Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abarracoso, F. Male Reproductive System
Abarracoso, F. Male Reproductive System
Uploaded by
fabarracoso24Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abarracoso, F. Male Reproductive System
Abarracoso, F. Male Reproductive System
Uploaded by
fabarracoso24Copyright:
Available Formats
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE
Gov. D. Mangubat Ave., Brgy. Burol Main, City of Dasmariñas, Cavite 4114, Philippines
Tel. Nos. (046) 416-4339/41 www.eac.edu.ph
ISO 9001:2015 CERTIFIED
SCHOOL OF NURSING QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
COLLABORATIVE MODULE FOR OUTCOMES-BASED AND
FLEXIBLE LEARNING IN Human Anatomy and Physiology -
Lab
Student:__Abarracoso, Flora May A.______Student Number: _20-1-03777_
Name of Professor:_Mrs. Leila de Villa- Masajo_
Year Level/Section:_1st/ BSN 1-5__________
LESSON/TOPIC:
Reproductive : Male
INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOME
1. Identify the principal structure of the male
reproductive system
2. Explain how male reproductive structure function.
• VIRTUE • EXCELLENCE • SERVICE
INTRODUCTION
Anatomy and Physiology of the Male Reproductive System
Unique for its role in human reproduction, a gamete is a specialized sex cell carrying 23
chromosomes—one half the number in body cells. At fertilization, the chromosomes in
one male gamete, called a sperm (or spermatozoon), combine with the chromosomes in
one female gamete, called an oocyte. The function of the male reproductive system is to
produce sperm and transfer them to the female reproductive tract. The paired testes are
a crucial component in this process, as they produce both sperm and androgens, the
hormones that support male reproductive physiology. In humans, the most important
male androgen is testosterone. Several accessory organs and ducts aid the process of
sperm maturation and transport the sperm and other seminal components to the penis,
which delivers sperm to the female reproductive tract.
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1. The external organs of the male reproductive system, the penis and the testes, lie outside
the pelvis.
QF-PQM-035 (09.26.2020) Rev.2
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE
Gov. D. Mangubat Ave., Brgy. Burol Main, City of Dasmariñas, Cavite 4114, Philippines
Tel. Nos. (046) 416-4339/41 www.eac.edu.ph
ISO 9001:2015 CERTIFIED
SCHOOL OF NURSING QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
2. Look at the dartos fascia, this will lead to the spermatic fascia that cover the testes.
• VIRTUE • EXCELLENCE • SERVICE
3. Follow the path of the spermatic fascia to the vas deferens, over the bladder, and
into the prostate.
4. Look at the paired seminal vesicles attached to the posterior part of the bladder
above the prostate.
5. Examine the bottom of the prostate and note how it attaches to the penis. Zoom in
and find the small paired bulbourethral (Cowper’s) glands. The bulbourethral
glands, the prostate, and the seminal vesicles are accessory glands of the male
reproductive system.
LABORATORY EXERCISE
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: TESTICLES AND SPERMATIC CORDS
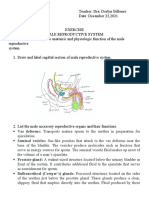
1. The Testicles.
a. What is the primary purpose of the testes?
Answer: Produce male gametes (sperm)
b. Testes are the __male gonads_______, the primary male sex organs.
c. What are gametes?
Answer: A sex cell that contains the haploid of chromosomes
d. What is the name for male gametes?
Answer: Sperm cell
e. Testes also secrete ____testosterone_________, a hormone important in the
development of male characteristics.
2. Look at the sheaths formed by the spermatic fascia that enter the pelvis via
the inguinal canal.
a.What are these sheaths called?
Answer: Spermatic cord
b.What is carried inside these sheaths?
Answer: Vas deferens
3. Testicle Section. Note the lobules formed by connective tissue inside the testis.
a.What are contained in these lobules?
Answer: Seminiferous tubules
4.Sperm cells develop inside these tubules from puberty throughout a man’s life.
a. The male sex cells, sperm, contribute ___half______ the genetic information
required to form an embryo.
QF-PQM-035 (09.26.2020) Rev.2
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE
Gov. D. Mangubat Ave., Brgy. Burol Main, City of Dasmariñas, Cavite 4114, Philippines
Tel. Nos. (046) 416-4339/41 www.eac.edu.ph
ISO 9001:2015 CERTIFIED
SCHOOL OF NURSING QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
5. The right epididymis, the small banana-shaped gland attached to the posterior
region of each testis.
a. The epididymis is divided into three regions: the _____body____, the
____head______, and the ___tail______.
b. The epididymis collects _____sperm________ from the seminiferous
tubules.
c. Sperm cells remain in the epididymis for two to three months and, as they mature
there, they acquire the ability to swim and to fertilize an egg. After they leave the
epididymis, sperm enter the ____vas deferens__________.
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: VAS DEFERENS, SEMINAL VESICLES,
AND THE PROSTATE GLAND
1. The Prostate.
a.Accessory glands add fluids to the sperm to form seminal fluid, which is ejaculated
from the urethra during sexual activity. The prostate is one of the accessory glands,
which are glands that contribute to the fluid containing sperm, of the male reproductive
system. Fluid from the prostate enters into the prostatic portion of the
_____urethra_____________.
b.Prostate fluid contributes ____enzymes________ and other substances to semen.
2. The urethra, the tube that drains from the urinary bladder into the penis. Note that
it passes directly through the prostate. The portion of the urethra that passes through
the prostate is called the _____prostatic portion____________.
3. Prostate Pathology. How could an enlarged prostate affect urination?
Answer: The prostate may obstruct urine flow from the bladder and out the urethra
4. The seminal vesicles, two glands attached to the posterior portion of the urinary
bladder. Spot where the seminal vesicles join with the vas deferens as they enter the
prostate.
a.What substances are secreted by the seminal vesicles?
Answer: pale, whitish brown fluid containing sugars, prostaglandins, and other substances
b.What proportion of the seminal fluid is contributed by the seminal vesicles?
Answer: two/thirds
• VIRTUE • EXCELLENCE • SERVICE
c. The vas deferens and the seminal vesicle ducts join to become the
___ejaculatory duct_________.
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: EJACULATORY DUCTS AND THE BULBOURETHRAL
GLANDS
1.Ducts. Look at the ejaculatory duct, which carries sperm from the vas deferens, along with
seminal vesicle secretions, through the prostate to the prostatic urethra.
2.Note that the first part of the prostatic urethra carries only urine from the bladder. After the
junction of the ejaculatory duct, the urethra is responsible for carrying both sperm and urine
(at different times).
3. Locate the portion of the urethra that lies between the prostate and the
penis.
a. What is this called?
Answer: Membranous urethra
4.Near the membranous urethra are the two paired bulbourethral (Cowper’s)
glands. Ducts from these glands join the urethra below the membranous urethra at the
proximal portion of the spongy portion of the urethra (the spongy urethra). a.What
do the bulbourethral glands secrete?
Answer: Alkaline mucus
b.What is the function of this secretion?
Answer: counteract traces of acid that can interfere with the motility of sperm.
5. Look at the corpus spongiosum of the penis. Study the spongy urethra and follow it to the
slightly enlarged ending where the urethra ends externally at the end of the glans penis.
QF-PQM-035 (09.26.2020) Rev.2
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE
Gov. D. Mangubat Ave., Brgy. Burol Main, City of Dasmariñas, Cavite 4114, Philippines
Tel. Nos. (046) 416-4339/41 www.eac.edu.ph
ISO 9001:2015 CERTIFIED
SCHOOL OF NURSING QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
PELVIS CROSS SECTION
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: PENIS
1.Penis. Note the skin (faded) that covers the penis. Look at the part of the skin that
covers the glans penis. Part of it is removed during a procedure called circumcision. a.
What is it called?
2. The glans penis, the paired corpus cavernosum, and the corpus spongiosum.
The latter two structures are made of spongy tissue that fills with blood to cause the
penis to become erected.
3. Look at the dorsal superficial vein of the penis and the dorsal artery of the
penis. Next, look at the paired deep arteries of the penis. The spongy portions of
the penis become engorged with blood from these arteries during sexual arousal and
the veins drain the blood after ejaculation.
4. The urethra exits the body at the tip of the glans penis.
PELVIS CROSS SECTION
Look at the following and state the function of each:
a. Corpus cavernosum - To facilitate penile erections. Muscles surround the cavernosum and
spongiosum.
b. Corpus spongiosum - To prevent compression of the urethra during erection.
c. Buck’s fascia - Covers the erectile bodies of the penis, the corpora cavernosa, and the
anterior urethra.
d. Deep dorsal vein of the penis - Drains oxygen-depleted blood away from the glans, which is
the external head of the sexual organ.
e.Prostate - Secretes a buffer (alkaline) that protects sperm in the acidic environment of the
vagina.
f. Prostate capsule - A capsule of connective tissue that contains muscle fibers surrounds the
prostate. This capsule makes the prostate feel elastic to the touch.
g. Urethra- Tube that carries urine and semen
• VIRTUE • EXCELLENCE • SERVICE
PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER
1. Name the structures through which sperm passes, from the testis to the glans
penis.
Answer: Rete testes, Efferent ducts, Epididymis, Ductus (vas deferens), Ampulla of
ductus deferens, Ejaculatory duct, Prostatic urethra, Membranous urethra, Spongy
urethra
2. List the accessory glands that contribute fluid to seminal fluid.
Answer: Bulbourethral gland, prostate, and seminal vesicles
QF-PQM-035 (09.26.2020) Rev.2
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE
Gov. D. Mangubat Ave., Brgy. Burol Main, City of Dasmariñas, Cavite 4114, Philippines
Tel. Nos. (046) 416-4339/41 www.eac.edu.ph
ISO 9001:2015 CERTIFIED
SCHOOL OF NURSING QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
• VIRTUE • EXCELLENCE • SERVICE
QF-PQM-035 (09.26.2020) Rev.2
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE
Gov. D. Mangubat Ave., Brgy. Burol Main, City of Dasmariñas, Cavite 4114, Philippines
Tel. Nos. (046) 416-4339/41 www.eac.edu.ph
ISO 9001:2015 CERTIFIED
SCHOOL OF NURSING QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
• VIRTUE • EXCELLENCE • SERVICE
QF-PQM-035 (09.26.2020) Rev.2
You might also like
- Science5 - q2 - Mod1 - The Parts of The Reproductive System and Their Functions - v4 PDFDocument23 pagesScience5 - q2 - Mod1 - The Parts of The Reproductive System and Their Functions - v4 PDFLezel Laracas64% (11)
- Sperm, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSperm, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Assessing Male Genitalia and InguinalDocument51 pagesAssessing Male Genitalia and InguinalJellaiza QuiozonNo ratings yet
- Biology M13 Human Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesBiology M13 Human Reproductive SystemEunice CorreaNo ratings yet
- Science 5 DLP 1 - Human Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesScience 5 DLP 1 - Human Reproductive SystemMark Cua89% (35)
- Histology of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument49 pagesHistology of The Male Reproductive SystemElvie ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Biology SS2 3RD Term E-NotesDocument56 pagesBiology SS2 3RD Term E-NotesINIOLUWA AKEJU100% (1)
- MISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Document27 pagesMISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Di VianNo ratings yet
- Maternal NursingDocument130 pagesMaternal NursingChristine MatasNo ratings yet
- The Parts of The Human Reproductive System and Their FunctionsDocument13 pagesThe Parts of The Human Reproductive System and Their FunctionsRhodora Rendon OrizonteNo ratings yet
- BIO202L+Lab+18+the Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesBIO202L+Lab+18+the Reproductive Systemmyra Thiong'oNo ratings yet
- Gbio 2122 Week 1 10 by Kuya CharlesDocument18 pagesGbio 2122 Week 1 10 by Kuya CharlesChoe Yoek Soek100% (2)
- NCM 101 Assessing Male GenitaliaDocument13 pagesNCM 101 Assessing Male GenitaliaKIM KALIBAYNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument181 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingKarina Jane Farnacio Purugganan100% (1)
- ScienceSLM - G10 - Q3 - M1 - The Role of Hormones in The Female and Male Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesScienceSLM - G10 - Q3 - M1 - The Role of Hormones in The Female and Male Reproductive SystemViktor InocNo ratings yet
- Feedback: The Correct Answer Is: PotassiumDocument38 pagesFeedback: The Correct Answer Is: PotassiumAlyssa Mae LatozaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Male Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Male Reproductive Systemkristel ludangcoNo ratings yet
- MERRIE COT PPT-SCIE10-Roles of Hormones in Reproductive SystemDocument61 pagesMERRIE COT PPT-SCIE10-Roles of Hormones in Reproductive SystemMerrie Anne Pascual BagsicNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet (Las) : Department of EducationDocument15 pagesLearning Activity Sheet (Las) : Department of EducationJoeffrie G. Costales100% (1)
- Exemplar 3rdDocument5 pagesExemplar 3rdRAYMUND RODILLONo ratings yet
- Cot Science 5Document5 pagesCot Science 5Gra Cey100% (1)
- Female Reproductive System2Document4 pagesFemale Reproductive System2Mhevafie Fuertes Dela Cruz - PaduaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Week 2 REPRODUCTION Organismal BiologyDocument7 pagesQuarter 4 Week 2 REPRODUCTION Organismal BiologyJEAN MARIE LOREDONo ratings yet
- s5 Michelle M. Ramos - Science 5 Describe The Part of Human Reproductive System and Their FunctionfinalDocument14 pagess5 Michelle M. Ramos - Science 5 Describe The Part of Human Reproductive System and Their FunctionfinalRandolf Cruz100% (7)
- Prelim Reviewer 2023Document83 pagesPrelim Reviewer 2023jakexsanchez1515No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument130 pagesReproductive SystemReymark NovecioNo ratings yet
- LAS 3rd Quarter FINALDocument58 pagesLAS 3rd Quarter FINALJustine Emilia100% (1)
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemJohn Daniel Paulino GumbanNo ratings yet
- WHO 5th Edition Classification 2023Document57 pagesWHO 5th Edition Classification 2023mohamaed abbasNo ratings yet
- Porfolio ReproductiveDocument2 pagesPorfolio ReproductiveDianne ColmoNo ratings yet
- Abala Lab Ex 5Document6 pagesAbala Lab Ex 5a19-1-00227No ratings yet
- SCIENCE-5-Q2-WK 1 SHLT 1 OkDocument10 pagesSCIENCE-5-Q2-WK 1 SHLT 1 OkMaria Renita BelcinaNo ratings yet
- Session #44 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document5 pagesSession #44 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab) (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Science10 q3 Mod1 Reproductiveandendocrineeystems v5Document25 pagesScience10 q3 Mod1 Reproductiveandendocrineeystems v5cubillanjoshuajames12No ratings yet
- Normal ObDocument108 pagesNormal ObDiana FernandezNo ratings yet
- Scie10 - Binded - SY 2021-2022 - Weeks 1 To 4Document38 pagesScie10 - Binded - SY 2021-2022 - Weeks 1 To 4Shin EscuadroNo ratings yet
- Science-5-Q2-Module 1-FinalDocument14 pagesScience-5-Q2-Module 1-FinalTeacher Lhor BaturiNo ratings yet
- Sci101 M3L3Document16 pagesSci101 M3L3Ej PunlaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 5Document11 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 5MELITO JR. CATAYLONo ratings yet
- Asc101 Lab Exercise No. 3Document10 pagesAsc101 Lab Exercise No. 3MELITO JR. CATAYLONo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 5 - Q2 - Mod1Document13 pagesSCIENCE 5 - Q2 - Mod13tj internetNo ratings yet
- Science5 q2 Mod1 ThePartsOfTheReproductiveSystemAndTheirFunctions v2Document24 pagesScience5 q2 Mod1 ThePartsOfTheReproductiveSystemAndTheirFunctions v2Shiela AsiloNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Eileen AycardoDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive System Eileen AycardojowieNo ratings yet
- Abaracoso, F. Module - Lab Activity Digestive EAC CDocument19 pagesAbaracoso, F. Module - Lab Activity Digestive EAC Cfloramay.abarracosoNo ratings yet
- Activity 5-Human Rep (Judy Mae)Document1 pageActivity 5-Human Rep (Judy Mae)Judy Mae RiconoseNo ratings yet
- B.ingg DeniDocument15 pagesB.ingg DeniDeny JabaliahNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Smear (Animal Development)Document8 pagesVaginal Smear (Animal Development)Dion Satrio PambudiNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 7 For Students PDFDocument118 pagesMod 2 7 For Students PDFpetergomez0119No ratings yet
- Science 5 Slem Week1 2nd Q QateamDocument10 pagesScience 5 Slem Week1 2nd Q Qateamlea eduardoNo ratings yet
- MCN Jane Lou GargaritanoDocument918 pagesMCN Jane Lou GargaritanoJanelle Estrabela GargaritanoNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System LessonDocument11 pagesMale Reproductive System LessonRobe Silva SolonNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System HandoutDocument21 pagesReproductive System HandoutJei SanNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive SystemGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Hr-Module 1-Lesson 1Document35 pagesHr-Module 1-Lesson 1Sevilla, Marpolo Joaquin Z.No ratings yet
- Reproductive Physiology "Female Reproductive Anatomy": ResearchDocument18 pagesReproductive Physiology "Female Reproductive Anatomy": ResearchCarol OrequesNo ratings yet
- ch-8 - TERM 2 - REVISION NOTES - 2021-22Document15 pagesch-8 - TERM 2 - REVISION NOTES - 2021-22Turani SinghNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesMale Reproductive System2020253350No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Human Reproductionjiya jainNo ratings yet
- InfosheetmcnDocument23 pagesInfosheetmcnAMIR LADJANo ratings yet
- Midterm 1Document18 pagesMidterm 1Jenelyn AbayatoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Science 5Document9 pagesLesson Plan Science 5Marj Reña LunaNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemTamie P. GalindoNo ratings yet
- Obstetric NursingDocument132 pagesObstetric NursingSteam LcNo ratings yet
- HARAMAY Reproductive Physiology and AI Course Handout Ashenafi andDocument72 pagesHARAMAY Reproductive Physiology and AI Course Handout Ashenafi andabrhamtafere700No ratings yet
- Reproductive System Physiology NotesDocument5 pagesReproductive System Physiology NotesKaye Alyssa EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System WebsiteDocument46 pagesHuman Reproductive System Websiteapi-258400031No ratings yet
- Mga Gawain Sa Agham: Lea M. Marcelo Principal IIDocument21 pagesMga Gawain Sa Agham: Lea M. Marcelo Principal IINomar CapoyNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesReproductive Systemjudy ann docotNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology With PathophysiologyDocument20 pagesWeek 1 Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiologyfabarracoso24No ratings yet
- Abarracoso, Flora May, SW8 BSN 1-6Document2 pagesAbarracoso, Flora May, SW8 BSN 1-6fabarracoso24No ratings yet
- ABARRACOSO A.-Act3-Ecfnurs1-6Document1 pageABARRACOSO A.-Act3-Ecfnurs1-6fabarracoso24No ratings yet
- Abarracoso, F. Urinary SystemDocument19 pagesAbarracoso, F. Urinary Systemfabarracoso24No ratings yet
- ABARRACOSO A.act2, Ecfnurs 1-6Document1 pageABARRACOSO A.act2, Ecfnurs 1-6fabarracoso24No ratings yet
- ABARRACOSO R. Act1, Ecfnur 1-6Document4 pagesABARRACOSO R. Act1, Ecfnur 1-6fabarracoso24No ratings yet
- ABARRACOSO A, Ass1, nstp1-6Document1 pageABARRACOSO A, Ass1, nstp1-6fabarracoso24No ratings yet
- Laboratory-3 Reproductive System of RuminantsDocument23 pagesLaboratory-3 Reproductive System of RuminantsJoshua CredoNo ratings yet
- Oleza Cannery S. Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesOleza Cannery S. Reproductive SystemCannery OlezaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesMale Reproductive SystemTracy zorcaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Name of Learner: - DateDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Name of Learner: - Datearies sumalbagNo ratings yet
- FM - TBC NCM 108 ModuleDocument23 pagesFM - TBC NCM 108 ModuleJoy B. DaladagNo ratings yet
- Cmca M1-M3Document511 pagesCmca M1-M3Shawn MichaelNo ratings yet
- 2nd Monthly Test in Science 5Document5 pages2nd Monthly Test in Science 5jessica holgadoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocument119 pagesLecture 1. Anatomy of Urinary SystemkrisnadewirahadiNo ratings yet
- 4 Phases of Health Care: RehabilitationDocument56 pages4 Phases of Health Care: RehabilitationmayangernszNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Class XIIDocument34 pagesBiology Project Class XIIBimal DasNo ratings yet
- Semen CollectionDocument3 pagesSemen CollectionVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- SG 5 Anaphy ActivityDocument4 pagesSG 5 Anaphy Activitykim christianNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument6 pagesHistologyarezoo bahramiNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity SheetsDocument7 pagesLearning Activity SheetsMei MCNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Gross AnatomyDocument13 pagesVeterinary Gross AnatomyTatenda MagejaNo ratings yet
- AP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab FA23Document14 pagesAP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab FA23reynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- WK 1ss1biologyDocument45 pagesWK 1ss1biologyUmoru LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive System in BullsDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive System in BullsnayayathNo ratings yet
- Impotentia Coeundi and Impotentia Generandi: A Male Infertility (Abstractview - Aspx?Pid 2016-8-2-8)Document15 pagesImpotentia Coeundi and Impotentia Generandi: A Male Infertility (Abstractview - Aspx?Pid 2016-8-2-8)Mittu KurianNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System and Female Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive System and Female Reproductive SystemLoriz DoronioNo ratings yet