Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3210 02 02 Student Guide
Uploaded by
Kenneth WevoyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3210 02 02 Student Guide
Uploaded by
Kenneth WevoyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab: Physical and Chemical Changes
Student Guide
Pre-Lab Information
Purpose Explore the differences between physical changes and chemical changes by performing
an experiment.
Time Approximately 45 minutes
Question How can you distinguish a physical change from a chemical change?
Hypothesis If a substance undergoes a physical change, then most of its original properties will be
retained because a new substance is not formed.
OR: If a substance undergoes a chemical change, then it will not retain its original
properties because a new substance is formed.
Summary You will conduct 8 experiments and determine whether you observed a physical or
chemical change.
Safety
Behavior in the lab must be purposeful. Be sure to do the following:
Keep work area clear and uncluttered.
Always wear a lab coat and safety goggles when performing an experiment.
Use the right gear such as chemical resistant gloves (when handling chemicals) and tongs
(when moving hot beakers and crucibles).
Use caution when handling chemicals and hot materials.
Check glassware such as beakers and crucibles for cracks and chips prior to use.
Do not smell or taste any of the chemicals.
Report all accidents ‒ no matter how big or small ‒ to your teacher.
Dispose of chemicals as instructed by your teacher.
Copyright © Edgenuity Inc.
Student Guide (continued)
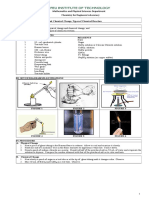
Procedure
Step 1: Materials
Steps 2 and 3 Step 4 Steps 6 Step 8
2 inch piece of calcium 40 mL water 1 spoonful iron filings 25 mL 1M
carbonate (white 100 mL beaker 1 spoonful powdered hydrochloric acid
chalk) hot plate sulfur 3 cm magnesium
25 mL 1M hot pad spoon (2) ribbon (2)
hydrochloric acid petri dish 50 mL beaker
mortar and pestle Step 5 magnet thermometer
spoon 2 g copper(II) sulfate tweezers
50 mL beaker pentahydrate Step 7
spoon Step 9
25 mL 0.1M
crucible
potassium iodide 1 candle on dish
crucible tongs
10 mL 0.1M lead matches
clay triangle
nitrate
tripod
50 mL beaker
Bunsen burner
25 mL graduated
cylinder
Step 2: Calcium carbonate
a) Place a 2-inch piece of calcium carbonate (from chalk) in a mortar. Crush the calcium
carbonate with the pestle.
b) Record all changes observed, the type of change, and your reasoning in the data table.
c) Keep for Step 3.
Step 3: Calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid
a) Pour approximately 25 mL of 1M hydrochloric acid into a 50 mL beaker.
b) Use the spoon to add crushed calcium carbonate from Step 2 to the hydrochloric acid.
c) Record all changes observed, the type of change, and your reasoning in the data table.
d) When finished, dispose of the mixture by pouring it into a receptacle provided by
your teacher.
Step 4: Water
a) Fill a 100 mL beaker with 40 mL of water. Note its physical characteristics.
b) Using a hot plate, heat the water until it boils.
c) Record all changes observed, the type of change, and your reasoning in the data table.
d) Use the beaker tongs to remove hot beaker from hot plate and place on a hot pad.
e) Turn off the hot plate and dispose of the water in a drain.
Step 5: Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate
a) To allow heating, place the clay triangle on top of the tripod and position the Bunsen burner
under the tripod.
b) Measure 2 g (approximately 1/2 tsp.) of copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate in a crucible. Note its
physical characteristics.
c) Place the crucible on the clay triangle.
Copyright © Edgenuity Inc.
Student Guide (continued)
d) Turn the Bunsen burner on to heat the crucible to see a change happen.
e) Record all changes observed, the type of change, and your reasoning in the data table.
f ) Use crucible tongs to remove crucible from clay triangle and let cool.
g) When cooled, dispose of the copper(II) sulfate powder into the receptacle provided by your
teacher.
Step 6: Iron filings and sulfur
a) Measure 2 g (approximately 1/2 tsp.) iron filings on the one side of a petri dish. Note the
physical characteristics of the iron filings.
b) Measure 2 g (approximately 1/2 tsp.) of sulfur on the other side of a petri dish. Note the
physical characteristics of the sulfur.
c) Mix the two materials with the spoon. Note the physical characteristics of the resulting mixture.
d) Run a magnet over the resulting mixture, but do not allow the magnet to touch the mixture.
e) Record all changes observed, the type of change, and your reasoning in the data table.
f) Place the iron filings and sulfur separately into receptacles provided by your teacher.
Step 7: Potassium iodide and lead nitrate
a) Fill a 50 mL beaker with 25 mL 0.1M potassium iodide.
b) Measure 10 mL of 0.1M lead nitrate into a 25 mL graduated cylinder.
c) Pour lead nitrate into the potassium iodide slowly.
d) Record all changes observed, the type of change, and your reasoning in the data table.
e) Dispose of the mixture in the receptacle provided by your teacher.
Step 8: Magnesium and hydrochloric acid
a) Fill a 50 mL beaker with approximately 20 mL of 1M hydrochloric acid.
b) Use a thermometer to measure the temperature of the hydrochloric acid in °C.
c) Use tweezers to drop the two 3 cm magnesium ribbons in the hydrochloric acid.
d) Measure the temperature of the solution again.
e) Record all changes observed, the type of change, and your reasoning in the data table.
(Be sure to consider the change of temperature!)
f) Following your teacher’s instructions, dispose of the mixture in a filter set-up provided by
your teacher.
Step 9: Candle
a) Clear the area of flammable materials.
b) Place the candle on a dish so that it is firmly on it.
c) Use a match to light the candle. Let it burn for approximately 1 minute.
d) Record all changes observed, the type of change, and your reasoning in the data table.
e) Blow out the candle and put the candle and matches in receptacles provided by your teacher.
Copyright © Edgenuity Inc.
Student Guide (continued)
Data
Record your data either in your lab notebook or in the space below.
Type of Change
Step Material Change(s) Observed Reasoning
(Physical/Chemical)
Volume and
Calcium carbonate mass were
Calcium
2 stick crashed, and Physical Change retained, and
carbonate
particles changed size color did not
change
New
Calcium Calcium carbonated
substances
3 carbonate and increased in volume; Chemical change
were formed
hydrochloric acid gas was evaporating
(gas)
Water was
going through
Water boiled and
4 Water Physical change state change,
steam was formed
but properties
were retained
Copper(II) sulfate New
Copper(II) sulfate
5 changed color and gas Chemical Change substances
pentahydrate
evaporated were formed
Even color
change each
Iron filings Colored change
6 Physical change material
and sulfur occurred
maintained it
properties
Lead nitrate and The mixed led to a new New substance
7 Chemical change
potassium iodide color formation was formed
Gas was
Two substances
Magnesium and produced and
``8 mixed; magnesium Chemical Change
hydrochloric acid Temperature
disappeared
changed
Light and heat
were formed,
Candle melted and Chemical and
9 Candle and Candle
burning occurred Physical change
changed shape
and size
Copyright © Edgenuity Inc.
You might also like
- 3210 02 02 Student GuideDocument4 pages3210 02 02 Student GuidePAULA DOMENICA CEVALLOS VACACELANo ratings yet
- Lab - Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument5 pagesLab - Physical and Chemical ChangesJulio RNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 VSDocument3 pagesActivity 7 VSJayson P. JalbunaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 7 - Physical and Chemical Changes 1Document5 pagesExperiment No. 7 - Physical and Chemical Changes 1Airame Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Physical Changes Vs Chemical Changes Atikah Nur Syahirah Program Studi Kimia, Universitas Negeri MedanDocument8 pagesPhysical Changes Vs Chemical Changes Atikah Nur Syahirah Program Studi Kimia, Universitas Negeri Medanronald sinagaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Classes and Changes in MatterDocument4 pagesExperiment 2 - Classes and Changes in MatterLaurrence CapindianNo ratings yet
- Ap Lab Manual 2 - Gravimetric Analysis of A Metal CarbonateDocument4 pagesAp Lab Manual 2 - Gravimetric Analysis of A Metal CarbonateJacob StephansNo ratings yet
- Expt 2 New Chem 1036Document6 pagesExpt 2 New Chem 1036leon fenrirNo ratings yet
- Chem Teachers Day Lab HandoutDocument12 pagesChem Teachers Day Lab HandoutСтелянNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1 LabsDocument38 pagesChemistry Unit 1 LabsNathaniel MorrisonNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes Lab Pre-Lab DiscussionDocument4 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes Lab Pre-Lab DiscussionDenver Monico MoscosoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Lab Manual PDFDocument2 pagesExperiment 8 Lab Manual PDFJuvvilyynGraceMahomat100% (2)
- Práctica 6 Atomic Structure. Flame TestDocument29 pagesPráctica 6 Atomic Structure. Flame TestCIPAMOCHA HUERTAS DAVID FERNANDONo ratings yet
- All LabsDocument38 pagesAll LabsKatie BanksNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions: I. Purpose: II. MaterialsDocument4 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions: I. Purpose: II. MaterialsJerneth Nyka FloresNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Change Lab ReportDocument2 pagesPhysical and Chemical Change Lab ReportPretha VijayakumaranNo ratings yet
- 1 Physical and Chemical ChangesDocument7 pages1 Physical and Chemical ChangesHoward KacheNo ratings yet
- Beyond Walls 3Document8 pagesBeyond Walls 3Ken Jethro CarinoNo ratings yet
- Testing 1Document15 pagesTesting 1John WongNo ratings yet
- 2018-2019 COE0002L Experiment No.3Document3 pages2018-2019 COE0002L Experiment No.3Kyle GuarinNo ratings yet
- CHEM 141 Lab 3 (Stoichiometry) ProcedureDocument5 pagesCHEM 141 Lab 3 (Stoichiometry) ProcedureKiersten RobertsNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 20 - Reactions LabDocument10 pagesPhysical Science 20 - Reactions Labapi-349567441No ratings yet
- Activity 1 Q 4 Module 2Document3 pagesActivity 1 Q 4 Module 2orcullo100% (1)
- Determining Properties and Transformation of Matte 2Document4 pagesDetermining Properties and Transformation of Matte 2Sandra JusiNo ratings yet
- Martinez, Escorcia, Garcia, RuizDocument6 pagesMartinez, Escorcia, Garcia, RuizParamoNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 Rearranging planetsREVDocument3 pagesExp 3 Rearranging planetsREVRonet Lopez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- SBA - Ligand ExchangeDocument2 pagesSBA - Ligand Exchangep berger100% (1)
- Energy Chnages in Chemical ReactionsDocument40 pagesEnergy Chnages in Chemical Reactionsmuhammadshadid4No ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Rate of Reactions 1Document6 pagesExperiment 8 Rate of Reactions 1VALLESTERO, GIAN LEAH J.No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Chemistry Types of Reactions LabDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Chemistry Types of Reactions Labapi-239587463No ratings yet
- Chemistry Student HandoutDocument4 pagesChemistry Student HandoutDascaliuc DanielNo ratings yet
- Coffee Cup CalorimetryDocument6 pagesCoffee Cup CalorimetryTrishia Mae PatalinghugNo ratings yet
- G10 Labs Sep 2023Document21 pagesG10 Labs Sep 2023dejonae651No ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 4&5Document12 pagesLaboratory Activity 4&5Pearl CartasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Chemical Transformations and The Law of Conservation of MassDocument7 pagesExperiment 2: Chemical Transformations and The Law of Conservation of MassWill HallNo ratings yet
- Lab PlanDocument4 pagesLab PlanAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lab Report-Elle Necole QuimadaDocument5 pagesLab Report-Elle Necole QuimadaElleNo ratings yet
- Cape Manual Unit 1 2015Document25 pagesCape Manual Unit 1 2015Orlanda EllisNo ratings yet
- FL53098 Chemical Analysis Brass Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesFL53098 Chemical Analysis Brass Lesson Planmbbk5783No ratings yet
- Lab - Investigating Chemical ReactionsDocument14 pagesLab - Investigating Chemical ReactionsYusuf RaheemNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 3 - Acid-Base Titration (Revised) PDFDocument7 pagesLab Activity 3 - Acid-Base Titration (Revised) PDFFranzei CandelariaNo ratings yet
- SPM ChemifDocument54 pagesSPM ChemifHui SanNo ratings yet
- Reboquio - experiment4.OxidationReductionReactions M7 C1Document9 pagesReboquio - experiment4.OxidationReductionReactions M7 C1Denampo Ivan MikhaelNo ratings yet
- 10 - SF9 - U02 - T02 Science Focus 9Document7 pages10 - SF9 - U02 - T02 Science Focus 9Nathan GavenlockNo ratings yet
- PekaDocument64 pagesPekamasitahadenanNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 A Practical Study of Some Group II ElementsDocument4 pagesLab 3 A Practical Study of Some Group II ElementsJahiem NembhardNo ratings yet
- PSP Ioe 1Document3 pagesPSP Ioe 1AdrianaNo ratings yet
- Nina Claire R. Bahin Chem 26.1 2019-02309 Pre-Lab Experiment No. 3 Iodine Clock Reaction I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesNina Claire R. Bahin Chem 26.1 2019-02309 Pre-Lab Experiment No. 3 Iodine Clock Reaction I. ObjectivesNiña Claire BahinNo ratings yet
- CM124-1L - Experiment 2 - Mansilungan-Labreport OnlyDocument8 pagesCM124-1L - Experiment 2 - Mansilungan-Labreport OnlytheressaNo ratings yet
- Science BookletDocument10 pagesScience BookletBEYZA POYRAZNo ratings yet
- A Substitution or Single Displacement Reaction Is Characterized by One Element Being Displaced From A Compound by Another Element. A + BC Ac + BDocument19 pagesA Substitution or Single Displacement Reaction Is Characterized by One Element Being Displaced From A Compound by Another Element. A + BC Ac + BESPITIA GARCIA LAURA CRISTINANo ratings yet
- Black CoringDocument8 pagesBlack CoringawadallaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Practical Manual Classs Xi 2023Document17 pagesCbse Practical Manual Classs Xi 2023Adarsh Kumar PadhanNo ratings yet
- Sba ChemistryDocument19 pagesSba Chemistrykeshane JohnsonNo ratings yet
- HN Lab - 1 2 Types of ReactionsDocument3 pagesHN Lab - 1 2 Types of Reactionskyle_tosh3382No ratings yet
- Percent Copper in Brass LabDocument4 pagesPercent Copper in Brass LabNaeem RehmanNo ratings yet
- FL53215 Chemical Analysis Brass Lesson Plan Uv VisDocument6 pagesFL53215 Chemical Analysis Brass Lesson Plan Uv VisNaeem RehmanNo ratings yet
- AP Review CH 12Document6 pagesAP Review CH 12ygtefferaNo ratings yet
- Electron Ionization Electron Ionization (EI, Formerly Known As Electron Impact) Is An Ionization MethodDocument12 pagesElectron Ionization Electron Ionization (EI, Formerly Known As Electron Impact) Is An Ionization MethodDiego RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Midterm Examination Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationDocument2 pagesMidterm Examination Fire Protection and Arson InvestigationRodne Badua RufinoNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry June 2013 P2 AnswersDocument7 pagesCSEC Chemistry June 2013 P2 AnswerscxcchemistryNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Concept TestDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding Concept TestBenelux ModeNo ratings yet
- Flotacion Ppt-Flotación 2018 - Alexis CamposDocument23 pagesFlotacion Ppt-Flotación 2018 - Alexis CamposLuis Katsumoto Huere AnayaNo ratings yet
- Evaluación de Reservorios Carbonaticos de La Formacion Quintuco, Cuenca Neuquina.Document16 pagesEvaluación de Reservorios Carbonaticos de La Formacion Quintuco, Cuenca Neuquina.Nelson LizarazoNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Empirical Formula of MgODocument7 pagesDetermination of The Empirical Formula of MgOCicy IrnaNo ratings yet
- Wa0019.Document30 pagesWa0019.Georgy BinuNo ratings yet
- Catalytic ConverterDocument17 pagesCatalytic ConverterRavi Donga93% (14)
- SFE - Learning About Chemistry - G B ShulpinDocument235 pagesSFE - Learning About Chemistry - G B ShulpinShiv7_som784100% (2)
- Prac 5.2 Winkler MethodDocument4 pagesPrac 5.2 Winkler MethodHadi AlnaherNo ratings yet
- Acs JPCC 8b06841Document13 pagesAcs JPCC 8b06841Septian Perwira YudhaNo ratings yet
- HCI Chem H2 Paper 1 Question PaperDocument17 pagesHCI Chem H2 Paper 1 Question PaperonnoezNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Principles and Mechanisms 2nd Edition Joel KartyDocument41 pagesOrganic Chemistry Principles and Mechanisms 2nd Edition Joel KartyjennieNo ratings yet
- Self-Assembled Monolayers of Silver Nanoparticles: From Intrinsic To Switchable Inorganic Antibacterial SurfacesDocument10 pagesSelf-Assembled Monolayers of Silver Nanoparticles: From Intrinsic To Switchable Inorganic Antibacterial SurfacesZ DzNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Jeeneetadda.in) NT - 13Document17 pages(WWW - Jeeneetadda.in) NT - 13Nanjundeswaran shanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakaAdestya S. RamadhanNo ratings yet
- InorgDocument273 pagesInorgAdan Khan100% (4)
- Efficient Method For The Direct Preparation of Amides From Carboxylic Acids Using Tosyl Chloride Under Solvent-Free ConditionsDocument4 pagesEfficient Method For The Direct Preparation of Amides From Carboxylic Acids Using Tosyl Chloride Under Solvent-Free ConditionsAhmed ElkamhawyNo ratings yet
- Acidification of UrineDocument14 pagesAcidification of UrineMohan BNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal ExpansiónDocument28 pagesCoefficient of Linear Thermal ExpansiónalexisvergararangelNo ratings yet
- Calabano Clinical Bacteriology Activity 1 (Lab)Document6 pagesCalabano Clinical Bacteriology Activity 1 (Lab)MarkJasperCalabanoNo ratings yet
- Botnay Notes Class 11Document138 pagesBotnay Notes Class 11Suresh chand100% (1)
- Avian HaematologyDocument49 pagesAvian Haematologyshendy canadyaNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Requirements of Copper Smelting Refractories in Refining'Document3 pagesMetallurgical Requirements of Copper Smelting Refractories in Refining'VictorNo ratings yet
- A-Glucosidase Inhibitors From The Seeds of Syagrus RomanzoffianaDocument6 pagesA-Glucosidase Inhibitors From The Seeds of Syagrus RomanzoffianaAlperay GirişbayNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2019Document30 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2019Ahmad MohdNo ratings yet
- 18OIL109 Eye ProductsDocument5 pages18OIL109 Eye ProductsNEELAVRO PALNo ratings yet
- Corrosion InhibitorDocument6 pagesCorrosion Inhibitorpadmesh awasthiNo ratings yet