Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
esterlitaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
esterlitaCopyright:
Available Formats
Objective: Interpret technical drawings and plans.
Subject: TLE (Technology and Livelihood Education)
Grade Level: Grade 8
Learning across curriculum:
1. Mathematics - Geometry and measurement concepts are essential in
understanding technical drawings and plans.
2. Science - Knowledge of scientific principles and processes can be applied in
interpreting technical drawings and plans.
3. Art - Elements of design, such as lines, shapes, and proportions, play a role in
technical drawings and plans.
Review Motivation:
1. Show a video clip of a famous architectural masterpiece and ask students to
identify the different elements of the building's design.
2. Present a real-life scenario where a technical drawing or plan was used to
construct a complex structure, such as a bridge or a skyscraper.
3. Conduct a hands-on activity where students are given an incomplete technical
drawing and asked to complete it, sparking their curiosity and interest in technical
drawings and plans.
Activity 1: Introduction to Technical Drawings and Plans
Materials: Whiteboard, markers, handouts with sample technical drawings,
rulers, pencils
Instructions:
1. Begin by defining technical drawings and plans, emphasizing their importance in
various fields, such as architecture, engineering, and construction.
2. Present sample technical drawings and explain the different elements, such as
lines, dimensions, and symbols, found in them.
3. Engage students in a discussion about the purpose and significance of each
element in a technical drawing.
4. Distribute handouts with sample technical drawings and ask students to identify
and label the different elements they have learned.
Rubrics:
Criteria:
- Correct identification and labeling of elements in technical drawings
- Understanding of the purpose and significance of each element
Points:
- Correct identification and labeling: 10 points
- Understanding of purpose and significance: 10 points
Assessment Questions:
1. What are the different elements found in a technical drawing?
2. Why is it important to accurately identify and label the elements in a technical
drawing?
Activity 2: Interpreting Technical Drawings and Plans
Materials: Whiteboard, markers, handouts with complex technical drawings,
rulers, pencils
Instructions:
1. Present more complex technical drawings and plans, such as building blueprints
or electrical circuit diagrams.
2. Discuss the key features and symbols used in each type of technical drawing.
3. Demonstrate how to interpret and understand the information presented in the
technical drawings, focusing on measurements, scales, and symbols.
4. Engage students in a guided practice activity where they interpret and extract
information from given technical drawings.
Rubrics:
Criteria:
- Accuracy in interpreting and extracting information from technical drawings
- Understanding of measurements, scales, and symbols
Points:
- Accuracy in interpretation: 15 points
- Understanding of measurements, scales, and symbols: 10 points
Assessment Questions:
1. How do you interpret measurements and scales in a technical drawing?
2. What are the common symbols used in electrical circuit diagrams?
Activity 3: Applying Technical Drawings and Plans
Materials: Whiteboard, markers, handouts with real-life scenarios, rulers,
pencils
Instructions:
1. Present real-life scenarios where technical drawings and plans are used, such as
designing a residential house or planning a landscaping project.
2. Divide students into groups and assign each group a scenario.
3. In their groups, students are required to create a technical drawing or plan based
on the given scenario, including all necessary elements and measurements.
4. Each group presents their technical drawing or plan and explains their design
choices.
Rubrics:
Criteria:
- Accuracy and completeness of the technical drawing or plan
- Clarity and coherence in explaining design choices
Points:
- Accuracy and completeness: 15 points
- Clarity and coherence in explaining design choices: 10 points
Assessment Questions:
1. How did you ensure the accuracy and completeness of your technical drawing or
plan?
2. Why did you make certain design choices in your technical drawing or plan?
Analysis:
Analyze the outcome of each activity, focusing on students' understanding of
technical drawings and plans, their ability to identify and interpret elements, and their
application of knowledge in creating their own technical drawings or plans.
Abstraction:
Summarize the key concepts and skills learned in interpreting technical drawings
and plans, emphasizing the importance of accuracy, attention to detail, and
understanding of measurements and scales.
Application:
Present a real-life problem, such as designing a floor plan for a classroom or
creating a technical drawing for a simple machine, and ask students to apply their
knowledge and skills in solving the problem.
Assessment:
Teachers can assess students' learning based on their accuracy in interpreting
technical drawings, their ability to identify and explain elements, and their proficiency
in creating their own technical drawings or plans. Assessment methods may include
written tests, practical exams, and group presentations.
Assignment:
Assign students to research and analyze a famous architectural structure, such as
the Eiffel Tower or the Taj Mahal, focusing on the technical drawings and plans used
in its construction. Students can create a presentation or a written report detailing the
elements, measurements, and design choices in the technical drawings and plans of
the chosen structure.
You might also like
- Notes on Mechanical Drawing - Prepared for the Use of Students in Mechanical, Electrical and Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandNotes on Mechanical Drawing - Prepared for the Use of Students in Mechanical, Electrical and Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - TD.L1.1Document5 pagesLesson Plan - TD.L1.1Chenie VillapañeNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanesterlitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanNicky John Doroca Dela MercedNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - TD.L1.2Document3 pagesLesson Plan - TD.L1.2Chenie VillapañeNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanTummy DocNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanRenz Nel CruzNo ratings yet
- Syllabus (td111)Document4 pagesSyllabus (td111)Ian BagunasNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesLearning ObjectivesFredrickNo ratings yet
- DraftsmenDocument5 pagesDraftsmenusman0280038No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - TD L1Document7 pagesLesson Plan - TD L1Chenie VillapañeNo ratings yet
- Manual Drafting: Calamba Manpower Development Center Technical Drafting NC IiDocument94 pagesManual Drafting: Calamba Manpower Development Center Technical Drafting NC Iialex pornes100% (1)
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanRenz Nel CruzNo ratings yet
- Challenges of "Teaching and Learning" in Technical Drawing Course: A Comparison of Architectural and Civil Engineering EducationDocument12 pagesChallenges of "Teaching and Learning" in Technical Drawing Course: A Comparison of Architectural and Civil Engineering EducationPhili-Am I. OcliasaNo ratings yet
- Khusnul Kotimah - Tugas 1 Gartek DDocument15 pagesKhusnul Kotimah - Tugas 1 Gartek DLiaaNo ratings yet
- TD SS 1 - Wk1 Lesson NoteDocument3 pagesTD SS 1 - Wk1 Lesson NoteTriplejayartNo ratings yet
- 4 CBLM Interpret TechnicalDocument31 pages4 CBLM Interpret TechnicalJohn snowNo ratings yet
- BTECLevel 3 National Engineering Teaching Resource Pack Unit 2Document29 pagesBTECLevel 3 National Engineering Teaching Resource Pack Unit 2princedotty0% (1)
- Final ICT - Technical Drafting Grade 7-10Document22 pagesFinal ICT - Technical Drafting Grade 7-10Margarito Salapantan67% (6)
- Basic Engineering Drawing and CAD I Lesson PlansDocument233 pagesBasic Engineering Drawing and CAD I Lesson Planskrristin80% (10)
- Engineering Drawing & CAD - Module DescriptionDocument5 pagesEngineering Drawing & CAD - Module DescriptionCynthia UmubyeyiNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Construction Graphics 3Document6 pagesCourse Outline: Construction Graphics 3Gratifying SoulNo ratings yet
- Automotive Engineering Program Revision NewDocument10 pagesAutomotive Engineering Program Revision NewGetachew TikueNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Ss1 Technical Drawing Scheme of Work and Note - EcolebooksDocument58 pages1st Term Ss1 Technical Drawing Scheme of Work and Note - Ecolebookschelaw RichardNo ratings yet
- CBLM Interpret Technical DrawingDocument81 pagesCBLM Interpret Technical DrawingDonabel NoveroNo ratings yet
- Juengineering 2019/20: Knowledge)Document3 pagesJuengineering 2019/20: Knowledge)Hyper - XNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING 2019/20: Knowledge)Document3 pagesENGINEERING 2019/20: Knowledge)Hyper - XNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson PlanTrisha Mae NatividadNo ratings yet
- ES 122-Engineering Drawing 2Document7 pagesES 122-Engineering Drawing 2Ricson BondadNo ratings yet
- NCE 2021 2022 Art Design Examiners ReportDocument18 pagesNCE 2021 2022 Art Design Examiners ReportAl-Ashmal FoolchandNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus: Cebu Technological University Ctu-Main CampusDocument5 pagesCourse Syllabus: Cebu Technological University Ctu-Main CampusRicson BondadNo ratings yet
- February 13, 2024Document3 pagesFebruary 13, 2024Meso, Airen Jean N.No ratings yet
- Course & Code: Projects & Seminars-Ii (Ce10601)Document2 pagesCourse & Code: Projects & Seminars-Ii (Ce10601)maheshNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Engineering ProjectDocument17 pagesUnit 3 Engineering Projectimtaz12420% (2)
- Concordia University: Other Issues: Cheung@encs - Concordia.caDocument10 pagesConcordia University: Other Issues: Cheung@encs - Concordia.caParv SinghNo ratings yet
- Mecha Perform CalculationsDocument8 pagesMecha Perform CalculationsvorexxetoNo ratings yet
- Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesCivil EngineeringAmico PaneNo ratings yet
- Problem Based Lesson Plan Ed12Document3 pagesProblem Based Lesson Plan Ed12Irish Jane SuyoNo ratings yet
- Project 2 Brief - B Con 1 March 2017Document4 pagesProject 2 Brief - B Con 1 March 2017api-302681845No ratings yet
- ARCH Design PDFDocument27 pagesARCH Design PDFtejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Mecections X and MDocument8 pagesCourse Outline Mecections X and Muday kiran thagirchiNo ratings yet
- EWY 100S Subject GuideDocument6 pagesEWY 100S Subject GuideWilly K. Ng'etichNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EGLDocument100 pagesLab Manual EGLKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - GD T 1Document3 pagesLesson Plan - GD T 1api-399406916No ratings yet
- TD 111Document12 pagesTD 111Samuel VillaNo ratings yet
- Yr9 wk8 Plan.2324Document13 pagesYr9 wk8 Plan.2324Chilekezi DanielNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan EvidenceDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Evidenceapi-299002247No ratings yet
- 2-4 Basic Engineering Drawing and CAD I PDFDocument233 pages2-4 Basic Engineering Drawing and CAD I PDFsmendoza100% (2)
- Preparing and Interpreting Technical DrawingsDocument2 pagesPreparing and Interpreting Technical DrawingsFredrickNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Content Standard Performance StandardDocument134 pagesObjectives:: Content Standard Performance StandardEmi ElenaNo ratings yet
- Drafting Technology CBCDocument59 pagesDrafting Technology CBCJonathan Delos Santos50% (2)
- Course Introduction Engineering DrawingDocument18 pagesCourse Introduction Engineering DrawingKent Lewis GornezNo ratings yet
- Folding Architecture 13Document5 pagesFolding Architecture 13selinadelamotteNo ratings yet
- Ele ProjDocument34 pagesEle ProjRavi Nagar 47No ratings yet
- EE305 Course Project - Spring 2023Document8 pagesEE305 Course Project - Spring 2023khan aliNo ratings yet
- Electrical Drawing Learning Design InformationDocument7 pagesElectrical Drawing Learning Design InformationPaakwaku Mensah-aborampahNo ratings yet
- APSC 171 Syllabus 2020-1WDocument10 pagesAPSC 171 Syllabus 2020-1Wthilakunkili15No ratings yet
- D-TD TG Module4 Structural Layout & DetailsDocument10 pagesD-TD TG Module4 Structural Layout & DetailsNiño Solon100% (1)
- 717 Technical DrawingDocument5 pages717 Technical DrawingAkatew Haile MebrahtuNo ratings yet
- TLE 8 - Q1 LP - TECHNICAL DRAFTING - Week 4Document16 pagesTLE 8 - Q1 LP - TECHNICAL DRAFTING - Week 4esterlitaNo ratings yet
- TLE 8 DLP Week 1 Technical DraftingDocument11 pagesTLE 8 DLP Week 1 Technical DraftingesterlitaNo ratings yet
- TLE 8 DLP Week 3 Technical DraftingDocument13 pagesTLE 8 DLP Week 3 Technical DraftingesterlitaNo ratings yet
- Ict Css Formative TestDocument6 pagesIct Css Formative TestesterlitaNo ratings yet
- Week 8 ActivityDocument2 pagesWeek 8 ActivityesterlitaNo ratings yet
- Technical Drafting 1ST SummativeDocument3 pagesTechnical Drafting 1ST SummativeesterlitaNo ratings yet
- Joints and SplicesDocument1 pageJoints and SplicesesterlitaNo ratings yet
- LAS - Contemporary Artsweek 5Document12 pagesLAS - Contemporary Artsweek 5esterlitaNo ratings yet
- Remedial Activity TDDocument1 pageRemedial Activity TDesterlitaNo ratings yet
- Ict ReviewerDocument2 pagesIct RevieweresterlitaNo ratings yet
- LAS - Contemporary Artsweek 8Document7 pagesLAS - Contemporary Artsweek 8esterlitaNo ratings yet
- LAS - Contemporary Artsweek 3Document7 pagesLAS - Contemporary Artsweek 3esterlitaNo ratings yet
- LAS Contemporary-Arts Grade-12 Week-2Document7 pagesLAS Contemporary-Arts Grade-12 Week-2esterlitaNo ratings yet
- Aptitude TestDocument6 pagesAptitude Testswethashaki100% (1)
- Franchise Procedures 2005-University of SussexDocument10 pagesFranchise Procedures 2005-University of SussexSatyajeet BhagatNo ratings yet
- 0417 s13 QP 21 PDFDocument8 pages0417 s13 QP 21 PDFAnzarNo ratings yet
- School Silent Reading Profile in English (Pre-Test)Document2 pagesSchool Silent Reading Profile in English (Pre-Test)Mike Oliver GallardoNo ratings yet
- Resent Passport Size Photograph. Complete Formals: Curriculum VitaeDocument3 pagesResent Passport Size Photograph. Complete Formals: Curriculum VitaeSumit RoyNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: 1 Sarath Bhushan KaluturiDocument25 pagesResearch Methodology: 1 Sarath Bhushan KaluturiSarath Bhushan KaluturiNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Reading ScoresDocument2 pagesFoundation of Reading Scoresapi-251528741No ratings yet
- Core MBA Entrance Exam QuestionsDocument18 pagesCore MBA Entrance Exam QuestionspatalnoNo ratings yet
- Hogar Dulce Hogar - QuizDocument2 pagesHogar Dulce Hogar - QuizLiam JosephNo ratings yet
- 1000111774Document909 pages1000111774juancmuNo ratings yet
- Reading Exam Practice 2Document3 pagesReading Exam Practice 2fabrydjNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of The Media ImageDocument3 pagesThe Meaning of The Media ImageEdward StapelNo ratings yet
- 7 1 - Knowledge Claims and Knowledge Questions From Tok 2015 Course GuideDocument3 pages7 1 - Knowledge Claims and Knowledge Questions From Tok 2015 Course Guideapi-254774586No ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation in Social Studies (Chapter 1)Document6 pagesAssessment and Evaluation in Social Studies (Chapter 1)Lovely Quillobe67% (3)
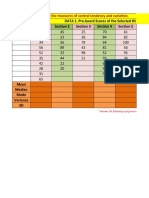
- DATA 1. Pre-Board Scores of The Selected BS Education Students (Per Section) Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5Document10 pagesDATA 1. Pre-Board Scores of The Selected BS Education Students (Per Section) Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5ariane galeno100% (1)
- Iimb Epgp PDFDocument5 pagesIimb Epgp PDFNiladri ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Djj2093Document3 pagesCourse Outline Djj2093AnahAlhabshiNo ratings yet
- Plant Attendant Grade IDocument13 pagesPlant Attendant Grade IKhushi BhadraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Giska Raissa - 827040) PDFDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 (Giska Raissa - 827040) PDFGiska RaissaNo ratings yet
- Alshenqeeti - 2014 - Interviewing As A Data Collection Method A Critical ReviewDocument8 pagesAlshenqeeti - 2014 - Interviewing As A Data Collection Method A Critical ReviewferedoNo ratings yet
- CBC-Automotive Servicing NC IIDocument130 pagesCBC-Automotive Servicing NC IIcrispyy turonNo ratings yet
- Communication PatternsDocument4 pagesCommunication PatternsMani GopalNo ratings yet
- METACOGNITIONDocument24 pagesMETACOGNITIONKri de Asis0% (1)
- GKDocument101 pagesGKAastha MishraNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of Teacher Educators in B.Ed. Department Under West BengalDocument6 pagesSWOT Analysis of Teacher Educators in B.Ed. Department Under West BengalSoulNo ratings yet
- Apostol, Jorielyn E. - 20231128 - 132308 - 0000Document30 pagesApostol, Jorielyn E. - 20231128 - 132308 - 0000Jorielyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Philosophy Essay 1-Moral Responsibility and Free WillDocument3 pagesPhilosophy Essay 1-Moral Responsibility and Free WillALDEN STEWART FARRARNo ratings yet
- Test Answer Key: UnitsDocument1 pageTest Answer Key: UnitsPaul Sebastian100% (2)
- ICO Residency-Curriculum PDFDocument219 pagesICO Residency-Curriculum PDFJujunNo ratings yet
- F4a 2018 LEEA Assessments - Information For Members & Students Version 2 December 2017Document4 pagesF4a 2018 LEEA Assessments - Information For Members & Students Version 2 December 2017VishnuNo ratings yet