Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bacte Midterm
Uploaded by
barbiegahibOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bacte Midterm
Uploaded by
barbiegahibCopyright:
Available Formats
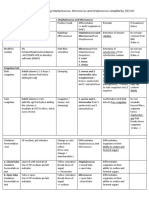
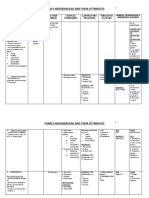
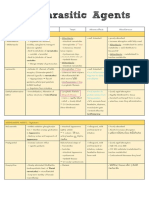
Name Family Describe/Morpho Test Other info
S. areus Staphylococcus (+), grapelike Coagulase (+); Septic shock
Produce acid from cluster, 37* Mannitol- yelow (exofoliative)
glucose anaerobic & Gray-golden halo (+) ; lookalike Food poisoning
glycerol from yellow colony S. saprophyticus; (enterotoxin)
erythromycin Thermo-Deoxy Penicillin resist (b-
Sensitive to (toluidine)- pink lactamase)
lysotaphin (+) halo; others same Susceptible
but nonhuman polymyxin
Tube coagulase
for methicillin
resist
S. epidermidis Pale transparent (-) coagulase, Cardiac valves, CNS
white colony mannitol, shunts
Skin & mucous trehalose
-/+ hemolysis
S. saprophyticus Lemon yellow (-) coagulase, UTI
hemolysis Resemble S.
(+) mannitol, epidermidis
Micrococcaceae
trehalose
Chapter 2
Resist novobiocin,
nalidixic,
MacConkey
M. varians Micrococcus Yellow (+) Salt tolerant,
(+) benzidine, reduce nitrate,
catalase, modified glucose anaerobic
oxidase (dark blue- (-) oxidase
M. luteus 2mins) Yellow (-) Salt tolerant,
Sensitive to reduce nitrate,
bacitracin (no glucose anaerobic
growth) (+) oxidase
M. roseus Pink (-) Salt tolerant,
glucose anaerobic
(+) reduce nitrate
(+/-) oxidase
S. mucilaginosus Stomatococcus Similar to staphy (-) catalase, salt Compromised, drug
but agar adhere tolerance (5%) users
due to capsule Resist vancomycin Endocarditis &
Susceptible PCN, septicemia
but used for initial
theraphy
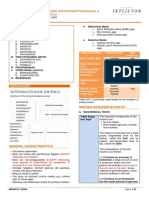
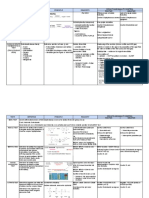
S. pneumoniae Streptococci (+) lanceolate Sensitive to bile 2nd most common
(-) catalase cocci, diplococcic 5-10% CO2, bacte meningitis
(+) gram in liquid A-hemolysis enriched Most common
Streptococci and Related Genera
Facult. Anaerobe Round, glistening, (+) bile soluble, community
Lactic acid from entire, optochin, inulin acquired, lobar
CHO metabolim transparent, ferment, Quallung Frielander’s
Devastating & not mucoid (BAP) reaction (capsular 83 capsule type
Chapter 2
normal Checker/ nail swelling)
head
S. pyogenes Group A B-hemolytic Sensitive to M protein- virulence
Facultative Pinpoint, bacitracin (only b- factor
anaerobe transparent, hemolysis) SLO- BAP hemolysis;
(-) catalase & convex, entire, (+) PYR test (red) toxic
oxidase circular, shiny SLS- BAP surface
(moisture beads) hemolysis; lytic
Streptokinase,
hyaluronidase
Sore throat
Childbed fever
S. agalactiae Group B Large, (+) Camp test, Salt Hemolysin ~ SLS
Normal in GUT translucent- tolerant (double zone, small)
Specific morpho; opaque, mucoid (-) BEM, optochin Neonatal sepsis
killed by pasteur
S. equisimilis Group C (-) trehalose, Streptokinase
Severe pharyngitis, sorbitol RTI of human and
bacteremia, animals
S. equi metastatic (-) Trehalose
S. zooepidemicus N-acetyl-D (+) Sorbitol Strepto GMN ; drink
galactosamine- Sequelae not milk
antigen occur
S. dysgalactiae determinant a/Y-hemolytic (+) trehalose Pharyngitis, sepsis,
(-) sorbitol endocardititis
S.faecalis Group D Grow at 45*C~ (+) salt tolerant, Human isolates
S. faecium -Enterococci 60* BEM
S. durans -Non-enterococci Buttery odor Resist PCN
Bacte endocarditis B-hemolytic
S. bovis (+) BEM only Human isolates
SBE infection seen septicemia
S. equinus A-hemolytic or
none
Viridans Normal Greenish Susceptible to SBE; ICP
inhabitants; hemolysis zone bacitracin (compared with
opportunistic Mucoid (large M (-) catalase, inulin, pneumonococcus)
A-hemolytic protein) or BEM, salt
smooth (small M tolerance
protein)
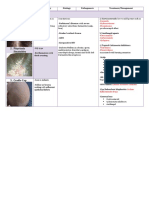
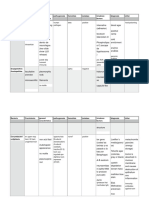
N. gonorrhea Neisseria G(-) diplococcic, (+) Glucose, Pathogenic
(+) oxidase coffee-bean, superoxal (gas Homosexual men
Anaerobe/ (AHU) Fastidious bubbles H2O2) Autolyzed without
facultative piliated (-) Sucrose, CO2
Use kingella to Not spore and not Maltose, Lactose
differentiate motile
Vulvovaginitis in T1(raised) & T2
children (umbonate)-
Opthalmia in piliated
infants T3 & T4 (not light
Sexual contact; reflect)-
Family Neisseriaceae
purelent nonpiliated
Chapter 4
N. meningitides A&C- capsule, (+) Glucose, Pathogenic
large, mucoid Maltose Waterhouse-
B- noncapsulated, (-) Sucrose, Fredericksen
small, rough, Lactose syndrome
yellow Same as N.
Both are mening subflava
epidemic Have capsule
X, Z, 29E- sporadic
cases
N. sicca (+) Glucose,
N. mucosa Sucrose, Maltose
(-) Lactose
N. lactamica (+) Glucose,
Maltose, Lactose
(-) Sucrose
N. flavescens
B. catarrhalis
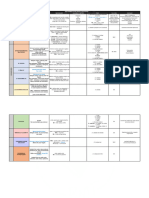
ETEC (toxic) Escherichia LT- heat-labile, Ileap loop (+), Traveler’s diarrhea,
Faculta. Anaerobe; 65* Chinese hamster, small intestine;
fecal contaminant; ST- heat-stable, reverse latex, copius, watery
motile, lactose 100*, not DNA hybridization
ferementer, antigenic infant assay, DNA
aerogenic hybridization
EIEC (invasive) O112 Sereny Test Keratoconjunctivitis;
To enterovytes;
large intestine,
uncommon
dysentery; common
fever, blood, pus;
scanty, purulent
EHEC (hemrhage) Verotoxin- HUS MacConkey Vero Cells
O157:H7 Serotyping Large intestine
Cytotoxin Prominent blood
EPEC (patho) O111 & O125 Adhere enterocyte,
s. intestine
Childhood diarrhea
Copius, watery,
MacConkey (+), Oxidase (-), Gram (-) Rods
common fever
EAEC ( aggre)
K. pneumonia Klebsiella Capsulated, (+) urease, IMViC Pneumono, UTI
nonmotile Friedlander’s
Large, pink.
mucoid
Chapter
E. cloacea Enterobacter
5
E. aerogenes Small capsule, less (+) lysine,
mucoid ornithine, urease
E. agglomerans Motile, ferment
E. sakazakii lactose, aerogenic Yellow pigment Neonatal sepsis,
meningitis
S. marcescens Serratia Prodigiosin- red @ 3 enzymes; Nocosomial
Motile, not/small 25*, nonwater DNase, infection
ferment lactose soluble, gelatinase, lipase
pseudohemolysis
H. alvei Hafnia (+) lysine,
ornithine @ 25*C
(-) indole, citrate,
urease
E. tarda Edwardsiella Normal flora of (+) H2S, indole Rsmble salmonellae
Motile reptiles
Not ferment
lactose
C. freundii Citrobacter Greenish metallic (+) H2S
Lactose ferment sheen in EMB
P. vulgaris Proteus Phenylethyl (+) indole Rickettsial disease
Not ferment Alcohol Agar (Weil-Felix), UTI
lactose
P. mirabilis Motile, rapid (+) o UTI
Many H2S & decarboxylase
P. penneri urease UTI
Deanimate lysine &
phenylalanine
P. rettgeri Providencia (+) citrate UTI
Not ferment (-) H2S, OD
lactose
P. stuartii Motile, rapid Burn infection
Many urease
Deanimate lysine &
phenylalanine
M. morganii Morganella (+) OD UTI
Not ferment (-) H2S, citrate
lactose
Motile, rapid
Many urease
Deanimate lysine &
phenylalanine
S. paratyphi Salmonella Aerogenic, motile (+) H2S, lysine, Salmonellosis
Pathogenic to ornithine Gastroentertis
S. paratyphi A man/ animals Aerogenic, motile, ornithine (cytotoxins)
(+) MR Vi antigen (typhmurium,
S. choleraesuis (-) indole, VP Aerogenic, motile, Lysine, ornithine enteritidis
~ citrate Vi antigen (gardner’s)
S. typhi Widal Test Motile (+) H2S, lysine Bacteremia,
Monocyte extraintestinal
intracell infection (from but
not involve GIT)
S. gallinarum (+) H2S, lysine,
(cholerasius, Dublin)
ornithine
Enteric Fever
S. pollorum aerogenic (+) H2S, lysine,
- typhoid- typhi-man
ornithine
only host (most
severe)
-Paratyphoid
S. dysenteriae Shigella More severe illness
S. flexneri Not motile,
S. boydii capsulated,
S. sonnei ferment lactose SLF (-) indole Watery diarrhea,
(-) H2S, citrate most common
Man only host, isolate
limit to GIT
Y. pestis Pinpoint, bacteriocin- Bubonic plague
cauliflower; pesticin 1 Septicemic plague
stalactite pattern; coagulase Pneumonic
bipolar safety-pin fibrinolysin
not ferment envelope antigen
lactose and motile
Y. enterocolitica Heat-stable (+) ornithine, Gastroenteritis,
enterotoxin; @ urease, VP @ RT Yersinios
37*
A-hemolytic
Cold enrichment
Bulls-eye colony
SLF
Y. pseudotu- Motile @ RT, (-) ornithine, VP
berculosis anerogenic
Not ferment
lactose or sucrose
B. cepacia Burkholderia NFB~lysine PC agar Cystic fibrosis
Gram (-) straight &
Smooth @ 72 hrs, OFPBL
slender bacilli 35*
(+) oxidase, Dirtlike odor
B. pseudomallei aerobes, motile, Dry, wrinkled Melloidosis
meso, some are purple @ 42* Aussie & SEA
psychrophilic Earthy odor
Oxidize carbo Bipolar safety-pin
B. mallei (-) acetoin Not motile and BHIA w/ glycerol Glander’s
NFB grow 42* on BA
P. aeruginosa Pseudomonas Opportunistic TSI- Alk/Alk glassy Most isolated NFB
Moist area Flat, colorless, Pyocyanin (w/ Jacuzzi syndrome;
along streak lines chloro), pyoverdin contact lens;
Flat, serrated, Pyorubin ecthyma
metallic sheen, B- pyomelanin gangrenosum
hemolytic on BA Exotoxin A- inhibit
Grape-like protein synthesis
monotrichous Endotoxin- sepsis
P. fluorescnes Produce (+) gelatin
fluorescein hydrolysis
P. putida psychrphilic
C. Chryoseobacterium Yellow, smooth, (+) indole, Neonatal meningitis
meningosepticum circular, entire gelatinase,
II-forms, capsule, DNase, catalase
not motile
A. xylosoxidans
A. faecalis Feather-edge Transient colonizer
Green zone of
hemolysis (a-
hemolysis)
Fruity odor
S. putrefaciens Only NFB produce
H2S in TSI butt
Otitis media
V. cholerae (+) String test Rice water stool
TCBS
You might also like
- Gram Positive Cocci: (+) Catalase (-)Document4 pagesGram Positive Cocci: (+) Catalase (-)jeffreyNo ratings yet
- Microb Summary 3314Document28 pagesMicrob Summary 3314KPNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Differentiation PDFDocument7 pagesMicrobiology Differentiation PDFRomina LacsonNo ratings yet
- MCB Lectures 8-10 High Yield Notes in 5 PagesDocument5 pagesMCB Lectures 8-10 High Yield Notes in 5 PagesfmlpletaNo ratings yet
- Enterics Reviewer For MicrobiologyDocument8 pagesEnterics Reviewer For MicrobiologyGea MarieNo ratings yet
- Anaerobes: Gram Positive CocciDocument4 pagesAnaerobes: Gram Positive CocciCindy Mae Flores UtlegNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument2 pagesCulture Mediarkenlaurenceorevor9No ratings yet
- Topnotch Microbiology Supertable UPDATED Jan 2016 by DR - Cocoy Calderon PDFDocument75 pagesTopnotch Microbiology Supertable UPDATED Jan 2016 by DR - Cocoy Calderon PDFDre Valdez100% (1)
- Biochemical Tests For Staph-Strep - OutputDocument5 pagesBiochemical Tests For Staph-Strep - OutputJoshua Ty CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Bacteee MnemonicsDocument1 pageBacteee Mnemonicsblazem720No ratings yet
- 18.1-FAMILY ENTEROBACTERIACEAE and TESTSDocument2 pages18.1-FAMILY ENTEROBACTERIACEAE and TESTSJesette KhoNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus AureusDocument11 pagesStaphylococcus Aureusdorsolya92No ratings yet
- All BacteriaDocument14 pagesAll Bacteriamorale28100% (2)
- Week 8 - Bacteriology LectureDocument7 pagesWeek 8 - Bacteriology LectureReangg SerranoNo ratings yet
- BACTE NonfermentativeDocument3 pagesBACTE NonfermentativeRichelyn Grace B. VenusNo ratings yet
- Module 6.2 AntibioticsDocument6 pagesModule 6.2 AntibioticsPNo ratings yet
- MICRO 11. EnterobacteriaceaeDocument22 pagesMICRO 11. EnterobacteriaceaeCindy Mae MacamayNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Amebiasis: Vaginalis), GiardiasisDocument6 pagesDrugs For Amebiasis: Vaginalis), GiardiasisCarla C. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Micrococcaceae and Streptococcaceae TransesDocument9 pagesMicrococcaceae and Streptococcaceae TransesaguirreangNo ratings yet
- Bacteria ChartDocument3 pagesBacteria Chartsakai33No ratings yet
- Tabel 1: Gram Positif Coccus Aerob Katalase PositifDocument7 pagesTabel 1: Gram Positif Coccus Aerob Katalase PositifAnonymous yQ9ILMfNo ratings yet
- EnterobacteriaceaeDocument8 pagesEnterobacteriaceaeWansun MaglangitNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument1 pageMicrobiologyKimberly CollantesNo ratings yet
- Family Neisseriaceae and Their AttributesDocument2 pagesFamily Neisseriaceae and Their AttributesJesette KhoNo ratings yet
- StaphylococcusDocument13 pagesStaphylococcusZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- Non Fermentative GramDocument2 pagesNon Fermentative GramKarryle AbinanNo ratings yet
- Foodborne Diseases: Clostridium BotulinumDocument3 pagesFoodborne Diseases: Clostridium BotulinumChristopher CastorNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Lecture MidtermsDocument13 pagesBacteriology Lecture MidtermsEvanka BaguistanNo ratings yet
- MICRO Master ListDocument63 pagesMICRO Master ListDaniel Del RiscoNo ratings yet
- BacteriaDocument3 pagesBacteriaviju josephNo ratings yet
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Desonide Hydrocortisone MometasoneDocument2 pagesSeborrheic Dermatitis: Desonide Hydrocortisone MometasoneRiena Austine Leonor NarcillaNo ratings yet
- Student Notes: Micro 1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDocument2 pagesStudent Notes: Micro 1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentMelody Jane PardilloNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae Handout (Lec & Lab)Document15 pagesEnterobacteriaceae Handout (Lec & Lab)Lucille MarieNo ratings yet
- GENUS SPDocument3 pagesGENUS SPJoanne Faith ManayagNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Reviewer: Important Notes and Tests for Common Aerobic Gram-Positive CocciDocument18 pagesBacteriology Reviewer: Important Notes and Tests for Common Aerobic Gram-Positive CocciAJNo ratings yet
- Bacte Methods Part II of Part IIDocument3 pagesBacte Methods Part II of Part IILea Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- V Antiparasitic Agent (Preclinic)Document3 pagesV Antiparasitic Agent (Preclinic)KHETSOPHON POOCHIPAKORNNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-06-27 at 4.04.28 PMDocument98 pagesScreenshot 2022-06-27 at 4.04.28 PMikraanmohamedmahamuudNo ratings yet
- Compiled Notes - Seminar Micro 1Document7 pagesCompiled Notes - Seminar Micro 1Tooter KantuterNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument2 pagesCulture MediaJobelleNo ratings yet
- Gram-Positive Non-Spore Forming Bacilli: Human Pathogen Beta Positive Food PoisoningDocument11 pagesGram-Positive Non-Spore Forming Bacilli: Human Pathogen Beta Positive Food PoisoninghectorNo ratings yet
- BACTERIADocument14 pagesBACTERIARochelle Joyce AradoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Review HandoutDocument53 pagesMicrobiology Review HandoutAndrei Tumarong Angoluan100% (1)
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocument3 pagesSphere: These Diarrheamed testNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Endocrine System, Metabolism: VitaminsDocument25 pagesVitamins: Endocrine System, Metabolism: VitaminsMonica J Ortiz PereiraNo ratings yet
- Glycosides and Tannins NotesDocument10 pagesGlycosides and Tannins NotesSTEM B 12 PELEGRIN,MELISSANo ratings yet
- ????? ?????????Document2 pages????? ?????????KIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- 8 ToxicologyDocument5 pages8 ToxicologyMd Sakil AminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - Week 5 PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 21 - Week 5 PDFSamanthaNo ratings yet
- List of Common Antidotes Nurses Should Know - NurseslabsDocument14 pagesList of Common Antidotes Nurses Should Know - NurseslabsKc Mea Paran Borja100% (1)
- Histopath - STAININGDocument2 pagesHistopath - STAININGvoreb84649No ratings yet
- Agars & TestsDocument73 pagesAgars & Testssana khanNo ratings yet
- Small Coccobacilli: Pinpoint ColoniesDocument33 pagesSmall Coccobacilli: Pinpoint ColoniesPaul Avila SorianoNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument1 pageInflammationmp658t952dNo ratings yet
- Toxicology SummaryDocument9 pagesToxicology SummaryPatricia JaneNo ratings yet
- AcinetobacterDocument3 pagesAcinetobacterAyessa AguilarNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Cocci Reviewer 1Document6 pagesGram Positive Cocci Reviewer 1alianaNo ratings yet
- FIKE RD Combo With Relief ValvesDocument11 pagesFIKE RD Combo With Relief ValvesAnkit GandhiNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Field Testing at Wastewater Treatment FacilitiesDocument11 pagesSampling and Field Testing at Wastewater Treatment FacilitiesSundarapandiyan SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- Proximity Sensing and Warning Technology For Heavy Construction Equipment OperationDocument10 pagesProximity Sensing and Warning Technology For Heavy Construction Equipment OperationAnand ReddyNo ratings yet
- Form WorkDocument25 pagesForm Workhina khanNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractramyaNo ratings yet
- Rajagiri Public School Unit Test PhysicsDocument3 pagesRajagiri Public School Unit Test PhysicsNITHINKJOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Iot PresentationDocument9 pagesIot PresentationAbdul Majid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Essotherm 500 PDFDocument8 pagesEssotherm 500 PDFdonyaNo ratings yet
- PMR205 DR Shawn BakerDocument31 pagesPMR205 DR Shawn Bakerspiridon_andrei2011No ratings yet
- Week 7: Nurses Role in Disaster: Home Mitigation and PreparednessDocument10 pagesWeek 7: Nurses Role in Disaster: Home Mitigation and PreparednessRose Ann LacuarinNo ratings yet
- Textiles and Clothing SustaninabilityDocument134 pagesTextiles and Clothing Sustaninabilitydike100% (1)
- Basics of Scientific Writing, Scientific Research, and Elementary Data AnalysisDocument12 pagesBasics of Scientific Writing, Scientific Research, and Elementary Data Analysisburhan sabirNo ratings yet
- B Ed 3 Sem Physics Teaching Group C Science 1 Paper 1 Summer 2018Document3 pagesB Ed 3 Sem Physics Teaching Group C Science 1 Paper 1 Summer 2018Rrr KkkNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Excavator RH 200 1,568 kW 30.5 m3Document8 pagesHydraulic Excavator RH 200 1,568 kW 30.5 m3mchan1965100% (1)
- 9709 s15 QP 12Document4 pages9709 s15 QP 12Abrar JahinNo ratings yet
- Validation of Correlations Between A NSPT PDFDocument12 pagesValidation of Correlations Between A NSPT PDFAgus WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Binzel - Katalog MAGDocument64 pagesBinzel - Katalog MAGAdrian KustraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Food Changes During Storage: Group 7Document22 pagesChemistry of Food Changes During Storage: Group 7Sonny MichaelNo ratings yet
- Bentley Bentayga BrochureDocument9 pagesBentley Bentayga BrochureGerry CalàNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ SỐ 2Document98 pagesĐỀ SỐ 2van hoa nguyenNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas and Symbols: Physics I Symbol FormulaDocument5 pagesPhysics Formulas and Symbols: Physics I Symbol Formulakaparthy100% (9)
- Cadence Monte Carlo Simulation TutorialDocument51 pagesCadence Monte Carlo Simulation Tutorialkuomatt100% (1)
- Popular CultureDocument25 pagesPopular CultureVibhuti KachhapNo ratings yet
- Pantheon-Katalog Eng WebDocument16 pagesPantheon-Katalog Eng WebJoe DoeNo ratings yet
- Thyrotronic enDocument4 pagesThyrotronic enVladimirNo ratings yet
- With Machine Room - GAD-01Document1 pageWith Machine Room - GAD-01Nagarajan SNo ratings yet
- Understanding of AVO and Its Use in InterpretationDocument35 pagesUnderstanding of AVO and Its Use in Interpretationbrian_schulte_esp803100% (1)
- Creation Story From LuzonDocument4 pagesCreation Story From LuzonMartin SantelicesNo ratings yet
- VSD Power Supply Connections and EarthingDocument4 pagesVSD Power Supply Connections and EarthingHumaid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 09 Exp 11 Buffer SolutionsDocument8 pages09 Exp 11 Buffer SolutionsShainmaugne AdvientoNo ratings yet