Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GI Hormone Summary
Uploaded by
Hasan Shahzad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageGastrin is a peptide hormone released from stomach G cells that stimulates acid secretion and promotes mucosal growth. It is released in response to proteins, amino acids, and parasympathetic input. Gastrin release is inhibited by acid levels rising. Somatostatin is released from D cells and inhibits the release of gastrin, CCK, and secretin. Motilin stimulates the migrating motor complex to clear the stomach between meals. The migrating motor complex and pyloric sphincter function keep the stomach empty between meals.
Original Description:
HORMONE LECTURE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGastrin is a peptide hormone released from stomach G cells that stimulates acid secretion and promotes mucosal growth. It is released in response to proteins, amino acids, and parasympathetic input. Gastrin release is inhibited by acid levels rising. Somatostatin is released from D cells and inhibits the release of gastrin, CCK, and secretin. Motilin stimulates the migrating motor complex to clear the stomach between meals. The migrating motor complex and pyloric sphincter function keep the stomach empty between meals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageGI Hormone Summary
Uploaded by
Hasan ShahzadGastrin is a peptide hormone released from stomach G cells that stimulates acid secretion and promotes mucosal growth. It is released in response to proteins, amino acids, and parasympathetic input. Gastrin release is inhibited by acid levels rising. Somatostatin is released from D cells and inhibits the release of gastrin, CCK, and secretin. Motilin stimulates the migrating motor complex to clear the stomach between meals. The migrating motor complex and pyloric sphincter function keep the stomach empty between meals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
1.
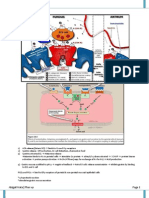
Gastrin Migrating Motor Complex (MMC) - slow
Gastrin (two types G17 and G34) - peptide peristaltic contractions from stomach every
hormone released from stomach G Cells 90 mins
Gastrin Function - stimulates acid secretion and Keeps the gut clean = less bacteria,
promotes mucosal growth
prevent reflux
Gastrin release stimulated by:
1. Proteins/amino acids Pyloric sphincter stays relaxed for anything to
2. Parasympathetic input/Ach (because of pass into small bowel
gastric stretch) - process mediated by
gastrin releasing peptide 5. Motilin
Motilin (22 alpha amino acid) - stimulates
Gastrin release INHIBITED by: MMC
H+ (negative feedback) Secreted by M Cells and erythromycin
Inhibited by feeding
Gastrin and CCK - part of the same family
Gastrin shares receptors with CCK (CCK-B
receptor)
Parietal Cell Acid Secretion:
2. Somatostatin Gastrin and Ach (from Vagus) stimulate
parietal cells
Somatostatin - 2 forms (peptide hormone) – binds SOMATOSTATIN inhibits parietal cells = stops
to G cells to stop GASTRIN, CCK and secretin
gastrin release
release
INDIRECT effect - mediated by
Two Types: histamine
1. 28 amino acid form - from D-Cells of
stomach, duodenum and pancreas
Release stimulated by H+
Inhibited by acetylcholine
2. 14 amino acid form (not common)
3. Secretin
Secretin (27 amino acids):
Secreted by S Cells of small intestines in
response to acid
Effect:
Stimulates bicarbonate secretion by
pancreas and liver
Inhibits gastric acid production
4. CCK
Cholecystokinin-Pancreaozymin (CCK) - 33 amino
acids (last 5 are identical to GASTRIN)
Secreted in response to LIPIDS/PEPTIDES
by I cells in small intestines
CCK A receptors - for CCK
CCK B receptors - for Gastrin
Effects:
1. Stimulates pancreatic secretion (from
acinar cells)
2. Stimulates gallbladder emptying
You might also like
- 2019-AGA-DDSEP-9-Chapter-2-1557871764749 1 ENFERMEDADES DEL ESTOMAGODocument24 pages2019-AGA-DDSEP-9-Chapter-2-1557871764749 1 ENFERMEDADES DEL ESTOMAGOEmilia GarciaNo ratings yet
- 4 Gi Hormones I: Endocrine HormonesDocument4 pages4 Gi Hormones I: Endocrine HormonesLinh PhanNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal DrugsDocument11 pagesGastrointestinal DrugsAbby MataNo ratings yet
- Img 20151230 0001 New 0009Document1 pageImg 20151230 0001 New 0009Ifah Inayah D'zatrichaNo ratings yet
- Img 20151230 0001 New 0009 PDFDocument1 pageImg 20151230 0001 New 0009 PDFIfah Inayah D'zatrichaNo ratings yet
- Gastricacidand Digestivephysiology: Philip T. Ramsay,, Aaron CarrDocument6 pagesGastricacidand Digestivephysiology: Philip T. Ramsay,, Aaron CarryorleNo ratings yet
- Gastric SecretionDocument50 pagesGastric SecretionYanglem AmarjitNo ratings yet
- Gastric Juice RegulationDocument22 pagesGastric Juice Regulationjanuian75% (4)
- 1920 GI HormonesDocument12 pages1920 GI HormonesKarl McNamaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5 Hormonal Regulation of Intestinal MotilityDocument4 pagesLecture-5 Hormonal Regulation of Intestinal Motilityمرتضى حسين عبدNo ratings yet
- HORMONES-PHYSIO NotesDocument1 pageHORMONES-PHYSIO NotesANGELICA ADVIENTONo ratings yet
- Git Hormones Secreted by The GitDocument16 pagesGit Hormones Secreted by The GitSibatNo ratings yet
- Gi Hormones: Dr. Sharon M. PDocument50 pagesGi Hormones: Dr. Sharon M. PAleenaNo ratings yet
- GIT G I HormonesDocument13 pagesGIT G I HormonesRaja Rashid IqbalNo ratings yet
- Mar 15 - Diffuse Endocrine CellsDocument16 pagesMar 15 - Diffuse Endocrine CellsPutriNo ratings yet
- Hormone Site of Secretion Stimuli For Secretion Actions: BiliaryDocument5 pagesHormone Site of Secretion Stimuli For Secretion Actions: BiliaryLace AzoresNo ratings yet
- Git HormonesDocument17 pagesGit HormonesAniket MittalNo ratings yet
- Gastrin Release: To Increases Somatostatin (IncreasedDocument1 pageGastrin Release: To Increases Somatostatin (IncreasedIfah Inayah D'zatrichaNo ratings yet
- GitDocument4 pagesGitSabbir AhmedNo ratings yet
- CholecystokininDocument8 pagesCholecystokininMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- GIT Physiology: Powered by ATPDocument53 pagesGIT Physiology: Powered by ATPNashir MahmudNo ratings yet
- GI Hormones1277296434Document15 pagesGI Hormones1277296434mittal.shubham0007No ratings yet
- Mechanism of Gastric SecretionDocument11 pagesMechanism of Gastric Secretionmulya ningsihNo ratings yet
- Boron Medical Physiology 915 915Document1 pageBoron Medical Physiology 915 915danapetcu0% (1)
- Hormone of Gi TractsDocument2 pagesHormone of Gi TractsMehedi hasan aponNo ratings yet
- Gi PhysiolDocument8 pagesGi Physiol유예진No ratings yet
- ProductsDocument4 pagesProductsstudy mailNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcers: PHRM 304Document24 pagesPeptic Ulcers: PHRM 304Apurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- Gastric Secretion AND Motility: DR Shar Mariam Mohamed Human BiologyDocument45 pagesGastric Secretion AND Motility: DR Shar Mariam Mohamed Human BiologyWahida Amalin Ab RazakNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Peptic Ulcer 1920Document29 pagesDrugs Used in Peptic Ulcer 1920arthiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy For Gastric Acidity, Peptic Ulcers, and Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument10 pagesPharmacotherapy For Gastric Acidity, Peptic Ulcers, and Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseVera WatyNo ratings yet
- Physiology, Lecture 8, GIT 2 (Stomach) (Slides)Document24 pagesPhysiology, Lecture 8, GIT 2 (Stomach) (Slides)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (2)
- Physiology of Insulin SecretionDocument8 pagesPhysiology of Insulin SecretionChenai04No ratings yet
- Biochemical Structure & Function of Glucagon & SomatostatinDocument21 pagesBiochemical Structure & Function of Glucagon & SomatostatinSyedSaqibHussainNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Control of GitDocument42 pagesHormonal Control of GitM. Shahin Uddin KazemNo ratings yet
- Gastric SecretionDocument45 pagesGastric SecretionAzeeza Elya100% (1)
- Gastrin From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument23 pagesGastrin From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaVincent Lau Bi ShengNo ratings yet
- GIT - Lecture 1-2 UpdatedDocument57 pagesGIT - Lecture 1-2 UpdatedPushpa Paul 2021665649No ratings yet
- Digestive System - 2Document4 pagesDigestive System - 2Sherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- GIT Lec 4Document36 pagesGIT Lec 4Kim Sa-buNo ratings yet
- Fi DioDocument74 pagesFi DioAlicia NataNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument62 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusNicee SelpaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Pancreatic Hormones and DMDocument56 pagesLecture 4 Pancreatic Hormones and DMHomeground entertainmentNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Gastric Motility & Digestion: Sisay Molla (R1 Augest 2Document56 pagesPhysiology of Gastric Motility & Digestion: Sisay Molla (R1 Augest 2Worku KifleNo ratings yet
- Physio Gastrointestinal Motility PDFDocument11 pagesPhysio Gastrointestinal Motility PDFKim RamosNo ratings yet
- Ana of GITDocument6 pagesAna of GITjollypadillaNo ratings yet
- 11/9/2021 Biokimia Ternak Lab - Biokimia Nutrisi, FAPET UGM 1Document48 pages11/9/2021 Biokimia Ternak Lab - Biokimia Nutrisi, FAPET UGM 16 Vivi PermatasariNo ratings yet
- AUTACOIDSDocument29 pagesAUTACOIDSStrange eeNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument2 pagesPancreasVinayNo ratings yet
- GI NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageGI NeurotransmittersMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- ENDO) Pancreas. For The ClassDocument58 pagesENDO) Pancreas. For The ClassromaloiNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestin Al Hormones: Prof Suranjana RayDocument42 pagesGastrointestin Al Hormones: Prof Suranjana RayÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- GI HormonesDocument23 pagesGI Hormonesriskyy1No ratings yet
- Stomach: Clinical Clerk: Jarney Dyenn Bito-OnonDocument44 pagesStomach: Clinical Clerk: Jarney Dyenn Bito-OnonLajel S. LachicaNo ratings yet
- 10-Anti Ulcer H2-14-08-2023Document60 pages10-Anti Ulcer H2-14-08-2023ashwin kNo ratings yet
- 05 05 NOTES-HormonalDocument3 pages05 05 NOTES-HormonalSidney TyNo ratings yet
- Pancreas PDF (1) .Document14 pagesPancreas PDF (1) .Ahmed MemonNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Oxidation and The Production of UreaDocument64 pagesAmino Acid Oxidation and The Production of UreaAsif JavedNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentFrom EverandFast Facts: Acute and Recurrent Pancreatitis: Using evidence to support treatmentNo ratings yet
- Hand MusclesDocument5 pagesHand MusclesHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Viral and Prion Pathogens - Hand Out 2023Document1 pageViral and Prion Pathogens - Hand Out 2023Hasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31 - ThrombosisDocument2 pagesLecture 31 - ThrombosisHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- AS Obscure MarksDocument3 pagesAS Obscure MarksHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- GCSE Photosynthesis PowerpointDocument14 pagesGCSE Photosynthesis PowerpointHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- OCR A Biology 2019 Mark SchemeDocument27 pagesOCR A Biology 2019 Mark SchemeHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- OCR A Biology 2019 Question PaperDocument36 pagesOCR A Biology 2019 Question PaperHasan ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry OCR A - A Level DefinitionsDocument3 pagesChemistry OCR A - A Level DefinitionsHasan Shahzad100% (1)
- Srs For College WebsiteDocument6 pagesSrs For College WebsiteShree Kumar33% (3)
- Unit 2Document4 pagesUnit 2api-296199660No ratings yet
- Unit 9:: What Did You See at The Zoo?Document11 pagesUnit 9:: What Did You See at The Zoo?ARiFin MoHaMedNo ratings yet
- MATH3161 MATH5165 T1 2023 OutlineDocument10 pagesMATH3161 MATH5165 T1 2023 OutlineDouglusNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4 - 28june2023Document18 pagesLecture - 4 - 28june2023vanshikaNo ratings yet
- A Step by Step Approach To The Modeling of Chemical Engineering Processes, Using Excel For Simulation (2018)Document182 pagesA Step by Step Approach To The Modeling of Chemical Engineering Processes, Using Excel For Simulation (2018)Anonymous NxpnI6jC100% (7)
- Transition Case StudyDocument4 pagesTransition Case StudyNobert BulindaNo ratings yet
- Types of CounsellingDocument5 pagesTypes of CounsellingAnkita ShettyNo ratings yet
- 9702 s02 QP 1Document20 pages9702 s02 QP 1Yani AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1Jerard AnciroNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1 Activity and Analysis: Special Needs EducationDocument2 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1 Activity and Analysis: Special Needs EducationShalyn ArimaoNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Hate Hypocrites - Evidence For A Theory of False SignalingDocument13 pagesWhy Do We Hate Hypocrites - Evidence For A Theory of False SignalingMusic For youNo ratings yet
- Ms5 Stress 1Document26 pagesMs5 Stress 1NicolasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Adjusting EntriesDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Adjusting EntriesMuhammad AdibNo ratings yet
- Javier Guzman v. City of Cranston, 812 F.2d 24, 1st Cir. (1987)Document4 pagesJavier Guzman v. City of Cranston, 812 F.2d 24, 1st Cir. (1987)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Quiz Simple Present Simple For Elementary To Pre-IntermediateDocument2 pagesQuiz Simple Present Simple For Elementary To Pre-IntermediateLoreinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Consumer Behavior: by Dr. Kevin Lance JonesDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Consumer Behavior: by Dr. Kevin Lance JonesCorey PageNo ratings yet
- B.a.H Eco. 2nd Semester Mathematical Methods For Economics IIDocument3 pagesB.a.H Eco. 2nd Semester Mathematical Methods For Economics IINitinSharma100% (1)
- Compulsory CounterclaimDocument4 pagesCompulsory CounterclaimAlexandria FernandoNo ratings yet
- Teacher LOA & TermsDocument3 pagesTeacher LOA & TermsMike SchmoronoffNo ratings yet
- Astro ExamDocument7 pagesAstro ExamRitu DuaNo ratings yet
- LIFT OFF ModuleDocument28 pagesLIFT OFF ModulericardoNo ratings yet
- NyirabahireS Chapter5 PDFDocument7 pagesNyirabahireS Chapter5 PDFAndrew AsimNo ratings yet
- Muslimah's Handbook of PurityDocument60 pagesMuslimah's Handbook of PurityMuadh KhanNo ratings yet
- Study On SantalsDocument18 pagesStudy On SantalsJayita BitNo ratings yet
- Adeyinka Wulemat Olarinmoye - The Images of Women in Yoruban Folktales PDFDocument12 pagesAdeyinka Wulemat Olarinmoye - The Images of Women in Yoruban Folktales PDFAngel SánchezNo ratings yet
- CV Template - 2018-2020Document2 pagesCV Template - 2018-2020Rahul AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Hindu Dharma Parichayam - Swami Parameswarananda SaraswatiDocument376 pagesHindu Dharma Parichayam - Swami Parameswarananda SaraswatiSudarsana Kumar VadasserikkaraNo ratings yet
- FASUPDocument60 pagesFASUPPranjal KumarNo ratings yet
- Design of Solar Power System For Home ApplicationDocument43 pagesDesign of Solar Power System For Home ApplicationsanthosecvpNo ratings yet