Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UNIT and Measurements
Uploaded by
gnanavishaljonnalagaddaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT and Measurements
Uploaded by
gnanavishaljonnalagaddaCopyright:
Available Formats
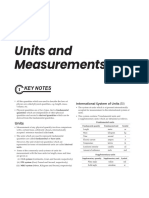
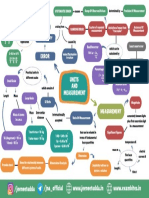
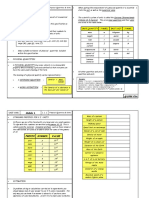
Physical Quantity
Units And Measurments
Numerical
Value
- Quantities which can be
measured by an Units ACCURACY PRECCISION
instrument and used to Accuracy is degree of
and
45 kg
describe Laws of physics closeness of measured
Precision is the range
are physical quantities value to the true value; of variation of true
- Physical quantity =
Dimensional Analysis Measurements - shows that how closely value during several
Numerical value (N) × Unit (U) the results with the observation
Unit
Dimension formula is the standard value.
expression for the unit of a
physical quantity in terms of PRINCIPLE OF HOMOGENITY
TYPES the fundamental quantities Principle of homogeneity VERNIER CALLIPERS
states that the ORDER OF MAGNITUDE ERRORS Pitch =
Fundamental quantities do Dimensional formula is dimension of each term
expressed in terms of on both sides of The uncertainty in Least Count (L.C) = displacement of screw
not depend upon other
power of M, L and T. dimensional equation It is defined as the power 1 MSD – 1 VSD; MSD = no. of rotations
quantities:
should be same. of 10 which is closest to measurement is called
(1) Length (2) Mass (3) Time errors main scale division; L.C. =
its magnitude
(4) Temperature VSD = Vernier
(5) Amount of Substance
Primary or fundamental Secondary or derived
N = n × 10x; x = order - Error = true value – scale division Pitch
Dimensional Formula dimensional Formula
(6) Electric current of magnitude. measured Value total no. of divisions
There are seven (i) Other than Fundame- coefficient exponent
(7) Luminous Intensity
fundamental ntal formula all other
dimensional formulas: are derived
- Derived quantities are (1) Mass = [M], (2) Length dimensional Formula TYPES OF ERROR Vernier scale
Main scale
= [L], (3) Time = [T], (ii) example: (1) [speed] = 6.022 x 1023
formed by combining more
than one fundamental (4) Temperature = [K] or [MoL1T-1], Absolute Error, =
[Q], (5) Electric Current
physical quantities = [I], (6) Luminous
(2) [Acceleration] true value –
- Area, Volume, velocity = [MoL1T2] base
intensity = [cd], measured value Total reading = Main
and acceleration are (7) amount of matter scale Reading Zero error = N × L.C
some Derived quantities = [mol] +(Vernier Coincidence
All non – zero
digits are × least Count) N = no. of circular
‘A’ is
significant
Mean absolute errors scale division that
Equivalent
Conversion of Units From RULE OF ROUNDING OFF
r
in area Area r2
4.125 - 4 sf; coincides with the
are system to another
r
r
1
a b
123 - 3 sf reference line
M L T ∆α1 + ∆α 2 + ............. + ∆αn
r
N2 = N1 1 1 1 - Rules of Rounding off the ∆αmean = Zero error = N × L.C;
Two supplementary S.I units are:- M2 L 2 T2 uncertain digits n N = no. of coinciding L.C = Least Count
Leading zeroes i.e
N1 = numerical part of (up to 3 Significant Figures) division;
(1) Radian(plane angle) , are never
, Q= , arc one system significant placed L.C = Least count of an
N2 = numerical part of Relative error instrunment.
radius to the left of the
(2) Steradian (solid angle),
Ω= arc
another system number
0.0403 - 3 sf; If digit > 5 ∆αmean
(radius)2
KNOW YOUR LCROS 0.04030 - 4 sf then, preceding digit +1
αmean Positive zero error Positive Zero Error
(SIGNIFICANT FIGURES)
0 1 Main Scale
UNITS 10.9 - 3 sf;
The number of digits in the 400.001 - 4 sf If digit <5 then, preceding Vernier scale 10
(1) Unit is defined as the measured values about the 0 5 10
All zero lie in digit remain same Percentage error, 0
reference standard used correctness are known as between the non 5
for measurements. significant figures. – zero digits are Negative zero error
(2) Measurements consists of significant If insignificant digit = 5; is difference the
a numerical value along with 0 1 Main Scale 0
Trailing zero digits (a) Preceding digit measured value and the
a relevant unit.
(3) Example: meter, newton, are significant only Order of magnitud remain same when true value as a 0 5 10
Vernier scale
Positive Zero Error
when they appear
joule, seconds etc. e is not considered
rounded off digit is even.; percentage of true value
after decimal 4.00 - 3 sf; 38.3 × 104 - 3 sf; Negaitive Zero Error
0.043010 - 5 sf 38.30 × 10-9 - 4 sf
(b) Preceding digit +1 when Percentage error
MKS CGS FPS (Ft, rounded off digit is odd ∆αmean
(m, kg, s) (m, gm, s) pound, s) SOME OTHER UNITS × 100 0
(1) mass:- 1 quintal = 100 kg, Constants and pure αmean 0
S.I Units 1 ton = 1000 kg numbers have infinite 95
- The system of units (2) length:- 1 light year = significant figures;
accepted internationally 9.46 × 1015 m
90
1 au = 1.496 × 1011 m
- S.I units of time is ‘sec’ (3) Temperature: Oo C =
is the example of S.I system 273 K 1o F = 255.928 K Negative Zero Error
You might also like
- Oro Youth CodeDocument16 pagesOro Youth CodeoroyouthcouncilNo ratings yet
- Bansal Units and MeasurementsDocument24 pagesBansal Units and MeasurementsAmbition Study Centre ButiboriNo ratings yet
- IWCF Principles & Procedures Test Paper (Answer)Document5 pagesIWCF Principles & Procedures Test Paper (Answer)andrzema100% (3)
- SYS600 - Connecting LONWORKS DevicesDocument120 pagesSYS600 - Connecting LONWORKS DevicesigorNo ratings yet
- Assignments DBMS 5-8Document27 pagesAssignments DBMS 5-8Anonymous pStrXsEQVb33% (9)
- SPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Document22 pagesSPM KSSM Physics Form 4 Chapter 1Sean71% (7)
- Instrument Technology: Measurement of Pressure, Level, Flow and TemperatureFrom EverandInstrument Technology: Measurement of Pressure, Level, Flow and TemperatureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Query PerformanceDocument6 pagesQuery PerformancemngtrajeshNo ratings yet
- (PDF) ASTM E2847.21990 - CompressDocument17 pages(PDF) ASTM E2847.21990 - Compressjulian moraNo ratings yet
- BT Business - Strategy and InnovationDocument25 pagesBT Business - Strategy and InnovationSanjay GhoshNo ratings yet
- VertiMillSim Reverse 1 .XLSMDocument51 pagesVertiMillSim Reverse 1 .XLSMW ZuoNo ratings yet
- MCQ MMC MU - Mechanical - Measurement - Control - CBCS PDFDocument3 pagesMCQ MMC MU - Mechanical - Measurement - Control - CBCS PDFNarayan ManeNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument8 pagesPhysics ReviewerSOLIS, John Ernest S.No ratings yet
- (L1) - (JLD 3.0) - Units & Dimensions - 8th April.Document16 pages(L1) - (JLD 3.0) - Units & Dimensions - 8th April.AnanayNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument47 pagesPhysicsdaniela.fresanNo ratings yet
- Units & Dimensions - Byju'sDocument24 pagesUnits & Dimensions - Byju'sGaurav BhandariNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Metrology NotesDocument18 pagesMeasurement and Metrology NotesAnything You Could ImagineNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementsDocument22 pagesUnits and MeasurementsManas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Volume and Density of Materials: Density Mass / Volume Density Mass / Volume Density Mass / VolumeDocument1 pageVolume and Density of Materials: Density Mass / Volume Density Mass / Volume Density Mass / VolumeAmit GauravNo ratings yet
- Engineering Measurements Lec NotesDocument22 pagesEngineering Measurements Lec NotesFady KamilNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Full NotesDocument33 pagesModule 4 Full NotesAskar BashaNo ratings yet
- 11 - General PhysicsDocument5 pages11 - General PhysicsMillare, PrincessNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument11 pagesPhysical Quantities and MeasurementSiti Rahma Fitri YaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1alyalaswad4445No ratings yet
- Chapter Two Static XtcsDocument26 pagesChapter Two Static XtcsAgirma girmaNo ratings yet
- O Physics 23 24Document16 pagesO Physics 23 24Natasha NaveedNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument20 pagesAnalytical ChemistryHersheen Magaddatu100% (1)
- Mebc Chapter 1Document17 pagesMebc Chapter 1Deep Khunt100% (1)
- Repeteability. Reproducibility. Stability.: MetrologyDocument2 pagesRepeteability. Reproducibility. Stability.: MetrologyRAFAEL ANDRES NOGUERA OCONNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 - Physical Quantities and Measurement - 24.6.2019Document17 pagesTOPIC 1 - Physical Quantities and Measurement - 24.6.2019che syakirNo ratings yet
- List StudiesDocument1 pageList Studieseugejem entertainmentNo ratings yet
- Senior High School - Year 1: Section 1 Introductory Physics and Properties of MatterDocument46 pagesSenior High School - Year 1: Section 1 Introductory Physics and Properties of MatterSharifNo ratings yet
- St. Mary's College of Catbalogan: Unit Learning Package S.Y. 2020 - 2021Document4 pagesSt. Mary's College of Catbalogan: Unit Learning Package S.Y. 2020 - 2021Jerom CanayongNo ratings yet
- 25 Apr 2022 PhysicsDocument55 pages25 Apr 2022 PhysicsA. SANDESHNo ratings yet
- UD Kinamatics NLMDocument45 pagesUD Kinamatics NLMSancia SamNo ratings yet
- Units and Measurement MCQDocument9 pagesUnits and Measurement MCQBhavya kanojia100% (1)
- UNIT I-Concept of Measurements 2 MarksDocument4 pagesUNIT I-Concept of Measurements 2 MarksS ABDUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Combine PDFDocument204 pagesCombine PDFsridevi73No ratings yet
- Physical World and Measurement: Day OneDocument9 pagesPhysical World and Measurement: Day OneKalyan RangavajjalaNo ratings yet
- Physics Dictionary KSSMDocument10 pagesPhysics Dictionary KSSMsueqingNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Errors Uncertainties and MeDocument7 pagesExperiment 1 Errors Uncertainties and MeFortunato GarciaNo ratings yet
- Measurement Chapter PDFDocument56 pagesMeasurement Chapter PDFNishu JainNo ratings yet
- Process Instrumentation Module 1Document44 pagesProcess Instrumentation Module 1ibuddhaNo ratings yet
- Neet Revision FullDocument130 pagesNeet Revision FullAYANTIK DAS STADNo ratings yet
- 2023 2024 Sanwa enDocument27 pages2023 2024 Sanwa enleo14pochNo ratings yet
- A Closer Look at Accuracy of Measuring and Test EquipmentDocument3 pagesA Closer Look at Accuracy of Measuring and Test EquipmentGonzalo VargasNo ratings yet
- Units and Measurement Colorful Mind MapDocument1 pageUnits and Measurement Colorful Mind MapKAMESH .GNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-ADocument1 pageChapter 1-AJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Sanwa 2021 2022 Sanwa en Japan OverseasDocument27 pagesSanwa 2021 2022 Sanwa en Japan Overseasbl2culo4No ratings yet
- Mechanical Measurement Unit-1 Two MarkDocument3 pagesMechanical Measurement Unit-1 Two MarkmanikandanNo ratings yet
- P6 ReviewerDocument4 pagesP6 ReviewerMisha ArquizaNo ratings yet
- Iare Ics PPT 0Document252 pagesIare Ics PPT 0mailasheeshNo ratings yet
- Common CompetencyDocument21 pagesCommon CompetencyRodel P. PilloNo ratings yet
- .Trashed 1702966746 1700363791524Document27 pages.Trashed 1702966746 1700363791524gno667533No ratings yet
- Dimensional AnalysisDocument3 pagesDimensional Analysisanandmay ramanNo ratings yet
- Measurements IntrodDocument30 pagesMeasurements IntrodHema BaskNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument33 pagesIntroVarshini PandianNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument38 pagesVectorsShailendra RajoraNo ratings yet
- For Multiplication Just Make Sure The Answer Has The Same Sig Figs As Your Least Precise Measurement. 60 X 5.0839 305.034 300.000 3.0 X 10Document4 pagesFor Multiplication Just Make Sure The Answer Has The Same Sig Figs As Your Least Precise Measurement. 60 X 5.0839 305.034 300.000 3.0 X 10Jade RepolloNo ratings yet
- Economics Term 2Document8 pagesEconomics Term 2Tanishka MehtaNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument11 pagesPhysics NotesAleah Angelarose BallesterosNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument2 pages1.1.1 Physical Quantities and UnitsNikitha SomaratneNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 Physical Quantities and Units PDFDocument2 pages1.1.1 Physical Quantities and Units PDFAmber100% (2)
- Genphys ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenphys Reviewerjustanony92No ratings yet
- Physics Lesson Plan FORM 4Document22 pagesPhysics Lesson Plan FORM 4Shahrul AnasNo ratings yet
- Goljan High Yield Flash CardsDocument2 pagesGoljan High Yield Flash Cardshabdulhye100% (1)
- Alif Sheikh I'D-18192107032 Assignment-1 TXE-206Document6 pagesAlif Sheikh I'D-18192107032 Assignment-1 TXE-206Alif SheikhNo ratings yet
- WhiteBook 2019 PDFDocument227 pagesWhiteBook 2019 PDFMinh TruongNo ratings yet
- Ankit Sharma: EducationDocument2 pagesAnkit Sharma: EducationAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- DPP-3 Geo Solution p65Document4 pagesDPP-3 Geo Solution p65Maddala NagendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Template Cover LetterDocument1 pageTemplate Cover LetterSadeepa Diluk JayatissaNo ratings yet
- 10th Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQDocument2 pages10th Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQBhalchandra MurariNo ratings yet
- Whats New Mastercam 2020Document82 pagesWhats New Mastercam 2020Eduardo Aleman ReynaNo ratings yet
- Scale of Universe - SH TemplateDocument2 pagesScale of Universe - SH TemplateLauren PicheNo ratings yet
- The Institute of Chartered Accountants of Sri Lanka: No. of Pages 06 No. of Questions 20Document13 pagesThe Institute of Chartered Accountants of Sri Lanka: No. of Pages 06 No. of Questions 20Amal VinothNo ratings yet
- App ElecDocument50 pagesApp Elecjayj_5No ratings yet
- Array ProgramsDocument2 pagesArray ProgramsVipinNo ratings yet
- Boolean AlgebraDocument5 pagesBoolean AlgebraSyste DesigNo ratings yet
- 9780521392938Document276 pages9780521392938SrramNo ratings yet
- Greedy Solution To The Fractional Knapsack ProbDocument3 pagesGreedy Solution To The Fractional Knapsack Probapi-3844034No ratings yet
- 4 Jan 2022 Practical Instruction 4 Preparation of Chemical RegisterDocument2 pages4 Jan 2022 Practical Instruction 4 Preparation of Chemical Registershafiqah wongNo ratings yet
- Digital Door Lock System MarketDocument11 pagesDigital Door Lock System MarketNamrataNo ratings yet
- Forces Motion Phet SimulationDocument4 pagesForces Motion Phet Simulationapi-542317996No ratings yet
- 1 Moon Project InstructionsDocument7 pages1 Moon Project InstructionsSan LiNo ratings yet
- M BisDevStudio enDocument24 pagesM BisDevStudio enSREEDHARNo ratings yet
- Bresle Salt Test GuidingDocument5 pagesBresle Salt Test GuidinglambtranNo ratings yet
- Correlation Coefficient Calculations For MIMO Antenna Systems: A Comparative StudyDocument14 pagesCorrelation Coefficient Calculations For MIMO Antenna Systems: A Comparative StudyUsman Qureshi100% (1)