Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parallel Lines - CW
Uploaded by
Himanshu JethwaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parallel Lines - CW
Uploaded by
Himanshu JethwaniCopyright:
Available Formats
INTEGRATED I PARALLEL LINES
SUCCESS CRITERIA:
1) Determine if lines are intersecting, parallel, or skew.
2) Use two-column proofs to justify statements regarding parallel lines.
3) Determine the value of angles formed by a transversal and parallel lines
INSTRUCTOR: Craig Sherman
Hidden Lake High School
Westminster Public Schools
PMI-NJ Center for Teaching & Learning ~1~ NJCTL.org
EMPOWER Recorded TARGET SCALE THEME
MA.09.G.01.04 Using Coordinates to find Distance Formula
PROFICIENCY SCALE:
SCORE REQUIREMENTS
4.0 In addition to exhibiting Score 3.0 performance, in-depth inferences and applications that go
BEYOND what was taught in class.
Score 4.0 does not equate to more work but rather a higher level of performance.
3.5 In addition to Score 3.0 performance, in-depth inferences and applications with partial success.
o Determine the appropriate solution in a Real World example.
3.0 The learner exhibits no major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and
processes (simple or complex) that were explicitly taught.
o Determine if lines are intersecting, parallel, or skew, AND
o Use two-column proofs to justify statements regarding parallel lines AND
o Determine the value of angles formed by a transversal and parallel lines
.
2.0 Can do one or more of the following skills / concepts:
There are no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes as the
learner…
o Identify if lines are intersecting, parallel, or skew, OR
o Identify the pairs of angle formed by parallel lines cut by a transversal, OR
o Determine the value of a linear pair of angles, OR
o Determine the value of a linear pair of angles, OR
o Determine the value of alternate interior angle, OR
o Determine the value of alternate exterior angles, OR
o Determine the value of vertical angles, OR
o Determine the value of corresponding angles, OR
o Prove statements about parallel lines using two-column proofs
1.0 Know and use the vocabulary
Identify the Basic Elements
With help, a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and process
PMI-NJ Center for Teaching & Learning ~2~ NJCTL.org
LINES: Intersecting, Parallel & Skew
WORD or CONCEPT DEFINITION or NOTES EXAMPLE or GRAPHIC REPRESENTATION
intersecting
parallel
skew
coplanar
INSTRUCTION 1: KHAN ACADEMY INSTRUCTION 2: SOPHIA
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~3~ NJCTL.org
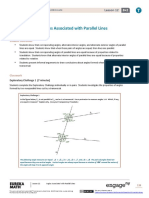
Class Work – Use image 1
1. Name all segments parallel toGH :
2. Name all segments skew to GH :
3. Name all segments intersecting with GH :
4. Are segmentsGH and BA coplanar? Explain your answer.
5. Are segments GH and BF coplanar? Explain your answer.
Is each statement true always, sometimes, or never?
6. Two intersecting lines are skew.
7. Two parallel lines are coplanar.
8. Two lines in the same plane are parallel.
9. Two lines that do not intersect are parallel.
10. Two skew lines are coplanar
Image 1
Homework - Use Image 1
11. Name all segments parallel to FE :
12. Name all segments skew to FE :
13. Name all segments intersecting with FE :
14. Are segments FE and CD coplanar? Explain your answer.
15. Are segments FE and HD coplanar? Explain your answer.
State whether the following statements are always, sometimes, or never true:
16. Two coplanar lines are skew.
17. Two intersecting lines are in the same plane.
18. Two lines in the same plane are parallel.
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~4~ NJCTL.org
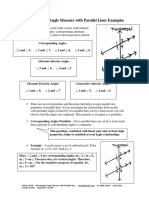
Lines & Transversals
WORD or CONCEPT DEFINITION or NOTES EXAMPLE or GRAPHIC REPRESENTATION
parallel lines
transversal
same side interior
angles
same side exterior
angles
corresponding angles
alternate interior
angles
alternate exterior
angles
INSTRUCTION 1: KHAN ACADEMY INSTRUCTION 2: SOPHIA
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~5~ NJCTL.org
Class Work
Classify each pair of angles as alternate interior, alternate exterior, same-side interior, same-side exterior,
corresponding angles, or none of these.
19. ∠11 and ∠16 are
20. ∠12 and ∠2 are
21. ∠14 and ∠8 are
22. ∠6 and ∠16 are
23. ∠7 and ∠14 are
24. ∠3 and ∠16 are
Homework
Classify each pair of angles as alternate interior, alternate exterior, same-side interior, same-side exterior,
corresponding angles, or none of these.
25. ∠7 and ∠12
26. ∠3 and ∠6
27. ∠6 and ∠11
28. ∠7 and ∠11
29. ∠4 and ∠10
30. ∠14 and ∠16
31. ∠2 and ∠3
32. ∠2 and ∠10
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~6~ NJCTL.org
Parallel Lines & Proofs
WORD or CONCEPT DEFINITION or NOTES EXAMPLE or GRAPHIC REPRESENTATION
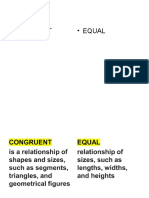
proof
statement
reason
substitution
transitive property
reflexive property
symmetric property
INSTRUCTION 1: KHAN ACADEMY INSTRUCTION 2: SOPHIA
Classwork
Match each expression/equation with the property used to make the conclusion.
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~7~ NJCTL.org
33. AB = AB
34. If m∠A = m∠B and m∠B = m∠C, then m∠A = m∠C.
35. If x + y = 9 and y = 5, then x + 5 = 9.
36. If DE = FG, then FG = DE.
a) Substitution Property of Equality
b) Transitive Property of Equality
c) Reflexive Property of Equality
d) Symmetric Property of Equality
PARCC type question:
37. Alternate Exterior Angles Proof: Complete the proof by filling in the missing reasons
with the “reasons bank” below.
Given: line m || line k
Prove: ∠2 ≅ ∠8
Statements Reasons
1. line m || line k 1.
2. ∠2 ≅ ∠6 2.
3. ∠6 ≅ ∠8 3.
4. ∠2 ≅ ∠8 4.
Reasons Bank
a) Transitive Property of Congruence
b) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a
transversal, then the corresponding
angles are congruent.
c) Vertical Angles are congruent.
d) Given
Homework
For #39-42 match the description on the left to the name of the property on the right.
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~8~ NJCTL.org
38. ∠A ≅ ∠B and ∠B ≅ ∠C, then ∠A ≅ ∠C. a) Substitution Property of Equality
39. If bc = 77 and b = 11, then 11c = 77. b) Transitive Property of Congruence
40. If ∠P ≅ ∠M, then ∠M ≅ ∠P. c) Reflexive Property of Equality
41. QR = QR d) Symmetric Property of Congruence
PARCC type question:
42. Alternate Interior Angles Proof: Complete the proof by filling in the missing reasons
with the “reasons bank” below.
Given: line m || line k
Prove: ∠3 ≅ ∠5
Statements Reasons
1. line m || line k 1.
2. ∠3 ≅ ∠7 2.
3. ∠7 ≅ ∠5 3.
4. ∠3 ≅ ∠5 4.
Reasons Bank
a) Vertical Angles are congruent.
b) Given
c) Transitive Property of Congruence
d) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal,
then the corresponding angles are
congruent.
Properties of Parallel Lines
Classwork
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~9~ NJCTL.org
Use the given diagram to answer problems #33-41.
If m∠9 = 54°, then find the measure the following angles:
43. m∠1=
44. m∠2=
45. m∠4=
46. m∠5=
47. m∠15=
If m∠2 = (12x-54)° and m∠10 = (7x+26)°, then find the measure the following angles:
50.m∠6= 52. m∠9=
51. m∠11= 53. m∠16=
Find the values of the unknown variables in each figure.
54. 56.
State which segments (if any) are parallel.
56. 57.
Solve for the unknowns
58.
Homework
If m ∠9 = 62°, then find the measure the following angles:
59. m∠1=
60.m∠2=
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~10~ NJCTL.org
61.m∠4=
62.m∠5=
63m∠15=
If m ∠2 = (14x-24)° and m ∠10 = (6x+72)°, then find the measure the following angles:
64.m∠6= 66m∠9=
65m∠11= 67.m∠16=
Find the values of the unknown variables in each figure. (#78-82)
68. 69.
State which segments (if any) are parallel.
70 71. .
72.
PARALLEL LINE SUMMARY
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~11~ NJCTL.org
ANGLES
ADJACENT SAME SIDE ALTERNATE VERTICAL
LINEAR
PAIR
CORRESPONDIN
INTERIOR EXTERIOR
G
1-int 1-ext
INTERIOR EXTERIOR
CONGRUENT ( ≅
Supplementary )
Def of suppl Def of ≅
+ = 180 =
Parallel Lines UNIT Review
Multiple Choice
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~12~ NJCTL.org
1. Name the segment parallel to GH and skew to EA .
a. FB
b. DA
c. JI
d. HD
2. Name the segment parallel to BC and skew to EI .
a. FB
b. DA
c. JI
d. HD
3. Determine if the statement is always, sometimes, or never true:
Two skew lines are coplanar.
a. Always
b. Sometimes
c. Never
4. Determine if the statement is always, sometimes, or never true:
Two intersecting lines are coplanar
a. Always
b. Sometimes
c. Never
5. Determine if the statement is always, sometimes, or never true:
Two lines that do not intersect are skew.
a. Always
b. Sometimes
c. Never
6. Determine the relationship between ∠1 & ∠10.
a. Alternate Interior
b. Same-side Interior
c. Corresponding Angles
d. None of these
7. Determine the relationship between ∠5 & ∠15.
a. Alternate Exterior
b. Alternate Interior
c. Same-side Interior
d. None of these
8. Given in the diagram to the right, m∠2=3x-10 and m∠15=2x+30 , what
is m∠12?
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~13~ NJCTL.org
a. 32o
b. 40o
c. 86o
d. 110o
9. Given in the diagram to the right, m∠5= (7x+2)°and
m∠11=(5x+14)°, what is m∠14?
a. 6°
b. 44°
c. 46°
d. 136°
In 10-11, use the diagram at the right.
10. Given ∠2 ≅ ∠6, what justifies k || m.
a. Converse Alternate Interior Angles Theorem
b. Converse Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
c. Converse Corresponding Angles Theorem
d. there is not enough info to state parallel
11. Given n || p , what justifies ∠1 ≅ ∠12
a. Alternate Interior Angles Theorem
b. Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
c. Corresponding Angles Theorem
d. there is not enough info to make this statement
Extended Constructed Response
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~14~ NJCTL.org
1. Complete the proof by filling in the missing reasons with the
“reasons bank” to the right. Some reasons may be used more
that once.
Given: ∠1 ≅ ∠3; MN || PQ
Prove: ∠2≅∠3
Statements Reasons
1. ∠1 ≅ ∠3 1. Reasons Bank
2. MN || PQ 2. a) Transitive Property of Congruence
3. ∠1 ≅ ∠2 3. b) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a
4. ∠2≅∠3 4. transversal, then the alternate interior angles
are congruent.
c) Given
2. Complete the proof by filling in the missing reasons with the “reasons bank” to the right. Some reasons
may be used more that once.
Given: n || p, k || m
Prove: ∠2 & ∠13 are
supplementary
Statements Reasons
1. n || p, k || m 1.
2. ∠2 ≅ ∠12 2.
3. ∠12 ≅ ∠14 3.
4. ∠2 ≅ ∠14 4.
5. m∠2 = m∠14 5.
6. m∠13 & m∠14 are 6.
supplementary
7. m∠13 + m∠14 = 180° 7.
8. m∠13 + m∠2 = 180° 8.
9. ∠2 &∠13 are supplementary 9.
Reasons Bank
a) Transitive Property of Congruence
b) Definition of supplementary angles
c) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the alternate interior
angles are congruent.
d) Definition of Congruent Angles
e) Given
f) If 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the alternate exterior
angles are congruent.
g) Angles that form a linear pair are supplementary
h) Substitution Property of Equality
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~15~ NJCTL.org
Geometry: Parallel Lines ~16~ NJCTL.org
You might also like
- SLM - Math - 8 Q4 WK 3 Module - 3 SCDocument15 pagesSLM - Math - 8 Q4 WK 3 Module - 3 SCAngelle Espiritu Jaramilla100% (2)
- Math 7 Quarter 3 Week 3Document7 pagesMath 7 Quarter 3 Week 3Rovic John TicmanNo ratings yet
- Parallelism and Perpendicularity: I. Introduction and Focus QuestionsDocument40 pagesParallelism and Perpendicularity: I. Introduction and Focus QuestionsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- Directions: Consider The Table Below. Given Each Figure, Recall The Definition of Each Quadrilateral and Write It On The Space ProvidedDocument19 pagesDirections: Consider The Table Below. Given Each Figure, Recall The Definition of Each Quadrilateral and Write It On The Space ProvidedJaninne Villa Del ReyNo ratings yet
- LM Geometry8 Q3 W1Document10 pagesLM Geometry8 Q3 W1Shaira Nicole ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Workshop 1: I. Quadrilaterals Ii. OverviewDocument10 pagesWorkshop 1: I. Quadrilaterals Ii. OverviewRonieta VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Determining Angles with Parallel Lines ExamplesDocument13 pagesDetermining Angles with Parallel Lines ExamplesVijetha ShenoyNo ratings yet
- FINAL ELECTIVE MATHEMATICS 8 Module 2 4th QuarterDocument14 pagesFINAL ELECTIVE MATHEMATICS 8 Module 2 4th QuarterCharles Darryl ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q4 SLM WK4Document11 pagesMath8 Q4 SLM WK4Juvelyn Teves MunalemNo ratings yet
- Geometry End Of The Year Final Exam ReviewDocument48 pagesGeometry End Of The Year Final Exam ReviewAngelo BoujaoudeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics8 Quarter4 Week4 Module4Document6 pagesMathematics8 Quarter4 Week4 Module4nathan lucasNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 8 Fourth Week 4Document5 pagesMathematics Grade 8 Fourth Week 4Lorenzo CohenNo ratings yet
- Module 9 TGDocument54 pagesModule 9 TGJoan Olante100% (4)
- Conditional StatementDocument5 pagesConditional StatementDon CelladorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument16 pagesChapter 6 Notestae hyungNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q3 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver1.0Document41 pagesMath9 Q3 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver1.0Ann HurbodaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Week 5: NAME: - YR & SEC: - CompetencyDocument11 pagesQuarter 4 Week 5: NAME: - YR & SEC: - CompetencykattNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bhopal Pre-Board Examination Class XII Set B MathsDocument6 pagesDelhi Public School Bhopal Pre-Board Examination Class XII Set B MathsYashg79No ratings yet
- 9Document14 pages9api-332361871No ratings yet
- Opt Math Class X (MP 1)Document95 pagesOpt Math Class X (MP 1)Himrashmi HschoolNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Math LAA 3rd QuarterDocument74 pagesGrade 9 Math LAA 3rd QuarterSJ HarNo ratings yet
- 1 MATH 9 - M1 - Lesson 1A Final Qa DIGITAL 1Document10 pages1 MATH 9 - M1 - Lesson 1A Final Qa DIGITAL 1Timothy ArtusNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review 2014 CPDocument13 pagesMidterm Review 2014 CPapi-169207896No ratings yet
- Opt Math Book PG 1-14 MPDocument14 pagesOpt Math Book PG 1-14 MPHimrashmi HschoolNo ratings yet
- Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Geometry Chapter 3 Key ConceptsDocument48 pagesParallel and Perpendicular Lines Geometry Chapter 3 Key ConceptsSharmaineNo ratings yet
- Discussion Properties of CongruenceDocument107 pagesDiscussion Properties of CongruenceDanica QuizonNo ratings yet
- Angle Theorems and PostulatesDocument84 pagesAngle Theorems and Postulatesalyssa joy bagsicNo ratings yet
- Joy Activity 10Document7 pagesJoy Activity 10api-279213523No ratings yet
- 3 Proving 3rd 4th 5th Property of ParallelogramDocument31 pages3 Proving 3rd 4th 5th Property of Parallelogramtcshs.antoque.sheinnadayneNo ratings yet
- Test 4Document6 pagesTest 4sheanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Full Student PacketDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Full Student PacketJillian MarceloNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument28 pagesMathsSjNo ratings yet
- G8 Math Q3 Module-2Document18 pagesG8 Math Q3 Module-2Elijah Shamir A. RefugioNo ratings yet
- Geometry Final Review f20Document6 pagesGeometry Final Review f20clara.hyun.baeNo ratings yet
- Special Angles Ws 2Document8 pagesSpecial Angles Ws 2api-445198464No ratings yet
- 12 Math Pre Board 1 Sahodaya Jan 2018 Set I PDFDocument5 pages12 Math Pre Board 1 Sahodaya Jan 2018 Set I PDFshruthi sNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 3rd Quarter Module 1Document37 pagesMathematics 9 3rd Quarter Module 1OneDuhhNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency of Ungrouped DataDocument6 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency of Ungrouped DataKhenchy FalogmeNo ratings yet
- Calculus IDocument197 pagesCalculus IVickyNo ratings yet
- Math - Lesson1 - Parallelogram and Its PropertiesDocument9 pagesMath - Lesson1 - Parallelogram and Its PropertiesFree TemplatesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 22Document10 pagesLesson 22Jeany Pearl EltagondeNo ratings yet
- Dll-Properties of ParallelogramDocument9 pagesDll-Properties of ParallelogramPatrick GuerraNo ratings yet
- Geometry Section 3 3Document10 pagesGeometry Section 3 3api-262621710No ratings yet
- Math 7 USLeM Wk2 RTPDocument10 pagesMath 7 USLeM Wk2 RTPken dahunanNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Triangle CongruenceDocument80 pagesModule 7 Triangle CongruenceMarlon Hernandez Jr100% (2)
- RENDAL, JOSE MARIE M. - Geometry Module 3 Sy 2022-2023Document52 pagesRENDAL, JOSE MARIE M. - Geometry Module 3 Sy 2022-2023RENDAL, JOSE MARIE M.No ratings yet
- Grade 9-Demonstration (Theorems On Rectangle and Rhombus) : University of San Jose-RecoletosDocument7 pagesGrade 9-Demonstration (Theorems On Rectangle and Rhombus) : University of San Jose-RecoletosChristine Mae FrioloNo ratings yet
- Math g8 m2 Topic C Lesson 12 Teacher PDFDocument9 pagesMath g8 m2 Topic C Lesson 12 Teacher PDFIsmail AbariNo ratings yet
- Math9 KS3 G9 ADM Q3 Module 1-9 (Printing) (1) - 1Document40 pagesMath9 KS3 G9 ADM Q3 Module 1-9 (Printing) (1) - 1Clarisse Abegail AhatNo ratings yet
- Directions: Answer The Following Question(s) .: A. B. C. D. E. FDocument6 pagesDirections: Answer The Following Question(s) .: A. B. C. D. E. FdiamondtressNo ratings yet
- 2014 Division Mid-Year Inset On Content and Pedagogy For Secondary Mathematics EducationDocument28 pages2014 Division Mid-Year Inset On Content and Pedagogy For Secondary Mathematics EducationAlfie BurbosNo ratings yet
- Q4 Similarity of FiguresDocument24 pagesQ4 Similarity of FiguresSamantha Reese BaliliNo ratings yet
- Math Subject For High School Probability and StatisticsDocument86 pagesMath Subject For High School Probability and StatisticsMaricelNo ratings yet
- NPS INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL HOLIDAY HOMEWORKDocument10 pagesNPS INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL HOLIDAY HOMEWORKChaandneeka ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- DLP Transversal Third Quarter ObservationDocument7 pagesDLP Transversal Third Quarter Observationnhslrc2022No ratings yet
- Exam 2 Review SheetDocument3 pagesExam 2 Review SheetmsleonchuNo ratings yet
- Identify properties of parallel lines cut by a transversalDocument1 pageIdentify properties of parallel lines cut by a transversalWalter ManliguezNo ratings yet
- A Collection of Problems in Analytical Geometry: Three-Dimensional Analytical GeometryFrom EverandA Collection of Problems in Analytical Geometry: Three-Dimensional Analytical GeometryNo ratings yet
- Ncert ExercisesDocument17 pagesNcert ExercisesHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- Worksheet CirclesDocument1 pageWorksheet CirclesHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- CVTECH4Document2 pagesCVTECH4Himanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 Back To Workplace TrainingDocument31 pagesCOVID 19 Back To Workplace TrainingHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- NcertDocument8 pagesNcertHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument5 pagesNotesHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions Algebraic ExpressionsDocument9 pagesAlgebraic Expressions Algebraic ExpressionsHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionsDocument20 pagesAlgebraic Expressionsrohaba100% (8)
- CBSE Class 9 CirclesDocument11 pagesCBSE Class 9 CirclesHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 9 ScienceDocument220 pagesNCERT Class 9 Sciencesailabk67% (3)
- Class 7 Chapter 7 - Algebraic ExpressionsDocument26 pagesClass 7 Chapter 7 - Algebraic ExpressionsHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Chapter 12 NcertDocument41 pagesClass 7 Chapter 12 NcertHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing 2nd Mid SemDocument1 pageDigital Image Processing 2nd Mid SemHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- CVTECH4Document2 pagesCVTECH4Himanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- CSPCDocument1 pageCSPCHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- Ainew 3Document2 pagesAinew 3Himanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions Part 2Document35 pagesReasoning Questions Part 2Himanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- Modern theory of international trade and the factor-proportions analysis of OhlinDocument3 pagesModern theory of international trade and the factor-proportions analysis of OhlinHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- C Programming Lab ManualDocument16 pagesC Programming Lab ManualHimanshu JethwaniNo ratings yet
- MSc, BSc, MCA, MBA books for Chemistry, Mathematics, PhysicsDocument13 pagesMSc, BSc, MCA, MBA books for Chemistry, Mathematics, PhysicsAMMUAMAN0% (1)
- Dif TD1 (19 20)Document6 pagesDif TD1 (19 20)Leng Buntith100% (1)
- Application of Derivatives in One Shot PDFDocument85 pagesApplication of Derivatives in One Shot PDFvimalNo ratings yet
- Robust Repair of Polygonal Models with Octree Grid and ContouringDocument8 pagesRobust Repair of Polygonal Models with Octree Grid and Contouringwacdev DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Math 432 HW 1.4 Solutions: Dy DXDocument7 pagesMath 432 HW 1.4 Solutions: Dy DXsamiNo ratings yet
- PKT Myp 3 Sa4Document3 pagesPKT Myp 3 Sa4uchiharanveer0987No ratings yet
- Cone Step MappingDocument14 pagesCone Step MappingLubosz_Sarneck_1758No ratings yet
- Pythagorean TheoremDocument27 pagesPythagorean Theoremapi-241390860No ratings yet
- Crystallography Symmetry GuideDocument68 pagesCrystallography Symmetry GuideMajid AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Solutions 1Document10 pagesAssignment 1 Solutions 1boyarskyNo ratings yet
- Two-dimensional steady conductionDocument81 pagesTwo-dimensional steady conductionYash MoreyNo ratings yet
- User's Manual: Wound Composite Modeler For AbaqusDocument45 pagesUser's Manual: Wound Composite Modeler For AbaqusMaikson TonattoNo ratings yet
- March Formative Assessment MYP-III RetakeDocument3 pagesMarch Formative Assessment MYP-III RetakeArslan Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Steady State Bifurcation TheoryDocument19 pagesSteady State Bifurcation TheoryJohn StarrettNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument22 pagesGeometrycharles gueta100% (1)
- Precalculus Essentials 5Th Edition Blitzer Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesPrecalculus Essentials 5Th Edition Blitzer Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkevahanhksf88% (8)
- 11th Class Physics :kinematics in One Dimension + Calculus at VireshDocument2 pages11th Class Physics :kinematics in One Dimension + Calculus at VireshViresh SinghNo ratings yet
- 3D Grid GenerationDocument5 pages3D Grid Generationsiva_ksrNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Teaching MathematicsDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On Teaching Mathematicsafmzuiqllaaabj100% (1)
- Mathematics Compulsory Part: Paper 2Document16 pagesMathematics Compulsory Part: Paper 220/21-5B-(05) HoMeiYi/何美誼No ratings yet
- Forces in Space) PDFDocument64 pagesForces in Space) PDFJagdish Dhanuskar100% (1)
- Solving Trig EquationsDocument12 pagesSolving Trig Equationsapi-285179261No ratings yet
- A Guide To Quantum Field TheoryDocument112 pagesA Guide To Quantum Field Theorymshafee57100% (3)
- JAMB Mathematics Sample Questions and Answers To CBT ExamsDocument12 pagesJAMB Mathematics Sample Questions and Answers To CBT ExamsÃdë Kùñ LëNo ratings yet
- 6.2 AAS Triangle Congruence: Exploring Angle-Angle-Side CongruenceDocument12 pages6.2 AAS Triangle Congruence: Exploring Angle-Angle-Side CongruenceOpticoNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering MCQ'S: Ans. (D)Document2 pagesCivil Engineering MCQ'S: Ans. (D)Nishikanta Mondal100% (1)
- Mathematics For TeachersDocument869 pagesMathematics For TeachersRamón Marcelo Bustos MéndezNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Math 134: Elizabeth Denne 18th December 2006Document4 pagesFinal Exam Math 134: Elizabeth Denne 18th December 2006Otavio Marçal Leandro GomideNo ratings yet
- Differential and Integral Calculus: Name: Section: Assignment No. 3Document2 pagesDifferential and Integral Calculus: Name: Section: Assignment No. 3Matt Julius CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 8th EditionDocument61 pagesTrigonometry 8th Editionbernice.hickman158100% (38)