Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Screenshot 2023-05-21 at 22.25.04
Uploaded by
aneyarajaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Screenshot 2023-05-21 at 22.25.04
Uploaded by
aneyarajaCopyright:
Available Formats
GCSE Separate Science
AQA
Chemistry – Paper 1
Higher Tier
Predicted Paper 2023
Name ……………………………………………………………………
Date …………………
1 hour 45 minutes allowed.
You may use a calculator and an AQA periodic table.
Grade boundaries Possible Marks
Question
marks gained
These are VERY rough guesses! Getting a 1 11
7 on this paper does not guarantee you the 2 12
same mark in the exam. 3 12
4 19
5 14
• 9 70% 6 12
• 8 60% 7 8
• 7 50% 8 12
• 6 45% Total 100
• 5 35%
• 4 30%
• 3 25%
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
01 Atoms are made up from subatomic particles; electrons, neutrons
and protons.
a) Describe the structure of the atom, stating the location of each of
the subatomic particles.
[3 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
b) The model of the atom has changed over time as new
experimental evidence arises.
State the order in which the subatomic particles were discovered.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
c) State who suggested the location of electrons.
[1 mark]
______________________________________________________
d) State who discovered neutrons.
[1 mark]
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
e) Rutherford wanted to study the plum pudding model of the atom,
by running an alpha scattering experiment.
Describe what Rutherford found and explain how this changed the
model of the atom.
[4 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
02 Ammonia, NH3, is a small molecule that is a liquid at -35°C and a gas
at -30°C.
a) State the bonding seen in ammonia.
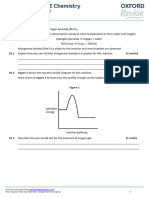
[1 mark]
______________________________________________________
b) Draw the bonding in ammonia using a dot and cross diagram.
[3 marks]
c) Compare the behaviour of the particles in ammonia liquid and
ammonia gas.
[4 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
d) When ammonia boils, bonds are broken, and it turns from a liquid
to a gas.
Describe which bonds are broken and why and which ones are not
broken and why.
[4 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
03 Iron oxide is used as a catalyst in the Haber process.
a) Transition metals can be used as catalysts.
State the property that leads to this behaviour.
[1 mark]
______________________________________________________
b) Iron oxide can have the formulae Fe2O3 or Fe3O2.
Determine which has the greater molecular mass.
[3 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
c) Explain how you could visually determine the difference between
solutions of iron (ii) oxide and iron (iii) oxide.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
d) Both iron and lithium can form compounds with oxygen to form
oxides.
State the type of bonding that is seen in both iron and lithium
oxide.
[1 mark]
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
e) Draw the bonding that is seen in lithium oxide using a dot and
cross diagram.
[3 marks]
f) Compare how iron and lithium react with oxygen.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
04 Sulphuric acid is a common solution that is used in the manufacture
of fertilisers and salts.
a) Suggest a pH for sulfuric acid.
[1 mark]
______________________________________________________
b) Describe the general reaction between the ions produced from an
aqueous acid and the ions produced from an aqueous alkali.
You should include an equation in your answer.
[3 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
c) Zinc metal reacts with sulphuric acid (H2SO4) to give two products.
Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
d) 2 mol/dm3 sulfuric acid is a strong, concentrated acid.
Explain what scientists mean when they use the terms ‘strong’ and
‘concentrated’ in terms of an acid.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
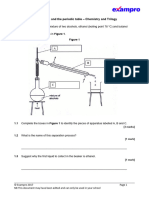
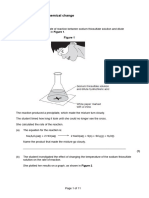
e) A student wanted to look at the reaction between a strip of zinc
metal and sulfuric acid. They set up the equipment as shown in
the image below
Method
1. Place a conical flask on a mass balance.
2. Measure out 20cm3 of sulfuric acid and add it to the conical flask.
3. Measure 2cm strip of zinc ribbon.
4. Add ribbon to conical flask.
5. Record the initial mass.
6. Record the mass every 30 seconds.
7. Repeat to get 3 sets of results.
The student recorded this data in the table below:
Time Change in mass(g)
(seconds) Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Mean
0 0 0 0 0
30 15 19 20 18
60 25 27 29 27
90 29 45 31
120 33 34 35 34
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
i. Calculate the mean value for change in mass at 90 seconds
[2 marks]
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
ii. Describe and explain how the mass changed.
[2 marks]
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
iii. Give one way in which the student ensures this was a fair
test, and how they measured it.
[2 marks]
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
iv. The table shows loss of mass, explain why this is not what
the student measured.
[2 marks]
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
v. Sketch a graph for mean loss of mass vs. time
[3 marks]
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
05 Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells are suggested as an alternative to
rechargeable batteries.
a) The overall reaction the occurring within a hydrogen oxygen fuel
cells is shown below
Hydrogen + Oxygen Water
H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l)
Give the states of each substance in the equation.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
b) Give the half equations that happen at each electrode.
i. Negative electrode…
[3 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
ii. Positive electrode….
[3 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
c) Use the information given in the question and your prior
knowledge to evaluate the use of hydrogen-oxygen fuels cells.
[6 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
06
a) A student carried out electrolysis on an aqueous solution of copper
(II) chloride. Give the expected products at each electrode:
i. At the cathode______________________ [1mark]
ii. At the anode_______________________ [1 mark]
b) One of the products was a gas, state how you could determine the
identity of this gas.
[1 mark]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
c) State the role of the power pack in this experiment.
[1 mark]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
d) No bubbles of gas were seen, suggest a modification that would
show the circuit had been set up correctly.
[1 mark]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
e) The students were told to limit the voltage on the powerpack for
health and safety reasons.
Thinking about the products of the reaction, explain why.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
f) Give the half equation for the reaction with copper ions.
[3 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
g) Explain why a solution must be used for electrolysis and not a solid
substance.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
07 Ethanol can be produced in two different ways:
By fermentation
Glucose carbon dioxide + ethanol
C6H12O6 2CO2 + 2C2H6O
By hydration
Ethene +water ethanol
C2H4 +H2O C2H6O
a) Calculate the atom economy of producing ethanol by
fermentation.
[4 marks]
Atom economy = _____________________
b) Describe which reaction has the highest atom economy.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
c) Explain how the atom economy of a reaction can be improved.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
08 Nanoparticles are very small.
a) Compare the volume of a cube that has sides of 10nm with the
volume of a smaller cube that has sides of 2nm.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
b) 125 of the smaller cubes could fit inside the larger cube.
Compare the surface areas of two sets of cubes with the same
volume.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
c) Comment on the surface area to volume ratio of the cubes.
[1 mark]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
d) One application for nanoparticles is sun cream.
Suggest two other applications for nanoparticles.
[2 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
e) Titanium dioxide is used in sun creams as it is very effective at
reflecting UV rays away from the skin and preventing damage.
This is partly responsible for the white colour and thick consistency
of sun creams; these can sometimes leave a thin film over the skin
as they can’t easily penetrate the skin.
Modern sun creams use nanoparticles of titanium dioxide, to
resolve the issues older suncreams had.
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using nanoparticles
in sun creams.
[5 marks]
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________
END OF QUESTIONS
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
MARKING GUIDANCE
Question Answer Additional Guidance Marks
1a -Electrons in shells/outside nucleus Accept energy levels or orbitals for shells 3
-Protons in the nucleus
-Neutrons in the nucleus
1b Electrons One mark for two in correct order, two marks 2
Protons for all correct
Neutrons
1c -(Niels) Bohr 1
1d -(James) Chadwick 1
1e -Some alpha particles were deflected (as 4
expected)
-most alpha particles went straight through/
were not deflected
-most of the mass of the atom is
concentrated in a small area
-(called) the nucleus
TOTAL 11
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
Question Answer Additional Guidance Marks
2a -Covalent 1
2b One mark for correct overlapping 3
One mark for correct outer electrons on
nitrogen
One mark for correct outer electrons on
hydrogen
(Does not need to be this shape to score
marks)
2c Similarities Max two from each section 4
-both flow
-both have particles moving
-both have more space between the particles
than in a solid
- both take the shape of the vessel
Differences
-liquid is incompressible whereas gases can
be compressed OR liquid has a fixed volume,
gas does not have a fixed volume.
-in a gas the particles have more movement
-the spaces between particles are larger in a
gas than in a liquid
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
2d -intramolecular bonds are not broken 4
-very strong covalent bonds
-intermolecular bonds are broken
-requires less energy to overcome these
attractions
TOTAL 12
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
Question Answer Additional Guidance Marks
3a -They can have a variety of different charged 1
ions
3b -Fe2O3 = (56x2) + (16x3) = 160 3
- Fe3O2 = (56x3) + (16x2) = 200
-Fe3O2 is greatest in mass
3c -Iron (ii) oxide is a green coloured solution 2
-Iron (iii) oxide is red/brown coloured
solution
3d -Ionic 1
3e One mark for correct outer electrons on 3
lithium AND showing 2 Lithium
One mark for correct outer electrons on
oxygen
One mark for brackets and correct charges
Accept diagrams which only show outer
electrons
OR shown as
3f -transition metals/iron are less reactive than Or reverse arguments 2
group 1 metals/ lithium
-transition metals/ iron will react slower than
group 1 metals/ lithium
TOTAL 12
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
Question Answer Additional Guidance Marks
4a -Any value between 1 and 6 1
4b -neutralisation -one mark for neutralisation 3
-H+ + OH- H2O -one mark for left hand side
-one mark for right hand side
4c Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 -one mark for left hand side 2
-one mark for right hand side
4d -Strong acids completely ionise/ fully 2
dissociate into their ions (in aqueous
solutions)
-Concentrated acids have a high number of
acid molecules (H+ ions) per unit volume
(dm3)
4ei (29+ 31)/2 One mark for calculation 2
=30 One mark for answer
One mark if answer incorrectly included
anomaly (=35)
4eii -decreased 2
-gas is released
4eiii -constant volume of acid 2 marks for linked points 2
-measuring cylinder
OR
-Constant width of ribbon
-ruler
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
OR
-constant time
-Stop watch
4eiv -mass was measured Two marks from list 2
-change in mass is calculated
-change in mass is not shown on the balance
4ev -correct x axis (label and units) No numbers are needed for this 3
-correct y axis (label and units)
-correct shape of graph (increasing the
levelling off)
e.g.
TOTAL 19
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
Question Answer Additional Guidance Marks
5a -hydrogen and oxygen are gases One mark for each bullet point 2
-water is a liquid
5bi 2H2 + 4OH- → 4H2O + 4e- -one mark for left hand side 3
-one mark for right hand side
-one mark for balancing
Allow
H2 + 2OH- → 2H2O + 2e-
5bii O2 + 2H2O + 4e- → 4OH- -one mark for left hand side 3
-one mark for right hand side
-one mark for balancing
Allow 2 marks for both parts i and ii if
equations are fully correct but given at the
wrong electrode
5c Points for; An evaluate question must cover points for, 6
points against, and include a reasoned
-water is the only waste product judgement.
-no combustion products
-reaction happens at a lower temperature 0 marks; no relevant points are made
-small and light
-no moving parts 1-2 marks; some relevant points are made but
the answer is not coherent, and points are not
logically linked.
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
Points against. 3-4 marks; all points made a relevant; the
answer is coherent, and the points are
-water is a greenhouse gas logically linked; a simple judgement as been
-high manufacture cost made.
-hydrogen is a very flammable gas
-hydrogen is difficult to store 5-6 marks; the answer is fully correct;
-expensive to manufacture coherent and logically linked. The answer
includes both points for and points against. A
judgement has been given and is supported by
a range of reasoned points.
TOTAL 14
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
Question Answer Additional Guidance Marks
6ai -Copper (metal) Red/brown colour change allowed 1
6aii -Chlorine (gas) 1
6b -Bleaches damp litmus paper 1
6c -Flow of electrons/electricity 1
6d -Addition of a bulb or voltmeter to check for 1
flow of electricity
6e -limit volume of chlorine gas produced 2
-chlorine gas is harmful
6f Cu2+ +2e- Cu -Correct charges 3
-Correct balancing
-Use of electrons
6g - Ions need to be free to move One mark for each bullet point 2
- In a solid they are in a fixed position
TOTAL 12
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
Question Answer Additional Guidance Marks
7a Mass of desired products /mass of all One marks for correct equation of use of 4
products equation
(2x46)/180 One mark for mass of ethanol
=51.1% One mark for mass of all reactants
One mark for final answer
7b -hydration 2
-no waste products
7c -change reaction to reduce waste 2
-find a use for the ‘waste’ products
TOTAL 8
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
Question Answer Additional Guidance Marks
8a 10x10x10 = 1,000nm3 Allow 1 mark for large cube is 125 times the 2
volume of the small cube if no calculations
2x2x2 = 8nm3 shown
8b 10x10x6x1 = 600nm2 Allow 1 mark for small cube is 5 times the 2
surface area of the large cube if no
2x2x6x125 = 3,000nm2 calculations shown
8c -Smaller particles have a higher surface area 1
to volume ratio
8d -medicine Two from list 2
-electronics
-cosmetics
-deodorant
-catalyst
8e Advantages Max three marks from each list 5
-rubs in easier
-not white so looks better
-can get deeper into skin
-no need to reapply after water contact
Disadvantages
-hard to see areas that might have been
missed
-long term effects of nanoparticles on cells is
unknown
-could damage environment
TOTAL 12
Primrose Kitten – YouTube Tutorials for GCSE and A-Level
You might also like
- Ag Advace Check 8-30Document1 pageAg Advace Check 8-30AceNo ratings yet
- Biology: 2017 Mulanje Cluster Msce Mock ExaminationsDocument7 pagesBiology: 2017 Mulanje Cluster Msce Mock ExaminationsAlfred Mwayuta100% (1)
- Life Without A Centre by Jeff FosterDocument160 pagesLife Without A Centre by Jeff Fosterdwhiteutopia100% (5)
- Kasempa Boys Boarding Secondary School Grade 10 B Chemistry Test 2 TERM: 1 YEAR: 2019 Duration: 1 Hour 20 Minutes MARKS: 51Document3 pagesKasempa Boys Boarding Secondary School Grade 10 B Chemistry Test 2 TERM: 1 YEAR: 2019 Duration: 1 Hour 20 Minutes MARKS: 51Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Test Chemistry Year 10Document13 pagesTopic 3 Test Chemistry Year 10Do It Yourself - DIYNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Triple C7 Test 5 Advanced QPDocument20 pagesAQA GCSE Triple C7 Test 5 Advanced QPryanNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Chemistry Practice Paper 2 2023Document48 pagesAQA A Level Chemistry Practice Paper 2 2023William BackNo ratings yet
- Khenpo Tsultrim Gyamtso Rinpoche - Meditation On EmptinessDocument206 pagesKhenpo Tsultrim Gyamtso Rinpoche - Meditation On Emptinessdorje@blueyonder.co.uk100% (1)
- Principles of Marketing: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Marketing ResearchDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: Quarter 1 - Module 6: Marketing ResearchAmber Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Architect Magazine 2023 0506Document152 pagesArchitect Magazine 2023 0506fohonixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Supplier Quality ManagementDocument71 pagesChapter 8 Supplier Quality ManagementAnh NguyenNo ratings yet
- JCE Science Paper 2Document13 pagesJCE Science Paper 2Thabang Moduka100% (5)
- NURS 366 Exam 1 Study Guide and RubricDocument7 pagesNURS 366 Exam 1 Study Guide and RubriccmpNo ratings yet
- AQA - GCSE Separate Science - Higher - Physics - Paper 1 - 2023 PredictionsDocument26 pagesAQA - GCSE Separate Science - Higher - Physics - Paper 1 - 2023 PredictionsooooNo ratings yet
- Ques Pre-Pspm KMLDocument8 pagesQues Pre-Pspm KMLfatihah abdullahNo ratings yet
- AQA - GCSE Combined Science - Higher - Physics - Paper 1 - 2023 PredictionsDocument19 pagesAQA - GCSE Combined Science - Higher - Physics - Paper 1 - 2023 Predictionsa kamranNo ratings yet
- Biology Term2 Assessment Y10Document10 pagesBiology Term2 Assessment Y109hgdpyk96jNo ratings yet
- 6marker Revision Yr 11 Each TopicDocument15 pages6marker Revision Yr 11 Each Topiclinachouli7654No ratings yet
- c9 Chemistry of The Atmosphere HTDocument66 pagesc9 Chemistry of The Atmosphere HTMadhavi OchaniNo ratings yet
- Phy Mid Year ExamDocument13 pagesPhy Mid Year ExamKendrickNo ratings yet
- 6031 Q 2 SpecimenDocument16 pages6031 Q 2 Specimenmarume944No ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableDocument15 pagesChemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableRenee DisaNo ratings yet
- Sep 2013Document28 pagesSep 2013Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableDocument17 pagesChemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableVictor WuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Time Allowed: 1 Hour Paper 2 Theory Total Marks: /45Document10 pagesChemistry Time Allowed: 1 Hour Paper 2 Theory Total Marks: /45Salman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper IIDocument12 pagesChemistry Paper IIMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Paper 2Document28 pagesChemistry Practice Paper 2Nimisha RejiNo ratings yet
- C1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table HTDocument57 pagesC1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table HTAdnan BukhariNo ratings yet
- M23 AASL Paper 2Document12 pagesM23 AASL Paper 2Yewah Nzali Guy KyleNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument9 pagesYear 10 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Bonding Structure Properties of Carbon HigherDocument42 pagesBonding Structure Properties of Carbon Highermoizmohammad09No ratings yet
- Question Maximum Score Candidate'S ScoreDocument10 pagesQuestion Maximum Score Candidate'S ScoreVICTOR ONGWENNo ratings yet
- Balanced Equations and Associated CalcsDocument11 pagesBalanced Equations and Associated CalcsOliver JonesNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 (Pract Paper)Document19 pagesPaper 2 (Pract Paper)ephixNo ratings yet
- 4.6 Rate of Reaction HDocument14 pages4.6 Rate of Reaction HAysha NaseerNo ratings yet
- Year2guidedrevision Prac3and4Document9 pagesYear2guidedrevision Prac3and4alaynasharleezNo ratings yet
- 2021 SAJC Prelim P2 QnsDocument24 pages2021 SAJC Prelim P2 Qns6fhntwb78dNo ratings yet
- Test 3Document6 pagesTest 3Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (5070) Grade 12 B Mid Term Test 2020Document4 pagesChemistry (5070) Grade 12 B Mid Term Test 2020Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- C3 Quantitative Chemistry HTDocument65 pagesC3 Quantitative Chemistry HTMadhavi OchaniNo ratings yet
- F5S Chemistry Revision Worksheet (6) - Double DecompositionDocument8 pagesF5S Chemistry Revision Worksheet (6) - Double DecompositionRaymond ChanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 Question Paper Zeraki Achievers 10.0 July 2023Document10 pagesChemistry Paper 1 Question Paper Zeraki Achievers 10.0 July 2023vincent mosotaNo ratings yet
- Pre APhysics Required PracticalsDocument22 pagesPre APhysics Required PracticalsShaguNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Mais Nov 2020 10 IgcseDocument13 pagesChemistry: Mais Nov 2020 10 IgcseKrishvardhan GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Rate and Extent of Chemical ChangeDocument11 pagesThe Rate and Extent of Chemical ChangeKirsten AntonioNo ratings yet
- Science Exam QuestionsDocument10 pagesScience Exam QuestionscheetoNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 - Basic Elements in LifeDocument14 pagesCHP 1 - Basic Elements in LifeShaaru TharshiniNo ratings yet
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council Agriculture 4001/2Document12 pagesZimbabwe School Examinations Council Agriculture 4001/2Lloyd Chris100% (2)
- C Annual 2023Document12 pagesC Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- May 2015Document52 pagesMay 2015Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- Science Model Paper 2Document12 pagesScience Model Paper 2l82781103No ratings yet
- Topic 1 Assessment BookletDocument36 pagesTopic 1 Assessment BookletLinNo ratings yet
- Physics PI - FinalDocument12 pagesPhysics PI - FinalSaulosi SaidiNo ratings yet
- C2.1 ExamPro and 6-MarkDocument2 pagesC2.1 ExamPro and 6-MarkerskineravelNo ratings yet
- c3 Quantitative ChemistryDocument105 pagesc3 Quantitative Chemistryraja balaNo ratings yet
- c6 The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change HTDocument73 pagesc6 The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change HTewfjehwjfNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Part 6Document38 pagesAtomic Structure Part 6xenaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate Chemical ChangesDocument16 pagesChemistry Separate Chemical ChangesJoyel ZtephenNo ratings yet
- Anderson STPM Trial Chemistry P2 With AnswerDocument23 pagesAnderson STPM Trial Chemistry P2 With Answerlsueyin100% (1)
- Bonding (Level 4)Document27 pagesBonding (Level 4)Rishikesh MaharajNo ratings yet
- Intro To Atoms Moles and Stoichiometry: As Level Chemistry Test Name: Class: TeacherDocument8 pagesIntro To Atoms Moles and Stoichiometry: As Level Chemistry Test Name: Class: TeacherMatthew James PopeNo ratings yet
- CAPE Chemistry Unit 1 2013 P2Document18 pagesCAPE Chemistry Unit 1 2013 P2Ruchi MarajhNo ratings yet
- 2023 CHEMISTRY F3 P2 QS T2 Exam Teacher - Co - .KeDocument9 pages2023 CHEMISTRY F3 P2 QS T2 Exam Teacher - Co - .Kealooben2No ratings yet
- S1 Quiz3Document8 pagesS1 Quiz3buck albinoNo ratings yet
- Properties of Period 3 Elements and Their Oxides QPDocument11 pagesProperties of Period 3 Elements and Their Oxides QPfatma sNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding RevisionDocument11 pagesMetallic Bonding RevisionStaceNo ratings yet
- CHP 11: Setting Goals and Managing The Sales Force's PerformanceDocument2 pagesCHP 11: Setting Goals and Managing The Sales Force's PerformanceHEM BANSALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Creating and Managing TeamsDocument40 pagesChapter 13 Creating and Managing TeamsH.No ratings yet
- Text Mohamed AliDocument2 pagesText Mohamed AliARYAJAI SINGHNo ratings yet
- SAi Sankata Nivarana StotraDocument3 pagesSAi Sankata Nivarana Stotrageetai897No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledRoger GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 173544avaya Aura AES 7-0 JTAPI Programmers GuideDocument88 pages173544avaya Aura AES 7-0 JTAPI Programmers GuideAhmed SakrNo ratings yet
- Reflexive PronounsDocument2 pagesReflexive Pronounsquely8343% (7)
- Co-Publisher AgreementDocument1 pageCo-Publisher AgreementMarcinNo ratings yet
- Al-Baraa Ibn Malik Al-AnsariDocument3 pagesAl-Baraa Ibn Malik Al-AnsariRahbarTvNo ratings yet
- SBMPTN 2016 Kode 333Document6 pagesSBMPTN 2016 Kode 333Allisa MasithaNo ratings yet
- Sokkia GRX3Document4 pagesSokkia GRX3Muhammad Afran TitoNo ratings yet
- Brief For Community Housing ProjectDocument5 pagesBrief For Community Housing ProjectPatric LimNo ratings yet
- Right To Information: National Law University AND Judicial Academy, AssamDocument20 pagesRight To Information: National Law University AND Judicial Academy, Assamsonu peterNo ratings yet
- John Wick 4 HD Free r6hjDocument16 pagesJohn Wick 4 HD Free r6hjafdal mahendraNo ratings yet
- Pedia Edited23 PDFDocument12 pagesPedia Edited23 PDFAnnJelicaAbonNo ratings yet
- Wa0009.Document14 pagesWa0009.Pradeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Legend of September 2019 MagazineDocument40 pagesLegend of September 2019 MagazineAswathi ThatchinamoorthiNo ratings yet
- Degree Program Cheongju UniversityDocument10 pagesDegree Program Cheongju University심AvanNo ratings yet
- PH Scale: Rules of PH ValueDocument6 pagesPH Scale: Rules of PH Valuemadhurirathi111No ratings yet
- Independence of Costa RicaDocument2 pagesIndependence of Costa Ricaangelica ruizNo ratings yet
- Chapters Name in Sanskrit and English Setting The SceneDocument3 pagesChapters Name in Sanskrit and English Setting The Sceneishvarchandra dasNo ratings yet
- MoMA Learning Design OverviewDocument28 pagesMoMA Learning Design OverviewPenka VasilevaNo ratings yet
- 130004-1991-Maceda v. Energy Regulatory BoardDocument14 pages130004-1991-Maceda v. Energy Regulatory BoardChristian VillarNo ratings yet