Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 - Ch. 5 - Note Packet Filled in
Uploaded by
idzienisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8 - Ch. 5 - Note Packet Filled in
Uploaded by
idzienisCopyright:
Available Formats
8 – Ch.
5 – Note packet Name _______________________________________
Hour _______
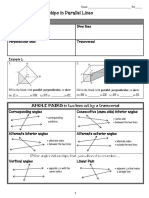
Lesson 5.1: Lines
Vocabulary
Term Definition Notation/Example
a line that intersects
two or more lines
Transversal
angles that lie inside
(3,24
Interior Angles lines
the
25,24
angles that lie outside , 22,
Exterior Angles
the lines 17.28
have the same N
Congruent
measure
that
are Interior
angles on
of the 24524
Alternate Angles opposite sides
Exterior
transversal
*
congruent -8522
angles that are in the
Corresponding
Angles
same position on the
<85 <4
*
congruent two lines
that the Interior
angles are on
250 < 4
Same Side Angles same side of the Exterior
transversal 27d22
opposite angles when
Vertical Angles
two lines intersect
-|a c3
*
congruent
Course 3 · Chapter 5 Triangles and The Pythagorean Theorem 1
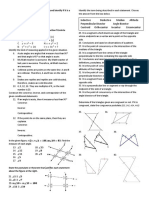
8 – Ch. 5 – Note packet
Classify each pair of angles as alternate interior,
alternate exterior, or corresponding.
a. ∠3 and ∠7 b. ∠2 and ∠8
corresponding alternate
interior
Mr. Adams installed the gate shown, 𝑐 ∥ 𝑑 and 𝑚∠4 =
40°.
a. Find 𝑚∠6. Justify your b. Find 𝑚∠7. Justify your
answer. answer.
mc x 400
=
mc 7 1480
=
because 4 and because 4 and
26 are alternate -3 equal 1800
and 3 and <7
interior
are corresponding
angles
Lesson 5.2: Geometric Proof
Vocabulary
Term Definition
a mathematical statement that is
Conjectures made using inductive and deductive
reasoning to be proven
Inductive Reasoning Deductive Reasoning
make a conjecture make conjecture
a
after observing based on facts, laws,
several examples definitions, or rules
Course 3 · Chapter 5 Triangles and The Pythagorean Theorem 2
8 – Ch. 5 – Note packet
a conjecture has
that been
Theorem
proven
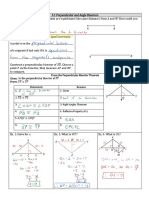
Refer to the figure. Complete the two-column proof to show that if 𝑬𝑮 =
𝟑𝒙 − 𝟏, 𝑬𝑫 = 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟒, and 𝑬𝑮 = 𝑬𝑫, then 𝒙 = 𝟓
Statement Reason
a) EG 3x
=
Given
-
EG ED =
ED 2x 4= +
b)
3x -
1 2x 4 = +
substitution
c) subtraction property
1 4
=
x
-
equality
of
d) addition property of
X 5
=
equality
If ∠1 and ∠2 are supplementary and 𝒎∠𝟏 = 𝐦∠𝟐, then ∠1 and ∠2 are right
angles.
Statement Reason
a) <1 and <2 are supplementary
mc1 m
=
> 2 Given
b) definition of supplementary
mc1 + mc 2 180°
=
angles
c)
mc1 +
mc 1 1800
=
substitution
d)
2(m(1) =
1800 Addition
e) Division Property of
mc1 900 =
Equality
f)
mc2 900 mc1 m < 2 (given)
=
Course 3 · Chapter 5 Triangles and The Pythagorean Theorem 3
8 – Ch. 5 – Note packet
Lesson 5.3: Angles of Triangles
Vocabulary
Term Definition
The sum of the interior angles
Triangle Angle
Sum of a triangle equals 180:
the angles formed
inside the sides
Interior Angle
x c1 180
triangle
+
=
of the
-A B C 180
+ =
+
cA xB cC
+
2 x)
+
+
=
Exterior Angles <I Remote Interior Angles - C
- C
21 cA xB
angles formed by the two angles
+
=
that do NOT
extending one
touch the exterior
side of the
triangle angle
The city park is in the Find the value of 𝑥 in the
shape of a triangle. Find triangle.
the value of 𝑥. -C + 112 180 =
-
112-112
180 C 48
44 20 x
=
+
+ =
08 32 x 180
x 180
+
04
+
=
=
+
-04 100 x 180
04
+
=
-
-
100 100-
x 1160
x 80a
=
Course 3 · Chapter 5 Triangles and The Pythagorean Theorem 4
8 – Ch. 5 – Note packet
Lesson 5.4: Polygons and Angles
Vocabulary
Term Definition
a simple closed figure of three or
Polygon more sides that only connect at
the end points
polygons that all the angles and
have the
Regular Polygon side lengths same
measure
·
The sum of the interior Formula
angles is two less
Interior Angle Sum
triangles than number
S (n 2) 180
= -
sides times 180
of
·
find the sum of the Formula
and (n-2) 180
Interior Angle interior angles A =
Measure M
divide by the number
ofsides
Icosadigon (22-sided)
Find the sum of the interior angles. Find the measure of one interior angle.
(n -2) 180
S (n 2) 188 A -
= - =
2) 188 (22-2) 180
=143.44°
=(22 -
--
22
3,400
o
=
the sum of the
is 360
Exterior Angle exterior angles E =
Measures ALWAYS n
3400
Find the measure of an exterior angle of a regular icosadigon (22-sided).
360
E=
T
~10.34
-
Course 3 · Chapter 5 Triangles and The Pythagorean Theorem 5
8 – Ch. 5 – Note packet
Lesson 5.5: The Pythagorean Theorem
Vocabulary
Term Definition
a form the right angle
Leg
b. they are the shorter
sides
·
side opposite the right
Hypotenuse angle
C
·
the longest side
Term Definition
If a triangle is a
righttriangle,
Pythagorean
Theorem then a+ b c2
=
Hypotenuse is missing: 92 b2 02+
=
A
02 22 +
02
=
34 4
+ 02
=
40o
. 32cm 4.324... C
=
Leg “a” is missing:
92 b2 c2
+ =
92 42 +
52
=
a 3m
=
D
a
a9 =
Course 3 · Chapter 5 Triangles and The Pythagorean Theorem 6
8 – Ch. 5 – Note packet
Leg “b” is missing
a
+ b2 C2 =
32 b2 112
+ =
9
C
9 b2 121
+
=
a -
9
b= 10.50cm 522
b 10.583...
=
flip the parts of the
Converse
theorem
If a
c
+b* c2, then= the
Converse of the
Pythagorean Theorem triangle is a right triangle
Determine whether each triangle is a right triangle. Justify your answer.
44 cm, 70 cm, 55 cm 24 m, 143 m, 145 m
A C D A D C
a2 b2 c c2
=
+b
a
=
+ =
442 592 02 1452
242 1432
=
+
+ =
1934 3025 02 +20449:21025
+ =
574
-
941 = 21025:21025
145 145 =
70.43 C
Right
Not a Right Triangle
Triangle
Course 3 · Chapter 5 Triangles and The Pythagorean Theorem 7
8 – Ch. 5 – Note packet
Lesson 5.7: Distance on the Coordinate Plane
Vocabulary
Term Definition
Distance Formula
/()
(y, 42)2 + -
Graph the ordered pairs (𝟎, −𝟔) and (𝟓, −𝟏). Then find the distance between the
points. Round to the nearest tenth.
Method 1: Pythagorean Theorem
92 b2 c2 + =
52 g2 02 +
=
25 25 + 22
= S
So d
⑳.
7.87C
Method 2: The Distance Formula (0,
-
b) (5,
-
1)
x2 2
+
x, 41
/(0-5)
2
(
+
-
x -
( -
1)
* 7.87
Course 3 · Chapter 5 Triangles and The Pythagorean Theorem 8
You might also like
- 12 Math Pre Board 1 Sahodaya Jan 2018 Set I PDFDocument5 pages12 Math Pre Board 1 Sahodaya Jan 2018 Set I PDFshruthi sNo ratings yet
- Geometry 03 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesDocument42 pagesGeometry 03 Parallel and Perpendicular LinescarlajanebaribaraleriaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Mathematics Q3-LAS Week 3Document9 pagesEnhanced Mathematics Q3-LAS Week 3mia laordenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics8 Quarter4 Week4 Module4Document6 pagesMathematics8 Quarter4 Week4 Module4nathan lucasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 22Document10 pagesLesson 22Jeany Pearl EltagondeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 Vertical and Adjacent AnglesDocument6 pagesLesson Plan 3 Vertical and Adjacent Anglesapi-457217519100% (1)
- Unit 2 Notes - Essentials of Geometry - 2017Document18 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Essentials of Geometry - 2017Solo YehNo ratings yet
- Interactive Se c02Document72 pagesInteractive Se c02coochiesalt4No ratings yet
- Math 7 Quarter 3 Week 3Document7 pagesMath 7 Quarter 3 Week 3Rovic John TicmanNo ratings yet
- 2.5 ChuchunessDocument19 pages2.5 ChuchunessChristian ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Inductive Deductive Median Altitude Perpendicular Bisector Angle Bisector Centroid Orthocenter Incenter CircumcenterDocument2 pagesInductive Deductive Median Altitude Perpendicular Bisector Angle Bisector Centroid Orthocenter Incenter CircumcenterAngelu Marienne SamsonNo ratings yet
- Pearson Geometry CH 2Document58 pagesPearson Geometry CH 2sharmaegayangosNo ratings yet
- Directions: Consider The Table Below. Given Each Figure, Recall The Definition of Each Quadrilateral and Write It On The Space ProvidedDocument19 pagesDirections: Consider The Table Below. Given Each Figure, Recall The Definition of Each Quadrilateral and Write It On The Space ProvidedJaninne Villa Del ReyNo ratings yet
- Angle Theorems and PostulatesDocument84 pagesAngle Theorems and Postulatesalyssa joy bagsicNo ratings yet
- Maths Year 10 EOS1 LO BookletDocument46 pagesMaths Year 10 EOS1 LO Booklet29x4rk8pgfNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Program Summary - Prelim Extension 1 Course: - . - . - . Parabola (Parametrics)Document1 pageMathematics Program Summary - Prelim Extension 1 Course: - . - . - . Parabola (Parametrics)DepurpleeNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work: Hrs Units Notes Examples ReferencesDocument17 pagesScheme of Work: Hrs Units Notes Examples ReferencesOluseye AkinNo ratings yet
- Proving Angles Congruent Using Vertical, Supplementary AnglesDocument5 pagesProving Angles Congruent Using Vertical, Supplementary AnglesKristell AlipioNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Year 9Document12 pagesAdd Maths Year 9Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- S1ExamSupplement KeyDocument4 pagesS1ExamSupplement KeyDwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- GeoGuidedNotes5 1KEYDocument2 pagesGeoGuidedNotes5 1KEY2020 MistakesNo ratings yet
- Parallel Lines - CWDocument16 pagesParallel Lines - CWHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Parallel Lines and Transversals LessonDocument9 pages3.2 Parallel Lines and Transversals LessonXxShadowGamingNo ratings yet
- MATH-8_Q4_M3Document4 pagesMATH-8_Q4_M3reynaldoanub9No ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 8 FourthDocument4 pagesMathematics Grade 8 FourthLorenzo CohenNo ratings yet
- Practice B: Pairs of AnglesDocument2 pagesPractice B: Pairs of AnglesAnoop SreedharNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Wise Plan of "Multivariable Caculus": Contact: 03002999903Document6 pagesLecture-Wise Plan of "Multivariable Caculus": Contact: 03002999903faiqa yousafNo ratings yet
- Topic Checklist Year 12 Core From SK18MathsDocument4 pagesTopic Checklist Year 12 Core From SK18MathsmosulNo ratings yet
- Parallel Lines Proofs and Mixed Practice 2022-2023Document6 pagesParallel Lines Proofs and Mixed Practice 2022-2023Devon DavisNo ratings yet
- Proving Properties of Parallel Lines week 4Document21 pagesProving Properties of Parallel Lines week 4Jumedeluna05yahoo.com Jumelynjumelyn199411No ratings yet
- Lines Angles and Polygons PracticeDocument7 pagesLines Angles and Polygons PracticeSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- EASE Module 3 Geometric RelationsDocument18 pagesEASE Module 3 Geometric RelationsYeye Lo CordovaNo ratings yet
- 9 5 Lines PlanesDocument13 pages9 5 Lines PlanesVenu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Week 5: NAME: - YR & SEC: - CompetencyDocument11 pagesQuarter 4 Week 5: NAME: - YR & SEC: - CompetencykattNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 8 Fourth Week 4Document5 pagesMathematics Grade 8 Fourth Week 4Lorenzo CohenNo ratings yet
- Congruent Triangles Packet 2013 With Correct Answers1Document87 pagesCongruent Triangles Packet 2013 With Correct Answers1光No ratings yet
- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Geometry Chapter 3 Key ConceptsDocument48 pagesParallel and Perpendicular Lines Geometry Chapter 3 Key ConceptsSharmaineNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Q3 Week-2 Las-3Document2 pagesMath 7 Q3 Week-2 Las-3Glydel Mae Villamora - Saragena100% (1)
- Year 8 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan MathsDocument4 pagesYear 8 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan MathsMahamed AbusnenaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3, Week 2: Mathematics 7 Activity SheetDocument4 pagesQuarter 3, Week 2: Mathematics 7 Activity SheetMariel Pastolero100% (1)
- Conditional StatementDocument5 pagesConditional StatementDon CelladorNo ratings yet
- Parallel LinesaDocument6 pagesParallel LinesaForam JivrajaniNo ratings yet
- Vector and Tensor Lecture NotesDocument96 pagesVector and Tensor Lecture NotesJhonnes ToledoNo ratings yet
- dlp-7_math8q4Document3 pagesdlp-7_math8q4Frejoles, Melva MaeNo ratings yet
- 2019 After Exam ChecklistDocument3 pages2019 After Exam Checklistkuanyo yoNo ratings yet
- Lessons 3-13-2 Parallel Lines and TransversalsDocument13 pagesLessons 3-13-2 Parallel Lines and Transversalsjeehan dolorosaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 2Document3 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 2Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Linear Algebra Notes PDFDocument82 pagesCambridge Linear Algebra Notes PDFRushil GholkarNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - Week 1Document5 pagesQuarter 3 - Week 1Valein PrincenaNo ratings yet
- Textbook 2 6Document10 pagesTextbook 2 6api-293865618No ratings yet
- Math g7 m6 Topic A Lesson 4 TeacherDocument11 pagesMath g7 m6 Topic A Lesson 4 TeacherENo ratings yet
- Introduction To Geometry ProofsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Geometry ProofsNaufalzzNo ratings yet
- FINAL ELECTIVE MATHEMATICS 8 Module 2 4th QuarterDocument14 pagesFINAL ELECTIVE MATHEMATICS 8 Module 2 4th QuarterCharles Darryl ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Geometry m2 Topic C Lesson 18 TeacherDocument12 pagesGeometry m2 Topic C Lesson 18 TeacherNestor Bong Bordaje NemeñoNo ratings yet
- Steps To Solving Equation Transformable To Quadratic EquationsDocument2 pagesSteps To Solving Equation Transformable To Quadratic EquationsShane MuctarNo ratings yet
- FV As m10q2w5Document9 pagesFV As m10q2w5Angel Anne PinedaNo ratings yet
- The Method of Summary Representation for Numerical Solution of Problems of Mathematical PhysicsFrom EverandThe Method of Summary Representation for Numerical Solution of Problems of Mathematical PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Discrete Orthogonal Polynomials. (AM-164): Asymptotics and Applications (AM-164)From EverandDiscrete Orthogonal Polynomials. (AM-164): Asymptotics and Applications (AM-164)No ratings yet
- 8 - Ch. 7 - Note Packet Filled inDocument5 pages8 - Ch. 7 - Note Packet Filled inidzienisNo ratings yet
- Who Was Thomas Alva EdisonDocument2 pagesWho Was Thomas Alva EdisonidzienisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document38 pagesChapter 02F190917 Zainab IjazNo ratings yet
- Reading Chemical Symbols ChemistryDocument3 pagesReading Chemical Symbols ChemistryidzienisNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Braking Resistor CalculationDocument10 pagesDynamic Braking Resistor CalculationMuugii AmgaaNo ratings yet
- SepaDocument4 pagesSepaRobert DelfinNo ratings yet
- M.Tech 1st Sem Machine Degine SyllabusDocument12 pagesM.Tech 1st Sem Machine Degine SyllabusHOD Department of Mechanical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Welding Fundamentals GuideDocument163 pagesWelding Fundamentals Guideharoub_nas100% (2)
- 56 - Isijint 2015 231 PDFDocument13 pages56 - Isijint 2015 231 PDFRaphael Mariano de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Application of Fault Current Limitation PDFDocument6 pagesApplication of Fault Current Limitation PDFudayakumartNo ratings yet
- RS 04Document5 pagesRS 04Essenam GOLINo ratings yet
- Hyo Sung EbaraDocument33 pagesHyo Sung Ebaraduongbk24 luu quang duongNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis and ApplicationsDocument86 pagesStress Analysis and ApplicationsJAMES TRIXIAN PARAJASNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Long Quiz q3Document3 pagesScience 7 Long Quiz q3JNA Moments and IdeasNo ratings yet
- 3va9988-0ba22-SHUNT TRIPDocument4 pages3va9988-0ba22-SHUNT TRIPLeonardo CAMARGO CAMARGONo ratings yet
- Egg DropDocument2 pagesEgg DropLeah ClovisNo ratings yet
- Ligand: HistoryDocument1 pageLigand: HistorySyimah UmarNo ratings yet
- Chimney SizingDocument7 pagesChimney SizingAli MustafaNo ratings yet
- ADEC™ - Error List - 2006 - MTU® PDFDocument33 pagesADEC™ - Error List - 2006 - MTU® PDFpevare100% (4)
- Light Reflection and Refraction WorksheetDocument2 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Worksheetdayanandan171% (7)
- PDT101 Datasheet B211082EN E PDFDocument2 pagesPDT101 Datasheet B211082EN E PDFAndrey ValeroNo ratings yet
- 01 - ED Technical Training Part 1Document76 pages01 - ED Technical Training Part 1Калин АнгеловNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Radiation Heat TransferDocument22 pagesChapter 4 Radiation Heat TransferFarooq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Fluid3a Trawneh PDFDocument39 pagesFluid3a Trawneh PDFWesam abo HalimehNo ratings yet
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Document11 pagesInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768wawan100% (1)
- Class 2 Lever Effort Force CalculationDocument10 pagesClass 2 Lever Effort Force CalculationvenkateswaranNo ratings yet
- Multiple choice questions in science for class VII as per NCERT Text BookDocument33 pagesMultiple choice questions in science for class VII as per NCERT Text BookIqra HanifNo ratings yet
- 2N2369A Silicon NPN Transistor DescriptionDocument4 pages2N2369A Silicon NPN Transistor DescriptionReymondJosuéArgüelloRojasNo ratings yet
- OPTI 370 Syllabus S22 (Updated)Document7 pagesOPTI 370 Syllabus S22 (Updated)AhmedphmaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science 9 - Module 1Document23 pagesQ4 Science 9 - Module 1Danilo Saliog67% (6)
- Energy Reports: Mostefa GhassoulDocument8 pagesEnergy Reports: Mostefa GhassoulEduardo DíazNo ratings yet
- Cu ElectrofacetingDocument12 pagesCu ElectrofacetingClark ChenNo ratings yet
- Making The Invisible VisibleDocument19 pagesMaking The Invisible VisibleGianna Barcelli FantappieNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Doppler Shift: Prior Knowledge Questions (Do These BEFORE Using The GizmoDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Doppler Shift: Prior Knowledge Questions (Do These BEFORE Using The GizmoCynta’jah AllisonNo ratings yet