Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ideal Gas Laws
Ideal Gas Laws
Uploaded by
wmayeza110 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesKinetic molecular theory states that all matter is composed of particles that are constantly in motion and have kinetic energy. The particles interact with each other through forces of attraction and repulsion. It describes the motion and interaction of particles in gases.
Original Description:
Chemistry g11
Original Title
Ideal gas laws
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentKinetic molecular theory states that all matter is composed of particles that are constantly in motion and have kinetic energy. The particles interact with each other through forces of attraction and repulsion. It describes the motion and interaction of particles in gases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views9 pagesIdeal Gas Laws
Ideal Gas Laws
Uploaded by
wmayeza11Kinetic molecular theory states that all matter is composed of particles that are constantly in motion and have kinetic energy. The particles interact with each other through forces of attraction and repulsion. It describes the motion and interaction of particles in gases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Kinetic molecular theory
Kinetic molecular theory states that:
● All matter is made up of particles (Atoms, molecules or ions).
● The particles of matter are always in constant motion.
● Due to their motion, the particles have kinetic energy.
● There are forces of attraction and repulsion between the particles.
Summary of the differences in the phases/states of matter
Summary of real vs ideal gases
Ideal gases Real gases
Does not really exist in real life It really exists in real life environment
environments and is a hypothetical gas
No intermolecular attraction forces Has Intermolecular attraction forces
Independent Interacts with others
Elastic collision of particles Inelastic collisions between particles
No definite volume Definite volume
The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
Gas particles must collide with :
I. The correct orientation
II. And sufficient energy, equal to or greater than the activation energy
III. In order for effective collisions to take place.
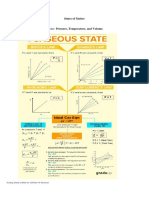
When does a real gas deviate from an ideal gas?
● A real gas deviates most from an ideal gas at low temperatures and high pressures.
● Gases are most ideal at high temperature and low pressure.
Gases deviate from ideal gas behavior at high pressure
Real gases deviation from ideal gases
Gases deviate from ideal gas behavior at low
temperature
Boyle’s Law
The volume of an enclosed gas is inversely proportional to pressure at
constant temperature.
● P1V1 = P2V2 (on formula sheet)
You might also like
- Ideal Gas Law: P Pressure in AtmDocument5 pagesIdeal Gas Law: P Pressure in AtmAbhishek Saxena100% (1)
- Ideal Gas Law: Pressure in AtmDocument5 pagesIdeal Gas Law: Pressure in AtmHabibNo ratings yet
- Real Gas: Deviations From Ideal BehaviourDocument15 pagesReal Gas: Deviations From Ideal BehaviourCHOY YIM YENG MoeNo ratings yet
- Notes On States of Matter .pdf-76Document7 pagesNotes On States of Matter .pdf-76PRITHVI KUMAR MNo ratings yet
- The Gaseous State Notes 24 SeptDocument12 pagesThe Gaseous State Notes 24 SeptP YNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Notes ch13 PDFDocument2 pages11 Physics Notes ch13 PDFTalha MukhtarNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Notes Ch13Document2 pages11 Physics Notes Ch13Rupak MoniNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE REVIEWER (1st Quarter Topics) For Grade 10 - PhysicsDocument2 pagesSCIENCE REVIEWER (1st Quarter Topics) For Grade 10 - PhysicsacrtannNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument22 pagesKinetic Theory of Gasesshan mackNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Part II (Student Version)Document67 pagesThermodynamics Part II (Student Version)Long Phan DuyNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument4 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesClayton NandlalNo ratings yet
- GroupDocument11 pagesGroupعلي حميد زغير صحنNo ratings yet
- Gas Properties and KMTDocument28 pagesGas Properties and KMTAndiNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument13 pagesGasesJhanny JNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy Surface Chemical Reaction Bonds: 176. What Is Activated Complex?Document2 pagesPotential Energy Surface Chemical Reaction Bonds: 176. What Is Activated Complex?Talal AshrafNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument11 pagesScience ReviewerMumay LobendinoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Thermal Physics - IB PhysicsDocument1 pageTopic 3 Thermal Physics - IB PhysicsFortNite KIDNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Notes ch13 PDFDocument2 pages11 Physics Notes ch13 PDFSiddharth SarkarNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Notes On Kinetic TheoryDocument2 pagesPhysics Class Notes On Kinetic TheorySiddharth SarkarNo ratings yet
- Gases and The AtmosphereDocument19 pagesGases and The AtmosphereJhon Louie LejanioNo ratings yet
- Week 7-8Document35 pagesWeek 7-8Muhammad Ubaid Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Physics Kinetic Theory LessonDocument24 pagesPhysics Kinetic Theory LessonRufat IsmayilovNo ratings yet
- 3 - The Mole ConceptDocument5 pages3 - The Mole ConceptSagi IbiNo ratings yet
- 4 - State of Matter IDocument41 pages4 - State of Matter IHenry ChongNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasDocument3 pagesIdeal Gasandyboi360No ratings yet
- Kinetics & EnergeticsDocument23 pagesKinetics & EnergeticsDoveNo ratings yet
- CHM 1102 Gases (Cont'd)Document6 pagesCHM 1102 Gases (Cont'd)EwartNo ratings yet
- H&T L-3Document6 pagesH&T L-3gitNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry, Chapter 19, ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesAP Chemistry, Chapter 19, Thermodynamicssethisodd100% (2)
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument8 pagesKinetic Molecular TheoryDanica Dolor PingkianNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - Chapter 2 - Lecture 1Document21 pagesThermodynamics - Chapter 2 - Lecture 1Dr-Amr HesseinNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 PDFDocument31 pagesLecture1 PDFJared ThamNo ratings yet
- Physci Simple Collision TheoryDocument34 pagesPhysci Simple Collision TheoryLovely benzelNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument9 pagesBehaviour of Perfect Gas and Kinetic Theory of Gasesvkr2225No ratings yet
- Gas Laws Notes KEY 2014-15 PDFDocument14 pagesGas Laws Notes KEY 2014-15 PDFJoela Faith Ming GongNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Project - Kinetics and EquilibriumDocument32 pagesAP Chemistry Project - Kinetics and EquilibriumSyarifahNo ratings yet
- The Model: The Volume Occupied by The Molecules of The Gas Is Negligible Compared To The Volume of The Gas ItselfDocument1 pageThe Model: The Volume Occupied by The Molecules of The Gas Is Negligible Compared To The Volume of The Gas ItselfSameer Singh PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Mod 1 Kinetic Theory RevisedDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Mod 1 Kinetic Theory RevisednicoleNo ratings yet
- Physics - Written ReportDocument5 pagesPhysics - Written ReportjennylasiclotNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory (The Gas Laws) - Chemistry Unit IDocument6 pagesKinetic Theory (The Gas Laws) - Chemistry Unit Imcleodtravis14No ratings yet
- Class9 ChemistryG12 Notes and HomeworkDocument54 pagesClass9 ChemistryG12 Notes and HomeworkAndy Rei KouNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project PhyDocument11 pagesInvestigatory Project Phylavanya rajaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases WorksheetDocument2 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory of Gases WorksheetJudi TurkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics & Equilibrium: Froilan Aron S. Faraon, R.PHDocument34 pagesChemical Kinetics & Equilibrium: Froilan Aron S. Faraon, R.PHKenneth TrogonNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document5 pagesModule 2Mello DiaxNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Unit 10: The Gas LawsDocument58 pagesChemistry: Unit 10: The Gas LawsDhea Angela A. CapuyanNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument19 pagesKinetic Molecular TheoryMariane HinanibanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (AS-Level) : Solid Liquid GasDocument6 pagesChapter 4 (AS-Level) : Solid Liquid GashoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - States of Matter (Chemistry AS - Level)Document6 pagesChapter 4 - States of Matter (Chemistry AS - Level)Mohamed AkkashNo ratings yet
- States of Matter-Gases, Liquids and SolidsDocument47 pagesStates of Matter-Gases, Liquids and SolidsSherazAhmedNo ratings yet
- Kinetic TheoryDocument26 pagesKinetic TheoryDelano PeteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory-1Document27 pagesChapter 12 Kinetic Theory-1Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Kinetic Molecular TheoryLyka Jade SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5 Gibbs Theorem-Ideal Gas MixturesDocument24 pagesLecture-5 Gibbs Theorem-Ideal Gas MixturesShiavm PatelNo ratings yet
- CHM111 State of Matter - Gas LawsDocument40 pagesCHM111 State of Matter - Gas LawsolufemisongNo ratings yet
- Chemical Thermodynamics: Lecture PresentationDocument27 pagesChemical Thermodynamics: Lecture PresentationlaraNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Gas Point Particles Elastic CollisionsDocument1 pageTheoretical Gas Point Particles Elastic CollisionsJagdeep SekhonNo ratings yet
- “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4From Everand“Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence: Cipher 4”: “Foundations to Flight: Mastering Physics from Curiosity to Confidence, #4No ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Chemistry for Students: The Only Chemistry Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseFrom EverandChemistry for Students: The Only Chemistry Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseNo ratings yet