Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coordinate Geometry
Uploaded by
Hedy LimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Coordinate Geometry
Uploaded by
Hedy LimCopyright:
Available Formats
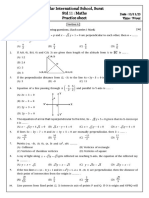
XYZ SECONDARY SCHOOL
Name: _________________ ( ) Date: ____________
Time allowed: 35 min
Class: _______ Marks:
9
Secondary 3 Multiple-Choice Questions
Chapter 4 Coordinate Geometry
1. Find the equation of the straight line that passes through the points A(0, 3) and
B( 1, 0).
1
(A) y = 3x – 3 (B) y = 3x – 3 (C) y = 3 x–3
1
(D) y = 3 x – 3 (E) y = x – 3 ( )
2. A straight line has a gradient of 2 and passes through the point (3, 4). The equation of
the straight line is
(A) 2x – y – 2 = 0 (B) 2x – y + 2 = 0 (C) x – 2y – 2 = 0
(D) x – 2y + 2 = 0 (E) 2x – y – 10 = 0 ( )
3. Which of the following lines is parallel to the line 4y = 6x + 5?
(A) 2y + 3x = 5 (B) 2y – 3x = 57 (C) y = 6x + 5
(D) 4y + 6x = 13 (E) none of the above ( )
4. The length between points (2, 5) and ( 1, 2) is
(A) 3 2 (B) 10 (C) 5 2 (D) 58 (E) 2 13 ( )
5. The equation x = 15 represents a straight line
(A) parallel to the x-axis. (B) parallel to the y-axis.
(C) passing through the origin. (D) having a gradient of 15.
(E) having a y-intercept of 15. ( )
6. The equation y + 15 = 0 represents a straight line
(A) parallel to the x-axis. (B) parallel to the y-axis.
(C) passing through the origin. (D) having a gradient of 15.
(E) having a gradient of 15. ( )
7. In the diagram, the line l has the equation
2y = mx + 2c. The length of OA is
(A) 2 units (B) 1 unit (C) 2c units
m
(D) c units (E) 2 units
( )
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
8. The distance between the points P(a, 5) and Q( 3, 2) is 5 units. The value of a must
be
(A) 1 (B) 7 (C) 7 (D) 1 or 7 (E) 7 or 1 ( )
9. The equation of the line AB in the diagram is
(A) x + 3y – 3 = 0 (B) x – 3y – 3 = 0
(C) 3x + y – 3 = 0 (D) 3x – y – 3 = 0
(E) x – 3y + 3 = 0
( )
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
Answers
1. B 2. A 3. B 4. A 5. B
6. A 7. D 8. D 9. B
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
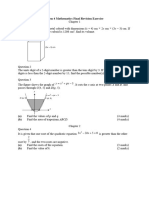
XYZ SECONDARY SCHOOL
Name: _________________ ( ) Date: ____________
Time allowed: min
Class: _______ Marks:
Secondary 3 Mathematics Test
Chapter 4 Coordinate Geometry
1. If (3, 7) is a point on the line kx + 3y = 37, find the value of k. [2]
Using separate diagrams, sketch the graphs of
(a) y = kx2
k
(b) y = x , where k is a positive constant and x is not equal to zero in (b). [4]
2. A straight line passes through the points (0, 5) and (2, 13). Find
(a) its gradient, [1]
(b) its equation. [2]
3. The coordinates of P, Q and R are P(8, 12), Q(9, 4) and R( 5, 4) respectively. M is the mid-
point of QR. Calculate the distance of PM. [4]
4. Find the equation of the straight line
(a) passing through the point (5, 7) and parallel to the x-axis. [1]
(b) passing through the point ( 2, 5) and parallel to the y-axis. [1]
5. Find the equation of the straight line l which passes through the points (0, 1) and ( 2, 4). If
the point (k, 9) lies on l, find the value of k. [3]
6. A straight line with gradient m and y-intercept c passes through the points (2, 5) and ( 4, 9).
Find the values of m and c. [3]
7. The points (3, 2), ( 2, 5) and (5, k) lie on a straight line. Find the value of k. [2]
x y
8. The equation of the line l is 3 + 4 = 1.
(a) Find its gradient. [1]
(b) The line cuts the x-axis at A and the y-axis at B. Find the area of OAB where O is the
origin. [2]
9. Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the point ( 2, 4) and is parallel to
the line y = 2x + 5. [3]
10. Find the equation of the straight line which has a gradient of 2 and which passes through the
point (2, 1). [3]
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
11. (a) Given that the line 2x + 3y = k passes through the point (2, 4), find k. [1]
(b) The line 5x + 7y = 15 is parallel to the line 2y = kx + 13. Find the value of k. [2]
12. The point ( 2, t) lies on the line 3y + 2x = 7. Find the value of t. [2]
13. The equation of a straight line is 2x + y = 8.
(a) Find the gradient of the line. [1]
(b) Given that the point ( 3, k) lies on the line, find the value of k. [2]
1
14. The coordinates of the three points are A(0, 3), B(t, 0) and C(2 t, t). If AB = 2AC, find the
possible values of t. [3]
15. Given that the three points A(0, 1), B(k, 2.5) and C(2k, 4) lie on a straight line, find the value
of k. [3]
x y
16. (a) Find the gradient of the line 3 + 5 = 1. [2]
(b) The straight line y = mx + c is parallel to the line 3x + 2y = 13 and passes through the
1
point (1, 1 2 ). Find the values of m and c. [3]
17. The points (2, 0) and ( 2, 7) lie on the line kx + ky + 5 = 0. Find the values of h and k.
[3]
18. Write down
(a) the gradient of the straight line 3x + 5y = 17. [1]
(b) the coordinates of the point on the line 4x – 5y = 13 which has y = 1 as its y coordinate.
[1]
19. In the diagram, the coordinates A and C are
(0, 6) and (5, 2) respectively. The line AC
produced cuts the x-axis at B, and D is a
point on the x-axis where CD is parallel to
the y-axis.
(a) Find the gradient of the line AC. [1]
(b) Find the equation of the line AB. [1]
(c) Find the coordinates of B. [1]
(d) Calculate the area of BCD. [2]
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
20. The diagram shows a line segment AB where
A is the point (0, 4) and B is the point (3, 0).
(a) Find the equation of the line AB. [2]
(b) If the line AB is reflected in the y-axis,
find the equation of the image of the line.
[2]
21. (a) If the straight line 3y = k – 2x passes through ( 1, 5), find k. [1]
(b) If the gradient of the straight line (2k – 1)y + (k + 1)x = 3 is parallel to the line y = 3x – 7,
find the value of k. [2]
(c) Find the equation of the line joining the points A(1, 5) and B(7, 2). [2]
22. The coordinates of ABC are A( 4, 2), B(5, 0)
and C(4, 4).
(a) Calculate the lengths of AB, BC and AC.
[3]
(b) Show that ABC is a right-angled triangle.
[2]
(c) Calculate the area of ABC. [2]
(d) Calculate the perpendicular length from C
to AB. [2]
23. The coordinates of the points O, A and B of the
parallelogram OABC are (0, 0), (6, 3) and (10, 8)
respectively. Calculate
(a) the mid-point of OB. [1]
(b) the coordinates of C. [2]
(c) the areas of OAM, OBN and the
trapezium ABNM. [4]
(d) the area of the parallelogram OABC. [2]
24. The equation of a straight line is 2x + 5y = 20. Find
(a) the gradient of the line, [1]
(b) the coordinates of the point where the line crosses the y-axis, [1]
1
(c) the coordinates of the point at which the line intersects the line x = 2 2 , [1]
(d) the equation of the line which is parallel to 2x + 5y = 20 and which passes through the
point ( 1, 7). [2]
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
25. l is the line passing through the point (3, 8) and parallel to the line 2x – 3y + 5 = 0. Find the
equation of the line l. [3]
26. (a) Given that the points A( 2, 3), B(2, 2) and C(6, 1) are three vertices of the
parallelogram ABCD, find the coordinates of the point D. [3]
(b) Given also that the point E has coordinates E(5, k) and that A, B and E are collinear, find
the value of k. [2]
(c) Find the equation of the line passing through C and parallel to the line 5x – 7y = 84. [3]
(d) Given that the area of ABC is 16 units2, calculate the perpendicular distance from B to
AC, giving your answer correct to 2 decimal places. [4]
27. The diagram shows part of the graph of
2
y= x 3.
(a) A point P is on the curve with coordinates
( 1, k). Find the value of k. [1]
(b) Given that the straight line y = 2x + h passes
through P, find the value of h. [1]
(c) Another straight line l, parallel to
y = 2x + h, passes through the point Q. Find
the equation of the line l. [2]
2
28. The gradient of the line joining the points (5, k) and (k, 3) is 3 . Calculate the value
of k. [3]
29. Given that the coordinates of A and B are (1, 3) and (7, 1) respectively, find
(a) the gradient of AB (b) the equation of AB. [4]
4
30. A line passes through the points ( 2, k) and (5, 9). If the gradient of the line is 7 , find
the value of k. This line cuts the x-axis at P and the y-axis at Q. Find the area of
OPQ, where O is the origin. [3]
31. (a) A straight line passes through P(1, 1), Q(4, 1) and R(k, 3). Find the value of k.
(b) Find the equation of a straight line passing through the points A(4, 3) and B(0, 5).
[4]
2
32. (a) Find the equation of a line which has gradient 3 and which passes through the
point
( 2, 5). Give your answer for the equation in the form y = mx + c.
(b) Find the equation of the line on which both the points (0, 3) and (2, 5) lie. [6]
33. The straight line y = x + 2 cuts the x-axis at point A and the y-axis at the point B.
Calculate the area of AOB where O is the origin. [3]
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
34. Write down the gradient of the straight line 2x + 3y = 4 and find the equation of the
line which is parallel to 2x + 3y = 4 and which passes through the point (1, 7). [4]
35. For all values of m, the line 2y = mx + 6 passes through a fixed point K. State the
coordinates of K. [2]
36. Find the equation of the line parallel to 3x + 4y + 15 = 0 and passing through the point
(3, 7). [3]
37. The straight line 3y = mx + c is parallel to the line 2y – 3x = 5 and passes through the
point (1, 12). Find the value of m and of c. [3]
x y
38. Given that line 4 6 = 1, find
(a) its gradient, (b) the coordinates of the point at which it cuts the line x =
8. [4]
39. The lines ky – 2x + 5 = 0 and 6y – (k + 1)x – 3 = 0 are parallel. Find the value(s) of k.
[2]
40. Three of the vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are A( 1, 5), B(5, 1) and C(6, 2).
Find the coordinates of the fourth vertex D. [3]
41. The curve x2 + y2 – 6x – 8y = 0 cuts the x-axis at points O and A and the y-axis at O
and B.
(a) Find the coordinates of O, A and B.
(b) Find the gradient of the line AB.
(c) Write down the equation of the line AB.
(d) OAB is rotated through 90 clockwise about O to OPQ. Write down the
coordinates of P and Q. [8]
42. P, Q and R are the points (8, 3), (6, k) and ( 3, 8) respectively.
(a) If P, Q and R are collinear, find k.
(b) With this value of k, find the ratio PQ : QR.
(c) RQ is produced to T so that RQ = 2QT. Find the coordinates of T. [7]
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
Answers
1.
2. (a) 4 (b) y = 4x + 5
3. 180 = 13.4
4. (a) y = 7 (b) x = 2
1
5. 2y + 3x = 2 ; k = 5 3
2 1
6. m = 3
, c=63
4
7. k = 45
1
8. (a) 13 (b) 6
9. y = 2x + 8
10. y = 2x – 3
3
11. (a) k = 8 (b) k = 1 7
2
12. t = 3 3
13. (a) 2 (b) k = 14
1 1
14. t = 4 2 or 1 2
15. k = 3
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
2 1
16. (a) 13 (b) m = 1 2 ; c = 3
1 3
17. h = 2 2 , k = 1 7
3
18. (a) 5
(b) (2, 1)
4
19. (a) 5
(b) 5y + 4x = 30
(c) (7.5, 0) (d) 2.5 units2
20. (a) 3y + 4x = 12 (b) 3y = 4x + 12
2
21. (a) 17 (b) 7 (c) 2y + x = 11
22. (a) 85 , 17 , 68 (c) 17 (d) 3.69
23. (a) (5, 4) (b) (4, 5) (c) 9, 40, 22 (d) 18
2
24. (a) 5
(b) (0, 4)
1
(c) (2 2 , 3) (d) 2 x + 5y = 33
25. 3y = 2x + 5
3
26. (a) D(2, 6) (b) k = 54 (c) 7y = 5x – 23 (d) 3.88 units
27. (a) 5 (b) 3 (c) 3y = 6x – 4
1 1
28. 5 29. (a) 3 (b) 3y + x = 10
1
30. k = 5, 33 56 31. (a) 7 (b) y = 7x – 5
2 1
32. (a) y = 3 x + 6 3 (b) y = x + 3 33. 2 units2
2
34. 3 , 3y + 2x = 23 35. (0, 3) 36. 4y + 3x + 37 = 0
1 1
37. m = 1 2 , c = 9 38. (a) 1 2 (b) (8, 6)
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
39. 3, 4 40. (0, 2)
1
41. (a) (0, 0) , (6, 0) , (0, 8) (b) 13
(c) 3y + 4x = 24 (d) P (0, 6) , Q (8, 0)
1 1
42. (a) 1 (b) 2 : 9 (c) (10 2 , 5 2 )
Teachers’ Resource NSM 3 Oxford University Press
You might also like
- Straight Line GraphsDocument3 pagesStraight Line GraphsLi Tong ChowNo ratings yet
- 11 Sem 1 Trial 2023Document2 pages11 Sem 1 Trial 2023Hadi ShaifulNo ratings yet
- For More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)Document5 pagesFor More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)jaspreet singhNo ratings yet
- For More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)Document5 pagesFor More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)jaspreet singhNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xi Chapter 10 Straight Lines Practice Paper 07Document3 pagesMaths Class Xi Chapter 10 Straight Lines Practice Paper 07priyanshsrivastava457No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4.0 Vectors 2023Document6 pagesTutorial 4.0 Vectors 2023AdliHakimNo ratings yet
- Practicesheet - D13 Nov 2023Document13 pagesPracticesheet - D13 Nov 2023Rajat KumbharNo ratings yet
- 07march MainsDocument38 pages07march Mainsprakash karnaNo ratings yet
- Xercise: Jee ProblemsDocument2 pagesXercise: Jee ProblemspandaNo ratings yet
- Best Approach: Straight Line & CircleDocument20 pagesBest Approach: Straight Line & CircleIshhuNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2006 3U Prelim YearlyDocument3 pagesJames Ruse 2006 3U Prelim YearlyParpatiVasuNo ratings yet
- Alevel C1C2Document40 pagesAlevel C1C2nuddin123No ratings yet
- Math Studies ExercisesDocument6 pagesMath Studies ExercisesKonstantinos TakoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Straight Lines Mathongo PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Straight Lines Mathongo PDFNagireddy KalluriNo ratings yet
- Prelim Maths Part - 1Document5 pagesPrelim Maths Part - 1varadbhamare22No ratings yet
- Maths November 2010 Paper 2Document8 pagesMaths November 2010 Paper 2shealtielchigariso06No ratings yet
- Straight Lines QnsDocument8 pagesStraight Lines QnsAlok14741No ratings yet
- ASFGHJKLDocument3 pagesASFGHJKLKumar AtthiNo ratings yet
- Straight Line (Question Paper)Document4 pagesStraight Line (Question Paper)Vikas MeenaNo ratings yet
- 11thQBank On Straight Line - CircleDocument20 pages11thQBank On Straight Line - Circlealokyadav020206No ratings yet
- 2022 JC1 H2 Math Practice PaperDocument5 pages2022 JC1 H2 Math Practice PaperTimothy LauNo ratings yet
- Core 1 Revision PackDocument28 pagesCore 1 Revision PackSunny AfgNo ratings yet
- Solomon J QP - C1 EdexcelDocument4 pagesSolomon J QP - C1 EdexcelMuhammad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- IYGB Paper B For C1Document6 pagesIYGB Paper B For C1Sherine El-NakkadyNo ratings yet
- Straight Line DPP-9 QuesDocument2 pagesStraight Line DPP-9 QuesSameer SayyedNo ratings yet
- For More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)Document4 pagesFor More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)jaspreet singhNo ratings yet
- Iygb Gce: Core Mathematics C1 Advanced SubsidiaryDocument6 pagesIygb Gce: Core Mathematics C1 Advanced SubsidiarySherine El-NakkadyNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: Topic: SLDocument1 pageFiitjee: Topic: SLAmit GNo ratings yet
- Straight Line & Circle Only QuestionDocument15 pagesStraight Line & Circle Only QuestionShikhar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- G11 Add Maths P2Document18 pagesG11 Add Maths P2Trevor G. SamarooNo ratings yet
- 4exp AM Prelim6 P1Document3 pages4exp AM Prelim6 P1John GohNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 6 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 6 For Board Exam 2024ydprince111No ratings yet
- Math T STPM Semester 1 2013Document2 pagesMath T STPM Semester 1 2013tchinhuat82No ratings yet
- Test1 (Revision)Document47 pagesTest1 (Revision)hehey321No ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Geometry-2Document5 pagesThree Dimensional Geometry-2Gunn MadanNo ratings yet
- Straight Line and CircleDocument32 pagesStraight Line and CircleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 4exp AM Prelim2 P1Document3 pages4exp AM Prelim2 P1John GohNo ratings yet
- BSS Maths Assesment-1Document6 pagesBSS Maths Assesment-1sonaliNo ratings yet
- Ah Sam 1Document3 pagesAh Sam 1JASON_INGHAMNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1 p2Document12 pagesAdd Maths Perfect Score Module Form 4 Set 1 p2Yeow Pow Choo100% (1)
- I Pu Model Paper-2Document4 pagesI Pu Model Paper-2krishnabrunda72No ratings yet
- 25.1.2020 Maths TenDocument2 pages25.1.2020 Maths TenYe Htet NaingNo ratings yet
- Revision Exercise QuestionDocument11 pagesRevision Exercise QuestionGabriel FungNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths ST Line Functions KDDocument1 page11 Maths ST Line Functions KDAkash KaleNo ratings yet
- 3 D 03 ExerciseDocument10 pages3 D 03 ExerciseRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Weekly TestDocument2 pagesWeekly TestbabufatafatiNo ratings yet
- Core 2 Revision Pack PDFDocument55 pagesCore 2 Revision Pack PDFcandimathsNo ratings yet
- Sri Sri Ravishankar Vidya Mandir, Indore Subject - Mathematics Date: 12/08/2023 Worksheet:-Vrctors and 3-D Class - XiiDocument4 pagesSri Sri Ravishankar Vidya Mandir, Indore Subject - Mathematics Date: 12/08/2023 Worksheet:-Vrctors and 3-D Class - XiiJatin MoolchandaniNo ratings yet
- Class 7 ThmathsDocument3 pagesClass 7 ThmathsAditya JainNo ratings yet
- X MATHS Periodic 2 Practice Paper (23-24)Document2 pagesX MATHS Periodic 2 Practice Paper (23-24)eshaanjaiswal7No ratings yet
- W-Second QDocument7 pagesW-Second QTSEGAYE HILEMICHAELNo ratings yet
- Straight Line (Level 1)Document6 pagesStraight Line (Level 1)Frf FfNo ratings yet
- QUIZ - Straight Line - QDocument3 pagesQUIZ - Straight Line - QAsif RazaNo ratings yet
- C1 Practice Paper B2Document5 pagesC1 Practice Paper B2JohnNo ratings yet
- Board Pattern PapersDocument8 pagesBoard Pattern PapersSantoshNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Coordinate Geometry Module ExercisesDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 6 Coordinate Geometry Module ExercisesBid Hassan75% (8)
- 3D & Vectors - Adv Pattern TestDocument3 pages3D & Vectors - Adv Pattern TestA. K. R. DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Sep 2013Document8 pagesSep 2013anowNo ratings yet
- 2 - Civil Liberties Union Vs Executive SecretaryDocument3 pages2 - Civil Liberties Union Vs Executive SecretaryTew BaquialNo ratings yet
- EE 4702 Take-Home Pre-Final Questions: SolutionDocument11 pagesEE 4702 Take-Home Pre-Final Questions: SolutionmoienNo ratings yet
- Some People Say That Having Jobs Can Be of Great Benefit To TeensDocument2 pagesSome People Say That Having Jobs Can Be of Great Benefit To Teensmaia sulavaNo ratings yet
- Newcastle University Dissertation Cover PageDocument5 pagesNewcastle University Dissertation Cover PageThesisPaperHelpUK100% (1)
- Adverse Event Log TemplateDocument2 pagesAdverse Event Log TemplateLore LopezNo ratings yet
- Genose Massal D - 6 Juli 2021Document102 pagesGenose Massal D - 6 Juli 2021Phyto LianoNo ratings yet
- 12 Things You Must Know To Win A Full Scholarship in SwedenDocument51 pages12 Things You Must Know To Win A Full Scholarship in SwedenEmmanuel GeraldNo ratings yet
- MS For Surface Rock Bolts and Dowels (Rev-2)Document23 pagesMS For Surface Rock Bolts and Dowels (Rev-2)shahzadNo ratings yet
- LFT - Development Status and Perspectives: Prof. DR Michael SchemmeDocument7 pagesLFT - Development Status and Perspectives: Prof. DR Michael SchemmeabiliovieiraNo ratings yet
- Application & Registration Form MSC International Business Management M2Document11 pagesApplication & Registration Form MSC International Business Management M2Way To Euro Mission Education ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- Architect Strengths and Weaknesses - 16personalitiesDocument4 pagesArchitect Strengths and Weaknesses - 16personalitiesIsaacNo ratings yet
- 18 CHAPTER 18 Safety in Chemical IndustryDocument121 pages18 CHAPTER 18 Safety in Chemical IndustrySanika TalathiNo ratings yet
- Carreño Araujo Cesar - Capturas Calculadora Sesion 02Document17 pagesCarreño Araujo Cesar - Capturas Calculadora Sesion 02CESAR JHORCHS EDUARDO CARREÑO ARAUJONo ratings yet
- ENG18Document2 pagesENG18Lef RJNo ratings yet
- (2022) 5 SCC 661Document43 pages(2022) 5 SCC 661Swati PandaNo ratings yet
- Casio fx-82MSDocument49 pagesCasio fx-82MSPéter GedeNo ratings yet
- Romualdez v. SB, GR. No. 152259, July 29, 2004Document1 pageRomualdez v. SB, GR. No. 152259, July 29, 2004MonicaCelineCaroNo ratings yet
- Managing Digital Transformations - 1Document105 pagesManaging Digital Transformations - 1RamyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Ethernet and VLAN: Lab 1-1 Ethernet Interface and Link Configuration Learning ObjectivesDocument15 pagesModule 1 Ethernet and VLAN: Lab 1-1 Ethernet Interface and Link Configuration Learning ObjectivesChaima BelhediNo ratings yet
- LogisticsDocument5 pagesLogisticsHương LýNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Running EnergyPlusDocument29 pagesLecture 02 Running EnergyPlusJoanne SiaNo ratings yet
- NAVA - Credit TransactionsDocument79 pagesNAVA - Credit Transactionscarrie navaNo ratings yet
- Pro & Contra Hydropower: AdvantagesDocument16 pagesPro & Contra Hydropower: AdvantagesbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- Information For Producers of Emergency Fittings Acc. To Iec 60598 2 22Document10 pagesInformation For Producers of Emergency Fittings Acc. To Iec 60598 2 22mohammed imran pashaNo ratings yet
- 3HAC9821-1 Rev01Document8 pages3HAC9821-1 Rev01TensaigaNo ratings yet
- PAL-AT Operating ManualDocument60 pagesPAL-AT Operating ManualArmağan DemirelNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Power Platform Adoption PlanningDocument84 pagesMicrosoft Power Platform Adoption PlanningcursurilemeleNo ratings yet
- Bc-6800plus Series Auto Hematology Analyzer Operator's ManualDocument322 pagesBc-6800plus Series Auto Hematology Analyzer Operator's ManualHenock MelesseNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1technoDocument3 pagesAssignment 1technonadiyaxxNo ratings yet
- Lect 04Document22 pagesLect 04Beam MoonNo ratings yet