Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Characteristics and More of The Reactors
Uploaded by
ESAU ISAM PARTIDA ESPARZAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Characteristics and More of The Reactors
Uploaded by
ESAU ISAM PARTIDA ESPARZACopyright:
Available Formats
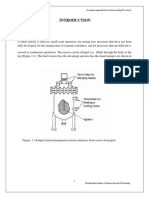
Characteristics and more of the reactors
Type of reactor
characteristics phases present use advantages disadvantages
Batch luquid and gas small productions, laboratory kinetic studies A single vessel can perform a sequence of multiple product affected by the cyclical
there is no inflow or outflow reactor, with a stirrer that homogenizes the mixture operations without the need to break containment nature
Stirred tank continuous flow reactors are normally applied in waste water
CSTR used to estimate key unit operating variables when a continuous stirred luquid and gas and solids treatment processes. CSTRs facilitate types of dilution which make them
tank reactor is used to achieve specified output. resistant to high pH and low pH volatile fatty acid residues. in flow and out flow, good mixing expencive, dificult cleaning
These reactors work in a steady state. That is, the properties at a given the tubular reactor (PFR) is used to model chemical
PFR Gas and liquid High conversion per unit volume, flexibility of
point in the reactor are constant over time. This model assumes ideal transformations of compounds that are transported in High operating costs.
operation.
piston flow, and the conversion is a function of position. systems that look like pipes
Article of chemical kinetics
Effect of water temperature on the reaction rate constant of pollutants in a constructed wetland for the treatment of swine wastewater
Temperature is an important factor in the processes that take place in biological systems. In wetlands, the pollutant removal capacity
is limited by environmental factors. The objective was to determine the effect of water temperature on the pollutant reaction rate
constant in a constructed surface flow wetland (HFSC) for the removal of pollutants in swine wastewater. The HFSC consisted of a
channel 9 m long by 3 m wide, covered with a high-density geo-membrane (4 mm). The HFSC bed consisted of a 30 cm layer of sand
and clay, with vegetation native to the study area. Twelve experimental runs were carried out between January 2014 and December
2015, with a hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 10 days. The average removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD) was 75 and 74%, the
average removal of nitrogen (ammonium) NH3-N was 65 and 69%, while the total nitrogen (NT) presented average removal of 69
and 63%, while the removal of total phosphorus (PT) presented values of 75 and 73% in 2014 and 2015 respectively. The water
temperature during the experimental phase ranged between 13 and 22 ° C. NH3-N removal showed the highest dependence on
water temperature with values of R 2 = 0.8787 in 2014 and R 2 = 0.8957 in 2015.
You might also like
- UntitledDocument15 pagesUntitledKELEBOGILE LEAGO MAKGAHLELANo ratings yet
- Theory Thesis PFR ReationDocument18 pagesTheory Thesis PFR ReationAmit RewatkarNo ratings yet
- Differential ReactorDocument3 pagesDifferential ReactorCik Tiem Ngagiman100% (1)
- 1.0 Summary: CKB 20104-Reaction Engineering: Experiment 4 Reactor Test Rigpage - 5Document14 pages1.0 Summary: CKB 20104-Reaction Engineering: Experiment 4 Reactor Test Rigpage - 5amirul ashrafNo ratings yet
- Eduria Assignment 3Document3 pagesEduria Assignment 3Crystal Joy EduriaNo ratings yet
- Reactor Sizing:) 9 Lecture (Document10 pagesReactor Sizing:) 9 Lecture (Eko PriyadiNo ratings yet
- Background Study On Continuously Stirred Tank ReactorDocument4 pagesBackground Study On Continuously Stirred Tank ReactorSyazani HussainiNo ratings yet
- Che 416Document42 pagesChe 416Ifiok UsoroNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 CPPDocument3 pagesExp 1 CPPAzwa FamiezaNo ratings yet
- Perancangan Pabrik Kimia I: Pemilihan ReaktorDocument11 pagesPerancangan Pabrik Kimia I: Pemilihan ReaktorHR 47No ratings yet
- PEN202 - Lecture 3 - Reactor Comparison and Semibatch ReactorDocument4 pagesPEN202 - Lecture 3 - Reactor Comparison and Semibatch Reactorfaltu facchaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument3 pagesChemical Reaction EngineeringMuhammad AlfiNo ratings yet
- 2012 CH 5 1 ReactorsDocument34 pages2012 CH 5 1 ReactorsKiran ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Palding, Justine Grace M. Operations and Applications of General Types of Reactors 1. Batch ReactorDocument3 pagesPalding, Justine Grace M. Operations and Applications of General Types of Reactors 1. Batch ReactorAngelica Joyce BenitoNo ratings yet
- Continuous Stirred Tank ReactorDocument11 pagesContinuous Stirred Tank ReactorFikrie Muhd100% (1)
- Classification & Selection of Chemical ReactorsDocument3 pagesClassification & Selection of Chemical ReactorsGhulam MurtazaNo ratings yet
- R SDocument6 pagesR S0a1l2i3.h4a5s6s7a8n9No ratings yet
- CSTR in SeriesDocument6 pagesCSTR in SeriesMuqarrabin Hairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Equipment Design Part 3 (R-101)Document37 pagesChapter 3 - Equipment Design Part 3 (R-101)aimanrsln0% (1)
- Tutorial Exp 4Document4 pagesTutorial Exp 4Faris Hamir100% (4)
- Types of Reactor2Document4 pagesTypes of Reactor2Aleem AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2013 CH 5-1 ReactorsDocument33 pages2013 CH 5-1 ReactorsronaldNo ratings yet
- 4 ReactorsDocument58 pages4 ReactorsKiran ShresthaNo ratings yet
- ChE422 Topic 01-2017Document9 pagesChE422 Topic 01-2017ARIANA NICOLE RELIGIOSONo ratings yet
- Bio Chem Engg Data-1 (2) - 1Document121 pagesBio Chem Engg Data-1 (2) - 1Abubakr KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduced Into The Reactor, While Products Are Continuously RemovedDocument2 pagesIntroduced Into The Reactor, While Products Are Continuously Removedurwah naveedNo ratings yet
- Mapping Reactor Operating Regimes For Heavy Gas Oil HydrotreatingDocument5 pagesMapping Reactor Operating Regimes For Heavy Gas Oil HydrotreatingIan MannNo ratings yet
- Reaction Mini ProjekDocument5 pagesReaction Mini ProjekMeck LotfiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document16 pagesUnit 5Sakthivel PandianNo ratings yet
- Types of ReactorsDocument8 pagesTypes of ReactorsAli Ahmad94% (17)
- Intro Lab Report Process Modelling & SimulationDocument3 pagesIntro Lab Report Process Modelling & SimulationSelly The SpiceNo ratings yet
- Cinética Química UDocument16 pagesCinética Química UJesus Manuel Yallerco VenegasNo ratings yet
- Lectura 4. Structured Packings For Multiphase Catalytic ReactorsDocument32 pagesLectura 4. Structured Packings For Multiphase Catalytic ReactorsTRIANA FORERO GABRIEL RICARDONo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 CRE Harshit Joshi179101014Document8 pagesExperiment 2 CRE Harshit Joshi179101014Harshit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Abstract, Intro-Cstr in SeriesDocument2 pagesAbstract, Intro-Cstr in SerieshishamNo ratings yet
- Reactors1 35Document2 pagesReactors1 35Mourad kharbachNo ratings yet
- PCE Lecture 5 3 CRE ReactorsDocument12 pagesPCE Lecture 5 3 CRE ReactorsDaniel MarkNo ratings yet
- Hysys Project of Chemical Reaction Engineering: Prepared By: Mahmoud Mohamed ID: 141761Document9 pagesHysys Project of Chemical Reaction Engineering: Prepared By: Mahmoud Mohamed ID: 141761Mahmoud HendawyNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor: Optical High Precision Components by Hellma in The European Columbus Space LaboratoryDocument16 pagesBatch Reactor: Optical High Precision Components by Hellma in The European Columbus Space Laboratoryangelie_gubatanNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow Reactor (PFR)Document11 pagesPlug Flow Reactor (PFR)Wan AfiffNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Operation of Chemical Reactors Friend or FoeDocument9 pagesDynamic Operation of Chemical Reactors Friend or FoeSteve Wan100% (1)
- Suspended Growth Biological TreatmentDocument21 pagesSuspended Growth Biological Treatmentsaiful islamNo ratings yet
- Reactors: CHML 404-01 Date: 03/11/2019 Unit Operation: 1 Instructor: Dr. MartinezDocument23 pagesReactors: CHML 404-01 Date: 03/11/2019 Unit Operation: 1 Instructor: Dr. MartinezKevin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Water Environment J - 2007 - Morgenroth - Sequencing Batch Reactor Technology Concepts Design and Experiences AbridgedDocument8 pagesWater Environment J - 2007 - Morgenroth - Sequencing Batch Reactor Technology Concepts Design and Experiences AbridgedNabil GyedNo ratings yet
- Conclusion and Tutorial EXP4 Reaction NewDocument1 pageConclusion and Tutorial EXP4 Reaction NewFATMIENo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactorDocument5 pagesChemical Reactornevelle4667No ratings yet
- CKB 20104 Reaction Engineering UniKL MICET Experiment 4: Reactor Test Rig Full Lab ReportDocument14 pagesCKB 20104 Reaction Engineering UniKL MICET Experiment 4: Reactor Test Rig Full Lab ReportSiti Hajar Mohamed100% (10)
- Plant-Wide Hierarchical Optimization and Control of An Industrial Hydrocracking ProcessDocument12 pagesPlant-Wide Hierarchical Optimization and Control of An Industrial Hydrocracking Processlino aroniNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Selection of Enzymatic ReactorDocument5 pagesCriteria For Selection of Enzymatic ReactorParnnika BaroliaNo ratings yet
- ENVE 302 Environmental Engineering Unit ProcessesDocument51 pagesENVE 302 Environmental Engineering Unit ProcessesfatmaNo ratings yet
- Reactors1 29Document2 pagesReactors1 29Mourad kharbachNo ratings yet
- Simulation, Sensitivity Analysis and Optimization of An Industrial Continuous Catalytic Naphtha Reforming ProcessDocument5 pagesSimulation, Sensitivity Analysis and Optimization of An Industrial Continuous Catalytic Naphtha Reforming Processck19654840No ratings yet
- Contoh Kalkulasi Perhitungan Kesetimbangan Massa Dan Aliran HidrolikDocument12 pagesContoh Kalkulasi Perhitungan Kesetimbangan Massa Dan Aliran HidrolikAllen KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Small Flow Liquid Liquid Coalescers FLTR Purple EngineeringDocument4 pagesSmall Flow Liquid Liquid Coalescers FLTR Purple EngineeringFLTR PURPLE E.No ratings yet
- 1.1 AbstractDocument25 pages1.1 AbstractZati TarhiziNo ratings yet
- Sequencing Batch Reactor Technology Conc111Document8 pagesSequencing Batch Reactor Technology Conc111Tho HoangNo ratings yet
- Fixed-Bed Reactor Design and Diagnostics: Gas-Phase ReactionsFrom EverandFixed-Bed Reactor Design and Diagnostics: Gas-Phase ReactionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Integrated Recycling Systems: Harris Complete PackageDocument4 pagesIntegrated Recycling Systems: Harris Complete PackageNicolás Toro ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- WS-250 4BB 60 Cells 40mm DatasheetDocument2 pagesWS-250 4BB 60 Cells 40mm DatasheetTejash NaikNo ratings yet
- Statics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersDocument25 pagesStatics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersProkopyo BalagbagNo ratings yet
- (1895) Indianapolis Police ManualDocument122 pages(1895) Indianapolis Police ManualHerbert Hillary Booker 2ndNo ratings yet
- Longley Rice PropagationDocument11 pagesLongley Rice Propagationy_m_algbaliNo ratings yet
- Payment Systems Worldwide: Appendix Country-by-Country AnswersDocument306 pagesPayment Systems Worldwide: Appendix Country-by-Country Answersravinewatia27No ratings yet
- MGT 201 Midterm Exam, Version BDocument8 pagesMGT 201 Midterm Exam, Version BCybelle TradNo ratings yet
- Aug 2020 Builders Line Tamil MonthlyDocument48 pagesAug 2020 Builders Line Tamil MonthlyBuildersLineMonthlyNo ratings yet
- Exercise Guide - Broad Crested WeirDocument18 pagesExercise Guide - Broad Crested Weirvipul anandNo ratings yet
- UNECE-Turkey-TCDO-Rail Freight Traffic in Euro-Asian LinksDocument20 pagesUNECE-Turkey-TCDO-Rail Freight Traffic in Euro-Asian LinksArseneNo ratings yet
- Telstra InterviewsDocument3 pagesTelstra InterviewsDaxShenNo ratings yet
- Template For Homework6Document2 pagesTemplate For Homework6Никола СтефановићNo ratings yet
- General Description Product Summery: Bvdss Rdson IDDocument4 pagesGeneral Description Product Summery: Bvdss Rdson IDJose Angel TorrealbaNo ratings yet
- Imp121 1isDocument6 pagesImp121 1isErnesto AyzenbergNo ratings yet
- Finman General Assurance Corporation Vs - The Honorable Court of AppealsDocument2 pagesFinman General Assurance Corporation Vs - The Honorable Court of AppealsNorie De los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mittal Corp LTD 22ND November 2022Document4 pagesMittal Corp LTD 22ND November 2022Etrans 9No ratings yet
- Millets: Future of Food & FarmingDocument16 pagesMillets: Future of Food & FarmingKIRAN100% (2)
- 819-5917-April 2021-Domestic Warranty Policy ManualDocument46 pages819-5917-April 2021-Domestic Warranty Policy ManualDean KershnerNo ratings yet
- 2023-2024 Draft Benzie County Budget BookDocument91 pages2023-2024 Draft Benzie County Budget BookColin MerryNo ratings yet
- Pa 28 151 161 - mmv1995 PDFDocument585 pagesPa 28 151 161 - mmv1995 PDFJonatan JonatanBernalNo ratings yet
- 04.CNOOC Engages With Canadian Stakeholders PDFDocument14 pages04.CNOOC Engages With Canadian Stakeholders PDFAdilNo ratings yet
- Vivado Power Analysis OptimizationDocument120 pagesVivado Power Analysis OptimizationBad BoyNo ratings yet
- TC 9-237 Welding 1993Document680 pagesTC 9-237 Welding 1993enricoNo ratings yet
- Formula Retail and Large Controls Planning Department ReportDocument235 pagesFormula Retail and Large Controls Planning Department ReportMissionLocalNo ratings yet
- Hi 3 Yt 318201Document3 pagesHi 3 Yt 318201partha khatuaNo ratings yet
- Home Work (Satistics AIUB)Document5 pagesHome Work (Satistics AIUB)fukscribdNo ratings yet
- Study For 33KV Sub-Marine Cable Crossings PDFDocument80 pagesStudy For 33KV Sub-Marine Cable Crossings PDFOGBONNAYA MARTINSNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Rate of Chemical Reactions Notes Key 1Document3 pagesFactors Affecting The Rate of Chemical Reactions Notes Key 1api-292000448No ratings yet
- New VLSIDocument2 pagesNew VLSIRanjit KumarNo ratings yet
- Estanislao Vs CADocument2 pagesEstanislao Vs CAChammy0% (1)