Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem F5C3 Thermokimia Note 4
Uploaded by
YashwinieCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem F5C3 Thermokimia Note 4
Uploaded by
YashwinieCopyright:
Available Formats
SPM question (2022)
Table shows the heat of neutralisation of Set l and Set ll
(a) What is the meaning of heat of neutralisation.
State the type of acid of HCl and CH3COOH.[3m]
(b) Write the ionic equation for this reaction.[1m]
(c) In Set l, 50 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution with 50 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 of
F5 Chemistry
hydrochloric acid. Calculate the highest temperature if the average initial temperature is
29 oC.[4m]
[Specific heat capacity of solution= 4.2 J g-1 oC-1, density of solution = 1 g cm-3]
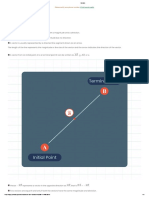
Chapter 3 : Thermochemistry (d) Draw an energy level diagram for this reaction.[2m]
Note 4 : Heat of Neutralisation
(e) Explain why there is different of value of heat of neutralisation of Set l and Set ll.[3m]
(f) The HCl in Set l is replaced with H2SO4 to react with excess NaOH.
Write a balance chemical equation for the reaction.
Predict the heat of neutralisation for the reaction.[3m]
Prepared by Mr. Brian
Comparing Heat of Neutralisation Question 1
In an experiment to determine the heat of neutralisation, 50 cm3 of 1.0 mol dm-3 ethanoic acid at
26 C is added to 50 cm3 of 2.0 mol dm-3 sodium hydroxide solution which is at 28 C in a polystyrene
o o
Differences Strong acid Weak acid Strong acid Weak acid
and and and and o
cup with cover. The mixture is then stirred and the highest temperature reached is 40 C. Calculate
in strong alkali strong alkali weak alkali weak alkali the heat of neutralisation. Explain why the heat of neutralisation obtained is lower than -57.3 kJ mol-1
o -1
HCl + NH3 CH 3COOH + NH 3 [Specific heat capacity of solution : 4.2 J g-1 C . Density of solution : 1 g cm-3 ]
Solution
Strong acid and Weak acid ionise Weak alkali ionise Weak acid and weak
strong alkali partially in water partially in water alkali ionise partially
ionise completely in to produce lower to produce lower in water to produce
water to produce concentration of concentration of lower concentration
high concentration H+ ions and some OH - ions and some of H+ ions, OH - ions,
of H+ ions and OH - CH3COOH molecules. NH3 molecules. CH3COOH molecules
ions. and NH 3 molecules.
H+ ions and OH - ions H+ ions and OH - ions
H+ ions and OH - ions combine to form combine to form H+ ions and OH - ions
combine to form water molecule and water molecule and combine to form
Question 2
water molecule and this releases heat this releases heat water molecule and
this releases heat energy to surrounding. energy to surrounding. this releases heat
energy to surrounding. energy to surrounding.
Heat energy released Heat energy released
Strong acid and is absorbed by the is absorbed by the Heat energy released 44
strong alkali do not CH3COOH molecules NH3 molecules to is absorbed by the
have any acid to ionise completely ionise completely to CH3COOH molecules
molecule or alkali to complete the complete the and NH 3 molecules
molecule in the neutralisation reaction. neutralisation reaction. to ionise completely
aqueous solution. to complete the
neutralisation reaction. 29
Solution
reactants reactants reactants reactants
- 2 - - 3 -
You might also like
- Experiment F5 C3 ThermochemistryDocument2 pagesExperiment F5 C3 ThermochemistryPrakkash RajantheranNo ratings yet
- Question Bank em - FINAL PDF 2024Document9 pagesQuestion Bank em - FINAL PDF 2024dhrumilkaushalmaheriyaNo ratings yet
- +2 Chem Ultimate Question BankDocument253 pages+2 Chem Ultimate Question Bankflex93948No ratings yet
- Thermochemistry TeacherDocument20 pagesThermochemistry TeacherjiaNo ratings yet
- FdsfdsDocument1 pageFdsfdsRitik KumarNo ratings yet
- 3.0 ThermochemistryDocument35 pages3.0 ThermochemistryRoddick BongNo ratings yet
- Checkup On Chapter 9: Questions Revision ChecklistDocument2 pagesCheckup On Chapter 9: Questions Revision ChecklistShahid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Comparison of 4 Thermo ExpDocument4 pagesComparison of 4 Thermo ExpSarah WongNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class XII Chemistry Board Paper - 2015 SolutionDocument14 pagesCbse Class XII Chemistry Board Paper - 2015 SolutionSaugata HalderNo ratings yet
- NeutcomDocument12 pagesNeutcomArvin DiNozzoNo ratings yet
- Aieee 2010-Chemistry: Q.1. A Solution Containing 2.675 G of CoclDocument13 pagesAieee 2010-Chemistry: Q.1. A Solution Containing 2.675 G of CoclSampad SarangiNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document50 pagesModule 4Abi VANo ratings yet
- Test - Solution and AmineDocument3 pagesTest - Solution and AmineaayushhariharanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument24 pagesChemistryShritan ShettyNo ratings yet
- AssignmentforSundayTest - D24 Jun 2023Document44 pagesAssignmentforSundayTest - D24 Jun 2023aadityabhagchandaniNo ratings yet
- Anfis Modul 4Document8 pagesAnfis Modul 4Karmila NusiNo ratings yet
- Aieee PapersDocument206 pagesAieee PapersDivyanshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Xii Cbse Half Grand Test Question PaperDocument7 pagesXii Cbse Half Grand Test Question PaperSrinivas NakkaNo ratings yet
- Solution AssignmentDocument4 pagesSolution AssignmentAnkitha shajiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: ObjectiveMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRINo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument10 pagesQuestionsOnyekachi Okafor ElishaNo ratings yet
- General-Chemistry LM8Document8 pagesGeneral-Chemistry LM8ShipsGonnaSailNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electrochemistry 2Document24 pagesAdvanced Electrochemistry 2Ahemdi BahmanNo ratings yet
- Energetics (Chem For CSEC p248)Document2 pagesEnergetics (Chem For CSEC p248)Laurie-Ann 大丽花 Edwards-MurdockNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Bùi Hữu ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Topic 07 Energetics I and II SupplementaryDocument7 pagesTopic 07 Energetics I and II SupplementaryTimNo ratings yet
- Sure-Shot Questions-Chemistry Class XII: 1markDocument5 pagesSure-Shot Questions-Chemistry Class XII: 1markudit pandyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 7Document16 pagesChapter # 7ALINA -No ratings yet
- Chemistry Capsule 30Document32 pagesChemistry Capsule 30Rohith SNo ratings yet
- Chang Problems Chapter 4Document13 pagesChang Problems Chapter 4ChaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Chemical Equilibrium AkitaDocument8 pagesConcept of Chemical Equilibrium AkitaunarawaikelaNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument1 pageProblem SetIrish Blanza PonceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Q.1. A Solution Containing 2.675 G of CoclDocument14 pagesChemistry: Q.1. A Solution Containing 2.675 G of CoclArun Kumar Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Sample PaperDocument9 pagesSample PaperPc xoixaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class Xii Sample Paper 01 AnswersDocument8 pagesChemistry Class Xii Sample Paper 01 Answerssouparnikar1No ratings yet
- Sample Questions - Final ExamDocument5 pagesSample Questions - Final ExamTonmoy KumarNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry: F CL, BR CH Oh, CH OCH H O, C H ODocument2 pagesInorganic Chemistry: F CL, BR CH Oh, CH OCH H O, C H OMichelle Tagumpay0% (1)
- Chemistry 51 Chapter 8 TYPES OF SOLUTIONS. A Solution Is A Homogeneous MixtDocument18 pagesChemistry 51 Chapter 8 TYPES OF SOLUTIONS. A Solution Is A Homogeneous MixtZudotaNo ratings yet
- Chem15 Problem Set 4 A. Gaseous Equilibrium: 2co O 2co Co Fe Co Feo O 4H S 2so 8HDocument5 pagesChem15 Problem Set 4 A. Gaseous Equilibrium: 2co O 2co Co Fe Co Feo O 4H S 2so 8HRoxanne de RoxasNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document10 pagesSet 1Jayant DhawanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Electrolyte SolutionsDocument52 pagesLecture 8 Electrolyte SolutionsUmesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Paper (DPS)Document3 pagesChemistry Question Paper (DPS)KAVERI JAINNo ratings yet
- Let's Get Started With Chemical Properties of Alkanes - 211209 - 205756Document13 pagesLet's Get Started With Chemical Properties of Alkanes - 211209 - 205756Nikhil PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Assignment - EquilibriumDocument5 pagesAssignment - EquilibriumYash KumarNo ratings yet
- CBQ ChemDocument35 pagesCBQ ChemIniya RajasekharNo ratings yet
- Solutions, TitrationsDocument34 pagesSolutions, Titrationsbilal.ahmadNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 Lec - Sample Third Exam I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Answer The Following by Writing The Best Answer From The ChoicesDocument6 pagesChem 16 Lec - Sample Third Exam I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Answer The Following by Writing The Best Answer From The ChoicesMaximillian LimNo ratings yet
- Halogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackDocument23 pagesHalogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackBritney PattersonNo ratings yet
- Halogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackDocument23 pagesHalogenalkanes: Unit 2 Chemistry C. Bailey PolackBritney PattersonNo ratings yet
- Examen Campinas InglesDocument7 pagesExamen Campinas InglesSharon Laurente RamónNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Sample Paper Set 1 Solution PDFDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Sample Paper Set 1 Solution PDFBalajiNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit7 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit7 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- AL Chemistry 1995 Paper 1+2Document10 pagesAL Chemistry 1995 Paper 1+2api-3734333100% (1)
- Screenshot 2022-10-09 at 6.48.23 PMDocument51 pagesScreenshot 2022-10-09 at 6.48.23 PMDanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class X ThursdayDocument1 pageChemistry Class X ThursdaySAYAK BARNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-10-16 at 7.16.17 PMDocument49 pagesScreenshot 2022-10-16 at 7.16.17 PMDanaNo ratings yet
- Thermo ChemistryDocument18 pagesThermo ChemistryfaridNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Capsule 30Document31 pagesChemistry Capsule 30carsk403No ratings yet
- Chekistry 2 Marks Imp - QuestionsDocument16 pagesChekistry 2 Marks Imp - Questionssrusti1745No ratings yet
- Reaction Heats and Bond Strengths: Based on a Series of Lectures Given to Postgraduate Students at the University of Keele, 1960From EverandReaction Heats and Bond Strengths: Based on a Series of Lectures Given to Postgraduate Students at the University of Keele, 1960No ratings yet
- Types of Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesTypes of Respiratory SystemYashwinieNo ratings yet
- Imocsea Bronze CertificateDocument1 pageImocsea Bronze CertificateYashwinieNo ratings yet
- Form 4novemberDocument4 pagesForm 4novemberYashwinieNo ratings yet
- Geografi: Cikgu DharshiniDocument4 pagesGeografi: Cikgu DharshiniYashwinieNo ratings yet
- Form 4novemberDocument4 pagesForm 4novemberYashwinieNo ratings yet
- F5C1 Newton Part 2 Note 3Document3 pagesF5C1 Newton Part 2 Note 3YashwinieNo ratings yet
- Color Mixing TemplateDocument1 pageColor Mixing TemplateYashwinieNo ratings yet
- F5C1 Newton Part 2 Note 2Document5 pagesF5C1 Newton Part 2 Note 2YashwinieNo ratings yet
- Senarai Nama Pegawai Dan Murid Senarai Nama Pegawai / Guru Bil Nama Pegawai Pasukan Alamat Pejabat/Sekolah TugasDocument2 pagesSenarai Nama Pegawai Dan Murid Senarai Nama Pegawai / Guru Bil Nama Pegawai Pasukan Alamat Pejabat/Sekolah TugasYashwinieNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument4 pagesVectorsYashwinieNo ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument4 pagesRefraction of LightYashwinieNo ratings yet
- YASH Reading ActivitiesDocument2 pagesYASH Reading ActivitiesYashwinieNo ratings yet
- Stimuli and Responses in PlantsDocument1 pageStimuli and Responses in PlantsYashwinieNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledhdawgNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Acid-Neutralizing Capacity of Commonly Antacids in Erbil CityDocument5 pagesComparison of Acid-Neutralizing Capacity of Commonly Antacids in Erbil CityNimesh ModiNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ka of Weak AcidsDocument3 pagesDetermination of Ka of Weak Acidshdlee888100% (1)
- Chapter - 7 EquilibriumDocument5 pagesChapter - 7 Equilibriumno nameNo ratings yet
- Nice ManualDocument3 pagesNice ManualajayNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium - Salt Hydrolysis Practice Questions (Level-1)Document3 pagesIonic Equilibrium - Salt Hydrolysis Practice Questions (Level-1)RSLNo ratings yet
- TB - 84AcidBasereactions Andbuffer - 61edfa34b42c35.61edfa364a8f42.17960494 PDFDocument7 pagesTB - 84AcidBasereactions Andbuffer - 61edfa34b42c35.61edfa364a8f42.17960494 PDF任思诗No ratings yet
- Enve102 Rec6 2020Document11 pagesEnve102 Rec6 2020Muhittin ÖzenNo ratings yet
- Expt 4-Ionic EquilibriaDocument42 pagesExpt 4-Ionic EquilibriatwinkledreampoppiesNo ratings yet
- Titration of A Strong Acid and Strong Base LabDocument4 pagesTitration of A Strong Acid and Strong Base Labdkatz001No ratings yet
- Anachem NeutralizationDocument2 pagesAnachem NeutralizationChristian Ghail MacapagalNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 4th Edition Smith Test BankDocument35 pagesOrganic Chemistry 4th Edition Smith Test Bankeffusiveflooder936r8o100% (21)
- IB Chemistry - SL Topic 8 Questions 1Document15 pagesIB Chemistry - SL Topic 8 Questions 1Yoshua YanottamaNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base WorksheetDocument4 pagesAcid and Base Worksheetapi-270967967No ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesCheat SheetHarshit MisraNo ratings yet
- PhenolphthaleinDocument5 pagesPhenolphthaleinspace slNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases & Oxides and HydroxidesDocument37 pagesAcids and Bases & Oxides and HydroxidesPrince HasanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 2 Determination of Ka Value of A Weak AcidDocument17 pagesLab Report Experiment 2 Determination of Ka Value of A Weak AcidarisyahariffNo ratings yet
- 2015 BiotechDocument74 pages2015 BiotechRosa DemlieNo ratings yet
- Principles of Physical Chemistry: Universiti Teknologi Mara Cawangan PerakDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Physical Chemistry: Universiti Teknologi Mara Cawangan PerakMOHAMMAD AMIN100% (2)
- Chapter 5 PDFDocument11 pagesChapter 5 PDFJun Elbert JaboliNo ratings yet
- Expt 6-Colorimetric Dtermination of PHDocument70 pagesExpt 6-Colorimetric Dtermination of PHtwinkledreampoppies100% (1)
- Experiment 4 Results and Discussion Report: Common Ion-Effect and BuffersDocument2 pagesExperiment 4 Results and Discussion Report: Common Ion-Effect and BuffersNathalie Dagmang67% (3)
- Acid and Bases SPM Chemistry Form 4Document9 pagesAcid and Bases SPM Chemistry Form 4Ct Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 1Document1 pageReviewer 1jc CincoNo ratings yet
- The Ca2 EDTA Chelation As Standard Reaction To Validate Isothermal Titration Calorimeter Measurements Rafols Est Al 2016Document9 pagesThe Ca2 EDTA Chelation As Standard Reaction To Validate Isothermal Titration Calorimeter Measurements Rafols Est Al 2016Ariel CondoriNo ratings yet
- Titulaciones Acuosas y No AcuosasDocument27 pagesTitulaciones Acuosas y No AcuosasMayerli LeónNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases: William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley Edward J. NethDocument91 pagesAcids and Bases: William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley Edward J. NethRezel C. PerezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry G12 TestDocument6 pagesChemistry G12 TestNigatu MAmoNo ratings yet
- F2 Is 003 AcidDocument4 pagesF2 Is 003 AcidLorraine TsoiNo ratings yet