Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Udd Delm 211
Uploaded by
JEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Udd Delm 211
Uploaded by
JEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZCopyright:
Available Formats
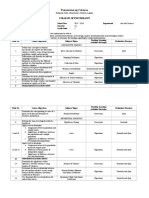
UNIVERSIDAD DE DAGUPAN
School of Professional Studies
Arellano St., Dagupan City
DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY
Major in Educational Leadership and Management
COURSE SYLLABUS
SUBJECT: DELM 211- ADVANCED STATISTICS
CREDIT: 3 UNITS
I. COURSE DESCRIPTION:
This subjects deals with the fundamentals of statistics to the students who have
virtually no mathematics background. The objective is to help students gain confidence
and understanding in applying basic statistical procedures to concrete research situations
in the educational behavioral sciences. It is divided in two (2) parts, namely; Part 1 is on
the descriptive statistics, which includes the measures of central tendency, measures of
variability, and the like, and Part 2 deals with inferential statistics, which include
samples, populations, hypothesis testing, etc. Emphasis is on the acquisition of
knowledge, competence and skills in the use of statistical tools and techniques in
analyzing and interpreting data and drawing conclusions of thesis or research study
II. OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the term, the graduate students are expected to be able to:
Discuss the interlink between statistics and research
Demonstrate skills in computing statistical equations.
Choose and decide the most appropriate statistics with reference to the research
design.
Identify statistical tests for measures of relationship and measures of differences
Interpret computed statistical data as integrated in the research design.
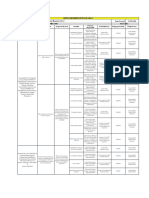
III.CONTENT OUTLINE:
Chapter 1 Overview on the interlink between Statistics and Research
Statistics as Descriptive Study
Statistics as Objective Study
General Concepts in Statistics:
Hypothesis and assumption, Level of Significance at .05 and .01,
Degrees of freedom, Tabular value,
Parametric and Non- parametric Statistics
Validity and Reliability
Chapter 2 Measures of Central Tendency
Calculation of the Mean by the “Assumed mean” or short method
Likert-Scale Method
Average Mean Method
Arithmetic Mean Method
Chapter 3 Measures of Variability
Range, Quartile Deviation, Average Deviation from ungrouped
data,
Ranking and Frequency Distribution
Standard Deviation from group data
Interpretation of standard Deviation
Chapter 4 Measures of Significant Relationship
Calculation of the Coefficients of correlation by the Product
Moment Method (Pearson), Characteristics, Uses, Advantage and
Disadvantage, Formulas/Equations, Pearson r Two distribution,
Pearson r calculated from raw or Obtained scores, Level of
significance, Degree of freedom
Spearman Rho Coefficient
Chi-Square
Chapter 5 Measure of Significant Difference
Calculation of z test and t-test as distribution for significant
differences.
ANOVA
Others under Parametric and Non Parametric Statistics
IV. METHODOLOGY/TEACHING STRATEGIES:
Submission of Activities
Class Participation in Model-sample Computation
V. COURSE REQUIREMENTS:
Regular Attendance
Active Class Participation
Major Exam (Midterm and Final)
Scholarly Written Researched and Internet-Surfed Topics Using the Prescribed
Format
Submission of Critiqued Articles/Reaction Papers
VI. EVALUATION
Active Participation 15%
Oral Reporting 20 %
Reaction Paper/Research Work 25 %
Examination 25 %
Attendance 15%__
100 %
VII. TEXTBOOK/REFERENCES:
Fundamental Concepts and Methods in Statistics (Part 1&2) George A. Garcia,
University of Santo Tomas Publishing House, Manila, Philippines, 2004
General Statistics Made Simple for Filipinos by Nocon, et. al.,National Bookstore
Publisher, Manila, 2000
Basic Statistical Methods by N.M. Downie and Robert W. Heath, Harper & Row
Publishers, New York Cambrige, San Francisco, 1984
Statistics Seventh Edition by McClave, Dietrich and Sincich, Prentice-Hall
International, Inc.1997.
Prepared by:
BARTOLOME A.
CARRERA
You might also like
- Module 1 - Basic Concepts in Statistics IDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Basic Concepts in Statistics IBellaNo ratings yet
- Module 1-4 Acctg Ed 16 BSADocument18 pagesModule 1-4 Acctg Ed 16 BSAChen HaoNo ratings yet
- Statistical Design and Analysis of Experiments: With Applications to Engineering and ScienceFrom EverandStatistical Design and Analysis of Experiments: With Applications to Engineering and ScienceNo ratings yet
- AP 10: Statistics & Data AnalysisDocument5 pagesAP 10: Statistics & Data AnalysisvrindaNo ratings yet
- Linear and Generalized Linear Mixed Models and Their ApplicationsFrom EverandLinear and Generalized Linear Mixed Models and Their ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Data Management ModuleDocument35 pagesData Management ModuleJoksian Trapela100% (1)
- Statistics For Business-IIDocument3 pagesStatistics For Business-IINagiib Haibe Ibrahim Awale 6107No ratings yet
- Lecture Note On Basic Business Statistics - I Mustafe Jiheeye-1Document81 pagesLecture Note On Basic Business Statistics - I Mustafe Jiheeye-1Nagiib Haibe Ibrahim Awale 6107No ratings yet
- Med 03Document3 pagesMed 03Rowelyn SisonNo ratings yet
- MFS 7104 Quantitative TechniquesDocument2 pagesMFS 7104 Quantitative TechniquesDavid KNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Course Requirement In: Quantitative Approach in ResearchDocument4 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Course Requirement In: Quantitative Approach in ResearchJovi AbabanNo ratings yet
- 15 Module in ADV NURSING STATDocument6 pages15 Module in ADV NURSING STATCEFI Office for Research and PublicationsNo ratings yet
- CRT, .4, Utztt. 196: Symbiosis College of Arts and Commerce: Statistical MethodsDocument1 pageCRT, .4, Utztt. 196: Symbiosis College of Arts and Commerce: Statistical MethodsRicha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Research II: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Interpretation of DataDocument18 pagesResearch II: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Interpretation of DataTrexia Singson100% (1)
- PHD - Advanced Educational StatisticsDocument8 pagesPHD - Advanced Educational StatisticsDenis CadotdotNo ratings yet
- Instructional Module in Statistics and Probability For ResearchDocument4 pagesInstructional Module in Statistics and Probability For ResearchKatlyn FaithNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics - H1UB105TDocument2 pagesBusiness Statistics - H1UB105TAryan PurwarNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus For Biostatistics For Applied Health Research STAT 301Document4 pagesCourse Syllabus For Biostatistics For Applied Health Research STAT 301beaNo ratings yet
- Psychological Statistics SyllabusDocument4 pagesPsychological Statistics SyllabusGrace Cadag100% (1)
- Mathematics in The Modern World Module Week 1 2Document30 pagesMathematics in The Modern World Module Week 1 2eloixxa samNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Introduction To StatisticsDocument9 pagesModule 3 Introduction To StatisticsRoella Trysha HinayonNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - SFMDocument4 pagesSyllabus - SFMsinnerNo ratings yet
- Business StatisticsDocument500 pagesBusiness StatisticsEsthee33% (3)
- Emcu002 Educational StatisticsDocument42 pagesEmcu002 Educational StatisticsDenisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Nature of Inquiry and ResearchCelyn Gahol100% (4)
- Data Analysis Course OutlineDocument4 pagesData Analysis Course OutlinebnmjgcNo ratings yet
- New SyllabusDocument3 pagesNew Syllabusblacklyfe1991No ratings yet
- Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences 3rd Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesStatistics For The Behavioral Sciences 3rd Edition Ebook PDFantonia.connor78998% (43)
- DICS1204Course ContentDocument3 pagesDICS1204Course Contentnogarap767No ratings yet
- Syllabus MAPSY103Document3 pagesSyllabus MAPSY103anilNo ratings yet
- Module of Introduction To StatisticsDocument107 pagesModule of Introduction To StatisticsyigremyeshwasNo ratings yet
- Statistcs - I Module PlanDocument8 pagesStatistcs - I Module PlanDipti PandeyNo ratings yet
- MB-207 Research Methodology (3 Credits) ObjectiveDocument3 pagesMB-207 Research Methodology (3 Credits) ObjectivethOUGHT fOR cHANGENo ratings yet
- Course Code: Caec 3A Course Title: College: Authors: Title of The Learning ResourceDocument30 pagesCourse Code: Caec 3A Course Title: College: Authors: Title of The Learning ResourceMaestro OdamitsalNo ratings yet
- MA Psychology Semester I SyllabusDocument22 pagesMA Psychology Semester I SyllabusSakshiNo ratings yet
- Statistics in PsychDocument2 pagesStatistics in PsychSidra KakarNo ratings yet
- How to Analyze and Present Chapter 4 DataDocument32 pagesHow to Analyze and Present Chapter 4 DataAdrian CatapatNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Statistic PDFDocument7 pagesModule 1 Statistic PDFKi xxiNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics and Probability Course OverviewDocument25 pagesDescriptive Statistics and Probability Course OverviewSurbhi ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- MST1102 Course OutlineDocument6 pagesMST1102 Course OutlineKaydina GirNo ratings yet
- Adfc Syllabus - Educational StatisticsDocument2 pagesAdfc Syllabus - Educational StatisticsMary Rose GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Written ReportDocument3 pagesWritten ReportShenron InamoratoNo ratings yet
- How To Write Chapter 4Document33 pagesHow To Write Chapter 4LJLCNJKZSDNo ratings yet
- Business Stastistics - PGDMDocument2 pagesBusiness Stastistics - PGDMDeepu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Research 2 2nd Quarter Data Presentation Analysis and InterpretationDocument19 pagesModule 6 Research 2 2nd Quarter Data Presentation Analysis and InterpretationMister PewDiePieNo ratings yet
- Psych Stat 1 Syllabus Parametric Tests 2023Document2 pagesPsych Stat 1 Syllabus Parametric Tests 2023Sailor MoonNo ratings yet
- Applied Statistics I. DescriptionDocument3 pagesApplied Statistics I. DescriptionMark Niño JavierNo ratings yet
- Learning Kit - P.Research 2 - Week 1Document6 pagesLearning Kit - P.Research 2 - Week 1Frances Nicole FloresNo ratings yet
- DLP# 1&2 Lising, BenjaminDocument3 pagesDLP# 1&2 Lising, BenjaminBenjamin LisingNo ratings yet
- Research Methods Descriptive StudiesDocument5 pagesResearch Methods Descriptive StudiesPearl GabornoNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Management NotesDocument87 pagesStatistics For Management NotesYuvashree MahendranNo ratings yet
- Bio StatisticsDocument174 pagesBio Statisticsimdad hussainNo ratings yet
- How To Write Chapter 4Document33 pagesHow To Write Chapter 4Jiyuvelle HeathcoteNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila: Course Code: Applied Statistics For Business and EconomicsDocument5 pagesPamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila: Course Code: Applied Statistics For Business and EconomicsEsmeraldo AlcarazNo ratings yet
- BBFH 404 Business Research Methods 1Document10 pagesBBFH 404 Business Research Methods 1ItdarareNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - Practical Research 2 Q1W1Document6 pagesGrade 12 - Practical Research 2 Q1W1Glychalyn Abecia 23No ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction of Statistics FinalDocument9 pagesModule 1 Introduction of Statistics FinalJordine UmayamNo ratings yet
- Reseacrch MethodsDocument32 pagesReseacrch MethodsNafraz JiffryNo ratings yet
- SY 20rr t4t4tDocument2 pagesSY 20rr t4t4tJEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- SHHH KKKK MKKHHBDocument2 pagesSHHH KKKK MKKHHBJEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- School Memorandum No. 47 (REITERATION OF THE NO COLLECTION POLICY)Document1 pageSchool Memorandum No. 47 (REITERATION OF THE NO COLLECTION POLICY)JEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZ0% (1)
- 33 FDFGFGDDGDDocument1 page33 FDFGFGDDGDJEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Instructional Supervisory Report First Semester (June - October 2018) SY 2018-2019Document11 pagesInstructional Supervisory Report First Semester (June - October 2018) SY 2018-2019JEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Election Deso and Staff 2019Document1 pageElection Deso and Staff 2019JEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Dove Eagle Class Advisers Science Mathematics: Mrs. Desiree Mangundayao Mrs. Sarah VillanuevaDocument26 pagesGrade 3 Dove Eagle Class Advisers Science Mathematics: Mrs. Desiree Mangundayao Mrs. Sarah VillanuevaJEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE PROCESSDocument3 pagesTECHNICAL ASSISTANCE PROCESSJoNe JeanNo ratings yet
- SCHOOL MEMORANDUM NO. 6, S. 2019, Hpta MeetingDocument1 pageSCHOOL MEMORANDUM NO. 6, S. 2019, Hpta MeetingJEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- ICP - Inventory Custodian Slip FormsDocument78 pagesICP - Inventory Custodian Slip FormsJEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZ100% (1)
- Calendar of LessonsDocument12 pagesCalendar of LessonsJoNe JeanNo ratings yet
- PRIMALS Training Design 4-6 English (7 DaysDocument1 pagePRIMALS Training Design 4-6 English (7 DaysJEAN FRANCIS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Steps To Spiritual MaturityDocument17 pagesSteps To Spiritual MaturityAce Mereria100% (2)
- Mestrado Hang GlidingDocument82 pagesMestrado Hang GlidingJuliana Silveira100% (2)
- Campus Event ReflectionDocument2 pagesCampus Event ReflectiondntbenfordNo ratings yet
- ZDocument6 pagesZDinesh SelvakumarNo ratings yet
- Beteq2010 Part 1Document198 pagesBeteq2010 Part 1Zilmar JustiNo ratings yet
- Case Study Assignment Sime Darby-R.M.A.Hasan Chowdhury (ID-1600061) PDFDocument13 pagesCase Study Assignment Sime Darby-R.M.A.Hasan Chowdhury (ID-1600061) PDFRaihan Mahmood50% (6)
- CRM Assignment FrankfinnDocument4 pagesCRM Assignment FrankfinnJyoti Choudhary60% (5)
- Strings: - A String Is A Sequence of Characters Treated As A Group - We Have Already Used Some String LiteralsDocument48 pagesStrings: - A String Is A Sequence of Characters Treated As A Group - We Have Already Used Some String LiteralsJNUNo ratings yet
- 5 - BOSCH I - O ModuleDocument21 pages5 - BOSCH I - O ModuleFELIPE ANGELES CRUZ ROMONo ratings yet
- Syntax Score Calculation With Multislice Computed Tomographic Angiography in Comparison To Invasive Coronary Angiography PDFDocument5 pagesSyntax Score Calculation With Multislice Computed Tomographic Angiography in Comparison To Invasive Coronary Angiography PDFMbak RockerNo ratings yet
- SEAFARERSDocument29 pagesSEAFARERSJohanna Arnaez100% (1)
- IMSP 21 Operational Control EMSDocument3 pagesIMSP 21 Operational Control EMSEvonne LeeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Form 1Document339 pagesMathematics Form 1JacintaRajaratnam67% (9)
- SMEDA (Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority)Document29 pagesSMEDA (Small and Medium Enterprises Development Authority)Salwa buriroNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra and Analytical Geometry: A B C Ab CDDocument3 pagesLinear Algebra and Analytical Geometry: A B C Ab CDTooba AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Tacana Project (15687597)Document1 pageTacana Project (15687597)jesusNo ratings yet
- Finite Element and Analytical Modelling of PVC-confined Concrete Columns Under Axial CompressionDocument23 pagesFinite Element and Analytical Modelling of PVC-confined Concrete Columns Under Axial CompressionShaker QaidiNo ratings yet
- HW3 Solutions 2017 SpringDocument4 pagesHW3 Solutions 2017 SpringAtaush Sabuj100% (1)
- CALCULATE TRADE AND CASH DISCOUNTSDocument13 pagesCALCULATE TRADE AND CASH DISCOUNTSrommel legaspi71% (7)
- Week 14 - LECTURE ACTIVITY 14 - Metamorphic RX Key ConceptsDocument4 pagesWeek 14 - LECTURE ACTIVITY 14 - Metamorphic RX Key ConceptsJessel Razalo BunyeNo ratings yet
- P Block Master NcertDocument40 pagesP Block Master Ncertrabindrasahoo1006No ratings yet
- Investigating and EvaluatingDocument12 pagesInvestigating and EvaluatingMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Insulation Coordination in Power System - Electrical4UDocument13 pagesInsulation Coordination in Power System - Electrical4UR.SivachandranNo ratings yet
- Emmanuel Oneka - CV-3Document3 pagesEmmanuel Oneka - CV-3Emmanuel OnekaNo ratings yet
- Satelec X Mind DC Brochure enDocument133 pagesSatelec X Mind DC Brochure enAndres Alberto Sanchez LaraNo ratings yet
- The Definition of WorkDocument2 pagesThe Definition of WorkCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- Understanding Social Problems - PPTDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Social Problems - PPTaneri patel100% (1)
- Showcase your talent and skills at Momentum 2021Document48 pagesShowcase your talent and skills at Momentum 2021Tanishq VermaNo ratings yet
- Ch2 MCQ PDFDocument6 pagesCh2 MCQ PDFPratibha BhondeNo ratings yet
- HAM Processing Technique for Ocular Surface ReconstructionDocument4 pagesHAM Processing Technique for Ocular Surface ReconstructionJoel JohnsonNo ratings yet
- T TableDocument7 pagesT TableMaguz GurniwaNo ratings yet