Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organelle Work
Uploaded by
blackman694202Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organelle Work
Uploaded by
blackman694202Copyright:
Available Formats
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
What are the functions of different organelles in a cell?
Why?
The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell.
These structures are called organelles.
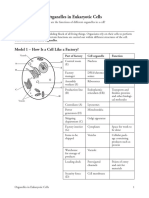
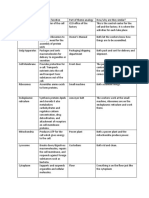
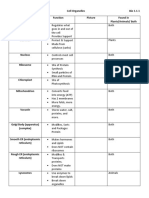
Model 1 – How Is a Cell Like a Factory?
Vacuole Part of factory Cell organelle Function
Cell membrane
D Control room Nucleus Contains and
Lysosomes A (E) protects genetic
ER E Nucleus material (DNA)
B
Factory DNA/chromo- Information for
manager somes making proteins
Assembly
F Ribosomes Make proteins
Ribosomes workers (F)
G
CytoplasmProduction line Endoplasmic Transports and
Golgi Body C
(B) reticulum (ER) finishes proteins
H and other biologi-
Mitochondria cal molecules
Vesicles
Break down substances
Custodians (A) Lysosomes
Produces
Power Mitochondria energy/powerhouse
generators (H) of the cell
Shipping Golgi apparatus Sorts proteins for
department (C) transport
Factory interior Cytoplasm Space for work to
(G) be done
Items to be Vesicles Cellular pack-
shipped age containing
products such as
protein
Warehouse Vacuole Stores
for storage of substances
products
Loading dock Pores/gated Points of entry
channels and exit for
materials
Selectively permeable
Security fence Cell membrane membrane that controls
(D) what enters/exits
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 1
1. Using the letters from the table in Model 1, label the cell diagram with the organelle names.
2. According to the table,
a. what substance is analogous to a factory manager?
DNA/Chromosomes
b. in what organelle would this substance be found?
Cell Nucleus
3. Using the information in Question 2, which cell organelle controls the activities of the entire cell?
Nucleus
4. Which organelle generates energy to power cellular activities?
Mitochondria
5. Which organelle is responsible for assembling proteins?
Riboosome
6. Once proteins have been assembled, to which organelle would they go next?
ER
7. Into what organelle might the cellular products be placed?
vacuoles
8. Fill in the missing functions of cellular organelles in the table in Model 1.
9. Starting with instructions from the factory manager (DNA/chromosomes), create a flow chart to
show how a protein is produced and shipped from a cell.
DNA --> RNA-->Ribosomes-->Golgi Body -->ER--> Cell membrane
Proteins are produced in different steps. For example, when the DNA is replicated in the nucleus of the
cell. Those DNA strands form to create mRNA which has the code to assemble/make the proteins. The
mRNA goes to the ribosome and the instructions are decoded. Then, the codons/amino acids attach to
the tRNA to make a protein.
2 POGIL™ Activities for High School Biology
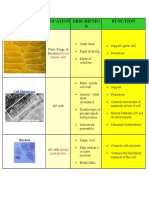
Model 2 – Animal Cells with Organelle(s) Removed
Cell 1 Cell 2 Cell 3
Missing nucleus Missing mitochondria Missing cell membrane
Cell 4 Cell 5 Cell 6
Missing dots in ER Missing Lysosome Missing Golgi Body
Cell 7 Cell 8 Cell 9
Missing ER Missing nucleus and ER Nothing missing
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 3
10. Study the cells in Model 2. Which cell is not missing any organelles compared to Model 1?
Cell 9
11. Look carefully at Cell 2 in Model 2. Compared to Model 1, what kind of organelle is missing?
Mitochondria
12. Using grammatically correct sentences, describe why Cell 2 would not function normally.
Cell 2 would not function properly because it is missing the mitochondria. Without the
mitochondria, the cell organelles would not be able to function due to lack of energy.
13. Which two cells in Model 2 will have difficulty containing and getting rid of wastes within the
cell? Why?
Cell 3 and cell 4 would have a hard time getting rid of waste because there is no cell
membrane to allow waste to leave. Also, cell 5 does not have Lysosomes to break down
different substances so it can't get rid of the waste.
14. Cell 1 is missing one organelle. List as many reasons as possible why Cell 1 will not survive.
Cell 1 will not survive because it is missing the nucleus. The nucleus carries instruction(DNA) on
how to synthesize proteins. Also, the nucleus control cell division and without a nucleus all these
function listed cannot be carried out.
15. Cell 4 and Cell 7 will not be able to synthesize a major biological molecule. What molecule is
this?
Protein
4 POGIL™ Activities for High School Biology
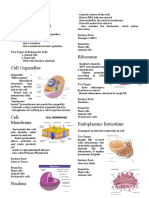
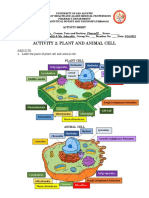
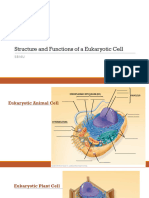
Model 3 – Animal Cell vs. Plant Cell
Animal Cell Plant Cell
16. Do both cells in Model 3 have a nucleus?
Yes, both cells do have a nucleus
17. Do both cells in Model 3 have mitochondria?
Yes, both cells do have a mitochondria
18. Describe at least three differences between the animal and plant cells shown in Model 3.
The animal cell have small vacuoles, no cell wall, and chloroplasts and plant cells have a cell wall,
chloroplasts, and big central vacuoles.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 5
Read This!
Plant cells have three organelles not found in animal cells. They include the cell wall, large central
vacuole, and plastids (including chloroplasts).
19. Complete the table below using the three plant organelles mentioned in the Read This! box.
Organelle Function
Fluid-filled organelle stores water, enzymes, and waste products.
Vacuole Size of this organelle can change.
cell wall Supports and protects the cell.
Some store food or pigments; some convert light energy to
chloroplasts chemical energy in the form of organic compounds.
20. Label each of these three organelles on the plant cell diagram in Model 3.
21. Individually, in one grammatically correct sentence, describe why it is necessary for plants to have
chloroplasts.
Plants need chloroplasts to turn sunlight, CO2, water for food. (This process is called
photosynthesis.)
22. As a group, reach a consensus on the answer to Question 21. Record the answer below.
Plants need chloroplasts to successfully do photosynthesis for energy.
23. The central vacuole stores water. What would happen to the size of the central vacuole if a plant
does not have enough water?
The vacuole would would decrease in size.
24. Describe the appearance of the vacuole in a well-watered plant. What effect would this have on
the cell wall of the plant?
The vacuole would increase in size storing more water for the cell and the cell wall would also
increase in size.
25. Using your response to Question 24, construct an explanation for why a plant has both a rigid
cell wall and a cellular membrane.
Plants need both a rigid cell wall and a cell membrane because the cell wall will keep the plant can
its structure as well as support the plant.
6 POGIL™ Activities for High School Biology
Extension Questions
Read This!
All cells undergo cellular respiration for the production of energy. Energy is necessary for all metabolic
activity within the cell.
The formula for cellular respiration is
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ⎯⎯→ 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy/ATP
Plants carry out photosynthesis for the production of glucose. The glucose then becomes the energy
source for cellular respiration.
The formula for photosynthesis is
Sun’s energy
6CO2 + 6H2O ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯→ C6H12O6 + 6O2
26. Study the information given in the Read This! box.
a. In what organelle does cellular respiration occur?
Mitochondria
b. Do plant and animal cells both have this structure?
Yes, both plant and animal cells have this structure.
27. In what organelle does photosynthesis occur? Do plant and animal cells both have this structure?
Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts which is only found in plant cells.
28. Using the equations above, explain the relationship between mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts make carbohydrates and the mitochondria convert the carbohydrates into energy.
29. Plants have both mitochondria and chloroplasts; they can produce their own glucose to fuel
cellular respiration. Animal cells, on the other hand, have only mitochondria. If an animal eats
only meat what would be its source of glucose?
If the animal only eats meat, it would not have a source of glucose since meat does not contain
glucose.
30. Where in the human body would you find cells with a large number of mitochondria? Why?
I would expect a large number of mitochondria in muscle cells because muscle cells need a
lot of energy to function.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells 7
You might also like
- 8 Organelles in Eukaryote Cells S PDFDocument7 pages8 Organelles in Eukaryote Cells S PDFHolden Kodish100% (1)
- Ynice Bostic - 8 Organelles in Eukaryote Cells-SDocument7 pagesYnice Bostic - 8 Organelles in Eukaryote Cells-SYnice BosticNo ratings yet
- Cells: Unit 1: Subject Standards/Content and OST AlignmentDocument17 pagesCells: Unit 1: Subject Standards/Content and OST Alignmentflorie jane macayaNo ratings yet
- B1 - Trilogy Cells - Knowledge GoalDocument2 pagesB1 - Trilogy Cells - Knowledge GoalmagentaihdNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory: Everything Is Made of CellsDocument2 pagesCell Theory: Everything Is Made of CellsRevathy J SNo ratings yet
- 8 Cells - Simile - AssignmentDocument4 pages8 Cells - Simile - AssignmentRileytucks8No ratings yet
- Answer Each Question of This Workshop With The Sources of Information That Are in The Last Page of This FileDocument7 pagesAnswer Each Question of This Workshop With The Sources of Information That Are in The Last Page of This Filejorge luis torresNo ratings yet
- 02 - Cell Worksheet Factory CardsDocument5 pages02 - Cell Worksheet Factory Cardsangeladel484No ratings yet
- Beige Watercolor Leaf Blank Notepaper 8.5 X 11 LetterDocument1 pageBeige Watercolor Leaf Blank Notepaper 8.5 X 11 LetterWallace RamosNo ratings yet
- CellDocument2 pagesCellJhon Rey LagosNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell: Organelle Function Factory PartDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Cell: Organelle Function Factory PartLeonarda Bagtindon LicayanNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesShakib al molik100% (1)
- Cell RioDocument7 pagesCell RioRyan Freud CuadrazalNo ratings yet
- Zoo Lab ActivityDocument1 pageZoo Lab ActivityHarold DavidNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 2.2 Cell Structure and Function: ScoreDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 2.2 Cell Structure and Function: ScoreCHONG KOK HIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganelleDocument9 pagesCell OrganelleGwencytech DomingoNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Func.Document6 pagesPlant and Animal Func.Mohamed YahiaNo ratings yet
- Plant Animal Cell ChartDocument1 pagePlant Animal Cell ChartKram YnothnaNo ratings yet
- 1B OrganellesDocument5 pages1B OrganellesqueyrhiaNo ratings yet
- Soll Nrm1333Document11 pagesSoll Nrm1333Jon BoNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of Cells (A) Diagram of Prokaryotes (B) Diagram of EukaryotesDocument3 pagesInternal Structure of Cells (A) Diagram of Prokaryotes (B) Diagram of EukaryotesKim Angelica AbongNo ratings yet
- Cell Analogy Chart ExampleDocument2 pagesCell Analogy Chart ExampleValeria ZumaetaNo ratings yet
- Name: Shany C. Bantayanon Grade & Sec. 12D-STEM Date: 08/31/21 Learning Activity No. 2 Organelle NicknamesDocument3 pagesName: Shany C. Bantayanon Grade & Sec. 12D-STEM Date: 08/31/21 Learning Activity No. 2 Organelle NicknamesShane BantayanonNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell StructureDocument2 pages2.1 Cell StructureZarmina KhanNo ratings yet
- LetsBuildAPlantCell PDFDocument7 pagesLetsBuildAPlantCell PDFmasturinaNo ratings yet
- Biological ScienceDocument4 pagesBiological ScienceMae CalumpianoNo ratings yet
- Cells: Structure and FunctionDocument31 pagesCells: Structure and FunctionlordniklausNo ratings yet
- Ph1F1-PhBioSCi1a-Activity 2-Individual-GloriaDocument7 pagesPh1F1-PhBioSCi1a-Activity 2-Individual-GloriaAllysa GloriaNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document29 pagesModule 2Erica Jazzanne LopezNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument27 pagesCell Structure and Cell OrganisationAzmaniza AdnanNo ratings yet
- Ciclo 3. Septimo4. Cell OrganellesDocument24 pagesCiclo 3. Septimo4. Cell OrganellesMarianita MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Hand Out For BiologyDocument7 pagesHand Out For BiologyLevin John BarcimoNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesrhdoiuaNo ratings yet
- Organelle Nicknames!: InstructionsDocument3 pagesOrganelle Nicknames!: InstructionsJay xeeNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cell StructureDocument1 page1.1 Cell Structuremii chanrNo ratings yet
- Monday 18th Tuesday 19th Wednesday 20 Thursday 21 Friday 22 Saturday 23 Sunday 24Document2 pagesMonday 18th Tuesday 19th Wednesday 20 Thursday 21 Friday 22 Saturday 23 Sunday 24Luka MaroNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument111 pagesBiologyHana JuiceNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Property Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsDocument4 pagesComparison Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Property Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsKarl Leo Hee YeongNo ratings yet
- Lecture For BiologyDocument39 pagesLecture For BiologyChristian MinayaNo ratings yet
- Bio Benchmark Review Menu 2018-19Document22 pagesBio Benchmark Review Menu 2018-19api-458291086No ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Cell Parts & FunctionDocument23 pagesLESSON 2 - Cell Parts & FunctionThe DarkCrafter 423No ratings yet
- Cell Bio MidtermDocument4 pagesCell Bio MidtermCó Tên KhôngNo ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument7 pagesCell NotesBrohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm: (Between Nucleus and Cell Membrane) Organelles Suspended in Gel-Like GooDocument31 pagesCytoplasm: (Between Nucleus and Cell Membrane) Organelles Suspended in Gel-Like Gooeden CoveNo ratings yet
- Bio - Cell Structure and Function QuizDocument2 pagesBio - Cell Structure and Function QuizAditi AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- 9 - Eukaryotic Cell - 2022Document22 pages9 - Eukaryotic Cell - 2022tireddoodleNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)Document46 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument20 pagesCellsRand HusseinNo ratings yet
- Cells: Nillena Maria SibyDocument7 pagesCells: Nillena Maria SibyNileena Maria sibyNo ratings yet
- Chapter07 Section02 EditDocument22 pagesChapter07 Section02 EditMarjunie CAMONGAYNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Functions Review ANSWER KEYDocument7 pagesCell Structures and Functions Review ANSWER KEY김꽁쥬No ratings yet
- Completed Concept Map PDFDocument1 pageCompleted Concept Map PDFBombo MartinNo ratings yet
- Tour of The Cell Recitation (Fa18)Document7 pagesTour of The Cell Recitation (Fa18)Michael AllisonNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Key Concepts in BiologyDocument15 pagesTopic 1 - Key Concepts in BiologyEshaal KhanNo ratings yet
- Cells F05Document31 pagesCells F05Fetro Dola SyamsuNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument1 pagePlant Cellallan.uyNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument15 pagesCell BiologyRania KhurshidNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab - Activity in Cell and MicroscopeDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lab - Activity in Cell and MicroscopeAlvin Cris RongavillaNo ratings yet
- BIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Document5 pagesBIO104E-Laboratory Activity. (The Cell)Stephen AzaresNo ratings yet
- Catalytic AntibodiesFrom EverandCatalytic AntibodiesEhud KeinanNo ratings yet