Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nervous System
Uploaded by
Hannahnel Anasco Quidato0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageIT IS THE NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ITS FUNCTION INTO PUR HUMAN BODY
Original Title
NERVOUS SYSTEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIT IS THE NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ITS FUNCTION INTO PUR HUMAN BODY
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageNervous System
Uploaded by
Hannahnel Anasco QuidatoIT IS THE NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ITS FUNCTION INTO PUR HUMAN BODY
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons
-are nerve cells
Nervous System Overview
-specialized cells designed to stimulate other cells
in the body in order to communicate
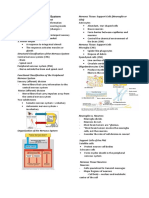
NERVOUS SYSTEM
-Your nervous system is your body’s command
STRUCTURE OF A NEURON
center. Originating from your brain, it controls
your movements, thoughts, and automatic
responses to the world around you. It also
CLASSIFICATION OF NEURON
controls other body systems and processes,
such as digestion, breathing and sexual
Function
development (puberty). Diseases, accidents,
• Sensory (afferent) neuron
toxins and the natural aging process can
• Interneuron (association)
damage your nervous system.
• Motor neuron
FUNCTION
Structure
Your nervous system uses specialized cells to
• Unipolar neurons
send signals, or messages, all over your
• Bipolar neurons
body. These electrical signals travel
• Multipolar neurons
between your brain, skin, organs, glands
and muscles
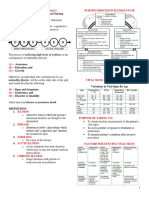
3 principles OF NERVOUS SYSTEM
Sensory Input
Integration
Motor Output
CELLS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
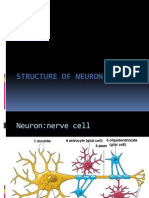
Neuron
-The functional unit of the nervous system is the
nerve cell, or neuron
Neurons have three fundamental
physiological properties
1. Excitability
2. Conductivity
3. Secretion
A typical neuron is divided into three
parts;
Soma or cell body (perikaryon)
Dendrites
Axon
Neuroglia
-Neuroglia or glial are supportive cells in the
nervous system that aid the function of
neurons
NEUROGLIA (Glia)
-There are six types of supportive cells
Four occur in the CNS
1. Oligodendrocytes
2. Microglia
3. Ependymal cells
4. Astrocytes
Two occur in the PNS
1. Schwann cells (Neurilemmocytes)
2. Satellite cells
You might also like
- Hhis Weeks 13 16 Lecture NotesDocument22 pagesHhis Weeks 13 16 Lecture NotesOwkay HNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Body CoordinationDocument16 pages2.1 Body CoordinationJia JiaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Class 10Document35 pagesNervous System Class 10Just JaenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 The Nervous System (ANAPHY)Document7 pagesChapter 7 The Nervous System (ANAPHY)Krisha AvorqueNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Anatomy of The NSDocument59 pagesCh3 Anatomy of The NSJoshua TuguinayNo ratings yet
- Neuron, Sensory Organ and Nervous System: Chew Woei Hong Pang Shan ShanDocument22 pagesNeuron, Sensory Organ and Nervous System: Chew Woei Hong Pang Shan ShanSyafiqah SabriNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemGracielle Angelyka PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue - UpdatedDocument129 pagesNervous Tissue - UpdatedPojangNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Ans IntroDocument27 pagesNervous System Ans IntroNadir KhanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Summary (Part 1)Document11 pagesNervous System - Summary (Part 1)s.tinaja.marieantonetteNo ratings yet
- Functions of The NS (Midterms)Document4 pagesFunctions of The NS (Midterms)initaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterms 1H Book and PPT 1Document35 pagesAnaphy Midterms 1H Book and PPT 1Elizabeth Louwel ConchaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument110 pagesThe Nervous System: © 2009 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- L6 - Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesL6 - Nervous TissueDea Marienila CuberoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System I: Essentials of Human AnatomyDocument40 pagesNervous System I: Essentials of Human Anatomyأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Nervous System in Mammals IDocument54 pagesChapter 13 - Nervous System in Mammals Iapi-3728508100% (2)
- Unit 2 - Reference NotesDocument18 pagesUnit 2 - Reference NotesRia JainNo ratings yet
- Nervous System CompleteDocument73 pagesNervous System CompleteRaven DoradoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesNervous SystemChloeNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesNervous SystemRaven Franklin RosarioNo ratings yet
- Emergency Plan 3Document6 pagesEmergency Plan 3Iman Hassan Ahmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Science Pointers To ReviewDocument8 pagesScience Pointers To ReviewAudrielle RejesusNo ratings yet
- Neuron and Glial CellsDocument25 pagesNeuron and Glial Cellsfakhar aliNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9No ratings yet
- Chapter 1,2,3Document8 pagesChapter 1,2,3세핌No ratings yet
- (Oct 1) Nervous-SystemDocument78 pages(Oct 1) Nervous-SystemBea GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: "The Control Center of The Body"Document19 pagesNervous System: "The Control Center of The Body"Ma. Pia Lorein JacintoNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 - The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesLecture4 - The Nervous SystemVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 2023Document31 pagesNervous System 2023Rayjie G RuleNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy: The Nervous System: Neural TissueDocument49 pagesHuman Anatomy: The Nervous System: Neural TissueLeilaNo ratings yet
- Intensive Nursing Appraisal 2 - MedSurg NotesDocument18 pagesIntensive Nursing Appraisal 2 - MedSurg NotesMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- GR 10 ReviewerDocument292 pagesGR 10 Revieweradrianigop29No ratings yet
- Nervous System Part 1 Functional Organization of The Nervous TissueDocument52 pagesNervous System Part 1 Functional Organization of The Nervous TissueleyluuuuuhNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Final Term HandoutsDocument52 pagesAnaphy Final Term HandoutsleyluuuuuhNo ratings yet
- SCience Group 1 q3 Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesSCience Group 1 q3 Nervous Systemapolancos50713No ratings yet
- Types of NeuronsDocument4 pagesTypes of NeuronsDeirdreNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Notes and ActivityDocument9 pagesNERVOUS AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Notes and ActivitySamantha SaavedraNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy - Nervous TissueDocument73 pagesAnaPhy - Nervous TissuesoraruNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCDocument52 pagesFisiologi Manusia: DR Mellova Amir MSCRizal adhitya100% (1)
- Nervous System 1Document13 pagesNervous System 1wasim akhtarNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Written Report 2Document24 pagesNervous System Written Report 2Noronisa PendalidayNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemChristine Joanne CelendroNo ratings yet
- Integration and Coordination - SG3Document180 pagesIntegration and Coordination - SG3Marcos AlbaridaNo ratings yet
- NervesDocument26 pagesNerveskentNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-06-14 at 8.06.45 PMDocument35 pagesScreenshot 2021-06-14 at 8.06.45 PMBarwako IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemCailah Sofia SelausoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAlliyah SalindoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Body Coordination 2.1 Body CoordinationDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Body Coordination 2.1 Body CoordinationMarcia PattersonNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemneotwiceskzNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Introduction To Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesLecture Notes Introduction To Nervous SystemKirstie Goc-ongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - The Nervous Tissue and The Central Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesLesson 2 - The Nervous Tissue and The Central Nervous SystemniaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesThe Nervous SystemNo NameNo ratings yet
- Altered Cognitive-Perceptual Patterns: Clients With Neuroligic DisordersDocument96 pagesAltered Cognitive-Perceptual Patterns: Clients With Neuroligic DisordersJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System For MBBSDocument20 pagesAutonomic Nervous System For MBBSjacobsNo ratings yet
- Biology 10Document3 pagesBiology 10Dwayne BaldozaNo ratings yet
- NURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDDocument50 pagesNURS1108 Lecture 8 - Nervous System Intro ENHANCEDJacia’s SpaceshipNo ratings yet
- Nervous System NotesDocument31 pagesNervous System NotesEMILIA VELEZ RESTREPONo ratings yet
- Psych ReviewerDocument20 pagesPsych ReviewerEllen Joyce P. CarnajeNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PendidikanDocument8 pagesJurnal PendidikanQothrun Nada FYNo ratings yet
- Structure of NeuronDocument12 pagesStructure of NeuronMurali SambhuNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Nervous System: Lesson A1.1Document40 pagesOverview of The Nervous System: Lesson A1.1Khobie PabilicoNo ratings yet
- Img 20240111 0002Document11 pagesImg 20240111 00029E EYAD AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 2022Document41 pagesNervous System 2022zahra nabilaNo ratings yet
- Nodes of RanvierDocument25 pagesNodes of RanvierHariharanNo ratings yet
- Synapse Neurobiology: Week 5 - Part 1Document27 pagesSynapse Neurobiology: Week 5 - Part 1bobobNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 Review Sheet ManualDocument3 pagesExercise 13 Review Sheet ManualchastityNo ratings yet
- Human HistologyDocument5 pagesHuman Histologyشمس عقيل سالم C2No ratings yet
- Biology Assignment Draft Copy Minna and AishDocument7 pagesBiology Assignment Draft Copy Minna and AishAish ThangalNo ratings yet
- Terminologia NeuroanatomicaDocument144 pagesTerminologia Neuroanatomicamatteo_vavassoriNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous TissueDocument54 pagesAnatomy of Nervous TissueNand PrakashNo ratings yet
- 12.1 Coordination & Response, 12.2 Nervous System, 12.3 Neurones & ResponseDocument4 pages12.1 Coordination & Response, 12.2 Nervous System, 12.3 Neurones & ResponseHAJAR LENNo ratings yet
- Degeneration & Regeneration of Nerve FibreDocument29 pagesDegeneration & Regeneration of Nerve FibreSana Fatima100% (2)
- LAPORAN LENGKAP Jaringan SarafDocument22 pagesLAPORAN LENGKAP Jaringan Sarafjeon niaNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafDocument31 pagesKonsep Dasar Ilmu Biokimia Dan Biologi Molekuler Untuk Sistem SarafdiandraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Essentials ofDocument56 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Essentials ofGalenn Barrion100% (1)
- Alysa Mae Paruli - Nervous System Activity PacketDocument4 pagesAlysa Mae Paruli - Nervous System Activity Packetarvin paruliNo ratings yet
- Organization of NSDocument20 pagesOrganization of NSnadine azmyNo ratings yet
- Anatomi WajahDocument9 pagesAnatomi WajahZanaAlmiraNo ratings yet
- Neural Charateristics, Types, CommunicationDocument18 pagesNeural Charateristics, Types, CommunicationAdeel AizadNo ratings yet
- Nerve CellsDocument20 pagesNerve CellsModerick SiasatNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue (NT) : Functions of Nerve TissueDocument14 pagesNervous Tissue (NT) : Functions of Nerve TissuekimNo ratings yet
- Nerve Muscle Physiology in Human Body..Document34 pagesNerve Muscle Physiology in Human Body..Mahfooz Nisar100% (1)
- Histology of Nervous TissueDocument40 pagesHistology of Nervous TissueSHARON MARIA SUNNYNo ratings yet
- On-Line Assignment DefinitionsDocument2 pagesOn-Line Assignment DefinitionsAbbey AdlerNo ratings yet
- The NeuronsDocument3 pagesThe NeuronsAsim ZafarNo ratings yet
- KEY MED 2 Updated 2021 Feb Unit 81Document10 pagesKEY MED 2 Updated 2021 Feb Unit 81huyenhungho5892No ratings yet
- Ns-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNs-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Lecture 30 Histology of CnsDocument56 pagesLecture 30 Histology of CnsJustin DawsonNo ratings yet