Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carbon 10 III
Uploaded by
rincyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carbon 10 III
Uploaded by
rincyCopyright:
Available Formats
CARBON AND COMPOUNDS
The amount of carbon present in the earth’s crust and in the atmosphere is
quite meagre. The earth’s crust has only 0.02% carbon in the form of minerals
(like carbonates, hydrogencarbonates, coal and petroleum) and the atmosphere
has 0.03% of carbon dioxide.
What is a covalent bond?
A chemical bond formed between two atoms by sharing of electrons is called
covalent bond. The shared electrons belong to the valence shell of both the
atoms
Simplest covalent molecule is H2
1. If two atoms share one pair of electrons, it is called single covalent
bond.
Eg: H2 H : H H - H
2. If two atoms share two pairs of electrons, it is called double covalent bond.
.. ..
O2 : O :: O : O=O
3. If two atoms share three pairs of electrons, it is called a triple covalent bond
N2 : N : : N: N≡N
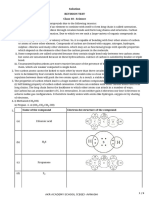
Q) Give Electron Dot structure of CH4, H2O, NH3, CO2, S8
a) H2O
H–O–H
..
H :O: H
¨
b) NH3
H H
I ..
H–N–H H : N : H
¨
c) CO2
.. ..
O=C=O :O::C::O:
d) S8
CHARACTERICTICS OF CARBON COMPOUNDS( COVALENT COMPOUND)
1. Carbon compounds are formed by sharing of electrons between atoms.
(covalent bond). So they do not form charged particles (ions). Hence, they
are poor conductors of electricity.
2. They generally have low melting point and boiling point because covalently
bonded molecules have strong bonds within the molecule but attraction
between molecules (intermolecular forces) is weak.
For e.g. Methane MP: 90 K B.P: 111 K
Ionic compounds
1. Have high melting and boiling points due to strong electrostatic force of
attraction between cations and anions.
2. They conduct electricity in solution or in the molten state due to
movement of ions to oppositely charged electrodes.
Why carbon forms large number of compounds? (Versatile nature of carbon)
Carbon forms about 3 million compounds.
This is due to the nature of the covalent bond formed by carbon which is due
to two factors.
1. Catenation: It is the unique property of carbon atoms to form long
chains, branched chains or rings through covalent bonding to its own
atoms giving rise to large molecules. The bonds may be single, double
or triple covalent bonds. I
- C – C – C – C – C –C –
The bond between carbon atoms and most other elements are very
strong due to the small size of carbon atom. This enables the carbon
nucleus to hold on to the shared pairs of electrons strongly and provide
stability to the compound.
No other element has this much tendency for catenation like carbon.
2. Tetra Covalency And Bonding In Carbon
Since carbon has a valency of four, it is capable of bonding with four
other carbon atoms or atoms of some other elements like oxygen,
hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine etc; giving rise to compounds
with specific properties.
Again the bonds that carbon forms with most other elements are very
strong making these compounds exceptionally stable.
One reason for the formation of strong bonds by carbon is its small
size. his enables the nucleus to hold on to the shared pairs of
electrons strongly.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Silicon has catenation tendency up to 7-8 atoms in its compounds with
hydrogen. But, the bonding between silicon atom is not very strong due to large
size of its atoms. Therefore these compounds are very reactive and unstable.
But C - C bond is very strong due to small size of carbon atoms. Hence, its
compounds are stable. Therefore carbon forms large number of compounds.
Why only carbon shows catenation?
The bond between carbon atoms are very strong due to the small size of
carbon atom. This enables the carbon nucleus to hold on to the shared
pairs of electrons strongly and provide stability to the compound.
The bonds formed by bigger elements like silicon are weaker due to their
larger atomic size.
Allotropes of carbon
Allotropes are different forms of an element occurring in nature.
They have similar chemical properties but different chemical properties.
Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon.
Difference in allotropes is due to difference in their structure.
In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms
forming a rigid three-dimensional structure. It is the hardest substance,
does not conduct electricity.
In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms in the
same plane giving a hexagonal layer structure. One of these bonds is a double-
bond.
Therefore, graphite is smooth and slippery. Also a very good conductor of
electricity
Diamonds can be synthesised by subjecting pure carbon to very high pressure
and temperature.
Fullerenes form another class of carbon allotropes. (purest form of carbon)
The first one to be identified was C-60 which has carbon atoms arranged in the
shape of a football.
You might also like
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument8 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- NOTES - Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument11 pagesNOTES - Carbon and Its CompoundsJanet GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Cl10 Chem Notes Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument18 pagesCl10 Chem Notes Carbon and Its CompoundsMaryamNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Class10Document10 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Class10panchalprince151No ratings yet
- L0 - Bonding NotesDocument23 pagesL0 - Bonding NotesRuha VNo ratings yet
- Te-Carbon and Its Compounds Final Revisor (20223-24)Document107 pagesTe-Carbon and Its Compounds Final Revisor (20223-24)Gautam SharrmaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Question BankDocument78 pagesCarbon Question Bankvvg .S0631No ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 Carbon and Its Compounds: Covalent BondsDocument9 pagesChapter - 4 Carbon and Its Compounds: Covalent BondsMaheshNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chemical BondingDocument14 pagesNotes - Chemical Bonding黄心盈No ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument21 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Carbon and Its CompoundsrajuramblrNo ratings yet
- Module - V.CH - 25 Carbon & Its CompoundDocument24 pagesModule - V.CH - 25 Carbon & Its CompoundHemant DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesChapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureYash PlayNo ratings yet
- Science Term 2 Class 10 EbookDocument137 pagesScience Term 2 Class 10 EbookHarshit Negi100% (1)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - .Document25 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - .h85195709No ratings yet
- Jesc104 PDFDocument21 pagesJesc104 PDFpraxis TDLNo ratings yet
- Why Should I Care About Carbon: Yes, 10 MillionDocument15 pagesWhy Should I Care About Carbon: Yes, 10 MillionYashNo ratings yet
- OrgChem NotesDocument33 pagesOrgChem NotesJoses CalindasNo ratings yet
- CH - 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument21 pagesCH - 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsClimaxNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding in ElementsDocument31 pagesCovalent Bonding in ElementsOsmany Madrigal100% (1)
- Carbon and Its Compounds Part 1Document9 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Part 1www.luciannarikaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds: Class NotesDocument22 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds: Class NotesMaria Joe.kNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Document62 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Sudhakar ChollangiNo ratings yet
- ch4 13Document26 pagesch4 13Jamunadevi RajkumarNo ratings yet
- (Q) YT - Carbon and Its CompoundDocument35 pages(Q) YT - Carbon and Its CompoundDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- All NCERT Books PDF From WWW - Ncert.online: Things Made Things Made Others of Metal of Glass/clayDocument21 pagesAll NCERT Books PDF From WWW - Ncert.online: Things Made Things Made Others of Metal of Glass/claySudhir Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument53 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsSaadxOPNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument15 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsGargi SapteNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Notes Part 1Document3 pagesCh4 Notes Part 1prabhat7969tiagoNo ratings yet
- CH - 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument21 pagesCH - 4 Carbon and Its CompoundsVensNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Note 1Document7 pagesChemistry Note 1Pakhi GoelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical Bonding and StructureDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Chemical Bonding and StructureTilak K CNo ratings yet
- IB Bonding Note Cards SL HLDocument59 pagesIB Bonding Note Cards SL HL陳定均No ratings yet
- Third Form Chemistry Packet 3Document12 pagesThird Form Chemistry Packet 3Lizbeth ChiNo ratings yet
- Structure of Solids 1Document5 pagesStructure of Solids 1zakNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument39 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsSimran BangaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds 1Document3 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds 1prathamseth1412No ratings yet
- Chemical BondDocument56 pagesChemical BondDzaky Zakiyal Fawwaz100% (1)
- 4.carbon and Its CompoundsDocument13 pages4.carbon and Its CompoundsayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document32 pagesChapter 8Danilo Fronda Jr.No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument11 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsJulia NithdaleNo ratings yet
- The Structural Characteristics of Carbon 3Document10 pagesThe Structural Characteristics of Carbon 3Kayelle Clyde LavarejosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 of OrganicDocument26 pagesChapter 1 of Organicsaadehkhaled7No ratings yet
- Solution 466049Document9 pagesSolution 466049S.N. RagulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Structure Hybridization and ResonanceDocument56 pagesChapter 1 Structure Hybridization and ResonanceLinearNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document16 pagesCH 4charanNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Fundamentals Org ChemDocument35 pagesUnit 11 Fundamentals Org ChemKavisha AshaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds (Notes 1)Document2 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds (Notes 1)Aarav SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds BY HUSAIN Abbas Zaidi - WatermarkDocument11 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds BY HUSAIN Abbas Zaidi - WatermarkGrizzly bearNo ratings yet
- Science 112 STUDY GUIDE 2Document15 pagesScience 112 STUDY GUIDE 2Dominador RomuloNo ratings yet
- 4.0 ChemicalbondingDocument219 pages4.0 ChemicalbondingTasya KassimNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry BondingDocument18 pagesIb Chemistry BondingAaron Bonner100% (1)
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument62 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryytutwNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument34 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemical BondingAwais altafNo ratings yet
- 10th - SC - Ch04 - Carbon - and - Its - Compounds - EnglishDocument107 pages10th - SC - Ch04 - Carbon - and - Its - Compounds - Englishshivakumara k tNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument21 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Carbon and Its CompoundsSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 10th Edition Tillery Solutions ManualDocument9 pagesPhysical Science 10th Edition Tillery Solutions Manualthoabangt69100% (28)
- CDBCEB1013 Lecture 1 PDFDocument87 pagesCDBCEB1013 Lecture 1 PDFPutri Nur Aisyah Halmy AzamNo ratings yet
- CarbonDocument17 pagesCarbonkulbantsingh1507No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Full Chapter 2022-23Document39 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Full Chapter 2022-23aarishsaifi9811100% (2)
- Lesson 1 JudgesDocument3 pagesLesson 1 JudgesrincyNo ratings yet
- CSK W RULES FOR COMPETITIONS - High SchoolDocument6 pagesCSK W RULES FOR COMPETITIONS - High SchoolrincyNo ratings yet
- Carbon 10 IIIDocument3 pagesCarbon 10 IIIrincyNo ratings yet
- AlloysDocument2 pagesAlloysrincyNo ratings yet
- B Tech Engg Phys Course Structure IIT RoorkeeDocument8 pagesB Tech Engg Phys Course Structure IIT RoorkeeSujithNo ratings yet
- Oct 2023 Unit 5 (Ial)Document28 pagesOct 2023 Unit 5 (Ial)zaksarah74No ratings yet
- Attenuation LabDocument11 pagesAttenuation Labapi-569589889No ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers Chapter 15 Asal PhysicsDocument5 pagesCoursebook Answers Chapter 15 Asal Physicssalaudeenaliyah9No ratings yet
- 5.2 Alkene 2Document6 pages5.2 Alkene 2Yusra IqbalNo ratings yet
- Radio - Electronics - February - 1981 (Project Tesla)Document4 pagesRadio - Electronics - February - 1981 (Project Tesla)Peeters GuyNo ratings yet
- Science: Whole Brain Learning SystemDocument16 pagesScience: Whole Brain Learning SystemKayrell AquinoNo ratings yet
- Glen Thiele Chemical Analysis of Metal Samples Using OES Copy For DistributionDocument21 pagesGlen Thiele Chemical Analysis of Metal Samples Using OES Copy For DistributionMUHAMMAD KHOLIDNo ratings yet
- Answers of Sample Paper 5 10 Physics 12Document47 pagesAnswers of Sample Paper 5 10 Physics 12Pankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Analysis IIDocument2 pagesInstrumental Analysis IIzebasilt0% (1)
- 1 BhattiAcademy - Com Physics 6. Scohlar SeriesDocument19 pages1 BhattiAcademy - Com Physics 6. Scohlar SeriesMoiz Rauf KhanNo ratings yet
- The Application of PlasmaDocument2 pagesThe Application of Plasmaabdelrahman waelNo ratings yet
- Sources of PlasmaDocument5 pagesSources of PlasmaVanteNo ratings yet
- FORMULA LIST First & Second PHYSICS Qasim SBDocument17 pagesFORMULA LIST First & Second PHYSICS Qasim SBzain aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SolutionDocument11 pagesChapter 5 SolutiongglrNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics EM Half Yearly Exam 2023 Question Paper Villupuram District English Medium PDF DownloadDocument2 pages12th Physics EM Half Yearly Exam 2023 Question Paper Villupuram District English Medium PDF DownloadPavithra JNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument7 pagesLesson Plan-Electromagnetic SpectrumDEBORAH JUBILEE MABAYAG100% (2)
- The Proton and Its Resonances NPP2.3Document46 pagesThe Proton and Its Resonances NPP2.3wyttenbachNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 Atoms Bonds RxnstestansDocument2 pagesMod 1 Atoms Bonds Rxnstestansrichardgharexd1No ratings yet
- Chem 11 Total Review With Answers Key UpdateDocument28 pagesChem 11 Total Review With Answers Key Updatemelissa.figueroamoralesNo ratings yet
- Mri ArtifactsDocument59 pagesMri ArtifactsMarc Michael Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CCC 2017 PtA ENDocument4 pagesCCC 2017 PtA ENsyavinaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Three Types of Chemical Bonds: 1Document5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Three Types of Chemical Bonds: 1Chris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- 2000-2019 Nesa Chemistry Advanced Level-1Document269 pages2000-2019 Nesa Chemistry Advanced Level-1Jeff AlbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 Nuclear PhysicsDocument29 pagesChapter 26 Nuclear PhysicsChong Xian LiNo ratings yet
- UNITIIIStereochemistryIsomerismGeometricalIsomerism BP401T PHARMACEUTICALORGANICCHEMISTRYIII B.pharmIVSem GITAMDeemedtobeUniversityDocument48 pagesUNITIIIStereochemistryIsomerismGeometricalIsomerism BP401T PHARMACEUTICALORGANICCHEMISTRYIII B.pharmIVSem GITAMDeemedtobeUniversityNIKITA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Crystals: Polaron Trapping and Migration in Iron-Doped Lithium NiobateDocument14 pagesCrystals: Polaron Trapping and Migration in Iron-Doped Lithium NiobateMony GarciaNo ratings yet
- (@bohring - Bot) FIITJEE AITS OPEN TEST 14-01-24 MAINSDocument90 pages(@bohring - Bot) FIITJEE AITS OPEN TEST 14-01-24 MAINSlavanyapadole736No ratings yet
- Reading Material Lecture 22Document18 pagesReading Material Lecture 22Syed Asad Asif HashmiNo ratings yet
- Chemisrty Questions For UDocument11 pagesChemisrty Questions For USushank GiriNo ratings yet