Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phys 202 Midterm 1 Equations
Uploaded by
Noah Graf0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pageThis document provides equations and constants for physics concepts related to electric fields and charges. Key equations included are:
- Coulomb's law for the electric force between two point charges
- The electric field and electric potential for a point charge
- Expressions for the electric field due to an infinite line charge, infinite plane of charge, spherical charge distribution, ring of charge, and disk of charge
- Gauss's law relating electric flux to enclosed charge
- Constants like the Coulomb constant, electric constant, elementary charge, and more.
Original Description:
Original Title
Phys 202 Midterm 1 Equations (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides equations and constants for physics concepts related to electric fields and charges. Key equations included are:
- Coulomb's law for the electric force between two point charges
- The electric field and electric potential for a point charge
- Expressions for the electric field due to an infinite line charge, infinite plane of charge, spherical charge distribution, ring of charge, and disk of charge
- Gauss's law relating electric flux to enclosed charge
- Constants like the Coulomb constant, electric constant, elementary charge, and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views1 pagePhys 202 Midterm 1 Equations
Uploaded by
Noah GrafThis document provides equations and constants for physics concepts related to electric fields and charges. Key equations included are:
- Coulomb's law for the electric force between two point charges
- The electric field and electric potential for a point charge
- Expressions for the electric field due to an infinite line charge, infinite plane of charge, spherical charge distribution, ring of charge, and disk of charge
- Gauss's law relating electric flux to enclosed charge
- Constants like the Coulomb constant, electric constant, elementary charge, and more.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
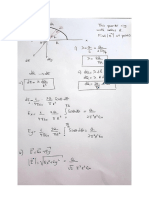
Physics 202 Midterm 1 – Equations and Constants Chapter 22, 23, 24 & 25
Electric Field of a Point Charge: (N/C) Electric Potential Energy
&|( | ( (
𝐸"⃗ = * +) 𝑟̂ ) +
∆𝑈01023 = 456 *
= 𝑞ΔV
7
Coulomb’s Law – Force – 2 Point Charges Electric Potential
&|( ||( | (
𝐹⃗ = 𝑞< 𝐸"⃗ = *)+ + 𝑟̂ 𝑉 = 456 V = Ed
7*
Electric field - Line of Charge of Length L Δ𝐸>02? = ΔKE + ΔU = 0 W=−qΔV
𝒌 |𝑸|
"𝑬⃗ = 𝒓O Parallel Plate Capacitor
𝑳 𝟐
𝒓I𝒓𝟐 KL N
𝟐
P Q STU
Electric field - Infinite Line Charge 𝐸2 = 6 = R6 =
7 7 V
𝟐 𝒌 |𝝀|
"𝑬⃗ = 𝒓O
𝒓 Constants
Electric field - Infinite Plane of Charge (in x-y plane)
𝑁𝑚<
𝜼 𝑘 = 9.0 𝑥 10œ
"𝑬⃗𝒛 = ± ]
𝒌 𝐶<
𝟐𝝐𝒐 𝐶<
𝜖 = 8.85 𝑥 10£¤<
Electric field - Sphere of Charge 𝑁𝑚<
𝑄 Charge electron: – 1.6 x 10-19 C
𝐸"⃗ = 𝑟̂ 𝑟 ≥ 𝑅𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑢𝑠 𝑆𝑝ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒
4𝜋𝜖b 𝑟 <
Charge proton: 1.6 x 10-19 C
Electric field – Ring of Charge
Mass electron: 9.11 x 10-31 kg
𝑧𝑄
𝐸"⃗ = s
q 𝑘 Mass proton: 1.67 x 10-27 kg
4𝜋𝜖b (𝑧 < + <
𝑅 )< 1
𝑘 =
Electric field – Disk of Charge 4𝜋𝜖b
Surface area sphere = 4 p r2
𝜼 𝒛 Area of a circle = p r2
"𝑬
"⃗ = t𝟏 − ]
x 𝒌
𝟐𝝐𝒐 𝟏
(𝒛𝟐 + 𝑹𝟐 )𝟐 Area side of Cylinder = 2p r L
Electric Flux 𝑚
𝑔 = 9.8
𝑠<
""⃗ 𝑨
𝚽=𝑬 ""⃗ = |𝑬| |𝑨| 𝐜𝐨𝐬 𝜽 = 𝑬𝒙 𝑨𝒙 + 𝑬𝒚 𝑨𝒚 + 𝑬𝒛 𝑨𝒛
From Physics 201
Gauss’s Law
𝑞„…†„V0 Kinetic Energy (Joules) = ½mv2
Φ = ‚ 𝐸"⃗ 𝑑𝐴⃗ =
𝜖b FNet = ma Fg = mg
Electric field – At Surface of Conductor xf = xi + vxDt Constant Velocity
𝜼 Constant Acceleration
"𝑬
"⃗𝒔𝒖𝒓𝒇𝒂𝒄𝒆 = 𝒑𝒆𝒓𝒑𝒆𝒏𝒅𝒊𝒄𝒖𝒍𝒂𝒓 𝒕𝒐 𝒔𝒖𝒓𝒇𝒂𝒄𝒆
𝝐𝒐 yf = yi + (vy)i Dt + ½ay(Dt)2
𝑸 vf2 = vi2 + 2aDx
𝑳𝒊𝒏𝒆𝒂𝒓 𝑪𝒉𝒂𝒓𝒈𝒆 𝑫𝒆𝒏𝒔𝒊𝒕𝒚 = 𝝀 =
𝑳𝒆𝒏𝒈𝒕𝒉
𝑸
v f = v i + a Dt
𝑺𝒖𝒓𝒇𝒂𝒄𝒆 𝑪𝒉𝒂𝒓𝒈𝒆 𝑫𝒆𝒏𝒔𝒊𝒕𝒚 = 𝜼 =
𝑨𝒓𝒆𝒂
1
You might also like
- Electric Circuits QPDocument12 pagesElectric Circuits QPishaNo ratings yet
- Calculations: Specimen Calculations For Test 1Document8 pagesCalculations: Specimen Calculations For Test 1Saman KumaraNo ratings yet
- Voltage Drop IEC Standard Calculation PDFDocument23 pagesVoltage Drop IEC Standard Calculation PDF7esabat7033100% (1)
- Exercise 1 3Document18 pagesExercise 1 3Jhon Alexander Carballo León0% (1)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical SolidsDocument534 pagesAdvanced Pharmaceutical SolidssevensonyNo ratings yet
- Tesla CoilDocument33 pagesTesla CoilANUPAM ghoshNo ratings yet
- CFD Methodology For Liquid Pressure Recovery PredictionsDocument9 pagesCFD Methodology For Liquid Pressure Recovery PredictionsAshok SureshNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Module 2Document4 pagesPhysics 2 Module 2jnnpctngNo ratings yet
- MV Cable Derating Factors NF C 13-200 (France)Document4 pagesMV Cable Derating Factors NF C 13-200 (France)Mothafukin MorrisseyNo ratings yet
- Math 7-Q2-WK 2Document16 pagesMath 7-Q2-WK 2Xyla Joy Perez100% (1)
- Phys 202 Midterm 1 EquationsDocument1 pagePhys 202 Midterm 1 EquationsNoah GrafNo ratings yet
- Additional Exercises: (Chapter - 1) (Electric Charges and Fields)Document14 pagesAdditional Exercises: (Chapter - 1) (Electric Charges and Fields)HARSHITNo ratings yet
- Plus Two Phy Imp Questions 2023-1Document26 pagesPlus Two Phy Imp Questions 2023-1aizah thameemNo ratings yet
- Phys 202 Midterm 2 EquationsDocument1 pagePhys 202 Midterm 2 EquationsNoah GrafNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulaDocument9 pagesPhysics FormulaAMAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- MCC Emt Never Miss A FormulaDocument4 pagesMCC Emt Never Miss A Formularammit2007No ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet by VishalDocument2 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet by Vishalabhinav yadavNo ratings yet
- L8 - Electrostatics - Dipoles & EnergyDocument14 pagesL8 - Electrostatics - Dipoles & Energyleochen0303No ratings yet
- HSSRPTR - Plus Two Phy Imp Questions 2023 Only For Backword Students-5Document26 pagesHSSRPTR - Plus Two Phy Imp Questions 2023 Only For Backword Students-5ahammedbinabdullah6No ratings yet
- Chapter 21-Electric Charge and Electric FieldsDocument28 pagesChapter 21-Electric Charge and Electric Fieldsdog171173No ratings yet
- Unit 8 NotesDocument14 pagesUnit 8 NotesEdward William ElgarNo ratings yet
- 2nd Year Notes PDFDocument18 pages2nd Year Notes PDFSaqib AzeemNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument20 pagesUntitledabood shabanehNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii Physics Solved Question Bank by Seema ElizabethDocument115 pagesHsslive Xii Physics Solved Question Bank by Seema ElizabethQWERtyNo ratings yet
- ELCN323 Electromagnetic Field Theory - Week (4) LectureDocument36 pagesELCN323 Electromagnetic Field Theory - Week (4) Lectureآيه سميرNo ratings yet
- Displacement Surface CartesianDocument3 pagesDisplacement Surface CartesianPaul CNo ratings yet
- Formula For Physics IIDocument1 pageFormula For Physics IIjunnoet21No ratings yet
- PHYS 118 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesPHYS 118 Formula Sheetemmacont2060No ratings yet
- University of The Philippines Chemical Engineering Society, Inc. (UP KEM)Document3 pagesUniversity of The Philippines Chemical Engineering Society, Inc. (UP KEM)sernameuayNo ratings yet
- Formula and Figures XIIDocument12 pagesFormula and Figures XIIDr SaabNo ratings yet
- Phys 122 Equation Sheet Exam 3Document3 pagesPhys 122 Equation Sheet Exam 3zxc100311No ratings yet
- Notes On Electro Statics 4 (Electric Potential) Class XII PDFDocument30 pagesNotes On Electro Statics 4 (Electric Potential) Class XII PDFashfaqspy10No ratings yet
- Physics 2 Lec.06 Direct-Current Circuits PDFDocument20 pagesPhysics 2 Lec.06 Direct-Current Circuits PDFYim JayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document25 pagesChapter 23hamzaxray38No ratings yet
- Couloms Law-Ctu 2020Document45 pagesCouloms Law-Ctu 2020Zllehb BhelayzNo ratings yet
- EE311 Notes+tutorialsDocument1,216 pagesEE311 Notes+tutorialslpl bobalobNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 1 Slow Learners MLM em 216923Document45 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Physics Volume 1 Slow Learners MLM em 216923Vathi N. KhalleelulahNo ratings yet
- PH1026 Examination Topics by DBH PH1026 Examination Topics by DBHDocument10 pagesPH1026 Examination Topics by DBH PH1026 Examination Topics by DBHLam NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Electric Field and PotentialDocument29 pagesLesson 6 Electric Field and Potential23 ZACH Benjamin Isaac IV LabayenNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 4Document88 pagesPhysics Unit 4Gubba YasodharNo ratings yet
- EEE 1287-Fall 2019-Topic 07Document46 pagesEEE 1287-Fall 2019-Topic 07Ahnaf AmerNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet - ElectromagnetismDocument26 pagesCheat Sheet - Electromagnetismu2100128No ratings yet
- 1.electrical Charges and FieldsDocument45 pages1.electrical Charges and FieldsOnetap solutionsNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Fields: Join Now: Https://join - Hsslive.in/group Downloaded From WWW - Hsslive.in ®Document84 pagesElectric Charges and Fields: Join Now: Https://join - Hsslive.in/group Downloaded From WWW - Hsslive.in ®Ajsal MNo ratings yet
- Physics 12th Full Q&ADocument115 pagesPhysics 12th Full Q&AKiranshreeNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity - Second Chapter, HSCDocument45 pagesStatic Electricity - Second Chapter, HSCAbdul AhadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 - Chapter 26 Part 2Document12 pagesLecture 16 - Chapter 26 Part 2Mircea PanteaNo ratings yet
- 9 AeDocument20 pages9 Aesai bNo ratings yet
- 60f99d83fa063e01ec54f50d - ## - Electric Potential & Electric Potential Energy - Lect NotesDocument86 pages60f99d83fa063e01ec54f50d - ## - Electric Potential & Electric Potential Energy - Lect Notesputtappaputtappa5173No ratings yet
- Physics: Key Points and Revision NotesDocument6 pagesPhysics: Key Points and Revision NotesAthulRKrishnanNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetsDocument1 pageCheat Sheetsag.printservices100No ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 NotesDocument144 pagesPhysics Class 12 NotesvridhiNo ratings yet
- Equation Reference SheetDocument2 pagesEquation Reference SheetwilliamsmarrenNo ratings yet
- Phy104 Physics Ii Important FormulasDocument1 pagePhy104 Physics Ii Important FormulasSkillers of TurkeyNo ratings yet
- Quantum Theory of Solids 2Document9 pagesQuantum Theory of Solids 2송지민No ratings yet
- Test 1 2017Document4 pagesTest 1 2017kalatzoiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field: 1-Biot-Savart LawDocument8 pagesMagnetic Field: 1-Biot-Savart Lawmark markNo ratings yet
- MTPDF4 Electric FieldDocument33 pagesMTPDF4 Electric Field202312329No ratings yet
- Practice Exam 1aDocument6 pagesPractice Exam 1afrazierNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Physics II Tala-IghilDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Physics II Tala-Ighildedo DZNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering: MSC Full-Time CourseDocument18 pagesElectrical Engineering: MSC Full-Time CourseFabiano Bezerra BezerraNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 9 PDFDocument4 pagesLab Report 9 PDFRajput JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Coulomb's Law and Electric Field IntensityDocument20 pagesLecture 2 - Coulomb's Law and Electric Field IntensitySir AsherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24a - Potential - SNDocument24 pagesChapter 24a - Potential - SNCharbel KaddoumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Electric Circuit Laws - Part 3Document26 pagesChapter 2 - Electric Circuit Laws - Part 3fayNo ratings yet
- Advanced Marine Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument20 pagesAdvanced Marine Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasmahakNo ratings yet
- Physics Letters A: Emmanuel YombaDocument11 pagesPhysics Letters A: Emmanuel YombaadilNo ratings yet
- Design of Deep FoundationDocument23 pagesDesign of Deep FoundationAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas ProcessesDocument71 pagesIdeal Gas ProcessesAnand NadgireNo ratings yet
- Mathematics A: Paper 4H Higher TierDocument28 pagesMathematics A: Paper 4H Higher Tiermanz 123No ratings yet
- On The Use of Rotary-Linear Generators in Floating Hybrid Wind and Wave Energy Conversion SystemsDocument6 pagesOn The Use of Rotary-Linear Generators in Floating Hybrid Wind and Wave Energy Conversion Systemsarnika33No ratings yet
- 13 Ijaet Vol III Issue II 2012Document6 pages13 Ijaet Vol III Issue II 2012Arun GargNo ratings yet
- Beam Vibration MemoDocument5 pagesBeam Vibration Memoapi-512393144No ratings yet
- 00.1 em Wave Propagation FULL NADocument12 pages00.1 em Wave Propagation FULL NAPiyush KhuleNo ratings yet
- KRL Test For EEDocument4 pagesKRL Test For EEasimnaqvi200383% (6)
- Coal Combustion Simulation in FLUENTDocument72 pagesCoal Combustion Simulation in FLUENTDanish Iqbal100% (1)
- Thermal Contact Resistance PDFDocument7 pagesThermal Contact Resistance PDFfahrgeruste3961No ratings yet
- What Is A Temperature Sensor?: ThermocouplesDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Temperature Sensor?: ThermocouplesanuradhaNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Engineering 2 (PVT & Fluid Properties)Document28 pagesReservoir Engineering 2 (PVT & Fluid Properties)okpaire lawsonNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY (CY11003) : Autumn 2021 - 2022Document15 pagesCHEMISTRY (CY11003) : Autumn 2021 - 2022Ashish RanjanNo ratings yet
- Soil Constitutive Models and Their Application in Geotechnical Engineering A Review IJERTV7IS040129 PDFDocument9 pagesSoil Constitutive Models and Their Application in Geotechnical Engineering A Review IJERTV7IS040129 PDFgamidi67No ratings yet
- An Visco - Hyperelastic Dielectric Elastomer With The Confined Compressible Fluid or Air MassDocument17 pagesAn Visco - Hyperelastic Dielectric Elastomer With The Confined Compressible Fluid or Air Massss133No ratings yet
- A. Alexakis PHD Thesis - FINALDocument438 pagesA. Alexakis PHD Thesis - FINALdodikNo ratings yet
- Abu PembahasanDocument55 pagesAbu PembahasanshasaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 14 MomentumDocument62 pagesIGCSE 14 MomentumMustayeen MahirNo ratings yet
- Vector Differentiation&Vector Integration QBDocument4 pagesVector Differentiation&Vector Integration QBS AdilakshmiNo ratings yet