Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scheme of Work YR8 T2
Uploaded by
FRANKA JLLA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views4 pagesScheme of Work YR8 T2
Uploaded by
FRANKA JLLACopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
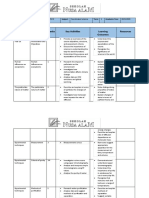
SCHEME OF WORK - YEAR 8
TOPIC PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
The Earth's Climate
Describe the difference between climate and
Weather and Climate
weather
Atmosphere and Climate Understand that the Earth's climate can
change due to atmospheric change
Understand that there is evidence that the
Earth's climate exists in a cycle between
Climate and Ice Ages
warm periods and ice ages, and the cycle
takes place over long time periods
Kinetic Particle Theory
State the particle theory and give the
Particle Theory
suporting statements
Use the particle theory to explain the
properties of solids, liquids and gases
Describe what happens to matter during
Heating and Cooling Substances changes in state in terms of particle theory
Describe what happens when solids expand
Distinguish between boiling and evaporation
Purity
Know that purity is a way to describe how
Pure and Impure Substances
much of a specific chemical is in a mixture
Explain the criteria for purity
Calculate percentage purity
ORK - YEAR 8
Describe trends and patterns in results, including
identifying any anomalous results.
Evaluate whether measurements and observations have
been repeated sufficiently to be reliable.
Make conclusions by interpreting results and explain the
limitations of the conclusions.
learn about the atmosphere of the Earth
learn how a change in the atmosphere can affect the
climate
learn about renewable resources
learn about how the Earth’s climate has changed in the
past
find out about ice ages, glacial periods and interglacial
periods
look at some of evidence that the Earth’s climate cycles
between colder and warmer periods
explain what is meant by purity
describe how it is difficult to get a pure product
SCHEME OF WORK - YEAR 7
TOPIC PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
Physical Properties of Matter
Understand that all substances have
Chemical and Physical Properties chemical properties and physical properties
Classify substances as metals and non-
Metals and Non-metals
metals in terms of their properties
State common applications of metals and
non-metals
Physical Properties of Materials Investigate everyday materials
Understand that alloys are mixtures that
Metal Mixtures (Alloys) have different chemical and physical
properties from the constituent substances
Use the physical properties of matter to
Separating Mixtures
separate mixtures
Chemical Reactions
Physical vs Chemical Changes Distinguish between physcial and chemical
changes
Chemical Reactions Distinguish between reactants and products
State common observations that occur
during chemical reactions
Deduce accurate inference from the
observations
SCHEME OF WORK - YEAR 7
KEY VOCABULARY
Chemical properties, physical properties, appearance,
Sort, group and classify phenomena, objects, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, magnetism,
materials and organisms through testing,
observation, using secondary information, and malleability, ductility, flexibility, density, hardness,
lustre,
making and using keys
chemical reaction
surface appearance, rigid, flexible, hard or soft,
malleable, brittle, absorbent, transparent, waterproof,
ductile
Use the particle model to explain the Alloy, mixture, chemical property, physical property,
difference in hardness between pure metals constituent, tensile strength, particle model, hardness,
and their alloys. pure metals, alloys
Plan and carry out an experiment to seprate magnetism, boiling point, particle size, solubility,
given mixtures using a given physical property electrical conductivity
effervesence, fizzing, bubbling, dissolving, colour, heat
change, precipitates formed, change in mass or size,
colour changes
You might also like
- 2023 Yr 8 Student Chemistry PlannerDocument4 pages2023 Yr 8 Student Chemistry Plannercaitlinyore09No ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Ncbts-Based Let 2009 TosDocument7 pagesPhysical Sciences Ncbts-Based Let 2009 TosEngineerEducatorNo ratings yet
- Marina International School: Science Scheme of WorkDocument13 pagesMarina International School: Science Scheme of WorkMariama KanyiNo ratings yet
- Chem 1012Document170 pagesChem 1012debela jufarNo ratings yet
- Subject Grade Learning Objective Unit 5 States of MatterDocument3 pagesSubject Grade Learning Objective Unit 5 States of MatterPutra Habib DhitarekaNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Year 7 Science 2017-18Document4 pagesScheme of Work Year 7 Science 2017-18Anonymous mYCBVO100% (1)
- 04 Unit 2. Matter and EnergyDocument29 pages04 Unit 2. Matter and EnergyKevin Mark IlaganNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Term 1 PlanDocument4 pagesYear 10 Term 1 PlanSarah-Jane RogersNo ratings yet
- Grade - 7 Scholarship Exam SyllabusDocument13 pagesGrade - 7 Scholarship Exam Syllabusstale cakeNo ratings yet
- Genchem ModuleDocument68 pagesGenchem ModuleThessa Vee Capuno RioNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1Document6 pagesStudy Guide 1Rochelle Anne BandaNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument56 pagesChem NotesEshita SuvarnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - CHEM 16Document23 pagesChapter I - CHEM 16rosalie toqueroNo ratings yet
- 01 The Study of Chemistry and MeasurementsDocument6 pages01 The Study of Chemistry and MeasurementsJoshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Learning PacketDocument20 pagesWeek 2 - Learning PacketMichael TayagNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - Introduction of The SubjectDocument35 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - Introduction of The SubjectNina Grace FamosoNo ratings yet
- What Is Chemistry?Document37 pagesWhat Is Chemistry?Evita Sandra PaculanangNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Chapter 1: Introduction: Matter and Measurement ChemistryDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Chapter 1: Introduction: Matter and Measurement ChemistryGIAN CARLONo ratings yet
- Least Learned CompetenciesDocument6 pagesLeast Learned CompetenciesMichaelAbdonDomingoFavoNo ratings yet
- Parent Science Curriculum 7.31.14 PDFDocument31 pagesParent Science Curriculum 7.31.14 PDFJesús Eduardo Carbonó NieblesNo ratings yet
- 1 Chem 103 ModuleDocument14 pages1 Chem 103 ModuleREIZYL MARGARETTE IMANNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 (Grade 11-STEM) : The Study of MatterDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 (Grade 11-STEM) : The Study of MatterRafael MalonzoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Module 1Document26 pagesGen Chem Module 1Honey DJNo ratings yet
- Enabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Document49 pagesEnabling and Enrichment Competencies For Science Melcs (Most Essential Learning Competencies)Zea May BiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Basic Concepts About Matter: Area Chemistry/Science What Is Being Studied EmphasisDocument9 pagesChapter 1. Basic Concepts About Matter: Area Chemistry/Science What Is Being Studied EmphasisYhena ChanNo ratings yet
- North Carolina Essential Standards 6-8 Science: Note On NumberingDocument10 pagesNorth Carolina Essential Standards 6-8 Science: Note On Numberingapi-277480617No ratings yet
- General Chemistry PPT-1Document31 pagesGeneral Chemistry PPT-1Temesgen SilabatNo ratings yet
- 01 States of MatterDocument3 pages01 States of MatterbadhriNo ratings yet
- 01 04 JournalDocument3 pages01 04 JournalAkshay KarthikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Matter and Its PropertiesDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Matter and Its PropertiesJennelyn BaylonNo ratings yet
- Elements: Context AreaDocument22 pagesElements: Context AreaEren SevinceNo ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument22 pagesProperties of MatterNicole Joyce Catabay FloresNo ratings yet
- Module Shs Chem1Document4 pagesModule Shs Chem1Ansel SotnasNo ratings yet
- Y8 Chemistry Assessment Outline 2023Document1 pageY8 Chemistry Assessment Outline 2023Komal SainiNo ratings yet
- CHE 1-2 Chapter 1 NotesDocument33 pagesCHE 1-2 Chapter 1 NotesCherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Documento Sin TítuloDocument14 pagesDocumento Sin Títulodiane24.stonehouseNo ratings yet
- Hapter Atter and Hange: Chemistry 1-2 Mr. ChumbleyDocument33 pagesHapter Atter and Hange: Chemistry 1-2 Mr. Chumbleyshahad mohammadNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry SOLO Student Objectives 2023Document1 pageStoichiometry SOLO Student Objectives 2023tangwindsonNo ratings yet
- Matter and OthersDocument54 pagesMatter and OthersAnonymous p1txoupQGvNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument38 pagesMattergabbie dumpNo ratings yet
- Integrated ScienceDocument6 pagesIntegrated Scienceiteachclassroom100% (2)
- IPC Chemistry TEKSDocument1 pageIPC Chemistry TEKSJo ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Module in General Chemistry 1 LessonDocument9 pagesSelf-Learning Module in General Chemistry 1 LessonGhaniella B. JulianNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade Science Scope and Sequence 2017-18Document2 pages5th Grade Science Scope and Sequence 2017-18api-292868056No ratings yet
- Chapter 1, PPT, NewDocument14 pagesChapter 1, PPT, Newyonatanteshome48No ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 PDFDocument254 pagesChemistry 1 PDFVinay ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- ModuleDocument7 pagesModuleapi-353861615100% (1)
- Lesson 13 Properties of MatterDocument12 pagesLesson 13 Properties of MatterKrish D.No ratings yet
- Special Science Elementary SchoolDocument5 pagesSpecial Science Elementary SchoolRobbie Rose LavaNo ratings yet
- Chem01 - General and InorganicDocument15 pagesChem01 - General and InorganicJetz Hontimara RegioNo ratings yet
- 2018 Year 9 Science ProgramDocument16 pages2018 Year 9 Science Programapi-364379734No ratings yet
- Teacher-Made Learner's Home Task: S7MT-ib-c-3 S7MT-id-e-2Document4 pagesTeacher-Made Learner's Home Task: S7MT-ib-c-3 S7MT-id-e-2Carissa Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- 2023 Year 8 Chemistry Program STUDENTDocument1 page2023 Year 8 Chemistry Program STUDENTSophia RoperNo ratings yet
- Phy-Sci Majorship Hand OutDocument166 pagesPhy-Sci Majorship Hand OutRowell PantilaNo ratings yet
- Matter - Lesson 1 - ChemistryDocument14 pagesMatter - Lesson 1 - ChemistryFontanilla, Nathaniel D.100% (1)
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument19 pagesIntroduction To ChemistryDianne Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work (Sci.7)Document6 pagesBudget of Work (Sci.7)Mariah ThezNo ratings yet
- Properties and Changes of MatterDocument21 pagesProperties and Changes of MatterMiraNo ratings yet
- CBSE XI Text BooksDocument254 pagesCBSE XI Text Booksmsk5in50% (2)
- AHA Fact Sheet 4. HEATING VENTILATION PDFDocument5 pagesAHA Fact Sheet 4. HEATING VENTILATION PDFEnyinnayaOnwubikoNo ratings yet
- Private Pilot Maneuvers C172Document26 pagesPrivate Pilot Maneuvers C172Yves LavrillouxNo ratings yet
- Wind Riders of The Jagged Cliffs PDFDocument138 pagesWind Riders of The Jagged Cliffs PDFBenn Doucet100% (1)
- 46 Dani Preventivne Medicine-Zbornik RezimeaDocument182 pages46 Dani Preventivne Medicine-Zbornik RezimeaМилош МујовићNo ratings yet
- ts102n - A Temp Sensors Introduction PDFDocument16 pagests102n - A Temp Sensors Introduction PDFARTHURS316No ratings yet
- Visit To Water BankDocument26 pagesVisit To Water BankMandar Vaman SatheNo ratings yet
- June 1, (Thursday) 2017Document10 pagesJune 1, (Thursday) 2017BS Central, Inc. "The Buzz"No ratings yet
- Science Lab Lists 2018 High School With PricesDocument35 pagesScience Lab Lists 2018 High School With Prices11Brad11No ratings yet
- Rune Factory 3 Magical Staff SpellDocument22 pagesRune Factory 3 Magical Staff SpellGintoki SakataNo ratings yet
- Commerzbank. Frankfurt, Germany. Sir Norman Foster & PartnersDocument7 pagesCommerzbank. Frankfurt, Germany. Sir Norman Foster & PartnersRehana P NawassNo ratings yet
- Exercise of (Dis) AgreementDocument5 pagesExercise of (Dis) Agreement可愛い roblox GachaNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagram WorksheetDocument6 pagesPhase Diagram WorksheetIsaiah Pinto100% (1)
- What Are The Causes and Consequences of Flooding in The Community of Kintyre, St. Andrew, Jamaica?Document45 pagesWhat Are The Causes and Consequences of Flooding in The Community of Kintyre, St. Andrew, Jamaica?Debbie DebzNo ratings yet
- PDS Hempadur 45883Document2 pagesPDS Hempadur 45883Fredy Xavier DomínguezNo ratings yet
- 26 - Using Figures of Seech Grade6Document11 pages26 - Using Figures of Seech Grade6Gie Escoto Ocampo100% (1)
- Adiabatic Gas Law Apparatus ManualDocument8 pagesAdiabatic Gas Law Apparatus ManualmarzinusNo ratings yet
- GCE Business Marketing Planning-CompletedDocument50 pagesGCE Business Marketing Planning-CompletedChand BhewaNo ratings yet
- IsraelDocument7 pagesIsraelRobert Ionut DinuNo ratings yet
- NTC Thermistors:: Type CLDocument3 pagesNTC Thermistors:: Type CLErnesto Moya-AlborNo ratings yet
- Useful Phrases Describing WeatherDocument2 pagesUseful Phrases Describing WeatherRasyidy 'Eddy' Alias87% (238)
- Ingles para TurismoDocument12 pagesIngles para TurismozurinefNo ratings yet
- Ethics EssayDocument12 pagesEthics EssayaprilianisNo ratings yet
- MES Test Preparation Series Part-1Document3 pagesMES Test Preparation Series Part-1Aziz Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- All The Lecture Notes of ME56Document31 pagesAll The Lecture Notes of ME56Kent NabzNo ratings yet
- Time Series Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesTime Series Interview QuestionsHadi RidaNo ratings yet
- TrapsDocument11 pagesTrapsAmandeep AroraNo ratings yet
- Hypixel The Pit's Mystic Price GuideDocument31 pagesHypixel The Pit's Mystic Price GuidekylantdNo ratings yet
- A. Identifying Adjectives and The Words They Modify: CrowdedDocument3 pagesA. Identifying Adjectives and The Words They Modify: CrowdedMarian Trisha PanesNo ratings yet
- SOLAS Pilot LadderDocument8 pagesSOLAS Pilot LadderManoj VarrierNo ratings yet
- TOEF Complete The Summary and Table Completion QuestionsDocument7 pagesTOEF Complete The Summary and Table Completion QuestionsHamod KingNo ratings yet