Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FoB CellTransport Vocabulary
Uploaded by
12620260 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
FoB_CellTransport_Vocabulary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesFoB CellTransport Vocabulary
Uploaded by
1262026Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Foundations of Biology
Cell Transport
Vocabulary Terms
1. Homeostasis - the process of keeping the internal conditions of an organism stable
2. Cellular Transport - the movement of materials into and out of the cell
3. Hydrogen Bond - the attraction between a hydrogen atom on one water molecule and
the oxygen atom on another water molecule
4. High Heat Capacity - the amount of heat energy required to increase its temperature
5. Adhesion - an attraction between molecules of different substances
6. Cohesion – an attraction between molecules of the same substance
7. Surface Tension - cohesion of water with a film-like quality on the surface of a liquid
8. Capillary Action - tendency of a liquid to draw up into a narrow tube due to the liquid’s
properties of cohesion and adhesion
9. Solution - composed of two parts: solute and solvent
10. Solute - the substance that is dissolved
11. Solvent - the substance in which the solute dissolves
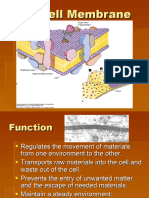
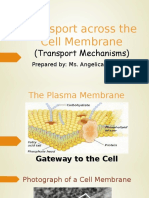
12. Cell Membrane - regulates what enters and leaves the cell and protects and supports
the cell
13. Selectively Permeable - that some substances can pass across them and others cannot
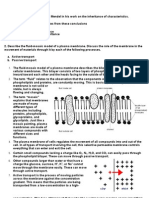
14. Phospholipid Bilayer - the composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered
sheet, which gives cell membranes a flexible structure and forms a strong barrier
between the cell and its surroundings
15. Hydrophobic – hates waters
16. Hydrophilic – loves water
17. Fluid Mosaic Model - describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of
components —including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates—that
gives the membrane a fluid character
18. Cell Walls - lie outside of the cell membrane and most are porous enough to allow
water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and certain other substances to pass through easily
19. Passive Transport - the movement of materials across the cell membrane without using
energy like osmosis and diffusion
20. Active Transport - the movement of materials against a concentration gradient using
ATP energy such as endocytosis and exocytosis
21. Dynamic Equilibrium - the state of having equal concentrations of molecules move into
or out of the cell at the same rate (exchange at the same time).
22. Concentration Gradient - a difference in the concentration of ions or other dissolved
particles between two regions
23. Diffusion - the process by which particles move from an area of high concentration to an
area of lower concentration
24. Facilitated Diffusion - uses carrier proteins or protein channel (ion channels or
aquaporins) to move ions and small molecules across the cell membrane; does not
require any additional use of the cell’s energy
25. Osmosis - the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane and the
dissolved particles (solute) cannot cross
26. Tonicity - the ability of an extracellular solution to make water move into or out of a cell
by osmosis
27. Isotonic - particle concentration is the same so no net movement of water
28. Hypertonic - particle concentration is greater outside of the cell so water moves out of
the cell causing the cell to shrink, shrivel, pull against the cell wall, or wilt
29. Hypotonic - particle concentration is greater inside the cell so water moves into the cell
causing the cell to swell, burst (animal cell), push against the cell wall, or stand upright
to support heavy structures like leaves or flowers
30. Turgot Pressure - the pressure created by osmosis as water enters the plant cell
31. Osmotic Pressure - the pressure at which osmosis (the flow of water across the
membrane) stops even if the concentrations are not equal on both sides of the
membrane
32. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) - adenine base, ribose sugar, and three phosphate
groups; releases energy when the bond between second and third phosphate group is
broken
33. Endocytosis - the process of taking materials into the cell by means of enfolding
(pockets) of the cell membrane.
34. Exocytosis - the process of releasing large amounts of materials from the cell
35. Phagocytosis - the transporting of solid objects into the cell; “cell eating”
36. Pinocytosis - the transporting of fluid into the cell; “cell drinking”
You might also like
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- 2.1.5 Biology Ocr ADocument5 pages2.1.5 Biology Ocr AFatima AfifiNo ratings yet
- Cell ConstituentsDocument8 pagesCell ConstituentsSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- General Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)Document4 pagesGeneral Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)alfonsogwenmnqNo ratings yet
- Science 2.1 ReviewDocument6 pagesScience 2.1 ReviewInes GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Cell TransportDocument4 pagesCell Membrane and Cell TransportAtasha MojecaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Membrane Structure and FunctionIrish Jem BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument24 pagesUntitled PresentationFreyacresaNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology Theory 2Document18 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory 2ao868598No ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument1 pageTransport MechanismsJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasismadhutkNo ratings yet
- Significance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport MechanismDocument10 pagesSignificance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport Mechanismroshan khanNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanisms in CellDocument28 pagesTransport Mechanisms in CellTrisha Loise VillacampaNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesCell MembraneQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisMal FujitakaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Bio QuizDocument5 pagesCell Membrane Bio QuizMafalda SeabraNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Transport NotesDocument24 pagesCell Membrane Transport NotesJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument5 pagesCell MembranesTiaraHadiAshariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Cell MembranesDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - Cell Membranessennakooiman04No ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisMaxellLanceClementNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ModifiedDocument58 pagesChapter 7 ModifiedJohnYooNo ratings yet
- BIO Ch.7VocabDocument2 pagesBIO Ch.7VocababNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument37 pagesCell TransportxspiirONo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology NotesDocument11 pagesYear 11 Biology Notesayaan.huss207No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneDocument15 pagesCell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneMariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Document7 pagesBIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Student Alejandro Zhou WeiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- 3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument67 pages3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsThom PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- The Cell MembraneDocument23 pagesThe Cell MembraneNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Reviewer 1Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Reviewer 1Shane Patricia CalmaNo ratings yet
- Cell Surface MembraneDocument3 pagesCell Surface Membraneb111broomNo ratings yet
- X Membrane and TransportDocument35 pagesX Membrane and TransportHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsVince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Cell Classix Notes Session2 Made by Purnima SharmaDocument4 pagesCell Classix Notes Session2 Made by Purnima Sharmajeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- The Cell TheoryDocument3 pagesThe Cell TheoryEARLRYAN TUMBALENo ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument7 pagesAbsorption by Rootsshreya morajkarNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Essay 1983Document3 pagesAP Bio Essay 1983pezxo6No ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesDocument9 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35No ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Lipid Bilayer - 2 Layers of PhospholipidsDocument18 pagesHomeostasis: Lipid Bilayer - 2 Layers of PhospholipidsLoraine Anne Marie BaguioNo ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument7 pagesAbsorption by RootsSaswatNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpDocument67 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpSilver CypressNo ratings yet
- MF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2Document33 pagesMF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- L-3 Cell Mech. of Transport PDFDocument33 pagesL-3 Cell Mech. of Transport PDFdemaNo ratings yet
- Bio 12 Plo b9 and b10 Transport Across Cell Membrane Vocabulary SolutionsDocument4 pagesBio 12 Plo b9 and b10 Transport Across Cell Membrane Vocabulary SolutionsChan KarlokNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesDocument11 pagesThe Plasma Membrane: Membranes Cover The Surface of Every Cell, and Also Surround Most OrganellesSyeda Kaneez Mohammadi MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Bio-Reviewer 12 STEM 1ST SEMDocument8 pagesBio-Reviewer 12 STEM 1ST SEMAiyana Bettina FelipeNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument19 pagesTransport MechanismAaron Roxas100% (2)
- LESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Document4 pagesLESSON - 11 - Gen Biology 1Jhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsCaroleNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3Document8 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3MSKNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 4Document6 pagesBiology - Module 4ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Movement of MoleculesDocument17 pagesMovement of MoleculesMatthew ThomasNo ratings yet
- Handout 4 Cell TransportDocument4 pagesHandout 4 Cell TransportCrissan Jejomar AbanesNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants Part 1Document12 pagesTransport in Plants Part 1Andre MorrisonNo ratings yet
- STD Ix Bio 1Document4 pagesSTD Ix Bio 1Sourav DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Transport Across Cell MembranesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Transport Across Cell Membranesnoreen dorani100% (1)
- 2 Cell TransportationDocument3 pages2 Cell TransportationxNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 4 Cell Transport ReviewerDocument7 pagesTOPIC 4 Cell Transport Reviewerashhii ramosNo ratings yet
- Act2 Bio SciDocument4 pagesAct2 Bio SciPamaran, Kristel DenishNo ratings yet
- Bell Ringer Unit 3 Day 2Document1 pageBell Ringer Unit 3 Day 21262026No ratings yet
- Bell Ringers Unit 2 Day 2Document1 pageBell Ringers Unit 2 Day 21262026No ratings yet
- Alaija Math ClassDocument2 pagesAlaija Math Class1262026No ratings yet
- Graphing Systems of Linear InequalitiesDocument2 pagesGraphing Systems of Linear Inequalities1262026No ratings yet
- Communist Vs Capitalist DBQDocument3 pagesCommunist Vs Capitalist DBQ1262026No ratings yet
- Detoxification of Hazardous ChemicalsDocument1 pageDetoxification of Hazardous ChemicalsBalaji Prasanna Kumar100% (2)
- ULT.A3X2G5+BK23187-A 000000000030246042 SDS GEN US en 9-0Document11 pagesULT.A3X2G5+BK23187-A 000000000030246042 SDS GEN US en 9-0mcincicNo ratings yet
- Technical Report of Formic Acid PlantDocument6 pagesTechnical Report of Formic Acid PlantMuzzamilNo ratings yet
- Mind Map MinorDocument43 pagesMind Map MinorAliia HamdanNo ratings yet
- P Block ElementsDocument24 pagesP Block ElementsAsish GeiorgeNo ratings yet
- Maders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Longenbaker Test BankDocument40 pagesMaders Understanding Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Longenbaker Test Bankashley100% (17)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 9iDocument7 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 9iBaby Joy Jovita-BasubasNo ratings yet
- B368-09 (2014) Standard Test Method For Copper-Accelerated Acetic Acid-Salt Spray (Fog) Testing (CASS Test) PDFDocument4 pagesB368-09 (2014) Standard Test Method For Copper-Accelerated Acetic Acid-Salt Spray (Fog) Testing (CASS Test) PDFdiego rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Washing Powder FormulationDocument4 pagesWashing Powder FormulationDeogracious Chawira71% (7)
- Iodine Value - WikipediaDocument9 pagesIodine Value - WikipediaFabio OliveiraNo ratings yet
- POCH Safety Data Sheet: MercuryDocument3 pagesPOCH Safety Data Sheet: MercuryRizkyNo ratings yet
- Cerami Flex FGDocument2 pagesCerami Flex FGdonaldoguerreroNo ratings yet
- PVC's Physical Properties - PVCDocument8 pagesPVC's Physical Properties - PVCalguzduxtanNo ratings yet
- Analysis On Pakistan Soft Grade PVC MarketDocument6 pagesAnalysis On Pakistan Soft Grade PVC MarketShahid IqbalNo ratings yet
- 2.306-Confined Space Entry1Document14 pages2.306-Confined Space Entry1kirandevi1981No ratings yet
- Types of MetamorphismDocument8 pagesTypes of MetamorphismLuis Miguel Mogollon RamosNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Stainless Steel and Carbon SteelDocument6 pagesDifference Between Stainless Steel and Carbon SteelQaisir MehmoodNo ratings yet
- CH2 Transition Metals Unit V A2 LevelDocument9 pagesCH2 Transition Metals Unit V A2 LevelbillaljavedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Chemical QuantitiesDocument44 pagesChapter 10 - Chemical Quantitiesapi-256257174No ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Process Safety and Environment ProtectionDocument75 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Process Safety and Environment ProtectionDiego TorresNo ratings yet
- 14th-Group Elements (45-60)Document16 pages14th-Group Elements (45-60)krish masterjeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Introduction To Composite Materials Lecture 1: Introduction To Composite MaterialsDocument75 pagesLecture 1: Introduction To Composite Materials Lecture 1: Introduction To Composite MaterialsUtsho DasNo ratings yet
- A Mechanical Aspect of Borides Formed On The AISI 440C Stainless SteelDocument6 pagesA Mechanical Aspect of Borides Formed On The AISI 440C Stainless SteelSergio Fernando Resendiz PerezNo ratings yet
- BUEFA®-Spezial+products GBDocument5 pagesBUEFA®-Spezial+products GBsearun327No ratings yet
- Salt Analysis: Exercise - I Exercise - IiDocument12 pagesSalt Analysis: Exercise - I Exercise - Iijash maniarNo ratings yet
- CH101 Tutorial Sheet 2Document2 pagesCH101 Tutorial Sheet 2Amelia IloNo ratings yet
- Boiler Cycle Control: Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesBoiler Cycle Control: Questions and AnswersChanBoonChewNo ratings yet
- What Is Limiting Excess ReactantDocument25 pagesWhat Is Limiting Excess Reactantjaeyoon shimibibiNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Ceramica Sanitaryware Eng Ita Rus 2017Document12 pagesCatalogo Ceramica Sanitaryware Eng Ita Rus 2017muhammad abidinNo ratings yet
- Contoh ESSAY Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesContoh ESSAY Dalam Bahasa Inggrisayoe yoesriyyaNo ratings yet