Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Defintion 3
Uploaded by
shueOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Defintion 3
Uploaded by
shueCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 4 : THE PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS
Periods The horizontal rows in the Periodic Table of Elements are called Periods.
Groups The vertical columns in the Periodic Table of Elements are called Groups.
CHAPTER 5 : CHEMICAL BOND
Chemical bond Chemical bond means a bond formed between atoms that transfer or share
electrons to form a compound.
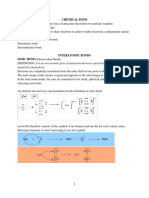
Ionic bond Ionic bond is formed by the transfer of electrons between a metal atom and a
non-metal atom.
Covalent bonds Covalent bonds are formed when non-metal atoms share their electrons to
achieve a stable duplet or octet electron arrangement.
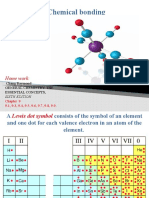
Lewis structure Lewis structure only shows the valence electrons of the atoms involved.
Diagram that shows the bonds between atoms in a molecule and the electron
lone pairs in a molecule.
Hydrogen bonds Hydrogen bonds are attraction forces between hydrogen atom, H that has
bonded with an atom of high electronegativity, such as nitrogen, N, oxygen,
O or fluorine, F with nitrogen, N, oxygen, O or fluorine, F in another
molecule.
Dative bond Dative bond or coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond where the electron
pair that is shared comes from one atom only.
Metallic bond. Electrostatic attraction force between the sea of electrons and the positively-
charged metal ions form the metallic bond.
Sea of electrons All delocalised valence electrons can move freely between the metal
structure and form a sea of electrons.
Delocalised Delocalised electron means electron that moves freely and is not owned by
electron any atom nor ion.
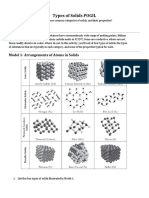
Lattice structure Lattice structure is the orderly arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules of a
compound in a solid crystal.
CHAPTER 4 : THE PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS
Periods The horizontal rows in the Periodic Table of Elements are called Periods.
Groups The vertical columns in the Periodic Table of Elements are called Groups.
CHAPTER 5 : CHEMICAL BOND
Chemical bond Chemical bond means a bond formed between atoms that transfer or share
electrons to form a compound.
Ionic bond Ionic bond is formed by the transfer of electrons between a metal atom and a
non-metal atom.
Covalent bonds Covalent bonds are formed when non-metal atoms share their electrons to
achieve a stable duplet or octet electron arrangement.
Lewis structure Lewis structure only shows the valence electrons of the atoms involved.
Diagram that shows the bonds between atoms in a molecule and the electron
lone pairs in a molecule.
Hydrogen bonds Hydrogen bonds are attraction forces between hydrogen atom, H that has
ALWAYS LIKE A PROTON & STAY POSITIVE
4S1 2023/2024
bonded with an atom of high electronegativity, such as nitrogen, N, oxygen,
O or fluorine, F with nitrogen, N, oxygen, O or fluorine, F in another
molecule.
Dative bond Dative bond or coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond where the electron
pair that is shared comes from one atom only.
Metallic bond. Electrostatic attraction force between the sea of electrons and the positively-
charged metal ions form the metallic bond.
Sea of electrons All delocalised valence electrons can move freely between the metal
structure and form a sea of electrons.
Delocalised Delocalised electron means electron that moves freely and is not owned by
electron any atom nor ion.
Lattice structure Lattice structure is the orderly arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules of a
compound in a solid crystal.
ALWAYS LIKE A PROTON & STAY POSITIVE
4S1 2023/2024
You might also like
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR GEOMETRYDocument4 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR GEOMETRYRen ManalotoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledManureet SinghNo ratings yet
- IONS, BONDING & PROPERTIESDocument21 pagesIONS, BONDING & PROPERTIESRoshan Jawad ZafirNo ratings yet
- W) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXDocument10 pagesW) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXSav OliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Bonding TheoriesDocument55 pagesChemical Bonding and Bonding Theoriesnxumalopat2No ratings yet
- Class 10th Chemistry NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10th Chemistry NotesRehan KhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesChemical BondingJr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding MDocument23 pagesChemical Bonding MnewmowneeshNo ratings yet
- Chemical bonding: The essential concepts of electron sharing and transferDocument54 pagesChemical bonding: The essential concepts of electron sharing and transferSam LoveNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes Ch04 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument4 pages11 Chemistry Notes Ch04 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureAkhed100% (1)
- CHM 112 Aspect Note-Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesCHM 112 Aspect Note-Chemical BondingOluwatosin KoyejoNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 SenguptaDocument38 pagesPhysics 2 SenguptaSashank PrayagaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshusa harshaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypeDocument8 pagesChemical Bond TypeShabbir TamboliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond Typesapi-287081563No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds ExplainedDocument19 pagesChemical Bonds Explained37 CM3Vijayalaxmi KambleNo ratings yet
- Lo5 1) Chemical BondsDocument9 pagesLo5 1) Chemical BondsabdogamreNo ratings yet
- S9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingDocument37 pagesS9Q2T2L2 Types of Chemical BondingMark Kevin Cagande EscletoNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesDocument9 pagesScience: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesAriel Lomugdang PatricioNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding For B.tech 1st Year byDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding For B.tech 1st Year byJishnuNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondDocument15 pagesIonic Bondemy.sajesajeNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument69 pagesChemical Bondingirenerielo19No ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and BondingDocument18 pagesCsec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and Bondingchelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- Bonding Models and Physical PropertiesDocument4 pagesBonding Models and Physical PropertiesShreyas KamathNo ratings yet
- Topic: Chemical Combination: Na 2, 8, 1 CL 2, 8, 7 Na 2, 8 CL 2, 8, 8 Na + CL NaclDocument2 pagesTopic: Chemical Combination: Na 2, 8, 1 CL 2, 8, 7 Na 2, 8 CL 2, 8, 8 Na + CL NaclVictor OkosunNo ratings yet
- Material Bonding Character Example: Primary Interatomic Bonds Ionic BondingDocument4 pagesMaterial Bonding Character Example: Primary Interatomic Bonds Ionic BondingCsir RimlaNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes CHPTR 5Document6 pagesChem Notes CHPTR 5Wan HasliraNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Ionic CrystalDocument24 pagesAtomic Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Ionic CrystalDr-Sushant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and The Shapes of MoleculesDocument73 pagesChemical Bonding and The Shapes of MoleculesKen Juliana Fe IsaacNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding NotesShaswat PattnayakNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Bonds: Created By: Amalia Heryani, Safira S. Dewinda, Fanny Eka, Fridayova Meidiana, and Raka SabarDocument27 pagesThe Chemical Bonds: Created By: Amalia Heryani, Safira S. Dewinda, Fanny Eka, Fridayova Meidiana, and Raka SabarAmalia HeryaniNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Bonds The title "TITLE Types of Chemical BondsDocument7 pagesTypes of Chemical Bonds The title "TITLE Types of Chemical Bondsmuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Unit 4 (Chemical Bonding)Document16 pagesLecture-Unit 4 (Chemical Bonding)Tericka JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument38 pagesChemical BondingBackup AccountNo ratings yet
- What is a covalent bondDocument2 pagesWhat is a covalent bondM3xobNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Document88 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Damz RtgNo ratings yet
- VNKU Medical Chemistry Lecture on Chemical Bonding and Coordination CompoundsDocument31 pagesVNKU Medical Chemistry Lecture on Chemical Bonding and Coordination CompoundsAmirs AmjadNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7 - Covalent Bonds and Molecular StructurDocument24 pagesChapter-7 - Covalent Bonds and Molecular StructurV KumarNo ratings yet
- 6 C15 Notes CH4 Chemical BondsSTEM StudentsDocument12 pages6 C15 Notes CH4 Chemical BondsSTEM StudentsDONNA JEAN ACOJEDONo ratings yet
- LoloDocument6 pagesLoloapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- Notes Chemistry - ch4 - 11Document17 pagesNotes Chemistry - ch4 - 11VikramNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7 Slides - General Chemistry - Open StaxDocument96 pagesChapter - 7 Slides - General Chemistry - Open Staxonline purchaseNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding in SolidsDocument3 pagesAtomic Bonding in Solidsazmatshahzad786786No ratings yet
- Week # 8 Chemcial BondingDocument3 pagesWeek # 8 Chemcial BondingDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Test 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionDocument7 pagesTest 3 Bonding Review Sheet-Final VersionJuventie PrimastutiNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE To ReviewDocument4 pagesSCIENCE To ReviewMichaela Gwyneth SantosNo ratings yet
- NEET Revision Notes For Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument21 pagesNEET Revision Notes For Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureTanushree DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Chemical Bonds101Document22 pagesLec 2 Chemical Bonds101memoryboybooNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Chemical BondingDe AktivedNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument12 pagesStructure and BondingNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- ch-3,chemDocument6 pagesch-3,chemAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument79 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureGanesh V GaonkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument177 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureGanesh V GaonkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds Chemical CompoundsDocument68 pagesChemical Bonds Chemical CompoundsRalph RebugioNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical BondsDocument8 pagesTypes of Chemical BondsdanNo ratings yet
- Materials Middle ExamDocument5 pagesMaterials Middle ExamAli M Ali100% (1)
- Definition of HybridizationDocument28 pagesDefinition of HybridizationMeg Dianne V. CañedaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Intro To OrbitalsDocument23 pagesWeek 1 - Intro To OrbitalsAdelin NemesNo ratings yet
- QUIZ: Chapter 02 Covalent Bonds, Molecules, and Ionic BondsDocument13 pagesQUIZ: Chapter 02 Covalent Bonds, Molecules, and Ionic BondsXul Manuel González PagánNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding New PDFDocument52 pagesChemical Bonding New PDFAniruddha KawadeNo ratings yet
- Campbell Lecture Notes Chemistry of LifeDocument42 pagesCampbell Lecture Notes Chemistry of LifeSophia Andrei VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 - Molecular Orbital RepresentationDocument7 pagesExercise 5 - Molecular Orbital Representationapi-235187189No ratings yet
- Crystal Blueprint Reconnect With Your Authentic Self Through The Ancient Wisdom and Modern Science of Quartz CrystalsDocument25 pagesCrystal Blueprint Reconnect With Your Authentic Self Through The Ancient Wisdom and Modern Science of Quartz CrystalsKaren LencinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Semester 2 Exam Study GuideDocument17 pagesChemistry Semester 2 Exam Study Guidefelkns27No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes for First Year Improvement ExamDocument35 pagesChemistry Notes for First Year Improvement ExamAnantha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Woods Ed508-5e-Lesson-PlanDocument8 pagesWoods Ed508-5e-Lesson-Planapi-617045317No ratings yet
- 1 Puc Chemistry Model Question Papers 2013 With AnswersDocument7 pages1 Puc Chemistry Model Question Papers 2013 With AnswersPrasad C M88% (16)
- CHEM Types of Solids POGILDocument7 pagesCHEM Types of Solids POGILKosakenNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding - Grade 10Document13 pagesCovalent Bonding - Grade 10sashana stoddartNo ratings yet
- ESAS - Pre Board August 2016 W AnswersDocument7 pagesESAS - Pre Board August 2016 W AnswersZnevba Quintano100% (2)
- Mindtap General Chemistry 4 Terms 24 Months Instant Access 1st Edition Vining Test BankDocument32 pagesMindtap General Chemistry 4 Terms 24 Months Instant Access 1st Edition Vining Test Bankarthrosisretake8hro100% (32)
- IGCSE Chemistry - NotesDocument46 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - NotesJason Graves86% (7)
- Lesson Proper #5 Resonance and Formal ChargeDocument35 pagesLesson Proper #5 Resonance and Formal ChargeSamantha CamposNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Richard F. Daley and Sally J. DaleyDocument47 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Richard F. Daley and Sally J. DaleySai Swaroop MandalNo ratings yet
- Water Properties Virtual LabDocument7 pagesWater Properties Virtual LabJaxon MorleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Test BankDocument18 pagesChapter 4 Test Bank陳禹誌No ratings yet
- Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Courses at AMU Department of ChemistryDocument23 pagesInorganic and Physical Chemistry Courses at AMU Department of ChemistryM KamranNo ratings yet
- Different Sample Multiple Choice Questions in General Chemistry and Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesDifferent Sample Multiple Choice Questions in General Chemistry and Organic ChemistryGeorge Isaac McQuilesNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Chemistry IA IBDocument3 pagesTopic 4 Chemistry IA IBDanisa IriantoNo ratings yet
- CY 1001 - Organic Chemistry: Anbarasan CY1001 Anbarasan CY1001Document21 pagesCY 1001 - Organic Chemistry: Anbarasan CY1001 Anbarasan CY1001Rashmi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopic Techniques and Applications SummaryDocument25 pagesSpectroscopic Techniques and Applications SummaryMuhammad SuhailNo ratings yet
- BMSID Practice Exercises Assignment 4Document5 pagesBMSID Practice Exercises Assignment 4Yuvraj UbovejaNo ratings yet
- Organic Reaction Mechanism & Named ReactionsDocument375 pagesOrganic Reaction Mechanism & Named Reactionsaggelisgeorge8546No ratings yet
- IOQC (Part-I) 2022-23 - (Answers & Solutions)Document12 pagesIOQC (Part-I) 2022-23 - (Answers & Solutions)Shaurya MittalNo ratings yet
- As Level Test - 1Document16 pagesAs Level Test - 1zafarchem_iqbal0% (1)