Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp#2 Diode Circuits, Rectification Circuits
Exp#2 Diode Circuits, Rectification Circuits
Uploaded by
Shehda ZahdaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp#2 Diode Circuits, Rectification Circuits
Exp#2 Diode Circuits, Rectification Circuits
Uploaded by
Shehda ZahdaCopyright:
Available Formats
Palestine Polytechnic University
College of Engineering
Electrical Engineering Department
Electronics Lab
Experiment #2
Rectification Circuits
Objectives
1. To understand the principles of rectification and the operation of Half-Wave and Full-Wave
rectification circuits.
2. To observe and compare the output waveforms of the half-wave and full-wave rectification
circuits for a specific input signal.
3. To measure and analyze the rectified output voltage, average output voltage, and ripple voltage
for both Half-Wave and Full-Wave rectification circuits.
4. To determine the efficiency of the rectification circuits by calculating the ripple factor.
5. Observe the effect of adding a capacitor filter to the output voltage of the rectification circuit.
6. To gain hands-on experience in constructing and troubleshooting rectification circuits on a
breadboard.
7. To reinforce theoretical knowledge through practical experimentation and analysis of rectification
circuits.
A. Half-Wave Rectification Circuit
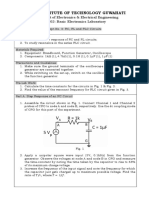
1.1 Connect the circuit shown in Figure 1.
1.2 Set the signal generator to generate a sine wave with a peak-to-peak amplitude of 10 volts
(10 𝑉𝑃𝑃 ) and a frequency of 50 𝐻𝑧.
1.3 Connect channel 1 of the oscilloscope to the input signal, and connect channel 2 to the output of the
circuit as shown in Figure 2.
1.4 Turn ON the signal generator and draw the input signal on grid plot 1.
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi 1
Figure 1: Half-Wave rectification circuit.
Figure 2: Half-Wave rectification circuit with the Oscilloscope.
1.5 Plot the obtained output waveform on grid plot 2. Determine the peak value of the output waveform
(𝑽𝑷 ), period of the output waveform (𝑻𝑷 ), and calculate the output frequency (𝒇𝑶 ).
1.6 Connect a Voltmeter to the output and measure the DC output Voltage (𝑽𝑫𝑪 ), Record your result in
table 1.
1.7 Connect a 10𝜇𝐹 capacitor filter in parallel with the output as shown in Figure 3. Draw the output
waveform on grid plot 4. Measure the 𝑽𝑫𝑪 and the ripple voltage (𝑽𝒓𝒊𝒑𝒑 ), record your results in
table 1.
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi
2
1.8 Replace the 10𝜇𝐹 capacitor with 100𝜇𝐹 and repeat step 1.7. Draw the output waveform on grid plot
5.
1.9 Reverse the diode and repeat steps from 1.5 to 1.8. Draw the output waveform on grid plot 3.
Figure 3: Half-Wave rectification circuit with capacitor filter.
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi
3
Grid Plot 1: Input signal of the Half-Wave rectifier circuit.
Grid Plot 2: Positive output of the Half-Wave rectifier circuit.
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi
4
Grid Plot 3: Negative output of the Half-Wave rectifier circuit.
Grid Plot 4: Output waveform with the 𝟏𝟎𝝁𝑭 capacitor.
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi
5
Grid Plot 5: Output waveform with the 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝝁𝑭 capacitor.
Table 1: Rectification circuits measurements.
DC Output Voltage(𝑽𝑫𝑪 )
With Capacitor
Without Capacitor
(Pract.) 𝒓
𝑽𝑷 (𝑽) 𝑻𝑷 (𝒎𝒔) 𝒇𝒐 (Hz) 𝑽𝒓𝒊𝒑𝒑 (𝑽)
With With
Theo. Pract.
10𝜇𝐹 100𝜇𝐹
Half-Wave
Positive
Rectification
Half-Wave
Negative
Rectification
Full-Wave
Rectification
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi
6
B. Full-Wave Rectification Circuit
2.1 Connect the circuit shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Full-Wave rectification circuit.
2.2 Turn ON the signal generator and draw the output waveform on grid plot 6.
2.3 From the obtained output, perform the measurements listed in table 1 and record your results in the
final row.
2.4 Connect a 10μ𝐹 capacitor filter in parallel with output as shown in Figure 5. Draw the output
waveform on grid plot 7. Measure the DC output Voltage and record your result in table 1.
2.5 Replace the 10μ𝐹 capacitor with 100μ𝐹 and repeat step 2.4. Draw the output waveform on grid plot
8.
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi
7
Figure 5: Full-Wave rectification circuit with capacitor filter.
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi
8
Grid Plot 6: Output waveform of the Full-Wave rectification circuit.
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi
9
Grid Plot 7: Full-Wave output waveform with the 𝟏𝟎𝝁𝑭 capacitor.
Grid Plot 8: Full-Wave output waveform with the 𝟏𝟎𝟎𝝁𝑭 capacitor.
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi
10
REFERENCES
[1] Floyd Thomas L. 2012. Electronic Devices: Electron Flow Version. 9th ed. Boston: Prentice Hall.
Eng. Moh’md Al-Qaisi
11
You might also like
- Experiment No.1 Group 3Document25 pagesExperiment No.1 Group 3Janpherson BellecaNo ratings yet
- Reaktor 5 - Classic Instruments GuideDocument78 pagesReaktor 5 - Classic Instruments Guideuser303100% (2)
- Ether Music and Espionage PDFDocument2 pagesEther Music and Espionage PDFDanny0% (1)
- (Experiment 7) Operational Amplifier - Basic Op-Amp Circuit (Comparator, Summing, Integrators, and Differentiators) PDFDocument13 pages(Experiment 7) Operational Amplifier - Basic Op-Amp Circuit (Comparator, Summing, Integrators, and Differentiators) PDFArik JuniarNo ratings yet
- Elab3 Jan 09Document13 pagesElab3 Jan 09Marlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- DC Motor ExamplesDocument13 pagesDC Motor ExamplesAnonymous AFFiZn100% (1)
- BEL ReportDocument35 pagesBEL ReportDurotan123100% (1)
- Expt No 3Document3 pagesExpt No 3puja maneNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document6 pagesExperiment 5VHIMBER GALLUTANNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #4 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Bridge RectifierDocument8 pagesElectronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #4 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Bridge RectifierEng. Ahmad ELsamakNo ratings yet
- Expt No 4Document3 pagesExpt No 4Aryan VermaNo ratings yet
- BXE Experiment No.4Document6 pagesBXE Experiment No.4DsgawaliNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab (Experiment 2 Report) : Submitted By: Group: G7 Ashutosh Garg (2018MEB1213) Ashwin Goyal (2018MEB1214)Document8 pagesBasic Electronics Lab (Experiment 2 Report) : Submitted By: Group: G7 Ashutosh Garg (2018MEB1213) Ashwin Goyal (2018MEB1214)Ashutosh GargNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Diode Bridge RectificationDocument4 pagesFull Wave Diode Bridge RectificationMuhammad Riyaz AliNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Integrator, Differentiator and Non-Linear Properties of OpampsDocument7 pagesExperiment 5 Integrator, Differentiator and Non-Linear Properties of OpampsEnes AyduranNo ratings yet
- ENGG 184.12 Lab Activity 4 - Manlapaz & DolalasDocument3 pagesENGG 184.12 Lab Activity 4 - Manlapaz & DolalasJuan Glicerio C. ManlapazNo ratings yet
- 6 Surname, Given Name, Middle Name, Course Code & Title, Experiment No. and TitleDocument5 pages6 Surname, Given Name, Middle Name, Course Code & Title, Experiment No. and TitleKenneth SanguyoNo ratings yet
- (ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportDocument11 pages(ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportLawrence Abram AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Expt No 4Document3 pagesExpt No 4puja maneNo ratings yet
- Eee DepartmentDocument11 pagesEee DepartmentAriston EtormaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Tumambing Evan John C PDFDocument31 pagesExperiment 1 Tumambing Evan John C PDFRafael AclanNo ratings yet
- 8 Surname, Given Name, Middle Name, Course Code & Title, Experiment No. and TitleDocument6 pages8 Surname, Given Name, Middle Name, Course Code & Title, Experiment No. and TitleKenneth SanguyoNo ratings yet
- ECE334 Lab3Document5 pagesECE334 Lab3star89690% (1)
- AEC Lab ManualDocument70 pagesAEC Lab ManualRohan BoseNo ratings yet
- Group-5 - Laboratory No. 4Document32 pagesGroup-5 - Laboratory No. 4Angel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lab 05Document3 pagesLab 05Juan TarquiNo ratings yet
- Electronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSDocument19 pagesElectronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSdark lionNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5: Half-Wave Rectifier Ece00L-Basic Electronics LaboratoryDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 5: Half-Wave Rectifier Ece00L-Basic Electronics LaboratoryJarome G. OblenaNo ratings yet
- BJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseDocument29 pagesBJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseKrista JacksonNo ratings yet
- Exp. 1 ManualDocument4 pagesExp. 1 Manualf20212001No ratings yet
- Common Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications QtyDocument0 pagesCommon Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications Qtyagama1188No ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document3 pagesExperiment 3Abdulmalek AkashaNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier and Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier and Full Wave RectifierAdvyth Vaman AkalankamNo ratings yet
- AEC LabManualDocument30 pagesAEC LabManualPrateek PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Ropar Electrical Engineering Departmentrahul.23eez0004No ratings yet
- 01 - Experiment Diode j09Document19 pages01 - Experiment Diode j09Ahmed Sobhy KhattabNo ratings yet
- Uncontrolled Half-Wave Rectifier: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesUncontrolled Half-Wave Rectifier: ObjectivesKamil Rasheed SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- EEE241L - Lab 4 - Parallel RLC CircuitsDocument4 pagesEEE241L - Lab 4 - Parallel RLC CircuitsMd. Imdadul Haque Nayan 2222846643No ratings yet
- Integrators, Differentiators, and Simple Filters: 6. PrelabDocument15 pagesIntegrators, Differentiators, and Simple Filters: 6. PrelabMIn LeNo ratings yet
- Lab Mannual PDFDocument26 pagesLab Mannual PDFssptc Magazine100% (1)
- DEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Document4 pagesDEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Pablo ChanNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Exp 8 - RectifierDocument7 pagesLab Manual Exp 8 - RectifierMohd Fazri SedanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 1Document9 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 1JAMIR ARIOLANo ratings yet
- Integrator DiffentiatorDocument7 pagesIntegrator Diffentiatorআব্দুল্লাহ আল ইমরানNo ratings yet
- Electroniccircuits Applications 1Document4 pagesElectroniccircuits Applications 1Hivda OzdenNo ratings yet
- LAB 2 RectifiersDocument2 pagesLAB 2 Rectifiersamerican dxb memesNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Laboratory Experiment No.3Document36 pagesGroup 2 Laboratory Experiment No.3odrhey hernandez0% (1)
- Durgapur: National Institute of TechnologyDocument10 pagesDurgapur: National Institute of TechnologyBishal SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Signal Clippers and Clampers PDFDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 - Signal Clippers and Clampers PDFAsyraf Norahairuzan0% (2)
- OscillatorsDocument9 pagesOscillatorsgezaegebre1No ratings yet
- Ecd LR - 8Document10 pagesEcd LR - 8Faaran Ahmed Zaheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Eee 3204Document22 pagesEee 3204Sarwar Hosen SimonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7: Procedure 1: Half Wave RectifierDocument4 pagesExperiment 7: Procedure 1: Half Wave Rectifiertashy richardsNo ratings yet
- Exp03 2019 368Document19 pagesExp03 2019 368Mohammad alhaboob2030No ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: Hartley OscillatorDocument3 pagesExperiment No.1: Hartley OscillatorBhadresh RenukaNo ratings yet
- ADE - Exp 1Document15 pagesADE - Exp 1Dhruv pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- AE PracticalDocument15 pagesAE Practicalabhi198808No ratings yet
- Updated Electronics Module 1 Question BankDocument3 pagesUpdated Electronics Module 1 Question Bankblehbo100% (1)
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator PDFDocument9 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator PDFA B ShindeNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Full Scheme Thinkingand Feature Transferfor Creationof Blue OceanDocument18 pagesFull Scheme Thinkingand Feature Transferfor Creationof Blue OceanShehda ZahdaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument3 pagesCase StudyShehda ZahdaNo ratings yet
- Dessler 09Document25 pagesDessler 09Shehda ZahdaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Heartbeat Sensor For Wearable DDocument6 pagesFlexible Heartbeat Sensor For Wearable DShehda ZahdaNo ratings yet
- Nero 8 Ultra Edition 8.2.8.0Document2 pagesNero 8 Ultra Edition 8.2.8.0Aurelian Cristian FraitorNo ratings yet
- Basics of Harmonics in Electrical SystemsDocument3 pagesBasics of Harmonics in Electrical Systemsavandetq15No ratings yet
- MIT2 627F13 Pset2 PDFDocument6 pagesMIT2 627F13 Pset2 PDFmusaNo ratings yet
- 68X2537 XT286 Technical Reference Aug86Document491 pages68X2537 XT286 Technical Reference Aug86kgrhoadsNo ratings yet
- HP 11664A ManualDocument41 pagesHP 11664A ManualjgalindesNo ratings yet
- 1RE PDS Bentley Instrumentation Wiring LTR en LR 0116Document2 pages1RE PDS Bentley Instrumentation Wiring LTR en LR 0116luciaNo ratings yet
- CH 44Document7 pagesCH 44zeru3261172No ratings yet
- IC Seminar (Integrated Circuit)Document10 pagesIC Seminar (Integrated Circuit)TB100% (1)
- 12 TMSS 03 R0Document0 pages12 TMSS 03 R0renjithas2005No ratings yet
- ELECTRONICDocument13 pagesELECTRONICMahmoued YasinNo ratings yet
- 2cpx208m V1.aspxDocument3 pages2cpx208m V1.aspxJorge BenavidezNo ratings yet
- Becker Varis Presentation Rev 1 4 21 15Document31 pagesBecker Varis Presentation Rev 1 4 21 15Jose RojasNo ratings yet
- BN0926710101 Manual Ultimo AegDocument50 pagesBN0926710101 Manual Ultimo AegOsmar Marca CondoriNo ratings yet
- Artificial Mastoid - Type 4930Document6 pagesArtificial Mastoid - Type 4930kazej61No ratings yet
- DT SignalDocument12 pagesDT SignalPrasad ShindeNo ratings yet
- Flatpack 2Document18 pagesFlatpack 2NamVTNNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Subsynchronous Resonance in Power SystemsDocument271 pagesAnalysis of Subsynchronous Resonance in Power SystemsAnonymous KTvCCMarbNo ratings yet
- 2009-10-20.PDF KOMTRAX Troubleshoot Guide - 68411Document35 pages2009-10-20.PDF KOMTRAX Troubleshoot Guide - 68411mfernaldt78% (9)
- Ed-15 Electric Propeller Shaft Revolutions and Electric Revolution Counter (Incl Inst and Test Report)Document58 pagesEd-15 Electric Propeller Shaft Revolutions and Electric Revolution Counter (Incl Inst and Test Report)BorysNo ratings yet
- Cir 0215Document3 pagesCir 0215ansonchongNo ratings yet
- CSC MCQ 2Document16 pagesCSC MCQ 2Kavinkumar NaiduNo ratings yet
- Color Television ReceiverDocument66 pagesColor Television ReceiverHugo Vilchis CoronaNo ratings yet
- High-Voltage Power Mosfets: New 600-V Mosfets With Super Junction TechnologyDocument2 pagesHigh-Voltage Power Mosfets: New 600-V Mosfets With Super Junction TechnologyLucas YeniddinNo ratings yet
- Pscad Model Report Breaker ArcDocument12 pagesPscad Model Report Breaker ArcratheeshkumardNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Instrument SystemsDocument53 pagesAircraft Instrument Systemsu2b11517100% (1)
- R20 ECE SyllabusDocument126 pagesR20 ECE Syllabussubbu subrahmanyamNo ratings yet