClass IX Chemistry Chapter 04Sam FisherNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of The ElementDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table of The ElementHoangTuan LyNo ratings yet
- Brief History and Features of the Periodic TableDocument19 pagesBrief History and Features of the Periodic Tablealexa de veraNo ratings yet
- Sci - 8 Elements of Periodic Table-Week 7-8Document37 pagesSci - 8 Elements of Periodic Table-Week 7-8SANTA ISABEL MERCADONo ratings yet
- PERIODIC_CLASSIFICATION_OF_ELEMENTSDocument67 pagesPERIODIC_CLASSIFICATION_OF_ELEMENTSreshma1917singhNo ratings yet
- Development of the Periodic Table HistoryDocument43 pagesDevelopment of the Periodic Table HistoryPeejayNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsDocument6 pagesChapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsAhmed shakilNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsDocument6 pagesChapter-5-Periodic-Classification-Of-Elements/: Dobereiner's TriadsAhmed shakilNo ratings yet
- Book 2Document59 pagesBook 2tony ho100% (1)
- Is 228 Part 1 - 1987Document4 pagesIs 228 Part 1 - 1987ferozNo ratings yet
- Test 2-P2Document8 pagesTest 2-P2Salman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Uodguzikvcsz) FszkjadDocument30 pagesUodguzikvcsz) FszkjadG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Metals and PolymerDocument14 pagesLecture Notes in Metals and PolymerjoyandreaNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 4Document1 pageChem Form 4baskieNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Estimating in Building Construction 8th Edition Peterson Solutions Manual PDF ScribdDocument32 pagesInstant Download Estimating in Building Construction 8th Edition Peterson Solutions Manual PDF Scribdbreannajordanxgydcitpre100% (13)
- UOP952Document12 pagesUOP952goodcharacter1No ratings yet
- The Essential Guide To The U.S. Trade in Gold and Silver JewelryDocument10 pagesThe Essential Guide To The U.S. Trade in Gold and Silver JewelryAFLAC ............No ratings yet
- Tugas VBT Kimia Anorganik 2-Melva Hilderia S. (06101381520043)Document6 pagesTugas VBT Kimia Anorganik 2-Melva Hilderia S. (06101381520043)Melva SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Decompisition of Baking Soda: Lab Report - Bruno Moulheres, Michael Branas, Daniel Deleon, Melanie MoronDocument2 pagesDecompisition of Baking Soda: Lab Report - Bruno Moulheres, Michael Branas, Daniel Deleon, Melanie MoronFrosty BR100% (1)
- Brammer Standard Online Catalog Combustion Materials ChartDocument7 pagesBrammer Standard Online Catalog Combustion Materials ChartLuis Miguel Reinel MorenoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and AnswersDocument24 pagesChemistry Paper 1 Questions and AnswersSueNo ratings yet
- Granular Media Gas Phase Filtration SystemsDocument2 pagesGranular Media Gas Phase Filtration SystemstsaifulNo ratings yet
- Mineralogical Patterns in Hydrothermal SystemsDocument45 pagesMineralogical Patterns in Hydrothermal SystemsJoe VentoNo ratings yet
- Stp944-Eb 1420Document146 pagesStp944-Eb 1420delta lab sangli100% (1)
- Fugleberg SigmundDocument130 pagesFugleberg SigmundEdon BediNo ratings yet
- The Flame Test I. Objectives:: Grade 9 - Science Activity SheetDocument3 pagesThe Flame Test I. Objectives:: Grade 9 - Science Activity SheetJoana Rose Fantonial100% (1)
- Calculations ExamplesDocument7 pagesCalculations ExamplesMduduzi Magiva MahlanguNo ratings yet
- MC Acids and AlkalisDocument12 pagesMC Acids and Alkalisapi-3826629100% (1)
- Soda Ash: Product Data Sheet (PDS)Document1 pageSoda Ash: Product Data Sheet (PDS)Mannar1No ratings yet
- Effects of High Silicon on Graphite Morphology and Properties of Ductile IronDocument11 pagesEffects of High Silicon on Graphite Morphology and Properties of Ductile IronYogesh S Yogi SNo ratings yet
- Class X Chapter 1Document5 pagesClass X Chapter 1Krish TiwariNo ratings yet
- Hindalco Industries LimitedDocument1 pageHindalco Industries LimitedRaj Kumar0% (1)
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument95 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsMR. LEGEND GAMER YT100% (1)
- Formulae, Equations, Amounts of Substance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPDocument19 pagesFormulae, Equations, Amounts of Substance (Multiple Choice) 1 QPveronica burlacuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry c1 Core PracticalsDocument18 pagesChemistry c1 Core PracticalsgriggansNo ratings yet
- Colors in Cosmetics: Regulation and Nomenclature in The United StatesDocument7 pagesColors in Cosmetics: Regulation and Nomenclature in The United StatesRosa Mª VillariñoNo ratings yet
- Metal Alloys: Components, Applications and Manufacturing ProcessesDocument6 pagesMetal Alloys: Components, Applications and Manufacturing ProcessesJanuszUlpindoNo ratings yet
- 0620 s05 Ms 3Document7 pages0620 s05 Ms 3Varun PanickerNo ratings yet