Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MAV Exam 1 Solutions
Uploaded by
Pradeep MahawattaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MAV Exam 1 Solutions
Uploaded by
Pradeep MahawattaCopyright:
Available Formats
The Mathematical Association of Victoria
Trial Examination 2018
MATHEMATICAL METHODS
Trial Written Examination 1 - SOLUTIONS
Question 1
a. y = 2 x log e (2 x) .
dy 1
= 2 x × + ( log e (2 x) × 2 ) 1M
dx x
dy
= 2 + 2 log e (2 x) 1A
dx
2
ex
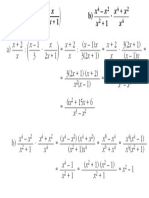
b. f ( x) = x .
e +1
( e x + 1) × e x × 2 x − e x × e x
2 2
f ( x) = 1M
( e x + 1)
2
f ′(0) =
(e 0
+ 1) × e0 × 0 − e0 × e0
1M
(e + 1)
0 2
0 −1 1
f ′(0) = = − 1A
( 2)
2
4
Question 2
a. f=( x) 18 x 2 − ax 4
f '(=
x) 36 x − 4ax 3
36 x − 4ax 3 = 4 x ( 9 − ax 2 ) = 0 for stationary point 1M
3
Gives x = 0, x = ±
a
3
Given stationary point at x = − where a ∈ R +
5
a = 5 as required 1M (Show that)
b. Coordinates
( 0, 0 ) 1A
3 81 3 81
, , − , 1A
5 5 5 5
© The Mathematical Association of Victoria, 2018
2018 MAV Mathematical Methods Trial Exam 1, Solutions 2
Question 3
1
a. g : , ∞ → R, g ( x=
) 2x −1
2
1
g (=
x) ( 2 x − 1) 2
1
g (1) =( 2 − 1) 2 =1
1
1 1
( 2 x − 1) 2 =
−
g ′( x) =
2× using the chain rule 1A
2 2x −1
1
=
m g= ′(1) = 1
2 −1
y − 1 = 1× ( x − 1)
y=x 1M (Show that)
b.
( )
2 1
=
A ∫ ( x)dx + ∫ x − 2 x − 1 dx
0 1
1M
2
1
1 3
x x 2 ( 2 x − 1) 2
2 2
= + −
2 0 2 3
1
2
1 1 1 1
= + − − − 0
8 2 3 8
1
= 1A
6
© The Mathematical Association of Victoria, 2018
2018 MAV Mathematical Methods Trial Exam 1, Solutions 3
OR
( )
1
=A Area of the triangle − ∫ 2 x − 1 dx 1M
1
2
1
3
1 ( 2 x − 1) 2
= −
2 3
1
2
1 1
= −
2 3
1
= 1A
6
Question 4
0.132 + 0.024 0.156
=
a. pˆ = = 0.078 1A
2 2
b. 0.132 − 0.078 = 0.054
pˆ (1 − pˆ )
2 = 2= σ X 0.054 1M
n
σ X = 0.027 1A
Question 5
a. 3 sin(2 x) = cos ( 2 x )
3 sin(2 x)
=1
cos ( 2 x )
1
tan(2 x) = 1A
3
π
2 x =+ nπ , n ∈ Z
6
π nπ
x=+ ,n∈Z 1A
12 2
d 2
b. ( tan(2 x) ) = 2
dx cos (2 x)
y = 3 tan(2 x)
dy 2 3
=
dx cos 2 (2 x)
For stationary point
dy 2 3
= = 0 gives no solution for x.
dx cos 2 (2 x)
So no stationary point. 1M (Show that)
© The Mathematical Association of Victoria, 2018
2018 MAV Mathematical Methods Trial Exam 1, Solutions 4
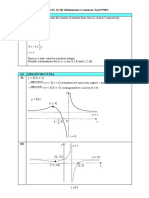
c. Shape 1A
π π 3π
Vertical asymptotes at x = −, , 1A
4 4 4
π 7π π
Points ,1 , ,1 , (0, 0), , 0 1A
12 12 2
Question 6
2 log 2 ( x − 2) + log 2 ( x) =
0
log 2 ( x − 2) 2 + log 2 ( x) =
0
( )
log 2 x( x − 2) 2 =
0 1A
x( x − 2) 2 =20 =1
x( x 2 − 4 x + 4) =
1
x 3 − 4 x 2 + 4 x − 1 =0 1A
( x − 1)( x 2 − 3 x + 1) =
0 1A
3− 5
x ≠ 1, x ≠ as x > 2
2
3+ 5
x= only 1A
2
© The Mathematical Association of Victoria, 2018
2018 MAV Mathematical Methods Trial Exam 1, Solutions 5
Question 7
1 12 πt
=
Average value ∫
12 − 0
0 −20sin + 10 + 20 dt
12
1M
20 12 πt
= ∫
12 0 − sin + 10 + 1 dt
12
5 12 πt
= ∫
3 0 − sin + 10 + 1 dt
12
12
5 12 πt
= cos + 10 + t 1M
3π 12 0
5 12 12
= cos (π + 10 ) + 12 − cos ( 0 + 10 ) + 0
3 π π
Average height
5 12 12
= cos (π + 10 ) + 12 − cos (10 )
3 π π
20 20
= cos (π + 10 ) − cos (10 ) + 20 1A
π π
cos(π + x) =− cos( x)
So the expression simplifies to
20 20
− cos (10 ) − cos (10 ) + 20
=
π π
40
− cos (10 ) + 20
= 1A
π
Question 8
a.i. 0.1 + a + b + 0.1 =
1
a + b = 0.8, b = 0.8 − a 1A
ii. E ( X ) =a + 2b + 0.3
=a + 1.6 − 2a + 0.3
=−a + 1.9 1M (Show that)
( ) (
( X ) E X 2 − E( X ) )
2
=
b. Var
a + 4b + 0.9 − (−a + 1.9) 2 =0.56 1M
a + 4b + 0.9 − (a 2 − 3.8a + 3.61) =
0.56
a 2 − 0.8a + 0.07 =
0 1A
(a − 0.1)(a − 0.7) =
0
= =
a 0.1, =
b 0.7 OR =
a 0.7, b 0.1 1A
© The Mathematical Association of Victoria, 2018
2018 MAV Mathematical Methods Trial Exam 1, Solutions 6
Question 9
=
a. Let y f= ( x) 2e1− x
Inverse swap x and y.
x = 2e1− y 1M
x
= e1− y
2
x
1− y = log e
2
x
y= − log e + 1
2
x
f −1 ( x) =
− log e + 1 1A
2
Range is R 1A
b. Shape and three points of intersection 1A
Asymptote x = 0 and intercept (2e, 0) 1A
END OF SOLUTIONS
© The Mathematical Association of Victoria, 2018
You might also like
- 2022 Mathematical Methods Trial Exam 1 Solutions 1Document2 pages2022 Mathematical Methods Trial Exam 1 Solutions 1martin juNo ratings yet
- MAV Exam 1 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMAV Exam 1 SolutionsPradeep MahawattaNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 2 Math QuestionsDocument16 pagesJEE Advanced 2022 Paper 2 Math QuestionsEVIN S MANOJNo ratings yet
- MAV Exam 1 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMAV Exam 1 SolutionsPradeep MahawattaNo ratings yet
- TJC 9758 2023 Prelim P1 SolutionDocument20 pagesTJC 9758 2023 Prelim P1 SolutionSierra KohNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Algebraicas 4ºesoDocument3 pagesEcuaciones Algebraicas 4ºesokkkkkNo ratings yet
- NYJC 2017 EOY Exam Paper Solutions 2Document12 pagesNYJC 2017 EOY Exam Paper Solutions 2Low Jia YingNo ratings yet
- Main 2021 SoltnDocument4 pagesMain 2021 SoltnEVIN S MANOJNo ratings yet
- 2023 MAV MathsMethods Trial Exam 1 SolutionsDocument10 pages2023 MAV MathsMethods Trial Exam 1 Solutionsmiddoka101No ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Fracciones Algebraicas (Con Solución)Document1 pageEjercicios de Fracciones Algebraicas (Con Solución)ISABEL100% (1)
- The International University (Iu) - Vietnam National University - HCMCDocument4 pagesThe International University (Iu) - Vietnam National University - HCMCDiệu Vi NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Maths Pre Board 2023-24 (Navodaya Vidhyalaya Samiti) SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass Xii Maths Pre Board 2023-24 (Navodaya Vidhyalaya Samiti) Solutionsrsarthak227No ratings yet
- Serie EquationsDocument2 pagesSerie EquationsZA9OF FFNo ratings yet
- 1920F4T2M1MSDocument11 pages1920F4T2M1MSLUI ansonNo ratings yet
- 2122F4T2M1MSDocument14 pages2122F4T2M1MSLUI ansonNo ratings yet
- VCAA Exam 1 SolutionsDocument7 pagesVCAA Exam 1 SolutionsPradeep MahawattaNo ratings yet
- PAST EDME3203 (Calculus III) FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONSDocument10 pagesPAST EDME3203 (Calculus III) FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONSDane SinclairNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi BAB 2: CorrelationDocument8 pagesEvaluasi BAB 2: CorrelationAldiansyahNo ratings yet
- 2016 mm34 Exam 1 SolutionsDocument9 pages2016 mm34 Exam 1 SolutionsSunny XiaNo ratings yet
- A-Level H2 Maths 2017 - Paper 1: A A Ax A X Aa X ADocument17 pagesA-Level H2 Maths 2017 - Paper 1: A A Ax A X Aa X AterrygohNo ratings yet
- TS Eamcet 2015 Engineering Question Paper Key Solutions PDFDocument39 pagesTS Eamcet 2015 Engineering Question Paper Key Solutions PDFSwayam Bhoi67% (3)
- Chapter 19 PDFDocument69 pagesChapter 19 PDFAnonymous 69No ratings yet
- JEE MAIN APNI KAKSHA STAR BATCH ANSWER KEYDocument41 pagesJEE MAIN APNI KAKSHA STAR BATCH ANSWER KEYBhavadip VamjaNo ratings yet
- Solution of Circle From JEE Main 2021 MarDocument6 pagesSolution of Circle From JEE Main 2021 MarrajuNo ratings yet
- 微乙上末 99Document7 pages微乙上末 99Bryan WLNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Differentiation: 1A. GraphingDocument16 pagesUnit 1. Differentiation: 1A. GraphingTaghi KhajeNo ratings yet
- 2021 NYJC JC1 H2MATH (Modified) Common Test SolutionsDocument9 pages2021 NYJC JC1 H2MATH (Modified) Common Test SolutionsGareth WongNo ratings yet
- Quardatic Equation-02-Solved ExamDocument14 pagesQuardatic Equation-02-Solved ExamRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Trabalho de Calculo Integral em RDocument8 pagesTrabalho de Calculo Integral em RVembe ReisNo ratings yet
- 2013 Past Paper and Specimen Paper PDFDocument5 pages2013 Past Paper and Specimen Paper PDFgeoNo ratings yet
- Tut 4 Graphing TechniquesDocument20 pagesTut 4 Graphing TechniquesselmerparisNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Sustituir B en Ecuación 2 Sustituir Cy B en La Ecuación 3Document2 pagesEcuaciones Sustituir B en Ecuación 2 Sustituir Cy B en La Ecuación 3ClaudiaEspinosaNo ratings yet
- 1920F4T1M1MSDocument8 pages1920F4T1M1MSLUI ansonNo ratings yet
- HSC Mathematics Assessment Task 1 Worked Solutions and Marking GuidelinesDocument4 pagesHSC Mathematics Assessment Task 1 Worked Solutions and Marking GuidelineswasaiyanNo ratings yet
- X X X X X X X X: X + 2 X X + 2 X X X - 1 X + 2 XDocument1 pageX X X X X X X X: X + 2 X X + 2 X X X - 1 X + 2 Xmarioheavy90No ratings yet
- Solu H.M 2Document5 pagesSolu H.M 2Amro BaradiyyhaNo ratings yet
- Gabarito - Prova 1 Área 2 UFPE 2019.1Document1 pageGabarito - Prova 1 Área 2 UFPE 2019.1André SilvaNo ratings yet
- Original Problem Series Week-2: WWM MathsDocument8 pagesOriginal Problem Series Week-2: WWM MathspiyushNo ratings yet
- Itute 2008 Mathematical Methods Examination 1 SolutionsDocument2 pagesItute 2008 Mathematical Methods Examination 1 SolutionsnochnochNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.3 (Solutions) : y X X XDocument6 pagesExercise 2.3 (Solutions) : y X X XSpell MasterTMNo ratings yet
- 1 (A) Suppose The Following Facts Are Known About The Function G and Its DerivativeDocument5 pages1 (A) Suppose The Following Facts Are Known About The Function G and Its DerivativeShereen LimNo ratings yet
- Multivariate CalculusDocument15 pagesMultivariate CalculusMartin De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- Ial pm1 Exam Practice SolutionbankDocument4 pagesIal pm1 Exam Practice SolutionbankDiyaNo ratings yet
- Nsghs 2013 Yr 11 2u t1 - SDocument2 pagesNsghs 2013 Yr 11 2u t1 - SYe ZhangNo ratings yet
- HIGH School IV REAL NUMBERS-LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLEDocument7 pagesHIGH School IV REAL NUMBERS-LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLENenad JanicijevicNo ratings yet
- Itf 1Document3 pagesItf 1shriteshNo ratings yet
- 334 RationexDocument8 pages334 RationexLouis GuyNo ratings yet
- January 2007 MS - C3 EdexcelDocument7 pagesJanuary 2007 MS - C3 Edexceljohn mNo ratings yet
- 01 6partial FractionsDocument4 pages01 6partial FractionseamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument4 pagesQuadratic EquationChristopher NelsonNo ratings yet
- 4B Ch7 Test Answers Multiple Choice Questions (5 Marks)Document5 pages4B Ch7 Test Answers Multiple Choice Questions (5 Marks)NicoleNo ratings yet
- NSGHS 2010 2U Trial SolutionsDocument11 pagesNSGHS 2010 2U Trial SolutionsYon Seo YooNo ratings yet
- 5b. Mixed exam-style questions on exponentials and logarithms - AnswersDocument2 pages5b. Mixed exam-style questions on exponentials and logarithms - Answerswaleedkhan567799No ratings yet
- Exercise No 3 - AnswerDocument4 pagesExercise No 3 - AnswerRabiahNo ratings yet
- 2014 RI (Yr6) H3 Math Prelim (Student Solutions)Document9 pages2014 RI (Yr6) H3 Math Prelim (Student Solutions)Po ToNo ratings yet
- Application of DeterminantDocument4 pagesApplication of Determinantswapnendudutta2003No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Algebra: 8 Grade Mathematics Summary Notes Vo.1Document3 pagesChapter 2: Algebra: 8 Grade Mathematics Summary Notes Vo.1Ak 47No ratings yet
- MJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Paper 1 SolutionsDocument17 pagesMJC JC2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Paper 1 SolutionsRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Insight 2016 Mathematical Methods Examination 1 SolutionsDocument15 pagesInsight 2016 Mathematical Methods Examination 1 SolutionsnochnochNo ratings yet
- (Methods) 2000 Heffernan Exam 1 SolutionsDocument12 pages(Methods) 2000 Heffernan Exam 1 SolutionsPradeep MahawattaNo ratings yet
- Insight 2017 Mathematical Methods Examination 2 SolutionsDocument43 pagesInsight 2017 Mathematical Methods Examination 2 Solutionsnochnoch0% (1)
- Insight 2017 Mathematical Methods Examination 2 PDFDocument27 pagesInsight 2017 Mathematical Methods Examination 2 PDFnochnochNo ratings yet
- Insight 2017 Mathematical Methods Examination 1 PDFDocument11 pagesInsight 2017 Mathematical Methods Examination 1 PDFnochnochNo ratings yet
- MAV Exam 2 SolutionsDocument29 pagesMAV Exam 2 SolutionsPradeep MahawattaNo ratings yet
- 06 - Branches of StylisticsDocument38 pages06 - Branches of StylisticsKashif Iqbal MS Student EarthQuake-Spring 22100% (1)
- Physics 72 EEE RecitationDocument2 pagesPhysics 72 EEE RecitationRalph EvidenteNo ratings yet
- Designing Itc v7 ExptsDocument5 pagesDesigning Itc v7 ExptsRigel_TNo ratings yet
- AGGREGATE SHAPE TEST RESULTSDocument9 pagesAGGREGATE SHAPE TEST RESULTSBeman EasyNo ratings yet
- NAPLAN 2011 Final Test Numeracy Year 7 CalculatorDocument13 pagesNAPLAN 2011 Final Test Numeracy Year 7 CalculatoraimanNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document5 pagesLab 2Rizkie Denny PratamaNo ratings yet
- UAE CST Framework PDFDocument280 pagesUAE CST Framework PDFChitra BharghavNo ratings yet
- 04Electrostatic-SenAct 44Document94 pages04Electrostatic-SenAct 44Prashant SinghNo ratings yet
- High SecureDocument6 pagesHigh SecureCrispNo ratings yet
- Visualising Solid ShapesDocument10 pagesVisualising Solid ShapesBharatNo ratings yet
- Computational Mathematics and Physics of Fusion Reactors - Paul R. GarabedianDocument5 pagesComputational Mathematics and Physics of Fusion Reactors - Paul R. GarabediandougnovaesNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 7 : Line with inclined FV, HT and VTDocument4 pagesPROBLEM 7 : Line with inclined FV, HT and VTnishant dhimanNo ratings yet
- A Review of Software Fault Detection and Correction Process, Models and TechniquesDocument8 pagesA Review of Software Fault Detection and Correction Process, Models and TechniquesDr Muhamma Imran BabarNo ratings yet
- IYPT Problemas 2020Document1 pageIYPT Problemas 2020Paul Kurono Palma GalvezNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Worksheet on Ch 8,9,1 and 11Document2 pagesComputer Science Worksheet on Ch 8,9,1 and 11prosenjit basak100% (1)
- Mass Storage Systems Chapter SummaryDocument15 pagesMass Storage Systems Chapter Summaryneha91No ratings yet
- Prediction of Flexural Strength of Natural Pozzolana and Limestone Blended Concrete Using Machine Learning Based ModelsDocument7 pagesPrediction of Flexural Strength of Natural Pozzolana and Limestone Blended Concrete Using Machine Learning Based ModelsOhiedul Haque Mohammad AsadNo ratings yet
- STEM General Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Module 6 Graphical Analysis of MotionDocument28 pagesSTEM General Physics 1: Quarter 1 - Module 6 Graphical Analysis of MotionStevenNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Theory of Large Displacement With Small StrainDocument13 pagesNotes On The Theory of Large Displacement With Small Strainjanaaidaas1996No ratings yet
- Closed Conduit FlowDocument5 pagesClosed Conduit FlowPatrick Joseph RoblesNo ratings yet
- Big oDocument9 pagesBig oSanan RasheedNo ratings yet
- The Latest On Quantitative Sampling Theory: Liberation, Shape and Granulometric FactorsDocument20 pagesThe Latest On Quantitative Sampling Theory: Liberation, Shape and Granulometric FactorsLuis Katsumoto Huere AnayaNo ratings yet
- Report Mat652 - 2021171741 - 2021119563Document6 pagesReport Mat652 - 2021171741 - 2021119563NUR DINI HUDANo ratings yet
- Free Keyboard Shortcuts (WIN) : Number PadDocument1 pageFree Keyboard Shortcuts (WIN) : Number PadLeonardo AguileraNo ratings yet
- 2009amc12 BDocument8 pages2009amc12 BChew Guo QiangNo ratings yet
- GDM2000Document38 pagesGDM2000api-3700706100% (3)
- Mathematics 11 Basic Calculus - Stem: Third Quarter - Week 4Document15 pagesMathematics 11 Basic Calculus - Stem: Third Quarter - Week 4Pede CasingNo ratings yet
- 200 Quadratic Equation QuestionsDocument7 pages200 Quadratic Equation QuestionsLatta SakthyyNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - Decision AnalyticsDocument10 pagesFinal Exam - Decision AnalyticsDara Clarize RomaticoNo ratings yet
- Algorithms 13 00053 v2 PDFDocument22 pagesAlgorithms 13 00053 v2 PDFJohn DoeNo ratings yet