Professional Documents
Culture Documents
From My Notes Only
Uploaded by
Effie MaeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
From My Notes Only
Uploaded by
Effie MaeCopyright:
Available Formats
✧ from my notes only ✧
— source from internet, other people, nursing students
anatomy is the branch of science that deals with the study of the physical structure and
internal workings of living organisms.
✧chapter;one✧
intro to anatomy and physiology ; overview of anatomy and physiology
Anatomy
The study of structure and shape of the body and body parts and their
relationships to one another
Gross anatomy - can be seen with eye such as muscle, bones, various organs
Microscopic Anatomy - cannot be seen with the eye
Cytology - study of cells
Histology - study of tissues
Regional Anatomy - study one region of the body at a time and learn everything
about the region
Systemic Anatomy – study one body system at a time
Anatomical Organization
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ Systems
Organism
Physiology
✧ from my notes only ✧ 1
Study of how the body and its parts work or function
Importance of Anatomy and Physiology
Understand how the body:
responds to stimuli
environmental changes
environmental cues
diseases
injury
Maintains stable, internal conditions despite continually changing environment
Level of Structural Organization
✧ from my notes only ✧ 2
Major Organs of The Body
✧ from my notes only ✧ 3
Organ System Overview
The highest level of structural organization, the organismal level, is made up of
11 organs
Integumentary System
external covering of the body, or the skin
Skeletal System
supports the body and provides a framework that the skeletal muscles use
to cause movement
Muscular System
composed of skeletal muscles, provides mobility to the body
Nervous System
body’s fast-acting control system
Endocrine System
✧ from my notes only ✧ 4
endocrine glands produce chemical molecules called hormones that
regulate other structures/organs
Cardiovascular System
primary organs of the cardiovascular system are the heart and blood
vessels. The heart acts as the blood pump, propelling blood through the
blood vessels to all body tissues
Lymphatic System
organs of the lymphatic system include the lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes,
the spleen and tonsils.
Respiratory System
primary function of the respiratory system is to keep the body constantly
supplied with oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide
Digestive System
is to break down food and deliver the products to the blood for dispersal to
the body cells
Urinary System
removes the nitrogen-containing wastes from the blood and flushes them
from the body in urine.
Reproductive System
exists primarily to produce offspring
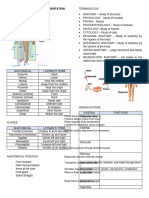
Anatomical Position
The body is erect with the feet parallel and the arms hanging at the sides
with the palms facing forward
Anterior Body Landmarks
Abdominal – anterior body trunk Fibular – lateral part of the leg
inferior to ribs Inguinal – area where thigh meets
Acromial – point of shoulder body trunk; groin
Antecubital – anterior surface of the Nasal – nose area
✧ from my notes only ✧ 5
elbow Oral – mouth
Axillary – armpit Orbital – eye area
Brachial – arm Patellar – anterior knee
Buccal – cheek area Pelvic – area overlying the pelvis
Carpal – wrist anteriorly
Cervical – neck region Pubic – genital region
Coxal – hip Sternal – breastbone area
Crural – leg Tarsal – ankle region
Digital – fingers, toes Thoracic – chest
Femoral – thigh Umbilical - navel
Posterior Body Landmarks
Calcaneal – heel of foot Olecranal – posterior surface of
Cephalic – head elbow
Deltoid – curve of shoulder formed Popliteal – posterior knee area
by large deltoid muscle Sacral – area between hips
Femoral – thigh Scapular – shoulder blade region
Gluteal – buttock Sural – posterior surface of lower
Lumbar – area of back between leg; the calf
hips Vertebral – area of spine
Occipital – posterior surface of Plantar – sole of the foot
head
Body Quadrants
Right Upper Quadrant - right lobe of liver, gallbladder, right kidney, portion of
stomach, small and large intestines
Left Upper Quadrant - left lobe of liver, stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen,
portion of large intestine
Right Lower Quadrant - cecum, vermiform, appendix, and portion of small
intestine. right ovary and spermatic cord. ureter
Left Lower Quadrant - most of small intestine, portion of large intestine, left
ureter, reproductive organs, left ovary and spermatic cord
Planes and Sections
✧ from my notes only ✧ 6
Sagittal section - divides the body into left and right sides: Mid Sagittal - straight
down the center: Transverse - straight across the body
Frontal section - divides the body into front and back sides
✧chapter;two✧
the cell and its structures
Cell Structures
the cell is the basic unit of biological organization
carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
major regions
nucleus
cell membrane
cytoplasm
eukaryotic vs prokaryotic
✧ from my notes only ✧ 7
eukaryote and prokaryote visual
History of the Cell Theory
Proposed in 1830’s by Schleiden and Schwann
Modern call theory
cells are the smallest complete living things
all organisms are composed of one or more cells
cells arise only from other cells
all existing cells are descendants of first cells
Anatomy of a Typical Eukaryotic Cell
✧ from my notes only ✧ 8
The Cell Membrane
Double phospholipid layer with embedded proteins
Membrane transport: selectively permeable membrane
osmosis
protein channels
active transport
fluid mosaic model
✧ from my notes only ✧ 9
the cell membrane visual
Cytoplasm of the Cell
Mostly water with chemical compounds in solution or colloid
🧠 Solution vs Colloid
Individual vs clumped atoms or icons distributed in medium
Polar compounds go into solution
Nonpolar compounds go into colloidal suspension
✧ from my notes only ✧ 10
The Nucleus
Control center of the cell
Nuclear membrane has pores to allow the passage of substances
Chromatin genetic material inside nucleoplasm
Nucleolus: site of ribosome formation
✧ from my notes only ✧ 11
The Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell
Cristae: inner folds where cellular respiration occurs
Energy requirements of cell determine cristae number
Lysosomes
✧ from my notes only ✧ 12
Digestive enzyme packages
Digest stored food
Maintenance and repair of organelles
Suicide agents for old or weak cells
Endoplasmic Reticulum
System of membranes that makes up channels
Connects with outer nuclear and cell membranes
Cisternae: sac like or channel like cavities
✧ from my notes only ✧ 13
You might also like
- Anaphy (Lab) ReviewerDocument3 pagesAnaphy (Lab) ReviewerAgatha Cristie AndradaNo ratings yet
- Tissue Organelle Atom Organ Organ System Cell Organism Molecule SmallestDocument5 pagesTissue Organelle Atom Organ Organ System Cell Organism Molecule Smalleststar fireNo ratings yet
- Anatomy IntroductionDocument34 pagesAnatomy IntroductionJoanne Tolopia100% (1)
- Chapter I Structural OrganizationDocument15 pagesChapter I Structural OrganizationTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY NotesDocument15 pagesANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY NotesAB AlmazoraNo ratings yet
- Hes 029 ReviewerDocument26 pagesHes 029 ReviewerRolaika Vien Elinzano LawanNo ratings yet
- Human Body OrientationDocument3 pagesHuman Body OrientationCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- 1 - Anatomical LanguageDocument21 pages1 - Anatomical Languageshahd elmaghraby (user206)No ratings yet
- 1 Anatomic Terms ModifiedDocument32 pages1 Anatomic Terms ModifiedNoraNo ratings yet
- Lecture (Unit-I)Document59 pagesLecture (Unit-I)Misbah Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy (Intro - Skeletal System) ReviewerDocument34 pagesAnaphy (Intro - Skeletal System) ReviewerYanna G.No ratings yet
- التشريح نظري م 1 غير مترجمةDocument11 pagesالتشريح نظري م 1 غير مترجمةبايNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SummaryDocument42 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SummaryBrythym Mojeca De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy-Human BodyDocument6 pagesAnaphy-Human BodyJASHEL M. CASTANARESNo ratings yet
- Anaphy LecDocument6 pagesAnaphy LecRachell Joy FloresNo ratings yet
- Ana & Physio-NotesDocument82 pagesAna & Physio-NotesAbbie Jane MatigaNo ratings yet
- Тіло Людини (the Human Body)Document14 pagesТіло Людини (the Human Body)Ира ГорNo ratings yet
- Biosci Chap1 (Notes)Document7 pagesBiosci Chap1 (Notes)Man DejeloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer AnaphyshioDocument15 pagesReviewer AnaphyshioANGELIKA GRACE PALANGGOYNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 HANDOUTS Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesMODULE 1 HANDOUTS Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyEricka ReyesNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument13 pagesAnaphyCHESKA LYKA ASILONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyreynaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Organ System Overview: Atoms Cell Tissue OrganDocument8 pagesAnatomy Organ System Overview: Atoms Cell Tissue OrganBea PrestoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Complete Study NotesDocument99 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology 1 Complete Study NotesSamuels JosepNo ratings yet
- Levels of Organization (From Simplest To Most Complex) : Organ SystemsDocument2 pagesLevels of Organization (From Simplest To Most Complex) : Organ SystemsGset Inst MandevilleNo ratings yet
- Anaphy-Chapter 1-7 Reviewer (Seeley's 12th Edition)Document15 pagesAnaphy-Chapter 1-7 Reviewer (Seeley's 12th Edition)Bullosos, Siera Jade Anne R.No ratings yet
- Unit 1 SummaryDocument21 pagesUnit 1 Summaryapi-277938466No ratings yet
- Summarization About AnatomyDocument12 pagesSummarization About AnatomyJhomer CabasNo ratings yet
- Scope of Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Notes NoteskartsDocument7 pagesScope of Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Notes NoteskartsManish BudhrajaNo ratings yet
- A&P Unit 1 IntroDocument43 pagesA&P Unit 1 IntroRido FarnandiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy & PhysiologyJung AbbyNo ratings yet
- Trimester One NotesDocument48 pagesTrimester One NotesHannah RossNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJan Andrew BuduanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Human BodyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To The Human BodyDeroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy IntroductionDocument9 pagesAnatomy IntroductionLoyd TuvillaNo ratings yet
- To Anatomy: Mrs Bincy Varghese Clinical Instructor Kgmu College of Nursing, Kgmu, LucknowDocument54 pagesTo Anatomy: Mrs Bincy Varghese Clinical Instructor Kgmu College of Nursing, Kgmu, LucknowLawrence GamboaNo ratings yet
- The Human Body: Gross /macroscopic AnatomyDocument8 pagesThe Human Body: Gross /macroscopic AnatomyMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
- Intro To Anatomy & Physiology. BM - STDTDocument176 pagesIntro To Anatomy & Physiology. BM - STDTMunungwe WìllíâmNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes-Anatomy and Physiology OverviewDocument5 pagesLecture Notes-Anatomy and Physiology OverviewBing58No ratings yet
- Essentials of Human AnatomyDocument54 pagesEssentials of Human Anatomyأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Class NotesDocument57 pagesAnatomy Class NotesClinical Psychology0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Worksheets Intro To AnaPhyDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Worksheets Intro To AnaPhyAnghel LopezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 PEED 101Document12 pagesLecture 2 PEED 101morireNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument3 pagesAnaphy Reviewerchicken nuggetsNo ratings yet
- 1 Human OrganismDocument5 pages1 Human OrganismEly Fructuoso100% (1)
- Human AnatomyDocument9 pagesHuman AnatomyJohaimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document60 pagesChapter 1Judy anne Anga-anganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnatomyDocument69 pagesIntroduction To AnatomybedadadenbalprosperityNo ratings yet
- Ana and Physio Lab Week 1Document29 pagesAna and Physio Lab Week 1Jobelle VergaraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Bones)Document48 pagesAnatomy (Bones)Jumrah KhumairahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology: Characteristics of LifeDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology: Characteristics of LifegilissaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Human BodyDocument55 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Human BodyLemuel CunananNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-An-Overview (JTO)Document79 pagesAnatomy-An-Overview (JTO)Zild DarkNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Organization of Human BodyDocument8 pagesLab 1 - Organization of Human BodyNicole DadulaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Animals-61-90Document30 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Animals-61-90Pavan PatilNo ratings yet
- Bones PDFDocument227 pagesBones PDFAtthapu ThirupathaiahNo ratings yet
- 1 - Intro and Histo GraysDocument67 pages1 - Intro and Histo GraystuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro and IntegumentaryDocument66 pages1 Intro and IntegumentaryGlen VillenaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Mutliple Choice W KeyDocument2 pagesNervous System Mutliple Choice W KeyArvie NasayaoNo ratings yet
- 5th Class Chapter 5 MCQ Test With Answer For Chapter 5Document12 pages5th Class Chapter 5 MCQ Test With Answer For Chapter 5My OfficeNo ratings yet
- History of Renal Neoplasia: Brett Delahunt MD Frcpa FrcpathDocument5 pagesHistory of Renal Neoplasia: Brett Delahunt MD Frcpa FrcpathrizkaNo ratings yet
- 4LIVfunctions ElizabethDocument23 pages4LIVfunctions ElizabethLunaLure100% (1)
- DR Henry G Bieler Lines of Defense Against DiseaseDocument6 pagesDR Henry G Bieler Lines of Defense Against DiseasebonifacesilveiraNo ratings yet
- Functional Matrix HypothesisDocument14 pagesFunctional Matrix Hypothesispriyab710No ratings yet
- Plant StemDocument6 pagesPlant StemAndreaaAAaa TagleNo ratings yet
- Moore's Clinically Oriented Anatomy 6th EdDocument4 pagesMoore's Clinically Oriented Anatomy 6th EdJohna Pauline Mandac67% (6)
- notice-EVS Class 5 U1 T1 WSDocument23 pagesnotice-EVS Class 5 U1 T1 WSGovind RajNo ratings yet
- EEG ReportDocument2 pagesEEG ReportxiakenliangNo ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma and Congenital Cholesteatoma Important PointsDocument6 pagesCholesteatoma and Congenital Cholesteatoma Important PointsSuprit Sn100% (1)
- Anatomy and Pathology of Testicular Tumors - UpToDateDocument26 pagesAnatomy and Pathology of Testicular Tumors - UpToDateBhargav YagnikNo ratings yet
- 1-Mechanism and Regulation of Respiration ModifiedDocument10 pages1-Mechanism and Regulation of Respiration Modifiedخالد القرشيNo ratings yet
- 12 Cranial NervesDocument13 pages12 Cranial Nervesapi-303065931No ratings yet
- Blood and Cell Physiology MCQs With KeyDocument9 pagesBlood and Cell Physiology MCQs With KeyHabib UllahNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Ultrasound Report FormatDocument3 pagesObstetric Ultrasound Report Formatሀይደር ዶ.ር60% (5)
- Circulatory SystemDocument31 pagesCirculatory SystemGeonardo100% (3)
- Rosemary Estrada - Histology Lab NotebookDocument12 pagesRosemary Estrada - Histology Lab NotebookRosemary EstradaNo ratings yet
- The Theater of Anatomy - The Anatomical Preparations of Honore Fragonard PDFDocument18 pagesThe Theater of Anatomy - The Anatomical Preparations of Honore Fragonard PDFFrancisco SantosNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument29 pagesSkeletal SystemCrii XiaNo ratings yet
- Giant Cell Epulis: Report of 2 Cases.: Oral PathologyDocument11 pagesGiant Cell Epulis: Report of 2 Cases.: Oral PathologyVheen Dee DeeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - LarynxDocument104 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - LarynxJSS Dharwad 2020 batchNo ratings yet
- The Sclera PDFDocument334 pagesThe Sclera PDFMaría Soledad Romero LópezNo ratings yet
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions Chapter 7: Animal NutritionDocument2 pagesAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions Chapter 7: Animal NutritionRNo ratings yet
- Cell Cell InteractionDocument45 pagesCell Cell InteractionErick Ello RodelNo ratings yet
- 2021-Review-Gut Microbiota in Cancer Immune Response and ImmunotherapyDocument14 pages2021-Review-Gut Microbiota in Cancer Immune Response and ImmunotherapyCristian Felipe Sandoval QuiñonezNo ratings yet
- The Plant CellDocument22 pagesThe Plant CellLuna Scorpius0% (1)
- Histological Variants:: PathogenesisDocument2 pagesHistological Variants:: PathogenesisPravin KumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Hepatobiliary SystemDocument46 pagesAnatomy of Hepatobiliary SystemAyu Tiara FitriNo ratings yet
- Module 27Document14 pagesModule 27Jerico CastilloNo ratings yet