Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TOPIC 2 - Cell - PDF - Cell (Biology) - Cell Membrane
TOPIC 2 - Cell - PDF - Cell (Biology) - Cell Membrane
Uploaded by
Kedir MohammedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TOPIC 2 - Cell - PDF - Cell (Biology) - Cell Membrane
TOPIC 2 - Cell - PDF - Cell (Biology) - Cell Membrane
Uploaded by
Kedir MohammedCopyright:
Available Formats
Search EN Upload Read free for 30 days
9 of 9 Search document
100% (1) · 4 views · 9 pages
TOPIC 2 - Cell
Uploaded by Al Johan Atienza on Oct 14, 2023 AI-enhanced title
Full description
Save 100% 0% Embed Share
9 of 9 Search document
You might also like
Document 10 pages
1.1cell concept
TOPIC 2: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Mokariya Sanjay
No ratings yet
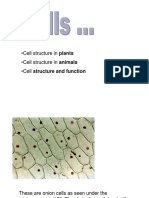
Cells are the basic, fundamental unit of life. So, if we were to break apart an organism to
the cellular level, the smallest independent component that we would find would be the
cell.
Explore the cell notes to know what a cell is, cell definition, cell structure, types, and
functions of cells. Document 10 pages
The cell.docx
Abeer Alnajjar ﻋﺒﯿﺮ اﻟﻨﺠﺎر
No ratings yet
Document 31 pages
Cells
Pranav Shinde
The Animal Cell No ratings yet
Cells are the fundamental unit of life. They range in size from 0.0001 mm to nearly 150
mm across.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ApvxVtBJxd0
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=URUJD5NEXC8
Cell Defini tion
“A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life’s
processes.”
Document 15 pages
Cell
prakash kushwaha
No ratings yet
Document 8 pages
CELLS_Biology
KYLENE ABELLANA
No ratings yet
Cells are the structural, functional, and biological units of all living beings. A cell can
replicate itself independently. Hence, they are known as the building blocks of life .
Each cell contains a fluid called the cytoplasm, which is enclosed by a membrane. Also Document 6 pages
present in the cytoplasm are several biomolecules like proteins, nucleic acids and lipids.
Cell Definition
Moreover, cellular structures called cell organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm.
Woobin Real
100% (1)
What is a Cell?
A cell is the structural and fundamental unit of life. The study of cells from their basic
structure to the functions of every cell organelle is called Cell Biology. Robert Hooke was
the first Biologist who discovered cells.
All organisms are made up of cells. They may be made up of a single cell (unicellular), or
many cells (multicellular). Mycoplasmas are the smallest known cells. Cells are the
building blocks of all living beings. They provide structure to the body and convert the
nutrients taken from the food into energy.
Cells are complex and their components perform various functions in an organism. They
are of different shapes and sizes, pretty much like the bricks of the buildings. Our body is
made up of cells of different shapes and sizes.
Cells are the lowest level of organization in every life form. From organism to organism,
the count of cells may vary. Humans have more number of cells compared to that
of bacteria.
Cells comprise several cell organelles that perform specialized functions to carry out life
processes. Every organelle has a specific structure. The hereditary material of the
organisms is also present in the cells.
Discovery of Cells
Discovery of cells is one of the remarkable advancements in the field of science. It helps
us know that all the organisms are made up of cells, and these cells help in carrying out
various life processes. The structure and functions of cells helped us to understand life in
a better way.
Who discovered cells?
Robert Hooke discovered the cell in 1665. Robert Hooke observed a piece of bottle cork
under a compound microscope and noticed minuscule structures that reminded him of
small rooms. Consequently, he named these “rooms” as cells. However, his compound
microscope had limited magnification, and hence, he could not see any details in the
structure. Owing to this limitation, Hooke concluded that these were non-living entities. Document 6 pages
Later Anton Van Leeuwenhoek observed cells under another compound microscope with Cell Structue and Functions
higher magnification. This time, he had noted that the cells exhibited some form of Drexel Dalaygon
movement (motility). As a result, Leeuwenhoek concluded that these microscopic entities No ratings yet
were “alive.” Eventually, after a host of other observations, these entities were named as
animalcules.
Document 7 pages
Module-1-2-Additional-
Material
Eli Joshua Evangelista
No ratings yet
In 1883, Robert Brown, a Scottish botanist, provided the very first insights into the cell
structure. He was able to describe the nucleus present in the cells of orchids.
Document 20 pages
Characteristics of Cells
????
APS Updates
Following are the various essential characteristics of cells:
No ratings yet
• Cells provide structure and support to the body of an organism.
• The cell interior is organized into different individual organelles surrounded by a
separate membrane.
• The nucleus (major organelle) holds genetic information necessary for
reproduction and cell growth.
• Every cell has one nucleus and membrane-bound organelles in the cytoplasm.
• Mitochondria, a double membrane-bound organelle is mainly responsible for the
energy transactions vital for the survival of the cell.
• Lysosomes digest unwanted materials in the cell.
• The endoplasmic reticulum plays a significant role in the internal organization of
the cell by synthesizing selective molecules and processing, directing, and sorting
them to their appropriate locations.
DIFFERENCES OF PLANTS AND ANIMAL CELLS
Types of Cells
Cells are like factories with different laborers and departments that work towards a
Document 15 pages
common objective. Various types of cells perform different functions. Based on cellular
Earth-Life-Science-Module-5
structure, there are two types of cells:
Rosalyn Pagatpatan Barola
• Prokaryotes
No ratings yet
• Eukaryotes
Prokaryotic Cells
Document 5 pages
Cell
shankaram shankaram
100% (1)
Document 11 pages
Inte Sci Grade 9 . Week 2
Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c F
No ratings yet
1. Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. Instead, some prokaryotes such as bacteria
have a region within the cell where the genetic material is freely suspended. This
region is called the nucleoid.
2. They all are single-celled microorganisms. Examples include archaea, bacteria,
and cyanobacteria.
3. The cell size ranges from 0.1 to 0.5 µm in diameter.
4. The hereditary material can either be DNA or RNA.
5. Prokaryotes generally reproduce by binary fission, a form of asexual reproduction.
They are also known to use conjugation – which is often seen as the prokaryotic
equivalent to sexual reproduction (however, it is NOT sexual reproduction).
Eukaryotic Cells
1. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a true nucleus.
2. The size of the cells ranges between 10 –100 µm in diameter.
3. This broad category involves plants, fungi, protozoans, and animals.
4. The plasma membrane is responsible for monitoring the transport of nutrients and
electrolytes in and out of the cells. It is also responsible for cell-to-cell
communication.
5. They reproduce sexually as well as asexually.
6. There are some contrasting features between plant and animal cells. For eg.,
the plant cell contains chloroplast, central vacuoles, and other plastids, whereas
the animal cells do not.
Cell Structure
The cell structure comprises individual components with specific functions
essential to carry out life’s processes. These components include- cell wall, cell
membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and cell organelles. Read on to explore more Document 11 pages
insights on cell structure and function.
Basic Concept about CELL
Cell Membrane jack ome
No ratings yet
• The cell membrane supports and protects the cell. It controls the movement of
substances in and out of the cells. It separates the cell from the external
environment. The cell membrane is present in all the cells.
• The cell membrane is the outer covering of a cell within which all other organelles,
such as the cytoplasm and nucleus, are enclosed. It is also referred to as the
plasma membrane.
Document 7 pages
• By structure, it is a porous membrane (with pores) which permits the movement of
selective substances in and out of the cell. Besides this, the cell membrane also The Cell - Zoology
protects the cellular component from damage and leakage.
Ethel May Granil
• It forms the wall-like structure between two cells as well as between the cell and
its surroundings. No ratings yet
• Plants are immobile, so their cell structures are well-adapted to protect them from
external factors. The cell wall helps to reinforce this function.
Cell Wall
• The cell wall is the most prominent part of the plant’s cell structure. It is made up Document 19 pages
of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. Cell Structures and Their
The cell wall is present exclusively in plant cells. It protects the plasma membrane
Functions SLA
•
and other cellular components. The cell wall is also the outermost layer of plant
cells. Maricar Baria
It is a rigid and stiff structure surrounding the cell membrane.
100% (1)
•
• It provides shape and support to the cells and protects them from mechanical
shocks and injuries.
Cytoplasm
• The cytoplasm is a thick, clear, jelly-like substance present inside the cell
membrane.
• Most of the chemical reactions within a cell take place in this cytoplasm.
• The cell organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, mitochondria,
and ribosomes, are suspended in this cytoplasm.
Nucleus
• The nucleus contains the hereditary material of the cell, the DNA.
• It sends signals to the cells to grow, mature, divide, and die.
• The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope that separates the DNA from
the rest of the cell.
• The nucleus protects the DNA and is an integral component of a plant’s cell
structure.
Cell Organelles
Cells are composed of various cell organelles that perform certain specific functions to
carry out life’s processes. The different cell organelles, along with its principal functions,
are as follows:
Document 18 pages
Cell Organelles and Their Functions
Cells Assignment
Muqadas
Nucleolus No ratings yet
The nucleolus is the site of ribosome synthesis. Also, it is involved in controlling cellular
activities and cellular reproduction.
Nuclear membrane
Document 45 pages
The nuclear membrane protects the nucleus by forming a boundary between the nucleus
cell theory
and other cell organelles. justine caintoy
No ratings yet
Chromosomes
Chromosomes play a crucial role in determining the sex of an individual. Each human
cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes.
Document 24 pages
Endoplasmic reticulum
***Parts of the Cell and Its
The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the transportation of substances throughout the Function
cell. It plays a primary role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, the synthesis of lipids, Ernest De Mesa Mendoza
steroids and proteins.
No ratings yet
Golgi Bodies
Golgi bodies are called the cell’s post office as it is involved in the transportation of
materials within the cell.
Ribosome
Ribosomes are the protein synthesizers of the cell.
Document 7 pages
Mitochondria Cells_tissues
Nisha Chauhan
The mitochondrion is called “the powerhouse of the cell.” It is called so because it No ratings yet
produces ATP – the cell’s energy currency.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes protect the cell by engulfing the foreign bodies entering the cell and help in
Document 14 pages
cell renewal. Therefore, they are known as the cell’s suicide bags.
Structure of Cells
Chloroplast Timothy Jones
No ratings yet
Chloroplasts are the primary organelles for photosynthesis. It contains the pigment called
chlorophyll.
Vacuoles
Document 2 pages
Vacuoles store food, water, and other waste materials in the cell.
What is a Cell
jose de jesus sanchez
Cell Theory No ratings yet
Cell Theory was proposed by the German scientists, Theodor Schwann, Matthias
Schleiden, and Rudolf Vircho w. The cell theory states that:
• All living species on Earth are composed of cells.
• A cell is the basic unit of life.
• All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
A modern version of the cell theory was eventually formulated, and it contains the
following postulates:
• Energy flows within the cells.
• Genetic information is passed on from one cell to the other.
• The chemical composition of all the cells is the same.
Functions of Cell
A cell performs major functions essential for the growth and development of an organism.
Important functions of cells are as follows:
Provides Support and Structure
All the organisms are made up of cells. They form the structural basis of all the organisms.
The cell wall and the cell membrane are the main components that function to provide
support and structure to the organism. For eg., the skin is made up of a large number of
cells. Xylem present in vascular plants is made of cells that provide structural support to
the plants.
Document 14 pages
Facili tate Growth Mitosis
Structure of Cells
In the process of mitosis, the parent cell divides into the daughter cells. Thus, the cells
Timothy Jones
multiply and facilitate the growth of an organism.
No ratings yet
Al lows Transp ort of Substances
Various nutrients are imported by the cells to carry out various chemical processes going
on inside the cells. The waste produced by the chemical processes is eliminated from the
cells by active and passive transport. Small molecules such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, Document 8 pages
and ethanol diffuse across the cell membrane along the concentration gradient. This is
Cell Biology.docx
known as passive transport. The larger molecules diffuse across the cell membrane
through active transport where the cells require a lot of energy to transport the
Mark Dave Benito Tolentino
substances. No ratings yet
Energy Production
Cells require energy to carry out various chemical processes. This energy is produced by
the cells through a process called photosynthesis in plants and respiration in animals.
Document 44 pages
Ai ds in Reproduc ti on Chapter 3
Altaf Hussain Khan
A cell aids in reproduction through the processes called mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is
termed as asexual reproduction where the parent cell divides to form daughter cells. No ratings yet
Meiosis causes the daughter cells to be genetically different from the parent cells.
Thus, we can understand why cells are known as life's structural and functional units. This
is because they provide structure to the organisms and perform several functions
necessary for carrying out life’s processes.
Fluid Mosaic Model Fluid
The fluid mosaic model was proposed by S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson. This model
explains animal cells' plasma membrane structure as a mosaic of components such as
phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. These components give a fluid
character to the membranes.
Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic head pointing outside and a hydrophobic tail forming
the inside of the bilayer.
Cholesterol and proteins are embedded in the bilayer which gives the membrane a
mosaic look. Each component has a specific function to perform.
Document 14 pages
Cell Definition
Farhan Ali
No ratings yet
Document 7 pages
Document (8)
Arslan Baba
No ratings yet
Document 17 pages
CBSE Class 8 Science
Fluid Mosaic Model
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ipa1vmQ7H_4 Chapter 8 Cell Structure a…
yashgodse…
Components of Plasma Membrane No ratings yet
Components Location
Phospholipid The main fabric of the plasma membrane
Cholesterol Between phospholipids and phospholipid bilayers
Integral proteins Embedded within phospholipid layers
Peripheral proteins The inner or outer surface of the phospholipid bilayer
Carbohydrates Attached to proteins on outside membrane layers
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules with a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail.
These are attached to a glycerol molecule by a covalent bond.
Cholesterol
It helps the plasma membrane to retain the fluidity. It is present between the phospholipids
and prevents the compaction of hydrophilic tails at low temperatures and their expansion
at high temperatures.
Proteins
The plasma membrane has three types of proteins:
• Integral Proteins: These proteins form channels to allow the movement of large
molecules and ions across the hydrophobic layer of the membrane.
Document 5 pages
Cell Structure and
Function.output
Raghav Chaudhary
No ratings yet
• Peripheral Proteins: These are found embedded in a single leaflet of the Document 18 pages
membrane. They carry signals from one segment of the membrane and relay it to
THE CELL
another.
• Glycoproteins: They stabilize the membrane and are responsible for intercellular Aleia Trixie
communication. No ratings yet
Factors Affecting Fluidity of Plasma Membrane
The fluidity of the cell membrane is influenced by three factors:
Temperature
Document 8 pages
Phospholipids are found close together when it is cold. When it’s hot, they move apart.
The Fundamental Unit of
Life Class 9 Notes
Cholesterol
Md Aurangjeb
The cholesterol molecules are randomly distributed along the phospholipid bilayer and
No ratings yet
hold it preventing it from separating too far, or compacting too tightly.
Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Aci ds
Fatty acids make up the phospholipid tails. Saturated fatty acid chains have a single bond
between the carbon atoms whereas, unsaturated fatty acid chains have double bonds
between the carbon atoms.
Double bonds make it harder for the chain to pack tightly by creating kinks. These kinks
increase the fluidity of the membrane.
Restri ctio n to Fluidi ty of Plasma Membrane
The fluidity of the plasma membrane is restricted due to:
Lipid Rafts
These are the lipid domains found on the external leaflet of the plasma membrane.
Cholesterol, glycosphingolipids, and glycosylphosphatidylinositol are the building blocks
of lipid rafts.
Protein Compl exes
Proteins and glycoproteins are diffused within the plasma membrane. These help in the
transport of ions and metabolites, cell signaling, adhesion, and migration.
Key Points on t he Fluid Mosaic Model
• The plasma membrane comprises amphiphilic, phospholipid molecules.
• The second important component of the plasma membrane is integral proteins that
are integrated completely into the membrane.
• Carbohydrates are found on the external surface of the membrane where they are
bound to proteins or lipids.
Document 76 pages
Cell Biology
Dave Arthur Robledo
100% (8)
Reward Your Curiosity
Document 38 pages
Everything you want to read. Cell _ Structure & Function
Anytime. Anywhere. Any device. 02 _ Theory Notes __ PDF…
wigiye6232
Read free for 30 days No ratings yet
No Commitment. Cancel anytime.
Document 4 pages
CELL BIOLOGY1
Share this document Ashlee Talento
No ratings yet
Document 10 pages
8 Science Cell Structure and
Functions Notes VL
Amiteshwar Singh
No ratings yet
Document 29 pages
APH Unit 1
Kripa N
No ratings yet
Document 2 pages
leoooo
alia
No ratings yet
Document 15 pages
CELLS for Class8
cbseisc
No ratings yet
Document 7 pages
Cell Structure
Prashant Patil
No ratings yet
Document 7 pages
class9_The Fundamental
Unit Of Life notes by zenit…
abhishek
No ratings yet
Document 10 pages
Chapter-4-Reviewer-In-
Biosci
Angelica Paulino
No ratings yet
Document 14 pages
GeneralBiology (1)
bon
No ratings yet
Document 5 pages
Reviewer in Science B
Ashliah Aira Marohom
No ratings yet
Document 48 pages
RSL CELL THEORY
Reynald Legarda Jr.
No ratings yet
Document 7 pages
1626143806-
CharacteristicsofCells (1)
Afrida Annan
No ratings yet
Document 11 pages
01-Cell-and-Tissue.pdf
Anand Classes
No ratings yet
Document 14 pages
fundamentel of life.docx
Shweta Shukla
No ratings yet
Document 34 pages
CELL-CYCLE-MODULE-Dec-
18
arnel Aguel
No ratings yet
Document 25 pages
Cell Theory
Rickyla Viente
No ratings yet
Document 25 pages
Cell
Cli joen “cjac15” Carurucan
No ratings yet
Document 3 pages
The Fundamental Unit of
Life
Amruth Bhargav
No ratings yet
Document 22 pages
CYTOGENETICS (2)
aybs solamo
No ratings yet
Document 5 pages
Chapter 8
Arpit Sharma
No ratings yet
Document 39 pages
Lecture 1(1) (4)
Mohammed Sindi
No ratings yet
Document 47 pages
Science Ready Reckner
Donibaba Don
No ratings yet
Document 27 pages
Gr 6-CELL- lesson ppt
shamshad
No ratings yet
Document 56 pages
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
Cell
KENT GARCIA
100% (1)
Document 18 pages
Rozy Khan
BANTU RANA
No ratings yet
Document 42 pages
Cell Theory
Rose Mariel Inso
No ratings yet
From Everand
The Animal Cell and Division
Biology for Kids | Children…
Baby Professor
No ratings yet
From Everand
Biology Fundamentals
IntroBooks Team
No ratings yet
Related titles
Document Document Document Document Document Document
1.1cell concept The cell.docx Cells Cell CELLS_Biology Cell Definition
Added by Mokariya… Added by Abeer… Added by Pranav… Added by prakash… Added by KYLENE… Added by Woobin Re
0 ratings 0 ratings 0 ratings 0 ratings 0 ratings 100%
About Support Legal Social Get our free apps
About Scribd Help / FAQ Terms Instagram
Everand: Ebooks & Audiobooks Accessibility Privacy Twitter
Press Purchase help Copyright Facebook
Join our team! AdChoices Cookie Preferences Pinterest
Contact us Do not sell or share my personal
information
Invite friends
Scribd for enterprise
Documents
Language: English Copyright © 2023 Scribd Inc.
You might also like
- Harcourt Education LTD Catalyst 1 ADocument125 pagesHarcourt Education LTD Catalyst 1 AJoeNo ratings yet
- 11.1 To 11.2 YellowDocument7 pages11.1 To 11.2 YellowKay0% (1)
- Cellsjw PDFDocument49 pagesCellsjw PDFToriNo ratings yet
- Cell ProjectDocument2 pagesCell Projectdasinori3No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Chapter 1Document51 pagesUnit 1 Chapter 1Connor GreenNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 8 - Learn CBSEDocument11 pagesCell Structure and Functions Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 8 - Learn CBSEshafitoxicNo ratings yet
- Notes 2024Document230 pagesNotes 2024nopscopNo ratings yet
- Cell ChartDocument3 pagesCell ChartMarisol Leal PradoNo ratings yet
- Science: Unit 1. Cells: 6th GradeDocument19 pagesScience: Unit 1. Cells: 6th GradeMoosa Mohammed PatelNo ratings yet
- Bio Reading Essentials Structures & OrganellesDocument5 pagesBio Reading Essentials Structures & OrganellesValerie FallerNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Structure and Function of Living ThingsDocument82 pagesUnit 7 Structure and Function of Living ThingsSUMMER JORDAN CARLUENNo ratings yet
- B1.1 Student GlossaryDocument4 pagesB1.1 Student GlossarymtauhidNo ratings yet
- BEST - BCL - 1 - 3 - Response - The Right Cell For The JobDocument5 pagesBEST - BCL - 1 - 3 - Response - The Right Cell For The JobmtauhidNo ratings yet
- 7ae Quick CheckDocument2 pages7ae Quick CheckMajdoline SadeddineNo ratings yet
- Cells Lesson 2Document8 pagesCells Lesson 2api-372328325No ratings yet
- Sas Week 8 17-18Document1 pageSas Week 8 17-18api-325945020No ratings yet
- CellsDocument18 pagesCellssurprisinglysarahytNo ratings yet
- Sop Pengkajian Pasien Risiko Jatuh - PDFDocument1 pageSop Pengkajian Pasien Risiko Jatuh - PDFsamuel lengkyNo ratings yet
- Dr. Yanga'S Colleges, Inc.: Name: Role: Course - Date Submitted: Group NoDocument3 pagesDr. Yanga'S Colleges, Inc.: Name: Role: Course - Date Submitted: Group NoJamil Samira E. BuizonNo ratings yet
- Inside CellsDocument31 pagesInside CellsWill GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan 11-12-98 Ed. 337 Sec.#1 Matt WermichDocument44 pagesUnit Plan 11-12-98 Ed. 337 Sec.#1 Matt WermichUmEr KhAnNo ratings yet
- Summary 7ADocument2 pagesSummary 7ATHJNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level Biology (D G Mackean, Dave Hay - 230919 - 121252Document78 pagesCambridge O Level Biology (D G Mackean, Dave Hay - 230919 - 121252ibrahim KhanNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell Diagrma - Google SearchDocument1 pagePlant and Animal Cell Diagrma - Google SearchaishiteruxoxoxNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument16 pagesHomeworksl07021No ratings yet
- Organisation of An Organism: Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument12 pagesOrganisation of An Organism: Cell Structure and OrganisationKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Year 9 GCSE Science Revision NotesDocument24 pagesYear 9 GCSE Science Revision Notesselviprabha12No ratings yet
- Cell - Structure, Function and OrganizationDocument1 pageCell - Structure, Function and Organization- adlina -100% (1)
- SAMPLEPAGES Unit11 1LivingThings topic1CellstissuesandorgansAuthorsMartinHansonwithDiaitiZure ThediscoveryofcellsDocument33 pagesSAMPLEPAGES Unit11 1LivingThings topic1CellstissuesandorgansAuthorsMartinHansonwithDiaitiZure Thediscoveryofcellsrobinasanga09No ratings yet
- Bio Tutor 2023 Notes BioDocument282 pagesBio Tutor 2023 Notes Biosahibzada mohsinbalochNo ratings yet
- 1 Comparing Plant and Animal CellDocument9 pages1 Comparing Plant and Animal CellLouise Meara Severo100% (1)
- Department of Education: Learner'S Activity Sheet For Quarter 2, Week - 4Document8 pagesDepartment of Education: Learner'S Activity Sheet For Quarter 2, Week - 4RubenNo ratings yet
- Session 4: Plant Tissues: Key ConceptsDocument14 pagesSession 4: Plant Tissues: Key ConceptsSarah Mae CabeltesNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument10 pagesScienceapi-315959236No ratings yet
- Cells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointDocument24 pagesCells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointJhyvril GulacNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument4 pagesThe CellOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- Cells & Organelles CompleteDocument33 pagesCells & Organelles CompleteShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- Cell Analogy AssignmentDocument2 pagesCell Analogy AssignmentSamantha JonesNo ratings yet
- Biology PROJECT (Plant and Animal Cells)Document10 pagesBiology PROJECT (Plant and Animal Cells)aroojammar0102No ratings yet
- Anatomy Grades 5-6 Book 1Document65 pagesAnatomy Grades 5-6 Book 1Miha MargineanNo ratings yet
- Read About Plant & Animal Cells: What Is A Cell?Document5 pagesRead About Plant & Animal Cells: What Is A Cell?Brijesh DwivediNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Chapter 2: Organisation of The OrganismsDocument5 pagesIGCSE Biology Chapter 2: Organisation of The OrganismsNabil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Drawing of A Plant Cell - Google SearchDocument1 pageDrawing of A Plant Cell - Google Searchyaseensh212No ratings yet
- CH 11 Cell Growth Divison and Reproduction (3) rYsR2Document14 pagesCH 11 Cell Growth Divison and Reproduction (3) rYsR2emancairoNo ratings yet
- Cell & TissueDocument11 pagesCell & TissuerahulpanditkgpNo ratings yet
- BW1 CellsDocument13 pagesBW1 CellsMichael KavanaghNo ratings yet
- Unspecialised Animal CellDocument9 pagesUnspecialised Animal CellPATRICIA BROOKSNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Cell TheoryDocument22 pages1.1 Cell TheoryAlexa Julienne RazNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Science Year 7 LB Lyp Removed CompressedDocument268 pagesCambridge Science Year 7 LB Lyp Removed CompresseddivyamohandasNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell: Key Question: What Are Some of The Structures Found in Animal Cells?Document7 pagesParts of A Cell: Key Question: What Are Some of The Structures Found in Animal Cells?vscriven1803No ratings yet
- 4 Structures and OrganellesDocument5 pages4 Structures and Organellessalmasadiq2008No ratings yet
- Cell Structure ASDocument40 pagesCell Structure ASYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- 02 Organization of The OrganismDocument10 pages02 Organization of The OrganismkaderovichNo ratings yet
- What Is The Fundamental Unit of An Organism?Document111 pagesWhat Is The Fundamental Unit of An Organism?Nicole Quek Choon YeeNo ratings yet
- The Cell History Structure of Cell Cell Organelles: Unicellular OrganismsDocument7 pagesThe Cell History Structure of Cell Cell Organelles: Unicellular OrganismsvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- L1 Structure of A Leaf1 STUDENTDocument16 pagesL1 Structure of A Leaf1 STUDENTSyed AliNo ratings yet
- Candy Cell Project 3Document4 pagesCandy Cell Project 3api-37576198050% (2)
- Bab 2 Ting 1 SainsDocument18 pagesBab 2 Ting 1 SainsbrownsofaNo ratings yet
- Time Academy Study Material For Scholastic Aptitude Test PreparationDocument41 pagesTime Academy Study Material For Scholastic Aptitude Test PreparationKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Unit Five-Human Body SystemDocument5 pagesUnit Five-Human Body SystemKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Part Three Writing EntranceDocument7 pagesPart Three Writing EntranceKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Part Two Vocabulary EntranceDocument6 pagesPart Two Vocabulary EntranceKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Units 7-12 GR 12 Summarised Text BookDocument23 pagesUnits 7-12 GR 12 Summarised Text BookKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- 2014 FIRST Sem 3rd WorkDocument8 pages2014 FIRST Sem 3rd WorkKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- BIO Powr Point G10thDocument175 pagesBIO Powr Point G10thKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Bio Powr Point G9Document276 pagesBio Powr Point G9Kedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Content FlowchartREVDocument15 pagesContent FlowchartREVKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Syllabus REVDocument10 pagesSyllabus REVKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To New STB rREvDocument7 pagesIntroduction To New STB rREvKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Odds RatioDocument1 pageOdds RatioKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- The Smallest Structural and Functional Unit in A Multicellular Organism Is ADocument7 pagesThe Smallest Structural and Functional Unit in A Multicellular Organism Is AKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- 1380960835.1698lecture 4 & 5. EnzymesDocument30 pages1380960835.1698lecture 4 & 5. EnzymesKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Basic Virology IntrodctionDocument94 pagesBasic Virology IntrodctionKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: ObjectivesDocument39 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: ObjectivesAndrian SiscarNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Streak, Pour and Spread PlatingDocument1 pageDifferences Between Streak, Pour and Spread PlatingCarlo Joseph Moskito100% (14)
- JKJKJKJDocument3 pagesJKJKJKJPaolo DioquinoNo ratings yet
- Cell - Revision Worksheet 2Document9 pagesCell - Revision Worksheet 2ariaNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Student (Answer Sheet) Microbes and Infectious DiseaseDocument6 pagesKami Export - Student (Answer Sheet) Microbes and Infectious DiseaseAylin Oropeza (578AylOrop)No ratings yet
- Nanosciences Evolution or RevolutionDocument9 pagesNanosciences Evolution or RevolutionClaramaria RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Qioptiq Optolines 29 Mar12 ENG PDFDocument36 pagesQioptiq Optolines 29 Mar12 ENG PDFgurjeetNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining: Course: MCB 103 Lab Section: 1 Name: Noor-E-Khadiza Shama ID: 1921168 Date: 04/02/20Document5 pagesGram Staining: Course: MCB 103 Lab Section: 1 Name: Noor-E-Khadiza Shama ID: 1921168 Date: 04/02/20ShamaNo ratings yet
- Histology Practice PracticalDocument38 pagesHistology Practice PracticalDeep Patel88% (8)
- Analysis of Hair Using Microscopic and Molecular Techniques To Ascertain Personal IdentificationDocument27 pagesAnalysis of Hair Using Microscopic and Molecular Techniques To Ascertain Personal IdentificationBijay KarkiNo ratings yet
- 2016 ANAT2241 Course Manual FinalDocument66 pages2016 ANAT2241 Course Manual FinalDijattx100% (1)
- 2019 JacsDocument5 pages2019 JacsJose Miguel Fierro BustosNo ratings yet
- B.sc. Medical Laboratory Sciences Medical Bacteriology (MLS 2413) (PDFDrive)Document101 pagesB.sc. Medical Laboratory Sciences Medical Bacteriology (MLS 2413) (PDFDrive)Isah MohammedNo ratings yet
- 1.7 How Do Cells Show Viral Growth?: Cell LysisDocument2 pages1.7 How Do Cells Show Viral Growth?: Cell LysisMona samantaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology 1Document35 pagesMicrobiology 1pikachuNo ratings yet
- Human Hair AnalysisDocument2 pagesHuman Hair AnalysisPriscillaL.SilvaNo ratings yet
- TEST I. TRUE or FALSE. Write TRUE If The Statement Is True, Otherwise Write FALSE If The StatementDocument3 pagesTEST I. TRUE or FALSE. Write TRUE If The Statement Is True, Otherwise Write FALSE If The StatementHasnairah Mautin LimbotonganNo ratings yet
- Efficient Flame Detection and Early WarningDocument9 pagesEfficient Flame Detection and Early WarningHiran ChathurangaNo ratings yet
- Acid Fast Staining FinalDocument3 pagesAcid Fast Staining Finaljennin3 lumangtadNo ratings yet
- 9 Unit 7 - Virology HODocument90 pages9 Unit 7 - Virology HOThirdy PinedaNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Light and Electron MicroscopesDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Light and Electron MicroscopesShania RoopnarineNo ratings yet
- Bio 102 Lecture Note (Bacteria) - 3Document9 pagesBio 102 Lecture Note (Bacteria) - 3Yin KuzNo ratings yet
- Organel Dan Membran SelDocument95 pagesOrganel Dan Membran SelRizki AdityawanNo ratings yet
- nl7b03206 Si 001Document22 pagesnl7b03206 Si 001Dimitris KatsidoniotisNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure 2Document5 pagesCell Structure 2slombez 150% (1)
- Huda Munir McqsDocument21 pagesHuda Munir McqsAngelo P. VeluzNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Neet Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument14 pagesClass 11 Neet Cell - The Unit of LifeViswaNo ratings yet
- Cells and Microscopes. Ms CooperDocument33 pagesCells and Microscopes. Ms CooperzeeNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure - FlashcardsDocument14 pagesCell Structure - Flashcardsvishal37256No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - 2.2 Mechanical OperationsDocument43 pagesTopic 2 - 2.2 Mechanical OperationsAmeen HussainNo ratings yet