Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2nd Quarter Health9
Uploaded by
Myra Ramirez Julian0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThis document provides information on first aid techniques for various common injuries and medical emergencies. It discusses how to assess vital signs, survey the scene and victim, control bleeding and provide immobilization for fractures, sprains and strains. Specific first aid procedures are outlined for wounds, burns, choking, heat exhaustion, food poisoning, drowning, heart attacks, and electric shock. The document also covers how to properly carry and transport an injured person while providing ongoing care.
Original Description:
Original Title
2nd quarter Health9 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on first aid techniques for various common injuries and medical emergencies. It discusses how to assess vital signs, survey the scene and victim, control bleeding and provide immobilization for fractures, sprains and strains. Specific first aid procedures are outlined for wounds, burns, choking, heat exhaustion, food poisoning, drowning, heart attacks, and electric shock. The document also covers how to properly carry and transport an injured person while providing ongoing care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pages2nd Quarter Health9
Uploaded by
Myra Ramirez JulianThis document provides information on first aid techniques for various common injuries and medical emergencies. It discusses how to assess vital signs, survey the scene and victim, control bleeding and provide immobilization for fractures, sprains and strains. Specific first aid procedures are outlined for wounds, burns, choking, heat exhaustion, food poisoning, drowning, heart attacks, and electric shock. The document also covers how to properly carry and transport an injured person while providing ongoing care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
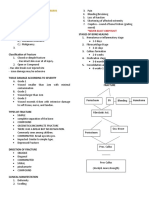
Unit II Health Unintentional Injuries: providing support for immobilization A.
Fracture- a break or crack in a bone
Prevention, Safety and First Aid for broken bones, sprains and strains Check vital signs
Lesson 1: The Basic of First Aid Two Phases of Bandaging Do not move injure part
First Aid 1. An open bandage is used for wounds Stop bleeding
An immediate care given to a person 2. A cravat bandage is use for wounds that Immobilize broken part by splint
who is suddenly get ill or injured needs extra support, the narrower the Seek medical help
Bridges that fills the gap between cravat, the greater the pressure it will B. Dislocation- partial or complete displacement
victim and physicians give of bone
Characteristics of a Good First Aider Techniques in Bandaging
Splint affected part
1. Gentle- not cause pain and panic 1. Always use the square knot
Do not try to move
2. Observant- notice all sign 2. Consider the size and location of the
Apply ice
3. Resourceful wound
C. Sprain and Strain
4. Tactful- not frighten the victim 3. Ensure that the bandage firm and
Use RICE Method
5. Sympathetic- comforts and reassures comfortable when there’s a swelling
D. Heat Exhaustion
the victim 4. Secure the bandage using tape, clip and
Principles (Do’s and Don’ts) square knot Transport the victim
Dos Give plenty of water
Stay calm Wounds E. Food Poisoning
Check for a medical condition A break in the continuity of a tissue in Gives plenty flavored fluid and bowl to
the body use if he/she vomits
Loosen any tight clothing
May be closed in which there is no F. Choking
Check the ABC
break or damage in the skin. Also called Encourage the victim to cough
Don’ts
hematoma or contusions. For Give a five back blows
Don’t give food and drink to
unconscious victim management of closed wounds, use Try abdominal thrust
Don’t move the victim unless you need RICE method Call medical help
Also be open in which there is a break G. Drowning
place him/her in the recovery position
in the skin Lay the person on his/her back
Kinds of Open Wounds Check breathing
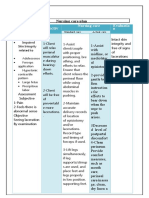
Lesson 2: Survey of the Scene and the Victim
1. Puncture- piercing wounds caused by Give rescue breath and chest
Vital Signs
pointed objects compression if necessary
Measures of various physiological
2. Abrasion- caused by rubbing the skin If the person is breathing, place him/her
statistics taken in order to assess the
against a rough surface in recovery position
most basic body function
3. Incision- is a cut caused by sharp Treat for hypothermia by removing wet
Recording: body temperature, pulse
object clothing and covering the victim with a
rate, blood pressure and respiratory
4. Laceration- blunt breaking or tearing dry blanket
rate
of soft tissue H. Heart Attack
Signs and Symptoms
5. Avulsion- forcible tearing or partial
Signs are details discovered by Help the person sit or lie down with
tearing away of tissues
applying your senses head elevated
First Aid for Open Wounds
o Bleeding Call for medical help
Wear gloves, remove or cut clothing if
o Swelling Constantly monitor vital signs
necessary
o Deformities I. Chemical Burns (Associated with Electric
Control bleeding
Symptoms are sensations that victim Shock)
Elevate the injured part except for eye
feels or experiences and may be able to Make sure that contact with the
injury and wounds with embedded
describe electrical source is broken
object
o Nausea Flood the site of injury (entry and exit
Cover the wound
o Vomiting point) with plenty of cold water
Care for shock
o Heat Wear disposable gloves
Seek medical attention
o Impaired Sensation Call for medical help
J. Burns
Lesson 4: Carrying and Transporting an
Two Ways to Conduct Physical Examination (Minor) Flood the affected area with
Injured Person
when giving First Aid cold water to relieve pain, cover the
Transporting an injured person to a
1. Primary Survey area with sterile non-adhesive dressing
safer place requires great care
Used when the victim is unconscious or bandage
When doing this, a first aider must
o Check for consciousness (Severe) help the person to lie won to
consider the following factors
o Open the airway prevent the burnt area from coming into
o Weight and Height of the victim
o Check for breathing contact with the ground
o Status of the victim (conscious or
o Check for circulation Douse plenty of cold water
unconscious)
2. Secondary Survey Seek for medical assistance
o Environment
Used when the victim is conscious that Carefully remove burnt clothing unless
o Special need consideration
aims to detect everything about the is it sticking to the skin
Kinds
patient’s condition Check vital signs, treat shock
A. One-man Carry
Make use of checking L. Heat Stroke
1. Fireman’s Carry- the easiest way to transport a
o Pulse rate Move the victim to cool place
light and smaller victim
o Temperature Remove mush of outer clothing if
2. Piggy Back- when the victim is conscious
o Respiration possible
3. Pack Strap Carry- use when the victim is
smaller than the first aider Call for medical help
Lesson 3: Dressing and Bandages 4. Shoulder Crag- used when the floor is smooth, Wrap the person in cold, wet sheet and
Dressing short distance transport keep the sheet until the temperatures
A piece of sterile cloth that covers a 5. Fireman’s Drag or Tied-Handled Crawl- used drops to 37.5 degree Celsius
wounds to prevent infections and/or when first aider and victim must crawl When person temperature has returned
stop the bleeding 6. Blanket Drag- used when the victim is to normal, replace wet sheet with dry
Techniques in applying dressing seriously injured and should not be lifted one
1. Wash hands and wear gloves if possible B. Two/Three or More-Man Carry M. Stroke
2. Unwrap the dressing close to the 1. Chair or Seated- used when two first aiders and If the person is unconscious, help him
wounds as possible a chair is available to lie down with his head and shoulder
3. Skin is not sterile, discard and used 2. Hammock Carry- for three first aider slightly raised and supported
fresh one if the dressings slips 3. Bearer Along Side Carry- carries will stay on Loosen any tight clothing
4. Place the dressings over the wounds, the uninjured side of the victim Monitor vital signs
make sure that the expose wounds is 4. Six Man Lift and Carry Give rescue breathing if the victim is
covered unconscious
Bandage Lesson 5: First Aid for Unintentional Injuries Call ambulance and call for help
Are used to apply pressure to bleeding; Unintentional Injuries- injuries which as not
for covering wounds and burns and expected, also known as ACCIDENT
You might also like
- Nursing Diagnoses For PT With Altered Level of ConsciousnessDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnoses For PT With Altered Level of Consciousnessmikaela_pascua95% (40)
- Post TestDocument9 pagesPost TestPradnya Paramitha100% (2)
- ABG Tic Tac Toe Part 1Document2 pagesABG Tic Tac Toe Part 1Shala Miller100% (1)
- HEALTH 9 HandoutsDocument5 pagesHEALTH 9 HandoutsEfren TuvillaNo ratings yet
- HK 11 Practical ReviewerDocument5 pagesHK 11 Practical ReviewerEugeneNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grading Health Notes First Aid and Unintentional InjuryDocument1 page3rd Grading Health Notes First Aid and Unintentional Injuryblairemeri09No ratings yet
- Health 9 Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 3, Week 6-8Document4 pagesHealth 9 Learning Activity Sheet Quarter 3, Week 6-8fe delgadoNo ratings yet
- Appropriate First Aid Injuries and Emergency Situations in Physical ActivityDocument4 pagesAppropriate First Aid Injuries and Emergency Situations in Physical ActivityJanine JanineNo ratings yet
- ALS FA Poster Workplace v3Document1 pageALS FA Poster Workplace v3rajNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid and BLS Reviewer Batch PDFDocument21 pagesBasic First Aid and BLS Reviewer Batch PDFDana Leen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid and BLS Reviewer BatchDocument21 pagesBasic First Aid and BLS Reviewer BatchDana Leen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal HandoutsDocument3 pagesThe Musculoskeletal Handoutsseigelystic100% (11)
- W2 - MEDSURG Guidelines For Nursing Interventions On Coma PatientsDocument6 pagesW2 - MEDSURG Guidelines For Nursing Interventions On Coma PatientsKyla L. Madjad100% (1)
- NCP Ko BabyDocument3 pagesNCP Ko BabyDaniel ApostolNo ratings yet
- Unintentional Injury Prevention, First Aid and SafetyDocument25 pagesUnintentional Injury Prevention, First Aid and SafetyCasNo ratings yet
- LP 21 Health Q3Document6 pagesLP 21 Health Q3Hazel Rubas SamsonNo ratings yet
- P.E 9 Week 6 Activity Sheets Q 3.final 2Document4 pagesP.E 9 Week 6 Activity Sheets Q 3.final 2NathanielNo ratings yet
- Module HEALTH-9 Q3Document4 pagesModule HEALTH-9 Q3Ola OrrabNo ratings yet
- Woc Acute Pancreatitis EngDocument10 pagesWoc Acute Pancreatitis EngMuhammad Alvin Fuzail IyazNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document3 pagesLesson 2soovkaiiiNo ratings yet
- Firstaid 190724134425Document93 pagesFirstaid 190724134425Nina BachoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Arrest Rescue BreathingDocument13 pagesRespiratory Arrest Rescue BreathingDJ Evan JulesNo ratings yet
- What Is First Aid?Document2 pagesWhat Is First Aid?Eleina Bea BernardoNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support Webinar NotesDocument5 pagesBasic Life Support Webinar NotesUreh RicardelNo ratings yet
- Roles and Responsibilities of The First AiderDocument8 pagesRoles and Responsibilities of The First AiderPascual Ronald PatrickNo ratings yet
- ALS FA Poster Aed CPR v3Document1 pageALS FA Poster Aed CPR v3seeNo ratings yet
- Unintentional Injury Prevention, Safety and First AidDocument27 pagesUnintentional Injury Prevention, Safety and First Aidbeni sumerNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument11 pagesFirst AidRhave MorenoNo ratings yet
- UNIT II in HEALTH9 - Injury Prevention Safety and First Aid Unintentional - STUDENTS LectureDocument7 pagesUNIT II in HEALTH9 - Injury Prevention Safety and First Aid Unintentional - STUDENTS Lectureitsmefuntassy100% (1)
- Bandaging: Saint Paul University ofDocument7 pagesBandaging: Saint Paul University ofjohannah reine buenaflorNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN On First Aid GNMDocument6 pagesLESSON PLAN On First Aid GNMSamiran Kumar Das100% (1)
- Overview:: Cast Care and Comfort - Overview of The SkillDocument8 pagesOverview:: Cast Care and Comfort - Overview of The SkillHannah Joy TabinNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument8 pagesMusculoskeletal DisordersMode Devi Publising IncorporatedNo ratings yet
- First Aid: NSTP 002Document5 pagesFirst Aid: NSTP 002Alvin VelasquezNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument5 pagesNSTPlainrossNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledPrancisco Yuan VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Workplace First AidDocument1 pageWorkplace First AidMOHAMAD SHAHRIZAD B SAIAAN KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- February 4Document6 pagesFebruary 4Ma. Ruffa GajoNo ratings yet
- ALS FA Poster Eye Injury v3Document1 pageALS FA Poster Eye Injury v3henrique magalhaesNo ratings yet
- ScoutingDocument1 pageScoutingPatrick RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Resource Unit. AdwcwdDocument6 pagesResource Unit. AdwcwdGreg Martin OrbegosoNo ratings yet
- 4832 Concept Map 1Document3 pages4832 Concept Map 1api-508452270No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcomes Intervention Evaluation Nursing Interventions Rationale Resources RequiredDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcomes Intervention Evaluation Nursing Interventions Rationale Resources RequiredSiena KaleiNo ratings yet
- Jonathan C. Lubag Unintentional Injuries Q3M1 W1-3Document26 pagesJonathan C. Lubag Unintentional Injuries Q3M1 W1-3Jonathan LubagNo ratings yet
- NSTP ReviewerDocument1 pageNSTP ReviewerAbegail SatoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Health Teaching TOPIC: Ilizarov External Fixator Specific Objectives Content Time Frame Methodolog y Resources Evaluation Human Materia LDocument4 pagesGroup 1 Health Teaching TOPIC: Ilizarov External Fixator Specific Objectives Content Time Frame Methodolog y Resources Evaluation Human Materia LSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- نسخة vaginal delieveryDocument4 pagesنسخة vaginal delieveryرهف الرفاعيNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Nursing CareDocument2 pagesPostoperative Nursing CareYeana AlonNo ratings yet
- Basic First AidDocument16 pagesBasic First AidJehanzaib EjazNo ratings yet
- Intraoperative NursingDocument41 pagesIntraoperative NursingBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (11)
- BLS - First Aid 2Document5 pagesBLS - First Aid 2jerry spiritNo ratings yet
- A Sample Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Educat Mam JDocument12 pagesA Sample Detailed Lesson Plan in Physical Educat Mam Jkathleenmaelahaman0No ratings yet
- Emergency First AidDocument12 pagesEmergency First AidObayomi KennyNo ratings yet
- First Aid Lesson HandoutsDocument3 pagesFirst Aid Lesson HandoutsGuia Camandang100% (1)
- Orthopedic NursingDocument2 pagesOrthopedic NursingMichelle TamorNo ratings yet
- Chinese General Hospital Colleges Nstp-Cwts 2 - Basic First AidDocument2 pagesChinese General Hospital Colleges Nstp-Cwts 2 - Basic First AidManelli Faten BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Quality Venipuncture: Special ConsiderationsDocument1 pageQuality Venipuncture: Special ConsiderationsAdicciòn entre LetrasNo ratings yet
- Unintentional Injury Prevention Safety First AidDocument25 pagesUnintentional Injury Prevention Safety First Aidcytho27 phNo ratings yet
- Hope Module 5-9Document6 pagesHope Module 5-9Gweneth Castisimo SubiaNo ratings yet
- First Aid & Emergency Companions: First Aid & Emergencies at SeaFrom EverandFirst Aid & Emergency Companions: First Aid & Emergencies at SeaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Health9Document2 pages3rd Quarter Health9Myra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Health9Document1 page1st Quarter Health9Myra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- Tableau RubricDocument1 pageTableau RubricMyra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- Longtest in Dance9 Q1 Sy 2023 2024Document2 pagesLongtest in Dance9 Q1 Sy 2023 2024Myra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- Baroque ArtDocument10 pagesBaroque ArtMyra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- Basketball Officiating Project ProposalDocument3 pagesBasketball Officiating Project ProposalMyra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- Music-Q1-Long TestDocument2 pagesMusic-Q1-Long TestMyra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- MUSIC 9-Q1-LectureDocument2 pagesMUSIC 9-Q1-LectureMyra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- 4 DLL Q3 MusicDocument2 pages4 DLL Q3 MusicMyra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- 5 DLL Q3 MusicDocument1 page5 DLL Q3 MusicMyra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- 1 DLL Q3 MusicDocument1 page1 DLL Q3 MusicMyra Ramirez JulianNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Neurologi Kelas 4BDocument1 pageTugas 1 Neurologi Kelas 4BWindhynrlNo ratings yet
- EAR First AidDocument4 pagesEAR First Aidr_lakshmi2722No ratings yet
- Damage Control Orthopaedics PDFDocument24 pagesDamage Control Orthopaedics PDFAnsar Trauma Doc100% (2)
- Assessment and Management of The Unconscious PatientDocument6 pagesAssessment and Management of The Unconscious PatientRed DevilNo ratings yet
- CPR and Firstaid PowerpointDocument21 pagesCPR and Firstaid PowerpointSizzy SkincareNo ratings yet
- Alphabet-Course-Breakdown-Nccp 1Document3 pagesAlphabet-Course-Breakdown-Nccp 1api-232950579No ratings yet
- ATLS Practice Test 1 With AnswersDocument11 pagesATLS Practice Test 1 With Answersemad mohamedNo ratings yet
- Abg PalicDocument82 pagesAbg PalicHarry James PotterNo ratings yet
- Abg CpuDocument49 pagesAbg Cpugwen pencerNo ratings yet
- Emergency Case Management - EDRM (HANS)Document3 pagesEmergency Case Management - EDRM (HANS)M. Azhari HakimNo ratings yet
- CH161 Lecture 9-10 - GIKIDocument42 pagesCH161 Lecture 9-10 - GIKIHabny ShaaNo ratings yet
- Trombektomi Mekanikal Pada Stroke Iskemik Dengan Awitan Kurang Dari 6 JamDocument12 pagesTrombektomi Mekanikal Pada Stroke Iskemik Dengan Awitan Kurang Dari 6 JamYulinda MoteNo ratings yet
- Advanced Life Support AssessmentDocument1 pageAdvanced Life Support AssessmentbbyesNo ratings yet
- Emergency Short Courses in SA - International Accredited 25-3-2021Document1 pageEmergency Short Courses in SA - International Accredited 25-3-2021JacquesNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmunary ResucitationDocument13 pagesCardiopulmunary ResucitationRussel OlivoNo ratings yet
- WZZ CAM Rev 23Document510 pagesWZZ CAM Rev 23Alex RoșuNo ratings yet
- JADWAL ATLS Semarang 10-12 Agustus 2018 (1654) Utk PesertaDocument5 pagesJADWAL ATLS Semarang 10-12 Agustus 2018 (1654) Utk PesertafebriNo ratings yet
- Uff TeccDocument19 pagesUff TeccEder OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Chest TraumaDocument39 pagesChest TraumaQuinnee VallejosNo ratings yet
- ATLS 10th Edition ChangesDocument71 pagesATLS 10th Edition Changessharvindan subramaniam67% (3)
- ACLS 2020 Update FOR CMEDocument51 pagesACLS 2020 Update FOR CMEyrx8k8j9qyNo ratings yet
- First Aid and Fire FightingDocument29 pagesFirst Aid and Fire FightingMaissam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Operative Maxillofacial Trauma Surgery Primary Repair of Facial Injuries (UnitedVRG)Document834 pagesAtlas of Operative Maxillofacial Trauma Surgery Primary Repair of Facial Injuries (UnitedVRG)Ahmad YNo ratings yet
- Deep Sulcus Sign - Print Friendly - STATdxDocument2 pagesDeep Sulcus Sign - Print Friendly - STATdxmihaelaNo ratings yet
- Seminar Head InjuriesDocument16 pagesSeminar Head InjuriesBONG AIKCHINGNo ratings yet
- Electrical InjuriesDocument1 pageElectrical InjuriesIkhwan SalamNo ratings yet
- Jessica Delcourt 102503542 WallDocument2 pagesJessica Delcourt 102503542 Wallapi-558053325No ratings yet
- NATO First Aid KitsDocument16 pagesNATO First Aid KitsxyzNo ratings yet