Professional Documents
Culture Documents
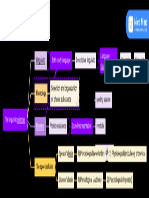
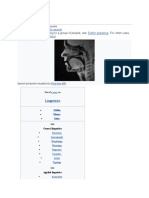
Branches of The Linguistics Tree2.1
Uploaded by
Kenedith Jhadira Orihuela SanchezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Branches of The Linguistics Tree2.1
Uploaded by
Kenedith Jhadira Orihuela SanchezCopyright:
Available Formats
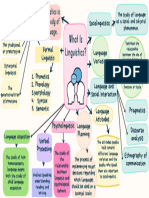
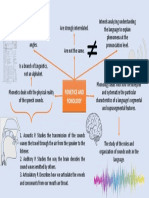
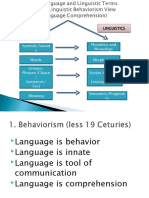
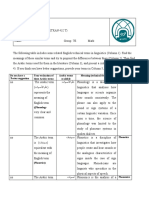
Human language ≠ Animal language
INTRODUCTION Flexible
Complex
Social science language Central to culture
MODERN LINGUISTICS Linguists ≠ Polyglots
Working of all language Speak many language
Speech sounds
Phonetics and Phonology Language sounds
Phonemes, basic units of sound
RANCHES OF THE
B Words
LINGUISTICS TREE Morphology and Syntax Study of words and grammar
The way words
MAIN BRANCHES Direct understanding of words
Semantics and Pragmatics Language and meaning
Different meanings
Sociolinguistics Link to society Phenomena Dialects and accents
Language
Psycholinguistics Mental activity
Thought
What's language?
QUESTIONS What causes language variation?
How is language learnt?
You might also like
- Activity in EnglishDocument8 pagesActivity in EnglishMa. Maureen DariaNo ratings yet
- MindmapDocument1 pageMindmapJeremias BarriosNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document3 pagesHomework 1NATALY GUADALUPE CARRILLO SARABIANo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind Mapnyu tsukiyomiNo ratings yet
- Linguistic TermsDocument34 pagesLinguistic TermsMEL45No ratings yet
- Vocabulary Bank Unit 3Document1 pageVocabulary Bank Unit 3Miguel Eduardo P GNo ratings yet
- Phonetics & PhonologyDocument10 pagesPhonetics & PhonologyBlasy Jean Baraga TalaidNo ratings yet
- Language & Linguisti CS: DR. R. SoundararajanDocument6 pagesLanguage & Linguisti CS: DR. R. Soundararajansoundar12No ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapANGELLY DANIELA MARTINEZ CHAMORRONo ratings yet
- Micro and Macro Linguistic StudiesDocument2 pagesMicro and Macro Linguistic StudiesMyles Joshua Astronomo100% (1)
- Introduction To LinguisticDocument4 pagesIntroduction To LinguisticMa Khristina S WongNo ratings yet
- Language: "It Is System of Conventional Signals Used For Communication by A Whole Community"Document18 pagesLanguage: "It Is System of Conventional Signals Used For Communication by A Whole Community"daniela_farreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Language - Boundless PsychologyDocument1 pageIntroduction To Language - Boundless PsychologyZara NurNo ratings yet
- Speech: Public Speaking Speech (Disambiguation)Document4 pagesSpeech: Public Speaking Speech (Disambiguation)Zarah Joyce SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Language and CurriculumDocument16 pagesLanguage and Curriculumhamka_dindaNo ratings yet
- Aligns With The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) From Kindergarten To Grade 5 For English Language ArtsDocument8 pagesAligns With The Common Core State Standards (CCSS) From Kindergarten To Grade 5 For English Language ArtsKhuc Huong TraNo ratings yet
- Universidad Montrer: Maestría en Inglés para La EnseñanzaDocument2 pagesUniversidad Montrer: Maestría en Inglés para La EnseñanzaEstefanía AlfaroNo ratings yet
- PNP Assignment - Difference Between Phonetics and PhonologyDocument6 pagesPNP Assignment - Difference Between Phonetics and PhonologyMuhammad Jawwad Ahmed100% (1)
- What Is The Universalist Theory of Language?Document78 pagesWhat Is The Universalist Theory of Language?LoraNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology Are Both Related To The Production of SoundDocument4 pagesPhonetics and Phonology Are Both Related To The Production of SoundElena Victoria DuarteNo ratings yet
- Phonology Hand OutDocument46 pagesPhonology Hand OutCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Non-Verbal CommunicationDocument1 pageUnit 4. Non-Verbal CommunicationAna FernándezNo ratings yet
- Speaking of Writing and Writing of Speaking: Written Language Vs Spoken LanguageDocument3 pagesSpeaking of Writing and Writing of Speaking: Written Language Vs Spoken LanguageIvánNo ratings yet
- Effective Interventions For Word Decoding and Reading ComprehensionDocument31 pagesEffective Interventions For Word Decoding and Reading ComprehensionLuz Maria LavalleNo ratings yet
- Theories of Language DevelopmentDocument7 pagesTheories of Language DevelopmentTamamaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Phonological AwarenessDocument6 pages1.2 Phonological AwarenessMaria P12No ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument5 pagesUnit 1 NotesFlory CabaseNo ratings yet
- Filipino LectureDocument11 pagesFilipino LecturePaula DavidNo ratings yet
- Speech: LinguisticsDocument3 pagesSpeech: LinguisticsDean Joyce AlborotoNo ratings yet
- Semantics 1Document6 pagesSemantics 1bluc3cl0udNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document7 pagesUnit 1gianfmarchiondaNo ratings yet
- Linguistic Theories, Branches and FieldsDocument13 pagesLinguistic Theories, Branches and FieldsChaima GuezzziNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology Concept MapDocument2 pagesPhonetics and Phonology Concept MapMargarito EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Mind Map II Describing LanguageDocument1 pageMind Map II Describing Languageputri yasminNo ratings yet
- Language FlashcardsDocument52 pagesLanguage FlashcardsLoraNo ratings yet
- The Phonemic PrincipleDocument8 pagesThe Phonemic PrincipleShruti SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Socio Activity 1Document2 pagesChapter 3-Socio Activity 1Maria Cristina ImportanteNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 7e2Document2 pagesAssignment 1 7e2DrRasha Abo ShoShaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Phonetics and PhonologyDocument2 pagesDifference Between Phonetics and PhonologyBenzzRaeyeldie100% (1)
- Difference Between Phonetics & PDFDocument3 pagesDifference Between Phonetics & PDFSharjeelazharNo ratings yet
- Welcom E: Language & LinguisticsDocument19 pagesWelcom E: Language & LinguisticsRSoundararajanengNo ratings yet
- Phonology: Michell Engracia 17063000044Document7 pagesPhonology: Michell Engracia 17063000044Michell515No ratings yet
- Lec.1.Introduction To LinguisticsDocument19 pagesLec.1.Introduction To LinguisticsLillyNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument84 pagesPhoneticsﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞﱞNo ratings yet
- Banaat Ain Shams November 2018 (Prof. Bahaa Mazeed)Document99 pagesBanaat Ain Shams November 2018 (Prof. Bahaa Mazeed)Omnia N. Elkholy100% (4)
- LinguisticsDocument12 pagesLinguisticsAngelica MalpayaNo ratings yet
- ch1Document17 pagesch1arie indra100% (1)
- Linguistics Vs Applied LinguisticsDocument1 pageLinguistics Vs Applied LinguisticsBRAHYMGS S.ttuarw0% (1)
- Pragmatics Phonology Semantics: MorphologyDocument9 pagesPragmatics Phonology Semantics: MorphologyGenevieve Guimbongan Siagto100% (1)
- Basic ConceptsDocument18 pagesBasic Conceptsss ssNo ratings yet
- Morphology and Syntax - MorphologyDocument13 pagesMorphology and Syntax - Morphologybera wellyNo ratings yet
- Cornell NotesDocument6 pagesCornell NotesJordan CarinuganNo ratings yet
- Introduction SlaDocument6 pagesIntroduction SlaLiliam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Expo - L'IVDocument13 pagesExpo - L'IVCarolina Flores BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Linguistics 2k20 I-SemesterDocument13 pagesLinguistics 2k20 I-SemesterMemon MemonNo ratings yet
- Diss 11-Lesson 6Document26 pagesDiss 11-Lesson 6Stephen Gagarin SidayonNo ratings yet
- Wednesday Figuartive Language PPDocument25 pagesWednesday Figuartive Language PPShooky LollipopNo ratings yet
- Syllabus LinguisticsDocument7 pagesSyllabus LinguisticsCasie ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Phonetics PhonologyDocument18 pagesBasic Concepts Phonetics Phonologyss ssNo ratings yet
- Sign Language of the Deaf: Psychological, Linguistic, and Sociological PerspectivesFrom EverandSign Language of the Deaf: Psychological, Linguistic, and Sociological PerspectivesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lesson Plan For EnglishDocument8 pagesLesson Plan For EnglishNOOR AZNINo ratings yet
- EBOOK 978 0123750976 Handbook of Neuroendocrinology Download Full Chapter PDF KindleDocument61 pagesEBOOK 978 0123750976 Handbook of Neuroendocrinology Download Full Chapter PDF Kindlejuan.speight804100% (36)
- Hatton, Christine - Young at Art Classroom Playbuilding in Practice PDFDocument205 pagesHatton, Christine - Young at Art Classroom Playbuilding in Practice PDFSabina BalanNo ratings yet
- A Century of Social Psychology PDFDocument21 pagesA Century of Social Psychology PDFMarcia JohnssonNo ratings yet
- GLOSSARY (Communication Skills Terms)Document12 pagesGLOSSARY (Communication Skills Terms)Janie100% (1)
- Educ 103. RamosDocument4 pagesEduc 103. RamosTeecoy RamosNo ratings yet
- Project SynopsisDocument7 pagesProject SynopsisAbinash MishraNo ratings yet
- Feminist Theoretical Frameworks: Gender StudiesDocument2 pagesFeminist Theoretical Frameworks: Gender StudiesMcdared GeneralaoNo ratings yet
- AnthologyDocument315 pagesAnthologycullen1224100% (1)
- Microsoft Solution Acceleration Hack PlaybookDocument11 pagesMicrosoft Solution Acceleration Hack PlaybookDaniel SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chap03 (1) With Answers PDFDocument76 pagesChap03 (1) With Answers PDFNihalAbou-GhalyNo ratings yet
- Artigo Salerno 1Document3 pagesArtigo Salerno 1Henrique Luiz WeberNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Arrival: Erasmus+ Programme - Student Mobility For TraineeshipsDocument1 pageCertificate of Arrival: Erasmus+ Programme - Student Mobility For TraineeshipsGt SergioNo ratings yet
- Laoang Elementary School School Boy Scout Action Plan Objectives Activities Time Frame Persons Involve Resources NeededDocument3 pagesLaoang Elementary School School Boy Scout Action Plan Objectives Activities Time Frame Persons Involve Resources NeededMillie Lagonilla100% (5)
- 49 Commencement Exercises Senior High School Department S.Y. 2018 - 2019Document8 pages49 Commencement Exercises Senior High School Department S.Y. 2018 - 2019rey anne danoNo ratings yet
- Review of Effective Human Resource Management Techniques in Agile Software Project ManagementDocument6 pagesReview of Effective Human Resource Management Techniques in Agile Software Project ManagementAmjad IqbalNo ratings yet
- How Many Hours Should One Study To Crack The Civil Services Exam?Document27 pagesHow Many Hours Should One Study To Crack The Civil Services Exam?654321No ratings yet
- Hypothesis Test - Difference in MeansDocument4 pagesHypothesis Test - Difference in Meansr01852009paNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Digital MarketingDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Digital Marketingsajjad sharifNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentation SkillDocument12 pagesOral Presentation SkillSyairah Ibrahim67% (3)
- Recursos Complementarios - SONGS, ONLINE GAMES - , APLICACIONESdocxDocument6 pagesRecursos Complementarios - SONGS, ONLINE GAMES - , APLICACIONESdocxMirtaMoratoNo ratings yet
- Policy Brief Social MediaDocument3 pagesPolicy Brief Social MediabygskyNo ratings yet
- Phil-IRI POST TEST Reading Selection Form A4Document6 pagesPhil-IRI POST TEST Reading Selection Form A4ariel mateo monesNo ratings yet
- Take Off - Workbook PDFDocument108 pagesTake Off - Workbook PDFSam Love0% (1)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Engineering (Adpharming) : Accreditation Course AimsDocument2 pagesAdvanced Pharmaceutical Engineering (Adpharming) : Accreditation Course AimsJohn AcidNo ratings yet
- Users of Financial Accounts - Tutor2u BusinessDocument5 pagesUsers of Financial Accounts - Tutor2u BusinessmwhaliNo ratings yet
- Resume 1Document2 pagesResume 1api-545477536No ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 7 Final DemoDocument9 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 7 Final DemoEljean LaclacNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications in English (Third Quarter) : Aysain IGH ChoolDocument1 pageTable of Specifications in English (Third Quarter) : Aysain IGH ChoolJanine Huelgas-AlbardaNo ratings yet
- Pe GradesDocument6 pagesPe Gradesarvin bermudezNo ratings yet