Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 6 Science Week 10 Lesson 1 - 2021 - Term 2
Uploaded by
Marco Robinson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views7 pagesGrade 6 Science Week 10 Lesson 1 - 2021 - Term 2
Uploaded by
Marco RobinsonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION.
PRIMARY ENGAGEMENT PROGRAMME
GRADE SIX WORKSHEET: TERM 2
SUBJECT: SCIENCE.
LESSON: 1 Week 10
Name:______________________________ Date:_______________
FACTS/TIPS:
THE HUMAN BODY
Composition of the Human Body
The human body is made up of water, cells, tissues, organs, organ
systems and six (6) elements.
The six elements which the human body consists of are:
Oxygen - O2
Carbon - C
Nitrogen - N
Calcium - Ca
Hydrogen - H
Phosphorous - P
Most of the human body is made up of water (about 75% of a child’s
body is water and an adult’s body is made up of 50-65% water).
Question: What do the terms: cells, tissues, organs and organ systems
mean?
Cells- the basic and smallest living units of life. Cells are very tiny and
can only be seen with a special instrument called a microscope.
Some animals and plants are made up of only one cell and are said
to be unicellular. The amoeba is a unicellular animal, and the
phytoplankton is a unicellular plant. There are many different types
of cells. These include bone cells, blood cells, skin cells, muscle cells,
nerve cells, brain cells, reproductive cells, among others.
Tissues- all the cells of the same kind are grouped together to form a
tissue. Example, nervous tissues are made up of cells forming the
brain. The cells forming the muscles are called muscular tissues and
the cells forming the bone are called bone tissues.
Organs- two or more tissues working together to do a specific job.
Tissues of the same kind form organs. Organs carry out special
functions e.g., the heart is the organ for pumping the blood, the
stomach is the organ for digestion, the kidneys are the organs of
excretion and the lungs are the organs for breathing.
Organ Systems/ Systems- groups of organs working together to do a
specific job. Organs are grouped together to form systems e.g.; the
digestive system is made up of many organs and is responsible for
the digestion of our food so that the body can use/utilize it.
Flow Chart showing the relationship among cells, tissues, organs and
organ systems
CELLS TISSUES ORGAN ORGANISM
SYSTEM
The human body is made up of many organs. The organs, in turn,
work in groups to form organ systems. A number of these systems are
responsible for the proper functioning of the human body.
Some major organ systems are
1. The Digestive System
2. The Muscular System
3. The Skeletal System
4. The Excretory System
5. The Respiratory System
6. The Circulatory System
7. The Nervous System
8. The Reproductive System
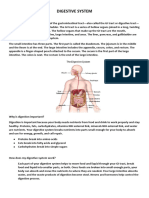
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
The digestive system helps to break down the food we eat so we
can absorb their nutrients.
The main parts of the digestive system are:
the mouth
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
anus.
The liver, gall bladder and the pancreas are accessory organs.
They are not part of the digestive system but they help in digestion.
PARTS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM.
HOW THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WORKS.
Mechanical digestion begins in the mouth when the food is
chewed by the teeth. Chemical digestion also begins in the
mouth as the saliva moistens the food.
Food is then swallowed and enters the oesophagus. In the
oesophagus, it is pushed by peristalsis into the stomach.
Chemical digestion continues in the stomach. In the stomach
the food is mixed with gastric juices and forms a liquid known as
chime.
Chime then leaves the stomach and enters into the small
intestine. Here it is further broken down by bile from the gall
bladder and pancreatic juices from the pancreas. Nutrients are
then absorbed to be taken to cells of the body for energy
production.
The undigested food or waste materials (faeces) passes into the
large intestine where it is stored. Water can be reabsorbed in
the large intestine.
When there is a buildup of faeces in the large intestine,
muscular contraction forces the faeces out the anus.
There are many diseases that affect how the digestive system works
including diarrhea, acid reflux and gastroenteritis.
IMPORTANT TERMS USED IN THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM.
Saliva – juice/liquid in the mouth.
Enzyme – a chemical substance that can change other
substances without changing itself.
Ptyalin – an enzyme found in saliva that changes all starch into
sugar.
Epiglottis – a muscle that covers the windpipe when food is
being swallowed.
Gastric juice – a liquid found in the stomach.
Chime – liquid state of food in the stomach
Villi - structures in the small intestines. These are lined with blood
vessels.
ON YOUR OWN:
1. Explain what is digestion.
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
2. Mechanical digestion begins in the
__________________________________________________________________
3. Chemical digestion begins in the
__________________________________________________________________
4. The action by which food moves down the esophagus into the
stomach is called
__________________________________________________________________
5. What juice is secreted in the stomach?
__________________________________________________________________
6. The liquid formed from the mixing of food in the stomach is called
__________________________________________________________________
7. Food is absorbed in the
__________________________________________________________________
8. Water is reabsorbed in the
__________________________________________________________________
9. Undigested material is stored in the _______________________, then
expelled through the _____________________________.
10. The _______________________ begins mechanical digestion.
HOMEWORK
Make a model of the digestive system.
Complete the word search below
You might also like
- Human Body Systems PDFDocument27 pagesHuman Body Systems PDFशशांक शेखर शुल्बNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Week 13-14Document22 pagesEarth and Life Science Week 13-14Aleli Joy Profugo DalisayNo ratings yet
- Major Organs of The BodyDocument27 pagesMajor Organs of The BodyAldwin Paul ParacNo ratings yet
- The Different Organ System of Representative Animal: Group 1Document13 pagesThe Different Organ System of Representative Animal: Group 1Jan SebyerNo ratings yet
- Digestive System GuideDocument20 pagesDigestive System Guiderocky2219No ratings yet
- Circulatory+Digestive System 2Document20 pagesCirculatory+Digestive System 2madeleine.gaudissartNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive SystemFrancisco D. AndaquigNo ratings yet
- Science PreDocument11 pagesScience PreCARL JUSTIN TUMALANo ratings yet
- Module 1 RAWDocument25 pagesModule 1 RAWCordelia TobinNo ratings yet
- Tarea de InglesDocument3 pagesTarea de InglesNatali de los santosNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 4 Week1 - Lesson1 - The Major Organs of The BodyDocument62 pagesSCIENCE 4 Week1 - Lesson1 - The Major Organs of The BodyARLENE PINERANo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 1 - Lesson 1Document19 pagesScience 8 - Q4 - Week 1 - Lesson 1Cris Tolentino100% (1)
- SCIENCE Strategic Intervention Materials on the Human Digestive SystemDocument39 pagesSCIENCE Strategic Intervention Materials on the Human Digestive SystemJavier AugustNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System 4th Quarter Updated 2Document36 pagesThe Digestive System 4th Quarter Updated 2Local ClownNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer FinalDocument19 pagesPeptic Ulcer FinalPrince DiuNo ratings yet
- Organ Tubuh Manusia EnglishDocument6 pagesOrgan Tubuh Manusia EnglishL-Viva'An Ri-l SpqNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System-Note NewDocument7 pagesHuman Digestive System-Note Newtinsae tewodrosNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Fall 2017Document4 pagesBody Systems Fall 2017amazingNo ratings yet
- Content in Demo TeachingDocument6 pagesContent in Demo TeachingAgustines, Marie Char C.No ratings yet
- Sana Ahmed DigestiveDocument8 pagesSana Ahmed DigestiveDlzar AbubakrNo ratings yet
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Nervous System As Well As Cognition. The Complexity of The Brain Is ExtremelyDocument7 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Nervous System As Well As Cognition. The Complexity of The Brain Is ExtremelySalagmaya ESNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition and DigestionDocument16 pagesAnimal Nutrition and DigestiongabrielwerneckNo ratings yet
- The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument25 pagesThe Gastrointestinal SystemAssyifaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument15 pagesDigestive SystemAlicia ValverdeNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument15 pagesThe Skeletal SystemErixMayaNo ratings yet
- Diet Assessment NBDocument6 pagesDiet Assessment NBnbaker2108No ratings yet
- EED 5 Unit 5Document19 pagesEED 5 Unit 5Lara Mariz FragataNo ratings yet
- GB2Q2-LAS-3-4Document10 pagesGB2Q2-LAS-3-4elyzaventura8No ratings yet
- MAKALAH. Memahami Dasar Anatomi Tubuh ManusiaDocument19 pagesMAKALAH. Memahami Dasar Anatomi Tubuh ManusiadediNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemKent Clark VillaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System:, Into Your Small IntestineDocument4 pagesThe Digestive System:, Into Your Small IntestineHazean Agustin-DatoyNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument116 pagesBody SystemskarunaNo ratings yet
- Jonaliza Empay - Chapter I SummaryDocument9 pagesJonaliza Empay - Chapter I SummaryJones EmpsNo ratings yet
- Introduction of AnatomyDocument71 pagesIntroduction of AnatomyPrasannaa BaleNo ratings yet
- Local Media8189533475074911973Document21 pagesLocal Media8189533475074911973Jerky JokerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiologydaculareyndel04No ratings yet
- Modular Handout and Worksheet For April 19-21-2023Document5 pagesModular Handout and Worksheet For April 19-21-2023ccam88743No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - DigestionDocument17 pagesChapter 6 - DigestionTrisha100% (1)
- Food Nutrient Digestion AbsorptionDocument34 pagesFood Nutrient Digestion AbsorptionvinodhknatrajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - The Digestive SystemDocument65 pagesChapter 7 - The Digestive SystemLama AlqarniNo ratings yet
- CUADERNILLO DE TEXTOS ESPECÍFICOS KINESIOLOGIA INSTRUMENTACION Q. INGLÉS I 2020Document9 pagesCUADERNILLO DE TEXTOS ESPECÍFICOS KINESIOLOGIA INSTRUMENTACION Q. INGLÉS I 2020Valeria DonzelliNo ratings yet
- A Well Organized Human BodyDocument8 pagesA Well Organized Human BodyRain Klien BobisNo ratings yet
- Resumen Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesResumen Digestive Systememily saborioNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive SystemAntonella AguileraNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument14 pagesBiologyPinky RanaNo ratings yet
- B2 Tissues and Organs Ict LessonDocument2 pagesB2 Tissues and Organs Ict LessonCharlie BlakeNo ratings yet
- Full Download Solution Manual For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Craver PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Craver PDF Full Chaptertracikennedyvw3z8d100% (18)
- Sistem Pencernaan ManusiaDocument8 pagesSistem Pencernaan ManusiaJovan Bimaa PramanaNo ratings yet
- Biology Sahil ArminDocument22 pagesBiology Sahil Arminarmin marandiNo ratings yet
- Systems of Human BodyDocument13 pagesSystems of Human BodyMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Cell Structure FunctionsDocument21 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Cell Structure FunctionsIon Logofătu AlbertNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Quiz NotesDocument8 pagesNutrition Quiz NotesThomas AssisNo ratings yet
- Explain The Role of The Following Organs in The Digestive System The Mouth and Salivary GlandsDocument6 pagesExplain The Role of The Following Organs in The Digestive System The Mouth and Salivary GlandsCameronweathersNo ratings yet
- 5e'slp Lindero Eed10Document4 pages5e'slp Lindero Eed10Hyacinth Mae LinderoNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument25 pagesHuman Digestive SystemVivek JainNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice CraverDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Holes Human Anatomy Physiology 16th Edition Charles Welsh Cynthia Prentice Cravertroul.cubit.nwjkgf100% (41)
- Part I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesPart I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemLleana TanNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Structure FunctionDocument11 pagesDigestive System Structure FunctionHema Jothy0% (1)
- 2 BDocument1 page2 BMarco RobinsonNo ratings yet
- 3 DDocument1 page3 DMarco RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Grade7 CurriculumDocument68 pagesGrade7 CurriculumMarco RobinsonNo ratings yet
- PDFfiller - Electronic Document Preparation and Management TextbookDocument753 pagesPDFfiller - Electronic Document Preparation and Management TextbookMarco RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Elements of PoetryDocument16 pagesElements of PoetryJayveeTria67% (3)
- 7FRENCH Christmas Term PlanDocument4 pages7FRENCH Christmas Term PlanMarco RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Nov2020 DisorderedEatingCourse Day4TranscriptDocument15 pagesNov2020 DisorderedEatingCourse Day4TranscriptMarco RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Intimate Moments 15 PersonsDocument2 pagesIntimate Moments 15 PersonsMarco RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Intimate Moments 15 PersonsDocument2 pagesIntimate Moments 15 PersonsMarco RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Women's Wellness OutlineDocument3 pagesWomen's Wellness OutlineMarco RobinsonNo ratings yet
- ColoursDocument11 pagesColoursMarco RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Prep Id 2016Document309 pagesPrep Id 2016a alrabiaahNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Biology SPM 2010 (Topics Aimed)Document1 pagePaper 3 Biology SPM 2010 (Topics Aimed)euginieNo ratings yet
- Rapid Test Detects COVID-19, Flu A & B in 15 MinutesDocument3 pagesRapid Test Detects COVID-19, Flu A & B in 15 MinutesmlgraziosiNo ratings yet
- The Life of A Flowering PlantDocument19 pagesThe Life of A Flowering PlantMedinaNo ratings yet
- Lab Photosynthesis InquiryDocument6 pagesLab Photosynthesis Inquirycorygunther100% (1)
- Unit 2 Ap Biology Review GuideDocument30 pagesUnit 2 Ap Biology Review Guideapi-605991044No ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA REFERENCES LISTDocument1 pageDAFTAR PUSTAKA REFERENCES LISTBintang UtamiNo ratings yet
- DNA Profilling Kasus Pembunuhan Di IndonesiaDocument9 pagesDNA Profilling Kasus Pembunuhan Di IndonesiaZazaezamNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science For Ymca Key AnswerDocument13 pagesReviewer in Science For Ymca Key AnswerCamille ManlongatNo ratings yet
- Biology Key VocabularyDocument4 pagesBiology Key VocabularyStudy NotesNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Gene Control: Suggested ActivitiesDocument2 pagesTopic 6 Gene Control: Suggested ActivitiesSemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- DLP in DnaDocument3 pagesDLP in DnaBenjamen Lapag Banaag Jr.100% (1)
- Vet Obst Lecture 1 Pregnancy in Domestic AnimalsDocument53 pagesVet Obst Lecture 1 Pregnancy in Domestic AnimalsgnpobsNo ratings yet
- Analogous Structures: Structures With Similar Functions But Different OriginsDocument13 pagesAnalogous Structures: Structures With Similar Functions But Different OriginsDaphne GuraNo ratings yet
- Metabolomics Basic Principles and StrategiesDocument16 pagesMetabolomics Basic Principles and StrategiesEmiliano TorresNo ratings yet
- Penyuluhan Penyakit Genetika Serta Cara Pencegahannya Di Kelurahan Duri Kepa Jakarta BaratDocument6 pagesPenyuluhan Penyakit Genetika Serta Cara Pencegahannya Di Kelurahan Duri Kepa Jakarta BaratHesty RosaryNo ratings yet
- Biodesulfurizare 1Document30 pagesBiodesulfurizare 1Stan Dragos-MihaiNo ratings yet
- Reading Test 1Document3 pagesReading Test 1Hoai AnNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Case - Cholera CombinedDocument90 pagesDiarrhea Case - Cholera CombinedLiz EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Pigment Disorders and Their PathologyDocument53 pagesPigment Disorders and Their PathologyRushi VaghelaNo ratings yet
- Human Biological DiversityDocument5 pagesHuman Biological DiversityJoyce Sarmiento100% (1)
- Genetic EngineeringDocument23 pagesGenetic EngineeringAlexander Salas EspaderaNo ratings yet
- The Insects. Structure and FunctionDocument788 pagesThe Insects. Structure and FunctionJuliana MaltaNo ratings yet
- PH Optimo de InvertasaDocument11 pagesPH Optimo de InvertasapsykhodelykNo ratings yet
- Anti-Infective AgentsDocument7 pagesAnti-Infective AgentsAlyssaGrandeMontimorNo ratings yet
- NMAT Biology Simulation Mock ExamDocument4 pagesNMAT Biology Simulation Mock ExamPhen Montalbo100% (1)
- Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesSexual vs Asexual Reproduction Exam QuestionsBenjamin Watson100% (1)
- Affiliations:: Zlshi@wh - Iov.cnDocument18 pagesAffiliations:: Zlshi@wh - Iov.cnMuraleetharan_BNo ratings yet
- ترجمة 2Document18 pagesترجمة 2habibNo ratings yet
- Food BiotechnologyDocument17 pagesFood BiotechnologyGabriela Vargas González0% (1)