Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GI Neurotransmitters
Uploaded by
Maryam Fadah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pagesummary
Original Title
GI neurotransmitters
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsummary
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageGI Neurotransmitters
Uploaded by
Maryam Fadahsummary
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
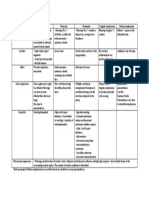
Stimulating Neurotransmitters
Duodenum Absorbs =>GIT Fe, folate, Ca+ and Zn Inhibiting Neurotransmitters
Ach, Subp Esophagus, LES VIP/NO
Distal ileum Absorbs => Vitb12, chylomicrons (fat), bile salt and intrinsic factor.
Ach, Histamine,Stomach
Gastrin Absorbs => Alcohol
Stomach Somatostatin
VIP, GRP, Ach Colon Absorbs => shortPancreas
chain fatty acid
CCK, Ach Gallbladder VIP/NO (Act on sphincter of oddi)
Ach, Subp Small intestine VIP/NO
Aldosterone Colon
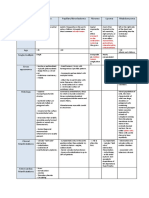
Hormone GI origin Cell Released in response to Hormone function
origin
Ghrelin Stomach/duodenum D1 In response to fasting, Circulating orexigen => stimulate appetite.
Anorexia, celiac disease
and peak with
scheduled feeding
Gastrin Gastric antrum/duodenum G Released by vagal Stimulates gastric acid secretion and growth (maintains the integrity of
stimulation from the the gastric mucosa)
CNS, gastric distension,
proteins and peptides in
the stomach
CCK Duodenum/Jejunum I Released by fat and Stimulates pancreatic secretion, contracts gallbladder, delays gastric
protein in meals emptying, and reduces meal size and duration
Secretin Duodenum/Jejunum S In response to low pH Stimulates pancreatic and hepatic bicarbonate secretion
of acid chyme
Motilin Duodenum/Jejunum M In response to - Triggers MMC.
interdigestive phase by - Speeds gastric emptying, increases small intestinal, gallbladder &
a neural mechanism to colonic motility
trigger the migrating
motor complex
GIP Duodenum/Jejunum K Incretin Effect-enhance insulin secretion.
- lipogenic and maintains integrity of adipocytes
- Increases bone growth
- Reduces energy expenditure
GLP-1 Ileum/Large bowel (mainly L In response to fat and Incretin Effect-enhance insulin secretion.
colon) glucose - Potently inhibits food intake
Oxyntumodulin L Satiating agent:
- Inhibits food intake for several hours and increase voluntary
movement.
- Inhibit gastric secretion & emptying
Anorectic effect:
- suppression of ghrelin release
PPY L
PP Pancrease PP
You might also like
- 2 The Crypt of Elder Hallow 2ndDocument13 pages2 The Crypt of Elder Hallow 2ndmike roulette100% (1)
- Acute COPD ExacerbationDocument65 pagesAcute COPD ExacerbationMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Explosive Ordnance Disposal & Canine Group Regional Explosive Ordnance Disposal and Canine Unit 3Document1 pageExplosive Ordnance Disposal & Canine Group Regional Explosive Ordnance Disposal and Canine Unit 3regional eodk9 unit3No ratings yet
- Guns and Thighs by Ram Gopal Verma PDFDocument100 pagesGuns and Thighs by Ram Gopal Verma PDFSoma ShekharNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station ChecklistDocument5 pagesCardiac Arrest VF/Pulseless VT Learning Station ChecklistMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Techniques To Prevent Food SpoilageDocument30 pagesTechniques To Prevent Food SpoilageCourtney GrahamNo ratings yet
- HC - Come Home To Yourself PDFDocument133 pagesHC - Come Home To Yourself PDFOtilia100% (1)
- Gept reading試題Document13 pagesGept reading試題Bateman Patrick100% (1)
- Physiology, Lecture 8, GIT 2 (Stomach) (Slides)Document24 pagesPhysiology, Lecture 8, GIT 2 (Stomach) (Slides)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (2)
- Gastrointestinal System and Drugs: Anatomy, Physiology and PharmacologyDocument85 pagesGastrointestinal System and Drugs: Anatomy, Physiology and PharmacologyKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Ranitidine, Metoclopramide, Ketorolac, and Omeprazole)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Ranitidine, Metoclopramide, Ketorolac, and Omeprazole)Akisan0% (1)
- Lecture-5 Hormonal Regulation of Intestinal MotilityDocument4 pagesLecture-5 Hormonal Regulation of Intestinal Motilityمرتضى حسين عبدNo ratings yet
- Gi Hormones: Dr. Sharon M. PDocument50 pagesGi Hormones: Dr. Sharon M. PAleenaNo ratings yet
- Research On Evolution Equations Compendium Volume 1Document437 pagesResearch On Evolution Equations Compendium Volume 1Jean Paul Maidana GonzálezNo ratings yet
- 2022ABFM ITEMultChoiceDocument71 pages2022ABFM ITEMultChoiceMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- 2022ABFM ITEMultChoiceDocument71 pages2022ABFM ITEMultChoiceMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Evogliptin Conference PresentationDocument77 pagesEvogliptin Conference PresentationKrishna Chaitanya100% (1)
- Advenginuse3 Ank Wbspa 16129Document32 pagesAdvenginuse3 Ank Wbspa 16129JMJPILOT75% (4)
- Self-Healing with Qigong for Digestive Disorders: Optimize your digestion, energy level, and metabolism: Self-Healing with Qigong, #3From EverandSelf-Healing with Qigong for Digestive Disorders: Optimize your digestion, energy level, and metabolism: Self-Healing with Qigong, #3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- GI hormones, their origin, function and responseDocument1 pageGI hormones, their origin, function and responseMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- GitDocument4 pagesGitSabbir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hormone of Gi TractsDocument2 pagesHormone of Gi TractsMehedi hasan aponNo ratings yet
- Regulare GastricăDocument3 pagesRegulare GastricăAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- CPH 1902 Group PresentationDocument15 pagesCPH 1902 Group PresentationNicole MicallefNo ratings yet
- Physio Gastrointestinal Motility PDFDocument11 pagesPhysio Gastrointestinal Motility PDFKim RamosNo ratings yet
- HungerDocument2 pagesHungermeeraNo ratings yet
- Feedback Circuites Regulate: Campbell 41.5Document26 pagesFeedback Circuites Regulate: Campbell 41.5Toka TariqNo ratings yet
- 05 05 NOTES-HormonalDocument3 pages05 05 NOTES-HormonalSidney TyNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Topics Program Powered by ATPDocument53 pagesTop Ten Topics Program Powered by ATPNashir MahmudNo ratings yet
- Relieve heartburn and acid reflux with PPIs and H2 blockersDocument3 pagesRelieve heartburn and acid reflux with PPIs and H2 blockersJohn FredNo ratings yet
- ProductsDocument4 pagesProductsstudy mailNo ratings yet
- Pharma ReviewerDocument74 pagesPharma ReviewerSamantha DiegoNo ratings yet
- Regulation of GIT by gastrointestinal hormonesDocument13 pagesRegulation of GIT by gastrointestinal hormonesRaja Rashid IqbalNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting in The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument14 pagesDrugs Acting in The Gastrointestinal SystemPrincess C. SultanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyMelody Forca FranciscoNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive System: A Concise Overview of its Key Components and FunctionsDocument257 pagesThe Human Digestive System: A Concise Overview of its Key Components and FunctionsAyushNo ratings yet
- Physiology DiabetesDocument48 pagesPhysiology Diabetesrajesh g100% (1)
- GI PHYSIOLDocument8 pagesGI PHYSIOL유예진No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument62 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusNicee SelpaNo ratings yet
- Oleh: Dr. Herdiantri Sufriyana: @herdiantsDocument25 pagesOleh: Dr. Herdiantri Sufriyana: @herdiantsSheillaMerlyanaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tract HormonesDocument10 pagesGastrointestinal Tract HormonesKevin SangNo ratings yet
- Digestive Physiology ExplainedDocument14 pagesDigestive Physiology ExplainedJãçk SparrowNo ratings yet
- Hormone Secreted by Stimuli For Release Major ActivitiesDocument4 pagesHormone Secreted by Stimuli For Release Major ActivitiesYule RoxasNo ratings yet
- Git SecretionDocument3 pagesGit Secretionstudy mailNo ratings yet
- GI Motility DrugsDocument1 pageGI Motility DrugspulmonologistNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument3 pagesDigestionPearlyn John BrittoNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Control of GitDocument42 pagesHormonal Control of GitM. Shahin Uddin KazemNo ratings yet
- GI HormonesDocument1 pageGI HormonesCarla CentenoNo ratings yet
- Controlled GI Transit in Enteral NutritionDocument36 pagesControlled GI Transit in Enteral NutritionSiti Ika FitrasyahNo ratings yet
- Hunger, Eating, Thirst and Drinking LectureDocument5 pagesHunger, Eating, Thirst and Drinking LectureOnin GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 11/9/2021 Biokimia Ternak Lab - Biokimia Nutrisi, FAPET UGM 1Document48 pages11/9/2021 Biokimia Ternak Lab - Biokimia Nutrisi, FAPET UGM 16 Vivi PermatasariNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal HormonesDocument3 pagesGastrointestinal HormonesDr Sanjeeb Kumar Dey BaidyaNo ratings yet
- SGD - DigestiveDocument4 pagesSGD - DigestiveSerious LeoNo ratings yet
- Glucagon and Its Metabolic EffectsDocument31 pagesGlucagon and Its Metabolic EffectsnikenNo ratings yet
- Control of DigestionDocument5 pagesControl of DigestionMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Integration I: BiochemistryDocument12 pagesMetabolic Integration I: BiochemistryManila MedNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesDigestive SystemAnamta AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Pages From Physio Term 2Document453 pagesPages From Physio Term 2Deshi SportsNo ratings yet
- Docusate, Trimetazidine, Salbutamol, and Spironolactone drug chartDocument8 pagesDocusate, Trimetazidine, Salbutamol, and Spironolactone drug chartzhapper2002No ratings yet
- GastricDocument21 pagesGastricParas TripathiNo ratings yet
- PHARMA-R4.2-Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic DrugsDocument14 pagesPHARMA-R4.2-Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic Drugscharmainemargaret.parreno.medNo ratings yet
- Ondansetron: Gastric EmptyingDocument4,170 pagesOndansetron: Gastric EmptyingdrsaidumerNo ratings yet
- 1.physiologe Emrcs2016Document117 pages1.physiologe Emrcs2016Farah FarahNo ratings yet
- Case Clue - 1 LinersDocument753 pagesCase Clue - 1 LinersOnly MrcpNo ratings yet
- Anti Diabetik Oral Dan InsulinDocument97 pagesAnti Diabetik Oral Dan InsulinSuci AlimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 62: General Principles of GI Function-Motility, Nervous Control, and Blood CirculationDocument36 pagesChapter 62: General Principles of GI Function-Motility, Nervous Control, and Blood Circulationjackie funtanillaNo ratings yet
- Gastrontestinal System: 2 Types of ContractionsDocument10 pagesGastrontestinal System: 2 Types of ContractionsReyjan Lozano ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 48,49 GIT-Liver Parts 1 and 2Document65 pagesLecture 48,49 GIT-Liver Parts 1 and 2yebadem228No ratings yet
- GI Hormones PDFDocument20 pagesGI Hormones PDFKgerb100% (1)
- 2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2From Everand2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2No ratings yet
- Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument108 pagesAcute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D DefeciencyDocument6 pagesVitamin D DefeciencyMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D ScreeningDocument7 pagesVitamin D ScreeningMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Iron Defeciency AnemiaDocument7 pagesIron Defeciency AnemiaMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Efast: Name Position Normal US Pic Abnormal US Pic SubcostalDocument4 pagesEfast: Name Position Normal US Pic Abnormal US Pic SubcostalMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Obesity in Adults AafpDocument2 pagesObesity in Adults AafpMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Epidemiology, Pathology, DiagnosisDocument2 pagesPapillary Thyroid Carcinoma Epidemiology, Pathology, DiagnosisMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Addison Disease Early Detection and TreatmentDocument6 pagesAddison Disease Early Detection and TreatmentNajib Al FatinNo ratings yet
- AAFP Cushing's Disease - Clinical Manifestations and Diagnostic Evaluation - American Family PhysicianDocument9 pagesAAFP Cushing's Disease - Clinical Manifestations and Diagnostic Evaluation - American Family PhysicianMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Chronic DiarrheaDocument1 pageChronic DiarrheaMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine Presentation - DysuriaDocument17 pagesFamily Medicine Presentation - DysuriaMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- E FastDocument4 pagesE FastMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- ND NDDocument1 pageND NDMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Ugib Esophagitis: Candida, Herpes Simplex Virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Human ImmunodeficiencyDocument1 pageUgib Esophagitis: Candida, Herpes Simplex Virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Human ImmunodeficiencyMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis SummaryDocument1 pageVasculitis SummaryMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Stimulating NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageStimulating NeurotransmittersMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Centriacinar Panacinar Paraseptal Irregular Emphysema Bullous EmphysemaDocument1 pageCentriacinar Panacinar Paraseptal Irregular Emphysema Bullous EmphysemaMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Hypotension DrugsDocument1 pageHypotension DrugsMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- The Right Clinical Information, Right Where It's Needed: Last Updated: Sep 12, 2019Document92 pagesThe Right Clinical Information, Right Where It's Needed: Last Updated: Sep 12, 2019Maryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Stimulating NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageStimulating NeurotransmittersMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Intrahepatic Biliary Tract DiseaseDocument1 pageIntrahepatic Biliary Tract DiseaseMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Primary Cardiac Tumors SummaryDocument2 pagesPrimary Cardiac Tumors SummaryMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Demand Ischemia: Not A Total Occlusion, So If YouDocument1 pageDemand Ischemia: Not A Total Occlusion, So If YouMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Red Vascular: Polygonal Cells Growing in Nests or Cords Lamellae of Dense CollagenDocument3 pagesRed Vascular: Polygonal Cells Growing in Nests or Cords Lamellae of Dense CollagenMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Stanolol From The Name Stanly (Male)Document2 pagesStanolol From The Name Stanly (Male)Maryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Thời gian làm bài: 90 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề)Document8 pagesThời gian làm bài: 90 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề)Nguyễn KiênNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Designing Your SolutionDocument22 pagesChapter 4 Designing Your SolutionRamona Isabel UrsaisNo ratings yet
- Statistical PhysicsDocument4 pagesStatistical PhysicsRenan ZortéaNo ratings yet
- Comparative ParadigmDocument4 pagesComparative ParadigmJovi Floresca AberinNo ratings yet
- 03 IoT Technical Sales Training Industrial Wireless Deep DiveDocument35 pages03 IoT Technical Sales Training Industrial Wireless Deep Divechindi.comNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- Alat Studio Dan KomunikasiDocument14 pagesAlat Studio Dan Komunikasiraymon akbarNo ratings yet
- Processed oDocument2 pagesProcessed oHemanth KumarNo ratings yet
- The Paul Sellers Router PlaneDocument6 pagesThe Paul Sellers Router PlaneAjay Vishwanath100% (1)
- Report For Court, Sale of Dowling College Brookhaven CampusDocument26 pagesReport For Court, Sale of Dowling College Brookhaven CampusRiverheadLOCALNo ratings yet
- Madhya Pradesh District Connectivity Sector ProjectDocument7 pagesMadhya Pradesh District Connectivity Sector Projectmanish upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Tetative Teaching Plan of Intro To BusinessDocument5 pagesTetative Teaching Plan of Intro To BusinessAhmed RaXaNo ratings yet
- Led PowerpointDocument35 pagesLed PowerpointArunkumarNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Mental Disorder ReportDocument6 pagesMental Health and Mental Disorder ReportBonJovi Mojica ArtistaNo ratings yet
- Calculating parameters for a basic modern transistor amplifierDocument189 pagesCalculating parameters for a basic modern transistor amplifierionioni2000No ratings yet
- NCM-111B - Concept Paper. Impact of COVID-19Document10 pagesNCM-111B - Concept Paper. Impact of COVID-19Ivy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Importance of Education: March 2015Document4 pagesImportance of Education: March 2015AswiniieNo ratings yet
- Self Unbound Ego Dissolution in PsychedelicDocument11 pagesSelf Unbound Ego Dissolution in Psychedelicszucsanna123456789No ratings yet
- EGNTDocument6 pagesEGNTTida Nicholas NyahunzviNo ratings yet
- CFLM-1 Chapter 5Document17 pagesCFLM-1 Chapter 5Rico T. MusongNo ratings yet
- Alison North - Sparkle Hoof The UnicornDocument9 pagesAlison North - Sparkle Hoof The Unicornlili francoNo ratings yet
- 515 AMA Must DO QuestionsDocument217 pages515 AMA Must DO QuestionsVenkataRajuNo ratings yet