Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02 Anatomy Supplemental Notes
Uploaded by
Christian Rey DagumanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
02 Anatomy Supplemental Notes
Uploaded by
Christian Rey DagumanCopyright:
Available Formats
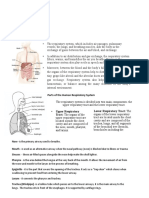
NCM 118 the trachea (windpipe) and the lower
ANATOMY SUPPLEMENTAL NOTES respiratory system when swallowing.
Clinical Instructor: Rhanz Rhudie Mongaya, RN
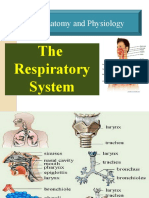
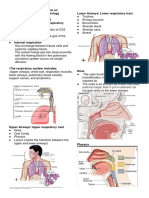
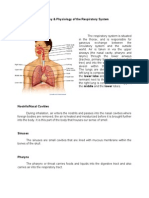
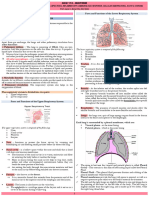
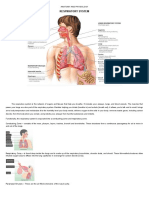
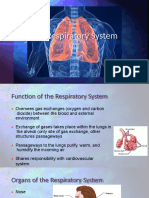
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM LOWER RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
● The respiratory system is a complex network of organs and ● Comprises the structures responsible for facilitating the
structures responsible for the process of respiration, which exchange of gasses between the bloodstream and the air in
involves the exchange of gasses between the body and the the lungs.
external environment. ● The lower respiratory system's primary function is to facilitate
● The primary goal of the respiratory system: the exchange of gasses between the air in the alveoli and
○ is to supply the body's cells with oxygen (O2) for the bloodstream.
energy production and to remove carbon dioxide ● Oxygen is taken up by red blood cells and transported
(CO2) throughout the body, while carbon dioxide is removed from
○ a waste product of metabolism the bloodstream and exhaled from the lungs.
● This intricate process ensures that the body's cells receive
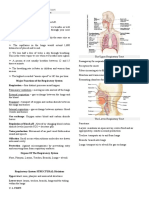
UPPER RESPIRATORY SYSTEM the oxygen they need for energy production and that waste
carbon dioxide is efficiently eliminated.
● Comprises the structures located above the trachea, which
play a crucial role in facilitating the initial processes of These structures are located below the larynx and include:
breathing, filtering, and warming the inhaled air. ● The trachea is a rigid, tubular structure
● The upper respiratory system's functions include: that connects the larynx to the bronchi.
○ Warming Trachea ● It is lined with ciliated mucous membranes
○ Humidifying (windpipe) that help trap and remove foreign
○ Filtering the air as it enters the body. particles, preventing them from entering
● The presence of mucous membranes and cilia in these the lungs.
structures helps trap and remove particles and
microorganisms from the inhaled air, preventing them from ● The trachea divides into two main
entering the lower respiratory system and potentially causing bronchi: the left and right bronchi.
infections. Bronchi ● These bronchi further branch into smaller
● Additionally, the upper respiratory system contributes to the and bronchioles, creating a branching network
sense of smell, speech resonance, and immune defense bronchioles of airways.
mechanisms. ● The bronchioles eventually lead to the
alveoli, where gas exchange occurs.
These structures include:
● The nose is the primary external organ of ● The lungs are the main organs of the
the upper respiratory system. lower respiratory system.
● It serves as the entrance for air into the ● They are divided into lobes: the right
Nose respiratory system. Lungs lung has three lobes (upper, middle, and
● The nasal passages are lined with lower), and the left lung has two lobes
mucous membranes and cilia, which filter (upper and lower) due to the space
and moisten incoming air. occupied by the heart.
● The nasal cavity is the hollow space ● Alveoli are tiny, thin-walled sacs located at
inside the nose. the ends of the bronchioles within the
● It contains the nasal septum (a partition lungs.
dividing the nose into left and right sides) Alveoli ● They are the primary sites for gas
Nasal and turbinates (scroll-like bones that exchange, where oxygen from inhaled air
cavity increase the surface area for air contact). diffuses into the bloodstream, and carbon
● The nasal cavity warms, humidifies, and dioxide from the bloodstream diffuses into
filters the air before it enters the lower the alveoli to be exhaled.
respiratory system.
● The pleura is a double-layered membrane
● These are air-filled spaces connected to that surrounds each lung and lines the
the nasal cavity. chest cavity.
Paranasal ● The paranasal sinuses include the ● The visceral pleura covers the lung
sinuses frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and Pleura surfaces, and the parietal pleura lines the
maxillary sinuses. chest cavity.
● They contribute to the resonance of the ● The pleura's fluid-filled space reduces
voice, reduce the weight of the skull, and friction during breathing and helps keep
may help humidify and warm the air the lung surfaces adhered to the chest
wall.
● The pharynx is a muscular tube connecting
the nasal and oral cavities to the larynx ● The diaphragm is a dome-shaped
and esophagus. muscle located beneath the lungs.
Pharynx ● It serves as a common passageway for Diaphragm ● It plays a crucial role in breathing by
(throat) both air and food. contracting and flattening during inhalation
● The nasopharynx, or upper part of the and relaxing during exhalation.
pharynx, helps direct air from the nasal
cavity to the lower respiratory system
● Tonsils are collections of lymphoid tissue
located in the pharynx.
Tonsils ● Adenoids are similar lymphoid tissue
and located in the nasopharynx.
adenoids ● These structures are part of the immune
system and help protect against infections.
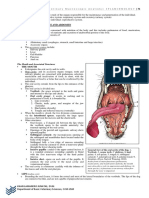
● The larynx, or voice box, is located at the
top of the trachea.
Larynx ● It contains the vocal cords, which vibrate
when air passes through, producing sound
(speech and singing).
● Specialized flap-like structure located in
Epiglottis the throat, specifically in the region of the
larynx (voice box)
● Prevent food and liquids from entering
You might also like
- Module 18 Respiratory FinalDocument15 pagesModule 18 Respiratory FinalJayR MendonesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: The Respiratory SystemDocument82 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The Respiratory SystemMaria Angelique Ofciar100% (2)
- Quadra Medical Services Pvt. LTD.: CT Scan of NeckDocument2 pagesQuadra Medical Services Pvt. LTD.: CT Scan of NeckTridibNo ratings yet
- Group1 Review of Respiratory SystemDocument41 pagesGroup1 Review of Respiratory Systemjohn obinaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Respiratory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AnjuDocument38 pagesRESPIRATORY SYSTEM Anjuanju rachel jose100% (1)
- NursingBulletin Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesNursingBulletin Respiratory Systemseigelystic100% (3)
- Physilogy of Mastication and DeglutitionDocument13 pagesPhysilogy of Mastication and Deglutitiondoctanmay100% (1)
- Introduction To Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Respiratory SystemRM100% (1)
- Rehabilitation Esophageal Speech & Artificial LarynxDocument50 pagesRehabilitation Esophageal Speech & Artificial LarynxKUNNAMPALLIL GEJO JOHN100% (2)
- Neurological History and Physical ExaminationDocument21 pagesNeurological History and Physical Examinationg3murtulu100% (1)
- Oral CavityDocument79 pagesOral CavityueumanaNo ratings yet
- 2D Planning Head Neck CancerDocument87 pages2D Planning Head Neck CancerKhumaira Santa100% (1)
- Physical Assessment Mouth Throat NoseDocument89 pagesPhysical Assessment Mouth Throat NoseDeeeee100% (2)
- Lect. 11 Respiratory SystemDocument43 pagesLect. 11 Respiratory Systemflex gyNo ratings yet
- MCQ S For StudentsDocument58 pagesMCQ S For StudentsJohn M. Hemsworth100% (2)
- Chapter 15Document6 pagesChapter 15Holy HaeinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document6 pagesChapter 15Holy HaeinNo ratings yet
- Airway Management Lec 1Document4 pagesAirway Management Lec 1Lenard SakiliNo ratings yet
- OXYGENATIONDocument13 pagesOXYGENATION20233651No ratings yet
- Module 5-Respiratory SystemDocument64 pagesModule 5-Respiratory SystemBorja MelanieNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMzDocument12 pagesANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEMzalthea jade villadongaNo ratings yet
- 8 29 23 Lesson 1 Respiratory SystemDocument36 pages8 29 23 Lesson 1 Respiratory SystemMoreen LamsenNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Mungcal, Dharlynette RTRPDocument85 pagesThe Respiratory System: Mungcal, Dharlynette RTRPDharlyn MungcalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Respiratory SystemKaryl AbinasaNo ratings yet
- Lec Activity15 Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesLec Activity15 Respiratory SystemPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AnatomyDocument38 pagesRespiratory System AnatomyAbdirazak AliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)Document57 pagesRespiratory System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)DiazNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Gas Exchange - Lesson 1 - Grade 8Document13 pagesLungs and Gas Exchange - Lesson 1 - Grade 8SAMI DHAOUINo ratings yet
- Finals - Medical TerminologyDocument88 pagesFinals - Medical Terminologyhatdog hatdogNo ratings yet
- OxygenationDocument24 pagesOxygenationJohn Anthony de GùzmanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument4 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemsAillen AgustinNo ratings yet
- Animalphysio2nd 180428184330Document28 pagesAnimalphysio2nd 180428184330environmentalgyanNo ratings yet
- Respiiiraatatoory SystemDocument78 pagesRespiiiraatatoory Systempriyanshuraj717No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Respiratory SystemDocument20 pagesChapter 8 - Respiratory Systemmnurnazri10No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory SystemPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Topic 11Document15 pagesTopic 11Lorraine RiegoNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument20 pagesScienceRonalyn CambeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22: The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 22: The Respiratory SystemMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument53 pagesANATOMYJocel Mae OrtegaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 11 Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesTOPIC 11 Respiratory SystemLorraine RiegoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory Systemkayeemperado997No ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument20 pagesRespiratoryBon BonselNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PhysiologyDocument15 pagesRespiratory PhysiologySahil SalluNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument85 pagesRespiratory SystemMiss Glozirie An BacangNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesRespiratory SystemCrisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- 13 - Respiratory SystemDocument68 pages13 - Respiratory SystemNur Shahirah Nasir Faculty of Social Science and FoundationNo ratings yet
- DT 103 New Topic 5Document22 pagesDT 103 New Topic 5CHRISTIAN SALABASNo ratings yet
- Module 13 Thorax and LungsDocument18 pagesModule 13 Thorax and LungsKristine Angie RamosNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The Respiratory Systemmohd nazmieNo ratings yet
- NCM 113 M1 Lesson 1Document10 pagesNCM 113 M1 Lesson 1Ryrl ShinNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 MidtermDocument18 pagesNCM 112 MidtermJULIANNAH ATHENA MERCADONo ratings yet
- UNIT 8 (Respiratory System)Document6 pagesUNIT 8 (Respiratory System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - Bio 2 ADocument31 pagesRespiratory System - Bio 2 A20181539No ratings yet
- Supplementary Material 3.1 Basic Concepts and Assessment (N) - 2Document13 pagesSupplementary Material 3.1 Basic Concepts and Assessment (N) - 2Kent Borro CantomayorNo ratings yet
- 05 Respiratory SystemDocument117 pages05 Respiratory SystemcelynjasminegNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in HumanDocument15 pagesGas Exchange in HumanThe Deep Sea IdNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in HaaaDocument15 pagesReviewer in HaaaabiogkristelannNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - TransesDocument4 pagesRespiratory System - TransesMLS1C - PLARISAN, VALENT DAVENo ratings yet
- Respiratory Systm1-2 BileşikDocument55 pagesRespiratory Systm1-2 BileşikDeniz asmazNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Unit 1 Structure and FunctionDocument21 pagesRespiratory Unit 1 Structure and FunctionNethul PereraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument37 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory SystemPal SedNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System Lec TransesDocument10 pagesThe Respiratory System Lec TransesVENUS LIRIA PANTINo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyBlessyl Mae EstenzoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument25 pagesRespiratory SystemNardos TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Bio 2Document2 pagesBio 2Mi Cha Cou UiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument74 pagesRespiratory SystemJonald Pulgo IcoyNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Miguel Carlos G. AradaDocument37 pagesRespiratory System: Miguel Carlos G. AradaJustine May S. ColicoNo ratings yet
- Ent Practical Examinations Slides For StudyDocument31 pagesEnt Practical Examinations Slides For StudyMuhdZaeedNo ratings yet
- Pharynx and LarynxDocument19 pagesPharynx and LarynxLaiba WarisNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Anatomy I Splanchnology 1Document17 pagesModule 5 Anatomy I Splanchnology 1neannaNo ratings yet
- mFljvnkhGvPApK1G3Krj PDFDocument110 pagesmFljvnkhGvPApK1G3Krj PDFAhxhsNo ratings yet
- CH 26 Student DigestiveDocument68 pagesCH 26 Student DigestiveMaski03No ratings yet
- Major Case 3Document3 pagesMajor Case 3Christine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Free To Sing Encouraging Postural Release For Vocal EfficiencyDocument17 pagesFree To Sing Encouraging Postural Release For Vocal Efficiency小羊No ratings yet
- Cphy.c180008 Muy BuenoDocument56 pagesCphy.c180008 Muy BuenoSportsciencesNo ratings yet
- Manual Sensorimotor Interventions Improve Social Emotional Cognitive FunctioningDocument36 pagesManual Sensorimotor Interventions Improve Social Emotional Cognitive FunctioningDevina RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemKarma DemaNo ratings yet
- Basic Physical Examination in ENT PDFDocument44 pagesBasic Physical Examination in ENT PDFJayricDepalobosNo ratings yet
- Abscesses Related To The PharynxDocument22 pagesAbscesses Related To The PharynxhamsNo ratings yet
- The Intraoral and Extraoral Exam: Nancy W. Burkhart, BSDH, Med, Edd Leslie Delong, RDH, As, BSHS, MhaDocument29 pagesThe Intraoral and Extraoral Exam: Nancy W. Burkhart, BSDH, Med, Edd Leslie Delong, RDH, As, BSHS, Mhamuhammad nauvalNo ratings yet
- Netter Atlas Conversion Sheet 5E To 6EDocument26 pagesNetter Atlas Conversion Sheet 5E To 6ESheenaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Examination in ScienceDocument8 pages3rd Quarter Examination in ScienceMyla LuayNo ratings yet
- Part 2 The Nose, Paranasal Sinuses and PharnyxDocument12 pagesPart 2 The Nose, Paranasal Sinuses and PharnyxLauraDernNo ratings yet
- 7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabDocument3 pages7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabIvy Cruz100% (1)
- The Respiratory SystemDocument77 pagesThe Respiratory SystemPridas GidNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Circular Breathing in Wind MusiciansDocument8 pagesMechanics of Circular Breathing in Wind MusiciansjwmmdNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Oral CavityDocument56 pagesAnatomy of The Oral CavitySaidu TanimuNo ratings yet