Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PSTM221
Uploaded by
Joyce Anne Cruz0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
17 views10 pageslecture notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentlecture notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
17 views10 pagesPSTM221
Uploaded by
Joyce Anne Cruzlecture notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
(PRINCIPLES and STRATEGIES of ● a persisting change in human
TEACHING MEDICAL LABORATORY performance or performance
SCIENCE) potential . . . (brought) about as a
result of the learner’s interaction
*INTRODUCTION TO TEACHING* with the environment” (Driscoll,
TEACHING & LEARNING PROCESS 1994)
Teaching defined… ● “the relatively permanent change in a
● Refers to the process of imparting person’s knowledge or behavior due
knowledge and skills from a teacher to experience” (Mayer, 1982)
to a learner. It encompasses the
activities of educating or instructing. ● an enduring change in behavior, or in
It is an act or experience that has a the capacity to behave in a given
formative effect on the mind, fashion, which results from practice
character or physical ability of an or other forms of experience”
individual. (Shuell, 1986)
● A working definition of teaching is
undertaking certain ethical tasks or *LEARNING THEORIES*
activities the intention of which is to
induce learning. ● SOCIAL CONDITIONING
- A type of learner that occurs when a
● It is deliberate intervention that behavior is observed and
involves planning and subsequently mimicked.
implementation of instructional
activities and experiences to meet - “ It takes a village to raise a child”
learner outcomes according to a
teaching plan ● CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
Some thoughts on teaching and learning… (Pavlovian conditioning or
respondent conditioning)
● Clearly, not all learning is
dependent on teaching… However, - Is a reflexive or automatic type of
all teaching regardless of quality is learning in which a stimulus acquires
predicted on learning.. - Brown, the capacity to evoke a response that
1993 was originally evoked by another
stimulus.
● Process of gaining knowledge or
skill by studying, practicing, being
taught, or experiencing something.
● OPERANT CONDITIONING Why was Pavlov’s hair so soft?
(Instrumental conditioning)
I was in psychology class yesterday…
- Described as a process that attempts And we couldn’t stop laughing about how
to modify behavior through the use stupid Pavlov’s dogs were. Then the bell
of positive and negative rang and we all had lunch.
reinforcement. Through operant
conditioning, an individual makes an
association between a particular THE “HOWs” OF TEACHING
behavior and a consequence.
A. STRATEGIES
- Is the art and science of directing
and controlling the movements and
activities of the army. If strategy is
good, we can get victory over our
enemies. In teaching this term is
meant those procedures by which
objectives of teaching are realized in
the class.
- Teaching strategy is a generalized
plan for a lesson which includes
● SOCIAL CONDITIONING structure, instructional objectives and
(Observational conditioning) an outline of planned tactics,
necessary to implement the strategies
- In this theory, people can learn new
information and behaviors by Strategy can be summarized as
watching other people. - Teaching is the generalized plan of
the whole lesson plan.
- In strategy of teaching, realization
of the objectives is given more
importance than presentation off
lesson.
- A strategy does not follow a single
track all the time, but it changes
according to the demands of the
situations such as age, level, needs,
interests and abilities of the students.
Thus strategy is more comprehensive ● GROUP WORK - s a method of
than method. instruction that gets students to work
together in groups.
- It is directional in nature. It refers to
goal directed activities of the ● QUESTIONING - The art of asking
teachers. Thus, it is more close to questions is at the heart of effective
science than arts. communication and information
exchange, which underpins good
TEACHING STRATEGIES teaching. If you use questioning
well, you can improve the student
● BRAINSTORMING - is a large or learning experience in a whole range
small group activity that encourages of Teaching Settings.
students to focus on a topic and
contribute to the free flow of ideas. ● SIMULATIONS- are instructional
scenarios where the learner is placed
● CASE STUDIES - are effective in a "world" defined by the teacher.
ways to get students to practically They represent a reality within which
apply their skills, and their students interact. The teacher
understanding of learned facts, to a controls the parameters of this
real-world situation. They are "world" and uses it to achieve the
particularly useful where situations desired instructional results. Students
are complex and solutions are experience the reality of the scenario
uncertain. and gather meaning from it.
● DEBATES - structured way of
exploring the range of views on an
issue. It consists of a structured
contest of argumentation, in which
two opposing individuals or teams
defend and attack a given
proposition.
● DISCUSSION - Discussion lets
class members work actively with
the ideas and the concepts being
pursued, and discussion sessions can
be an extremely effective in
changing behaviour or attitudes.
Consequently, teachers use them
frequently in instructional situations.
using the best skills and techniques
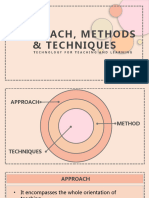
B. APPROACH available.
- Ways in which you try to engage - The facilitator approach- it places
students with the subject matter a high value on what students bring
(provide students with basic facts, to the classroom setting, it places
relate new knowledge to what considerable emphasis on making
students already know, build in use of students’ prior experience.
interaction, be passionate, be
enthusiastic) - The liberationist approach- is
rooted in notions of liberal
- The ways in which you support your education, wherein the goal is to
students (encourage questions, set liberate the mind to wonder, to know
formative assessments, provide and understand, to imagine and
constructive feedback). create, using the full intellectual
inheritance of ACCDRD TO THE
A description of your approach to ROLE OF TEACHER
teaching includes:
- The mode or manner of teaching Approach Accdr to nature of learning
(lecture, tutorial, bedside teaching, Discovery Learning
laboratory work); - takes place in problem solving
situations where the learner draws on
- Some understanding of how people his own experience and prior
learn (learning theory); knowledge and is a method of
instruction through which students
- Some understanding of how to interact with their environment by
facilitate learning (qualities of the exploring and manipulating objects,
teacher such as passion, principles wrestling with questions and
for good teaching practice such as controversies, or performing
providing timely and constructive experiments.
feedback, putting educational theory
into practice). a. DISCOVERY - refers to various
instructional design models that
TYPES OF TEACHING APPROACH: engages the students in learning
According to the role of the teacher through discovery.
- The executive approach - views the
teacher as manager of complex - An approach, which capitalizes on
classroom processes, a person the child’s natural curiosity and urge
charged with bringing about certain to explore the environment.
outcomes with students through - The child learns by personal
experience and experiment and this
is thought to make memory more - treats all writing as a creative act
vivid and help in the transfer of which requires time and positive
knowledge to new situations. feedback to be done well. In process
writing, the teacher moves away
Usually the pedagogical aims are threefold: from being someone who sets
(1) Promote “deep” learning students a writing topic and receives
(2) Promote meta-cognitive skills the finished product for correction
(develop problem-solving skills, without any intervention in the
creativity, etc.), writing process itself.
(3) Promote student engagement.
c. PROCESS
Conceptual teaching - An approach which provides
- Involves the learning of specific students with an abundance of
concepts, the nature of concepts, and projects, activities, and instructional
the development of logical reasoning designs that allow them to make
& critical thinking. decisions and solve problems.
b. CONCEPTUAL - Through this approach students get a
- Choosing and defining the content of sense that learning is much more
a certain discipline to be taught than the commission of facts to
through the use of or pervasive ideas memory. Rather, it is what children
as against the traditional practice of do with that knowledge that
determining content by isolated determines its impact on their
topics. attitudes and aptitudes.
- not a particular teaching method with
specific steps follow; it is more of a Unified Teaching
viewpoint of how facts and topics - This approach lends itself smoothly
under a discipline should be dealt to a unified teaching-learning
with. concept of education. The
- information handler, being a teacher,
- involves more data collection usually a student, or another educational
through research while the discovery environment, is at the center of this
approach actively involves students educational model. The main
to undertake experimental and inherent characteristics of this model
investigative work. are extreme flexibility, integration,
ease of interaction, and being
evolutional.
Process writing
d. UNIFIED - t is based on a breakdown of 1. Direct Instruction - relies on
knowledge to integrated modules of explicit teaching through lectures
information. The basic level of breakdown is and teacher-led demonstrations.
to be used in education to buildup concepts, Formal Authority - teachers are in a
while the higher ones are to be used to position of power and authority because of
buildup complex concepts of knowledge, their exemplary knowledge and status over
including those of experts. Key to the their students. Classroom management
success of this breakdown is the relational styles are traditional and focus on rules and
integration of the information leading to the expectations.
concept under consideration.
Expert - teachers are in possession of all
- This approach lends itself smoothly knowledge and expertise within the
to a unified teaching-learning classroom. Their primary role is to guide
concept of education. The and direct learners through the learning
information handler, being a teacher, process. Student are viewed solely as the
a student, or another educational receptors of knowledge and information
environment, is at the center of this (“empty vessels”)
educational model.
Personal Model - teachers who operate
- The main inherent characteristics of under the “Personal Model” style are those
this model are extreme flexibility, who lead by example, demonstrating to
integration, ease of interaction, and students how to access and comprehend
being evolutional. information. In this teaching model, students
learn through observing and copying the
teacher’s process.
STUDENT-CENTERED APPROACH -
student learning is continuously measured
during teacher instruction.
1. Inquiry Based Learning - focuses
on student investigation and
hands-on learning.
TEACHER-CENTERED APPROACH - - Teacher’s primary role is that of a
it is the primary role of teachers to pass facilitator, providing guidance and
knowledge and information onto their support for students through the
students. learning process.
Facilitator - place a strong emphasis on the
teacher-student relationship. Operating FOUR METHODS OF PRESENTING
under an open classroom model, there is a THE SUBJECT MATTER
de-emphasis on teacher instruction, and both 1. TELLING METHOD: Lecture
student and educator undergo the learning method, Discussion method, Story
process together. Student learning loosely telling method and so on.
guide by the teacher, and is focused on
fostering independence, hands-on learning 2. DOING METHOD: Project
and exploration method, Problem solving method,
Textbook method and so on.
Personal Model - teachers who operate
under the “Personal Model” style are those 3. VISUAL METHOD:
who lead by example, demonstrating to Demonstration method, Supervised
students how to access and comprehend study method and so on.
information. In this teaching model, students
learn through observing and copying the 4. MENTAL METHOD: Inductive,
teacher’s process. Deductive, Analysis, Synthesis
method etc.
Delegator - teachers act as a “resource”to
students, answering questions and reviewing
their progress as needed. Teachers play a D. TECHNIQUES
passive role in student’s learning; students - It is a procedure by which new
are active an engaged participants in their knowledge fixed in the minds of
learning. The main goal of a delegator is to students permanently. For this
foster a sense of autonomy in the learning purpose, a teacher does extra
process. activities in the class.
2. Cooperative Learning - These activities help the teacher to
- Emphasizes group work and take shift from one strategy to
a strong sense of community. another. Thus, teaching tactics are
- “Think-Pair-Share” that behavior of the teacher which he
manifests in the class i.e., the
developments of the teaching
strategies , giving proper stimulus for
C. METHOD timely responses, drilling the learn
- Method of teaching is directly responses , increasing the responses
related to the presentation of the by extra activities and so on.
lesson. Which a teacher should use,
depends on the nature of the subject,
and the tact of the teacher.
INSTRUCTIONAL MEDIA learning or increase understanding of
- Instructional media encompasses all your material.
the materials and physical means an
instructor might use to implement Of course, communicating to
instruction and facilitate students' facilitate learning can be a
achievement of instructional challenging process, often requiring
objectives creative efforts to achieve a variety
of implicit instructional goals
- may include traditional materials (University of Saskatchewan, n.d.).
such as chalkboards, handouts,
charts, slides, overheads, real
objects, and videotape or film, as Among the implicit goals that media can
well newer materials and methods help achieve are the following:
such as computers, DVDs, 1. Attracting attention
CD-ROMs, the Internet, and 2. Developing interest
interactive video conferencing. 3. Adjusting the learning
4. Promoting acceptance of the idea
WHAT IS INSTRUCTIONAL MEDIA?
- Instructional media encompasses all
the materials and physical means an INSTRUCTIONAL MEDIA
instructor might use to implement - Instructional media helps students
instruction and facilitate students' visualize a lesson and transform
achievement of instructional abstract concepts into concrete,
objectives. This may include easier to remember concepts.
traditional materials such as
chalkboards, handouts, charts, slides, - Media is an excellent way to pose
overheads, real objects, and assessment questions for the class to
videotape or film, as well newer V answer or give students task to
materials and methods such as complete.
computers, DVDs, CD-ROMs, the
internet and interactive video TYPES OF INSTRUCTIONAL MEDIA
conferencing. ● PROJECTED MEDIA
- Instructional materials that require
WHY USE INSTRUCTIONAL MEDIA? projection and electricity in their
- A good aid is like a window, it using process. Slides, filmstrips, and
should not call attention to itself, it overheads.
should just let in the light. In general, - Use to: Allow all students to view
you should use media whenever, in the same material at the same time.
your best judgment, it can facilitate Offer the students other perspectives
on the material.
● NON-PROJECTED MEDIA - Use to: Provide a playful
- Instructional materials that do not environment for learning, Structure
require the process of projection learning through rules, Motivating
before its operation can take place. for tedious or repetitive content,
Photographs, diagrams, and displays Uses problem solving skills.
- Use to: Illustrate concepts ,Enhance ● HEALTH EDUCATION
direct instruction ,Encourage - Health education is a social science
students to look at data in diverse that draws from the biological,
ways environmental, psychological,
physical and medical sciences to
● AUDIO MEDIA promote health and prevent disease,
- Cassettes and compact discs disability and premature death
through education-driven voluntary
- Use to: Allow students to hear other behavior change activities.
languages/dialects, Allow auditory
learners to review the lessons, - Health education is the development
Encourage creativity through music. of individual, group, institutional,
community and systemic strategies
● MOTION MEDIA to improve health knowledge,
- Videos, computer mediated attitudes, skills and behavior.
instruction, and television
- Simply, it is the profession of
- Use to: Offer supplemental educating people about health for
instruction, Experience concepts in a attainment of positive health.
manner that is not available in “real
life”.
CONCEPT OF HEALTH EDUCATION
● HYPER MEDIA Concept of Health:
- Computer networks, software, and - The word health is derived from Hal,
the Internet which mean “ hale ( strong, healthy),
sound ( body, family and
- Use to: Offer resources beyond the environment), whole.” Hahn and
library, Develop computer and word Payne describe health in terms of six
processing skills ,Offer interactive interacting and dynamic dimensions-
learning. physical, emotional, social,
intellectual, spiritual and occupation.
● GAMING MEDIA
- Computer games Definition of Health
- “Soundness of body or mind that 11. Feedback: should given to the
condition in which its are duly and community what change occur, how
efficiently discharged.” many people developed knowledge
and many others.
- WHO has given a comprehensive 12. Leaders
definition of health in its preamble to NEED AND IMPORTANCE OF
constitution in 1984. According to HEALTH EDUCATION
WHO, “Health is a state of complete ● Inform people about health, illness,
disability, and ways in which they
AIMS OF HEALTH EDUCATION can improve and protect their own
1. Health promotion and disease health, including more efficient use
prevention. of the delivery system;
2. Early diagnosis and management.
3. Utilization of available health ● Motivate people who want to change
services. to more healthy practices;
PRINCIPLES OF HEALTH ● Help them to learn the necessary
EDUCATION skills to adopt and maintain healthful
1. Credibility: message should be practices and lifestyles;
convey by the trusting people
2. Interest: firstly we should find the ● Foster teaching and communication
need of the community in-order to skills in all those engaged in
create interest educating consumers about health;
3. Participation: choice interest topic
4. Motivation: firstly convey the ● Advocate change in the environment
message in order to change the that facilitate healthful conditions
behavior and healthful behavior; and
5. Comprehension: firstly find the
capacity of the people which need ● Add to knowledge via research and
the baseline data evaluation concerning the most
6. Reinforcement: need repeat follow effective ways of achieving the
up above objectives.
7. Learning by doing
8. Known to unknown: starts what
knowledge they have up to the
knowledge they don't have
9. Setting an example
10. Good human relations: build
reporting to the communities people
You might also like
- Teaching Approaches, Methods, Techniques and Strategies ExplainedDocument72 pagesTeaching Approaches, Methods, Techniques and Strategies ExplainedDIOSA N.CAPISTRANONo ratings yet
- 5 Role of Pedagogy in Effective TeachingDocument5 pages5 Role of Pedagogy in Effective Teachingapi-378001294No ratings yet
- Module 3 - Teaching P.E & Health in Elementary GradesDocument4 pagesModule 3 - Teaching P.E & Health in Elementary GradesMichael MosendeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Lesson PlanningDocument4 pagesLecture Lesson PlanningAnne Bautista100% (1)
- Teaching Strategies and Approaches for Imparting KnowledgeDocument4 pagesTeaching Strategies and Approaches for Imparting KnowledgeEisha Louise Broqueza VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 PSTMDocument15 pagesLesson 1 PSTMNicole Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Principles & Strategies of Teaching in Medical Laboratory Science (PSTM221)Document16 pagesPrinciples & Strategies of Teaching in Medical Laboratory Science (PSTM221)29 REYES, BERNADETTE R.No ratings yet
- Psthe MidtermsDocument15 pagesPsthe MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- EDUC 90 Task 1Document6 pagesEDUC 90 Task 1Gliecy OletaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Teaching - pstm211Document58 pagesIntro To Teaching - pstm211Charlen Kylha GavinoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Intro To TeachingDocument6 pagesWeek 2 - Intro To TeachingKezia MadeloNo ratings yet
- Trends and Issues in Classroom ManagementDocument2 pagesTrends and Issues in Classroom ManagementMaria JocosaNo ratings yet
- PSTML 211 - PrelimsDocument22 pagesPSTML 211 - Prelimslily of the valleyNo ratings yet
- Approach, Methods & Techniques: Jon Vennie IbaleDocument22 pagesApproach, Methods & Techniques: Jon Vennie IbaleJON VENNIE IBALENo ratings yet
- Definitions of Basic TerminologyDocument12 pagesDefinitions of Basic TerminologySeham FouadNo ratings yet
- Interactive Teaching Strategies and Engaging ActivitiesDocument113 pagesInteractive Teaching Strategies and Engaging ActivitiesshellaNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Methods, Techniques StrategiesDocument21 pagesApproaches, Methods, Techniques Strategiessereen qasemNo ratings yet
- PSTM Week2Document59 pagesPSTM Week2Romeo DiestaNo ratings yet
- NE Unit II - Teaching LearningDocument72 pagesNE Unit II - Teaching LearningProf.R.Indhumathi ProfessorNo ratings yet
- The Teaching-Learning Process: Yenna Monica D. PDocument24 pagesThe Teaching-Learning Process: Yenna Monica D. Psanta lizardoNo ratings yet
- PSTMLS MidtermsDocument16 pagesPSTMLS MidtermsJohn Oliver AsiaNo ratings yet
- Educational vocabulary glossaryDocument1 pageEducational vocabulary glossaryCarlosValdesNo ratings yet
- Principles and Strategies of Effective TeachingDocument81 pagesPrinciples and Strategies of Effective TeachingMark Anthony B. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Managing Classroom Structure and Teaching StrategiesDocument3 pagesManaging Classroom Structure and Teaching StrategiesCarla LedinioNo ratings yet
- Types of Individualized InstructionDocument44 pagesTypes of Individualized InstructionanjmalicNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 FLCT. HANDOUTDocument32 pagesLesson 1 FLCT. HANDOUTKc BalderamaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Models: Definition, Elements, Merits & LimitationsDocument5 pagesTeaching Models: Definition, Elements, Merits & LimitationsRizza SandoyNo ratings yet
- Mardiatun Nisa 5C 2223141568 UTS ELSDocument12 pagesMardiatun Nisa 5C 2223141568 UTS ELSMardiatun NisaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 1 2 3 SocStEd 311Document41 pagesModule 2 Lesson 1 2 3 SocStEd 311Miguel Maribao Aquino Jr.No ratings yet
- MS SSC 102 - Act 3Document3 pagesMS SSC 102 - Act 3Jervyn GuiananNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document20 pagesUnit 3Cherrypink CahiligNo ratings yet
- PSTMLS 100 - Teaching and LearningDocument2 pagesPSTMLS 100 - Teaching and LearningMerjhana ArtizoNo ratings yet
- Effective Pedagogies in PersonDocument24 pagesEffective Pedagogies in PersonKiwinKoreaNo ratings yet
- 2010 Protheroe Metacognicion DisabilidadDocument5 pages2010 Protheroe Metacognicion DisabilidadpiedadcabreraNo ratings yet
- Strategies To Improve LearningDocument8 pagesStrategies To Improve Learninggeorgina_lingNo ratings yet
- Learning Strategies: Cognitive, Affective, Compensatory & SocioculturalDocument13 pagesLearning Strategies: Cognitive, Affective, Compensatory & SocioculturalLechir CabigasNo ratings yet
- Principles and Strategies of TeachingDocument4 pagesPrinciples and Strategies of TeachingsharlethNo ratings yet
- Effective Teaching StrategiesDocument6 pagesEffective Teaching StrategiesJohn Paul M. MoradoNo ratings yet
- S.G.R.D Institution of Nursing (Pandher) : Lesson PlanDocument22 pagesS.G.R.D Institution of Nursing (Pandher) : Lesson PlanCharanNo ratings yet
- Didactics Vs PefagogicDocument3 pagesDidactics Vs PefagogicVan Maie MarsNo ratings yet
- 2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoDocument4 pages2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoLovely PadernaNo ratings yet
- PED-323C-MIDTERM-Reviewer-Document4 pagesPED-323C-MIDTERM-Reviewer-Denver Ashley ManabatNo ratings yet
- Learning Habits: Sam Redding and Janet TwymanDocument13 pagesLearning Habits: Sam Redding and Janet TwymanfreyNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Education: Dr. M. Parimala Fathima DR - AR.SaravanakumarDocument9 pagesResearch Paper Education: Dr. M. Parimala Fathima DR - AR.SaravanakumarJoan JohnNo ratings yet
- 1 Differentiated Instruction - LectureDocument7 pages1 Differentiated Instruction - Lectureandrea dyanne AzoresNo ratings yet
- L & T-II UNIT I - DetailDocument30 pagesL & T-II UNIT I - DetailKitty BaluNo ratings yet
- Managing Learning EnvironmentsDocument2 pagesManaging Learning EnvironmentsDessiree CadizalNo ratings yet
- Abstraction-Lesson 1 FLTDocument29 pagesAbstraction-Lesson 1 FLTChristine Necole LeyteNo ratings yet
- Teaching Multi-Grade Classes: Topic 16. Direct and Indirect Strategy Direct InstructionDocument2 pagesTeaching Multi-Grade Classes: Topic 16. Direct and Indirect Strategy Direct InstructionMaricel ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document9 pagesLesson 4Mina M. SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Principles of TeachingDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Teachinghataki878No ratings yet
- Lecture On Principles of TeachingDocument9 pagesLecture On Principles of Teachingmaricel cuisonNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document13 pagesUnit 1Adriana Ysabelle Mercado ArimangNo ratings yet
- 9 Colegio Dela Purisima Concepcion: Name of Topics: The Teaching Profession: An OverviewDocument7 pages9 Colegio Dela Purisima Concepcion: Name of Topics: The Teaching Profession: An OverviewAlyza Mae D. DariaNo ratings yet
- Principles of LCT (SCT)Document4 pagesPrinciples of LCT (SCT)Chaé RiNo ratings yet
- Approach, Methods & StrategiesDocument29 pagesApproach, Methods & Strategieskalog vhoyzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Reflection: (Cambridge Learner Reflective Attribute)Document19 pagesChapter 3: Reflection: (Cambridge Learner Reflective Attribute)Isam MrahNo ratings yet
- FS1 WEEK 7 and 11Document12 pagesFS1 WEEK 7 and 11Edrian AngelesNo ratings yet
- Alexa Gandionco - Take-Away #5.0 Teaching Strategies in Elementary ScienceDocument2 pagesAlexa Gandionco - Take-Away #5.0 Teaching Strategies in Elementary ScienceAlexa GandioncoNo ratings yet