Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nutrition and Diet Therapy
Uploaded by
Joshua Ayson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy
Uploaded by
Joshua AysonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
FOOD- Any substance taken into the body that will
NUTRITION help to meet the body’s needs for energy,
maintenance, and growth.
-The sum of the processes by which food is selected
and becomes part of the body. ENERGY-Capacity to do work; also refers to
calories, that is, the “fuel” provided by certain
3 reasons to study Nutrition nutrients (carbohydrates,
fats, proteins).
1. Recognition the role of nutrition
2. Concern for adopting food patterns of KILOCALORIE (KCALORIE, KCAL)-
individuals to their nutritional needs Technically correct term for unit of energy in
3. Awareness of the need in specify disease nutrition, equal to the amount of heat
stakes to modify nutritional factor or required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water
therapeutic purposes 1°C.
NUTRITIONAL STATUS- State of the body
resulting from the intake and use of nutrients
NUTRIENTS- chemical substances that are found
OPTIMUM NUTRITION- The state of receiving in food; gives energy
and utilizing essential nutrients to maintain health
and well-being at the highest possible level. It Classifications of nutrients:
provides a reserve for the body.
1. Function- those that are from tissues in the
MALNUTRITION- An inadequate intake (or body
utilization) of nutrients to meet the body’s 2. Chemical properties- nutrients are either
requirements for energy, maintenance, and growth organic or inorganic
3. Essentiality- classified base on their
OVERNUTRITION- An excessive intake of one significant contribution of physiologic
or more nutrients, frequently referring to nutrients function
providing energy (kcalories). 4. Concentration- nutrients are either large or
small amount
POOR NUTRITIONAL STATUS-an inadequate
intake (or utilization) of nutrients to meet the body’s MACRONUTRIENTS- needed in large amount
requirements for energy, maintenance, and growth.
Carbohydrates- molecules compose of
GOOD NUTRITIONAL STATUS-The intake of a carbon, hydrogen, oxygen. Major “fuel”
balanced diet containing all the essential nutrients source
to meet the body’s requirements for energy, Proteins- chains of amino acid. Carbon,
maintenance, and growth. hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
DIET Fats- lipids, water insoluble. carbon,
hydrogen, oxygen
a) the foods that a person eats most frequently Water-only macronutrient that does not
b) food considered in terms of its qualities and yield energy. 2 hydrogen, 1 oxygen and does
effects on health not contain carbon
c) a particular selection of food, usually
prescribed to cure a disease or to gain or lose MICRONUTRIENTS-needed in small amount;
weight. not source of energy.
Vitamins (7 essentials) 3. Iodine- thyroid hormone production,
Minerals (16 essentials) growth and metabolism
4. Selenium- anti-oxidant
ENZYMES- proteins that catalyze or accelerate 5. Copper- co-enzyme, iron metabolism
chemical reaction in the body 6. Molybdenum- co-enzyme
7. Chronium- assist insulin in glucose
VITAMINS- organic substances in very small
metabolism
amounts or quantities which is essential for normal
8. Manganese- co-enzyme
metabolism.
9. Flouride- bone and teeth health
2 groups of vitamins maintenance and tooth decay prevention
Fat-soluble includes: Major minerals
1. Vitamin A(retinol)-Vision, 1. Sodium- fluid balance,nerve transmission
reproductive system 2. Chloride- fluid balance, stomach acid
2. Vitamin D (Sunshine vitamin)-Bone production
and teeth health maintenance 3. Potassium- fluid balance, nerve transmission,
3. Vitamin E (tocopherol)-Anti-oxidant, muscle contraction
cell membrane protection 4. Calcium- bone and teeth health maintenance,
4. Vitamin K (K1- Phylloquinone,K2- nerve transmission, muscle contraction
menaquinone, K3-Menadione)-Bone 5. Magnesium- protein production, nerve
and teeth health maintenance, blood transmission, muscle contraction
clotting 6. Sulfur- protein production
7. Phosphorus- bone and teeth health
Water-soluble includes: maintenance, acid base balance
1. B1- thiamine
2. B2- riboflavin
3. B3-niacin
4. B5-pantothenic acid
5. B6-pyridoxine
6. B7-biotin,H
7. B9-folic acid
8. B10-cobalamin COMPOSITION OF
9. Vitamin c- ascorbic acid
CELL
CELL- Made up of water, inorganic ions and
carbon containing molecule
MINERALS-inorganic substances
WATER - most abundant,70% of total cell mass,
2 groups of minerals:
polar molecule
Trace Minerals
1. Iron- carries oxygen,energy production
Figures of cell:
2. Zinc -protein and dna production,
Cell membrane
wound healing, growth and immune
function
aka plasma membrane
Made up of phospholipids, cholesterol,
protein
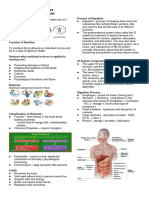
Antigen markers Parts of digestive system:
Receptor sites of hormones Mouth- first process of digestion,food is
broken down by chewing
Cytoplasm Throat- pharynx, transfer food from mouth to
Watery solutions of mineral gasses and esophagus
organic found in the cell membrane and Esophagus- muscullar tube extending from
nucleus pharynx to stomach
Stomach- Sca-like organ with tough muscular
Cell organelles walls ,folds, grinds, and mix food
Intracellular structured and bond in cell Small intestine- long loosely foiled tube, 20ft
membrane Pancreas- secretes enzyme
1. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)- passage way Duedenum- process the breaking down of food
2. Ribosomes -tiny structures of proteins Jejunum and ileum- absorption of nutrients
3. Golgi aparatus- membranous socks that through blood streams
synthesize Liver- produce and secretes by which helps in
digestion
Mithochodria Gal bladder- reservoir
Power house of the cell Large intestine- 5-6 ft long, connects the
Produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP) cecum and rectum
Rectum- connects colon to anus, digestive
Lysosome tracts ends
Single membrane structure 5 parts of Cecum:
Digestive enzyme that destroys and gulp 1. Ascending colon (right)
bacteria and other debris 2. Transverse colon (across)
3. Descending colon
Centrioles 4. Sigmoid colon
Pair rode shape structure that lie
perpendicular outside the nucleus
Flagella and Cilla
Moves the cell,threadlike project ions
Cilla is longer than flagella
Nucleus
Controls the cell
46 chromosome in the human body
PROCESS OF
DIGESTION
DIGESTION- breaking down of food into
substances that aid the body in different reaction
You might also like
- MetabolicRenewal - Start HereDocument3 pagesMetabolicRenewal - Start HereDiana Parracho67% (6)
- Primary Checkpoint Paper 1 Specimen 2020 InsertDocument4 pagesPrimary Checkpoint Paper 1 Specimen 2020 InsertCollin Tanaka Halim100% (2)
- GlycolysisDocument8 pagesGlycolysisdani2703No ratings yet
- Orthotrophy PDFDocument352 pagesOrthotrophy PDFmattiaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Their RegulationDocument48 pagesEnzymes and Their RegulationChathur Chandrasoorya100% (1)
- Nutrient Procurement and ProcessingDocument62 pagesNutrient Procurement and ProcessingClara Mae100% (2)
- Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument24 pagesNutrition and Diet TherapyKimberly Marie BayangNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NutritionDocument13 pagesFundamentals of NutritionGrace BuidNo ratings yet
- What in The Cell Is Going On - The Battle Over PHDocument13 pagesWhat in The Cell Is Going On - The Battle Over PHBiljana100% (1)
- Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument21 pagesNutrition and Diet TherapyMrz Alz100% (2)
- NCM 105 Lec&labDocument18 pagesNCM 105 Lec&labmary navalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To NutritionDocument17 pagesAn Introduction To NutritionAlejandra Diaz RojasNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test N EappDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Test N Eappcherish mae oconNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 - NDDocument2 pagesNCM 105 - NDYsabelle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Basic Interventions To Maintain Healthy LifestyleDocument13 pagesBasic Interventions To Maintain Healthy Lifestylehahahahaaaaaaa0% (1)
- Basic Nutrition 2009 RevisedDocument25 pagesBasic Nutrition 2009 Revisedken100% (3)
- Fermented Foods for Health: Use the Power of Probiotic Foods to Improve Your Digestion, Strengthen Your Immunity, and Prevent IllnessFrom EverandFermented Foods for Health: Use the Power of Probiotic Foods to Improve Your Digestion, Strengthen Your Immunity, and Prevent IllnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- BIO First Quarter ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO First Quarter ReviewerBb. JayNo ratings yet
- Nutrition & Diet Theraphy: 2 SEMESTER, A.Y. 2023 - 2024 (PRELIMS)Document5 pagesNutrition & Diet Theraphy: 2 SEMESTER, A.Y. 2023 - 2024 (PRELIMS)x9wmymnkn6No ratings yet
- 6 Essential Nutrients FinalDocument12 pages6 Essential Nutrients FinalAbas S. AcmadNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 7 (Health) : For LearnerDocument16 pagesMAPEH 7 (Health) : For LearnerRubie Ann Capila PanesNo ratings yet
- NDT LecDocument13 pagesNDT LecAia RecaidoNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Prelim Notes Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument21 pagesNCM 105 Prelim Notes Nutrition and Diet Therapys.labita.sherynejoelNo ratings yet
- L1 & L2 NotesDocument8 pagesL1 & L2 Notes17 ERMINO, Nicole AngelaNo ratings yet
- Basic of Nutrition: Acute Vs ChronicDocument1 pageBasic of Nutrition: Acute Vs ChronicCYRELLE ANNE MALLARINo ratings yet
- Unit I: Basic Concepts in NutritionDocument11 pagesUnit I: Basic Concepts in NutritionLea Angel Dominique MacamNo ratings yet
- Fats or LipidsDocument4 pagesFats or LipidsJudea PagedpedNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition - Lesson 1Document2 pagesFood and Nutrition - Lesson 1donny pangilinanNo ratings yet
- Cattle Nutrition and IntegumentDocument9 pagesCattle Nutrition and IntegumentMd. Ismail HosenNo ratings yet
- White Printable Notes Template Daily Planner Pages Habits Tracker Digital PlannerDocument3 pagesWhite Printable Notes Template Daily Planner Pages Habits Tracker Digital PlannerClarish Ann CaranzoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Nutrition TransDocument7 pagesBiochem Nutrition TransCyril Dayne Marie BaldeNo ratings yet
- Bio2 ReviewerDocument17 pagesBio2 ReviewerSophia Bianca LapuzNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Proteins: PE 2 - MidtermDocument4 pagesNutrition Proteins: PE 2 - Midtermgatuslao micaNo ratings yet
- The Body Will Become The Body's Source of Energy.: Food - Any Substance Which When Taken byDocument3 pagesThe Body Will Become The Body's Source of Energy.: Food - Any Substance Which When Taken byfrancyn correaNo ratings yet
- What Is NutritionDocument11 pagesWhat Is NutritionWing Yeng TanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesIGCSE Biology Digestive SystemDr.CharinNo ratings yet
- NutriLec NotesDocument2 pagesNutriLec NotesJOHN ROGER VILLEGASNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION - Nutrition and MacronutrientsDocument20 pagesINTRODUCTION - Nutrition and MacronutrientsChiz EscubuaNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument2 pagesBiology ReviewerROVIE LORAINE MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument9 pagesLecture - Nutrition and Diet TherapyLalaine Marie BianzonNo ratings yet
- Print Lecture 1 - Nutrition Overview - QuizletDocument6 pagesPrint Lecture 1 - Nutrition Overview - QuizletelanineNo ratings yet
- PROTEINSDocument5 pagesPROTEINSG tarangcoNo ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition and Diet TheraphyDocument3 pagesBasic Nutrition and Diet TheraphyJan Vincent BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Nutri Diet LecDocument4 pagesNutri Diet Lecdennise reyesNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN TLE Nutrient ContentDocument4 pagesLESSON PLAN TLE Nutrient ContentLerma CanuelNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Nutrition Part 1Document9 pagesCHAPTER 6 Nutrition Part 1NoniaqAmadNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition and Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesAnimal Nutrition and Digestive SystemJan Alixia BasilioNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument32 pagesProteinYo1No ratings yet
- Ncma 215 Lec 1 2Document4 pagesNcma 215 Lec 1 2KENSEY MOORE EBROLENo ratings yet
- Notes - Nutrition in MammalDocument15 pagesNotes - Nutrition in MammalEricNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT UNIT 4 - Nutrition and NutrientsDocument2 pagesPATHFIT UNIT 4 - Nutrition and NutrientsRhea Mae PerezNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiology ReviewerEndrea Kate EstolasNo ratings yet
- Nutritional and Dietary Lecture ReviewerDocument4 pagesNutritional and Dietary Lecture ReviewerJohn Mikelangelo V. AndonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Biology 2 1ST QuarterDocument21 pagesReviewer in Biology 2 1ST QuarterBeverly A PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Principles of NutritionDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Nutritionjeannyskelton13No ratings yet
- Ncm105 Nutrition and DietDocument13 pagesNcm105 Nutrition and DietRizald CordovaNo ratings yet
- Nutrient EsDocument1 pageNutrient EsJulieta GomezNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyorla earnshawNo ratings yet
- 3 Human Digestive SystemDocument62 pages3 Human Digestive SystemKip SkipperNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document6 pagesGeneral Biology 2no nameNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Humans Detailted Functions and AdvantagesDocument10 pagesNutrition in Humans Detailted Functions and AdvantagessameehaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1Document4 pagesChemistry 1cyprianNo ratings yet
- Human NutritionDocument18 pagesHuman NutritionVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- PE FinalDocument26 pagesPE FinalCheryz Angel LabillesNo ratings yet
- Diet and Growth (Carbs and Proteins)Document22 pagesDiet and Growth (Carbs and Proteins)Shaik ShaahidNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Nutrition in BiochemistryDocument3 pagesEssentials of Nutrition in BiochemistryReginald GironNo ratings yet
- Health Education On LeakemiaDocument5 pagesHealth Education On LeakemiaJyoti SidhuNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 and 2 Finals - 094511Document1 pageActivity 1 and 2 Finals - 094511Joshua AysonNo ratings yet
- Ayson Joshua RDocument3 pagesAyson Joshua RJoshua AysonNo ratings yet
- JekwhdlDocument2 pagesJekwhdlJoshua AysonNo ratings yet
- Ayson Joshua RDocument3 pagesAyson Joshua RJoshua AysonNo ratings yet
- Gordons C6Document2 pagesGordons C6Joshua AysonNo ratings yet
- Patient InfoDocument2 pagesPatient InfoJoshua AysonNo ratings yet
- Memo1 WPS OfficeDocument1 pageMemo1 WPS OfficeJoshua AysonNo ratings yet
- GoodNotes 4Document3 pagesGoodNotes 4Joshua AysonNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument2 pagesQuizJoshua AysonNo ratings yet
- NDT InfogDocument1 pageNDT InfogJoshua AysonNo ratings yet
- Iando Monitoring: CHN Ii Clinical InstructorDocument55 pagesIando Monitoring: CHN Ii Clinical InstructorJoshua AysonNo ratings yet
- Taskk 2 For BadmintonDocument1 pageTaskk 2 For BadmintonJoshua AysonNo ratings yet
- IskripDocument3 pagesIskripJoshua AysonNo ratings yet
- FNP Week 3 4Document7 pagesFNP Week 3 4Joshua AysonNo ratings yet
- Phed 1032 Module 1 2Document22 pagesPhed 1032 Module 1 2Joshua AysonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 7Document3 pagesWorksheet 7Joshua AysonNo ratings yet
- Kub Notes - PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesKub Notes - Photosynthesisapi-520249211No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 12 Respiration - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 12 Respiration - CIE Biology IGCSEJane LeaNo ratings yet
- Buddhism, Science and Atheism by Douglas M. BurnsDocument43 pagesBuddhism, Science and Atheism by Douglas M. Burnsclaughlinsr4721No ratings yet
- Stoichiometry of Cell Growth and Product FormationDocument2 pagesStoichiometry of Cell Growth and Product Formationmneilg0% (1)
- BIOB111 - Subject OutlineDocument7 pagesBIOB111 - Subject OutlineMine CraftNo ratings yet
- "Wanted: Dead or Alive?": Department of EducationDocument16 pages"Wanted: Dead or Alive?": Department of EducationJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- Disorder in Purines MetabolismDocument18 pagesDisorder in Purines MetabolismHikma PrajawatiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Fermentation ProcessesDocument59 pagesBiochemistry of Fermentation ProcesseslazytinkuNo ratings yet
- A Review of Microalgal Growth Under StressDocument7 pagesA Review of Microalgal Growth Under Stressapi-357824055No ratings yet
- Exosome-Mediated Metabolic Reprogramming: The Emerging Role in Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling and Its in Uence On Cancer ProgressionDocument13 pagesExosome-Mediated Metabolic Reprogramming: The Emerging Role in Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling and Its in Uence On Cancer ProgressionHossam El-basiounyNo ratings yet
- Enzymes STEM CaseDocument2 pagesEnzymes STEM Casegiamaj4No ratings yet
- 9 1 WKSTDocument3 pages9 1 WKSTapi-262378640No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 12 Respiration - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 12 Respiration - CAIE Biology IGCSEtrickster jonasNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Grade 10 2019 (Autosaved)Document40 pagesEnzymes Grade 10 2019 (Autosaved)Asawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument24 pagesDiabetes MellitusIgwe SolomonNo ratings yet
- 202incoperation of Nitrogen Into Amino Acids PDFDocument38 pages202incoperation of Nitrogen Into Amino Acids PDFnyasha chinyangaNo ratings yet
- Niara Baksh and Selina Beharry - Ketoacidosis ProjectDocument7 pagesNiara Baksh and Selina Beharry - Ketoacidosis ProjectSelina BeharryNo ratings yet
- Outline: Course Objectives Plan For The Semester Introduction To PharmacyDocument80 pagesOutline: Course Objectives Plan For The Semester Introduction To PharmacyLan FdzNo ratings yet
- Entropy: Autocatalytic Sets and The Origin of LifeDocument10 pagesEntropy: Autocatalytic Sets and The Origin of LifeKamagara Roland AndrewNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument10 pagesECOSYSTEMRyanKingjimDiezUyNo ratings yet
- Ketosis-Causes AND Consequences: Biochemistry For Medics WWW - Namrata.coDocument39 pagesKetosis-Causes AND Consequences: Biochemistry For Medics WWW - Namrata.corohishaakNo ratings yet
- METABÓLITOS SECUNDÁRIOS para TRATAMENTO DE DIABETESDocument67 pagesMETABÓLITOS SECUNDÁRIOS para TRATAMENTO DE DIABETESNathalia CibelleNo ratings yet
- Biochem of Carbohydrates - ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiochem of Carbohydrates - ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet