Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Separate Chemical Changes
Uploaded by
Joyel ZtephenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Separate Chemical Changes
Uploaded by
Joyel ZtephenCopyright:
Available Formats
4-4 Chemical changes – Chemistry
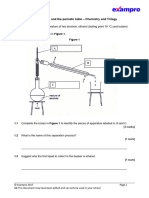
1.0 A student investigated the reaction of sodium carbonate with dilute hydrochloric acid.
The student used the apparatus shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Sodium carbonate
This is the method used.
1. Place a known mass of sodium carbonate in a conical flask.
2. Measure 15 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid using a measuring cylinder.
3. Pour the acid into the conical flask.
4. Place a bung in the flask and collect the gas as shown in Figure 1.
1.1 Balance the equation for the reaction.
[1 mark]
Na2CO3 (s) + _____ HCl (aq) → _____ NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
1.2 Name the substance produced as a gas.
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 1
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
Figure 2 shows the measuring cylinder.
Figure 2
1.3 What volume of gas has been collected?
[1 mark]
Volume = ____________________ cm3
1.4 Table 1 shows the student’s results.
Table 1
Mass of
Volume of gas in cm3
sodium carbonate in g
0.0 0
0.1 23
0.2 28
0.3 69
0.4 92
0.5 98
0.6 98
0.7 98
© Exampro 2017 Page 2
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
On Figure 3:
• Plot these results on the grid.
• Complete the graph by drawing two straight lines of best fit.
[4 marks]
Figure 3
Volume
of gas in
cm3
Mass of sodium carbonate in g
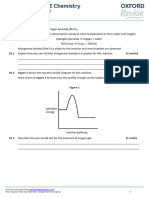
1.5 Describe two patterns the graph shows when sodium carbonate is added.
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 3
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
2.0 Describe a safe method for making pure crystals of magnesium chloride from
magnesium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid.
In your method you should name all of the apparatus you will use.
[6 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 4
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
3.0 A student investigated the reactivity of metals with acids.
Five different metals were investigated.
Figure 4 shows the apparatus the student used.
Figure 4
thermometer
boiling-tube
acid
Cu Mg Al Zn Fe
The method the student used was:
• measured 10 cm3 of dilute acid using a 50 cm3 measuring cylinder
• placed 10 cm3 of dilute acid in a boiling tube
• added a 2 cm length of metal to the dilute acid
• measured the highest temperature reached
• repeated the experiment using different metals.
Table 1 shows the student’s results.
Table 1
Metal Temperature change (°C)
Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Mean
Aluminium 33 10 35
Copper 1 0 2 1
Iron 22 21 20 21
Magnesium 44 46 45 45
Zinc 25 27 26 26
3.1 State the dependent and independent variables in the investigation.
[2 marks]
Dependent variable_______________________________________________
Independent variable _____________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 5
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
3.2 Name two control variables the student kept the same.
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
3.3 Calculate the mean temperature change for aluminium.
[1 mark]
Mean temperature change for aluminium = ___________________ °C
3.4 Suggest two changes that could improve the accuracy of the investigation.
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
3.5 Use the data in Table 1 to list the metals in order of reactivity from most reactive to
least reactive.
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
3.6 Suggest why the student did not use any Group 1 metals in the investigation.
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 6
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
4.0 A student investigated displacement reactions of metals.
The student added different metals to copper sulfate solution and measured the
temperature change.
The more reactive the metal is compared with copper, the bigger the temperature change.
The apparatus the student used is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5
The student repeated the experiment three times with each metal.
Table 2 shows the mean temperature change for each metal.
Table 2
Mean
Metal temperature
change in °C
Copper 0.0
Iron 6.5
Lead 1.2
Magnesium 10.0
Silver 0.0
Zinc 7.8
© Exampro 2017 Page 7
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
4.1 On Figure 6, draw a bar chart to show the results.
[3 marks]
Figure 6
4.2 Why is a bar chart the most suitable way of showing the results?
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
4.3 Explain how these results can be used to work out a reactivity series.
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
4.4 Iron can be extracted by reacting iron oxide with carbon in a blast furnace.
What type of reaction produces iron from iron oxide?
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 8
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
5.0 Magnesium is extracted by the electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride.
5.1 Complete the half equation for the formation of magnesium at the negative electrode.
[2 marks]
Mg2+ + →
5.2 Chlorine gas is also produced.
Describe how chlorine is produced during the process.
[4 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
5.3 Some metals are extracted from their ores using carbon.
Why is it not possible to extract magnesium using carbon?
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
5.4 Aqueous magnesium chloride is not used to extract magnesium.
Explain why.
[3 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 9
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
6.0 Bath bombs contain solid citric acid and solid sodium hydrogen carbonate.
6.1 Citric acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate to produce a salt, sodium citrate.
The equation for the reaction is:
H3C6H8O7 (s) + 3NaHCO3 (s) Na3C6H8O7 (aq) + 3CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l)
Which part of the equation shows that this reaction only takes place when bath bombs
are added to water?
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
6.2 Bath bombs fizz when added to water.
What causes the fizzing?
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
6.3 Citric acid is a weak acid.
State what is meant by the term weak acid.
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 10
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
7.0 A student used the equipment shown to do a titration.
7.1 Describe how the student should use this equipment to find the volume of sodium
hydroxide solution that reacts with 25 cm3 of nitric acid.
Include:
Which indicator would be suitable for use
The colour change seen
Any measurements the student should make
How the results should be processed.
[6 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 11
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 12
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
MARK SCHEME
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
1.1 Na2CO3 (s) + 2 HCl (aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + 1
H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
1.2 Carbon dioxide 1
1.3 56 (cm3) 1
1.4 All points correct ± ½ small square 2
allow 1 mark if 6 or 7 of the points are
correct
2 best fit lines drawn must not deviate towards anomalous 2
point
allow 1 mark if 1 line correct
1.5 Any two from: 2
• As mass of lithium carbonate increases
volume of gas produced increases
• No more gas is produced after 0.5 g of
sodium carbonate is added
• Until 0.4 g of sodium carbonate is added
the graph is linear / (directly)
proportional
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
2.0
Level 3: A coherent method is described with relevant detail, and in correct sequence which 5-6
demonstrates a broad understanding of the relevant scientific techniques and
procedures. The steps in the method are logically ordered. The method would lead to
the production of valid results.
Level 2: The bulk of the method is described with mostly relevant detail, which demonstrates a 3-4
reasonable understanding of the relevant scientific techniques and procedures. The
method may not be in a completely logical sequence and may be missing some detail.
Level 1: Simple statements are made which demonstrate some understanding of some of the 1-2
relevant scientific techniques and procedures. The response may lack a logical
structure and would not lead to the production of valid results.
Level 0: No relevant content 0
Indicative content
• Hydrochloric acid in beaker (or similar)
• Add magnesium carbonate one spatula at a time
• Until magnesium carbonate is in excess or until no more effervescence occurs
• Filter using filter paper and funnel
• Filter excess magnesium carbonate
• Pour solution into evaporating basin / dish
• Heat using Bunsen burner
• Leave to crystallise / leave for water to evaporate / boil off water
• Decant solution
• Pat dry (using filter paper)
• Wear safety spectacles / goggles
© Exampro 2017 Page 13
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
3.1 Dependent variable 1
Temperature change
Independent variable 1
Type of metal
3.2 Any two from: 2
• Concentration of acid
• Volume of acid
• Type of acid
• Mass of metal
• Size of metal
• Surface area of metal
3.3 34 (°C) 1
3.4 Any two from: 2
• Measure the mass of the metal (instead
of length)
• Use a thermometer that reads to more Allow use a digital thermometer that
decimal places/ has more scale reads to more decimal places
divisions.
• Use a burette or pipette to measure
volume of acid
• Use a 10 cm3 measuring cylinder
(instead of 50 cm3)
• Use a measuring cylinder with more
scale divisions
3.5 Most reactive Allow ecf from calculation of mean 1
Magnesium
Aluminium
Zinc
Iron
Copper
3.6 They would be too reactive/dangerous 1
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
4.1 Four bars of correct height tolerance is ± half square 2
allow 3 bars correct for 1 mark
Bars labelled 1
4.2 One variable is non-continuous / categoric allow qualitative or discrete 1
allow no values between the metals
4.3 Most reactive metal has the highest 1
temperature change
4.4 Reduction 1
© Exampro 2017 Page 14
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
5.1 Mg 2+ -
+ 2e → Mg 2
Allow 1 mark for e-
5.2 Chloride ions 1
attracted to positive electrode 1
(where they) lose electrons 1
chlorine atom / molecule produced 1
5.3 Magnesium too reactive 1
or
Carbon not reactive enough
5.4 Magnesium ions and hydrogen ions 1
attracted to negative electrode
Hydrogen is formed in preference to 1
magnesium
As hydrogen less reactive (than 1
magnesium)
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
6.1 (aq) Means aqueous solution 1
6.2 Carbon dioxide produced For 2 marks, allow carbon dioxide gas is 1
produced
Which is released as a gas 1
6.3 Does not fully ionise/dissociate Allow only partially ionises/dissociates 1
© Exampro 2017 Page 15
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
7.1
Level 3: A full, coherent description of a titration that would allow successful results to be 5-6
obtained. No major errors in science or in naming equipment or chemicals.
Level 2: The bulk of the titration is described with mostly relevant detail, which demonstrates a 3-4
reasonable understanding of the relevant scientific techniques and procedures. The
method may not be in a completely logical sequence and may be missing some detail.
There may be some minor errors in science or in naming equipment or chemicals.
Level 1: A simple description of using some of the equipment. Errors or omissions in science or 1-2
in naming equipment or chemicals.
Level 0: No relevant content 0
Indicative content
• Acid in (conical) flask
• Volume of acid measured using pipette
• Indicator in (conical) flask
• Suitable indicators include phenolphthalein / methyl orange / litmus
• Colour change seen:
phenolphthalein: colourless to pink
methyl orange: yellow to red
litmus: blue to red
• Sodium hydroxide in burette
• White tile under flask
• Slow addition
• Swirling
• Volume of sodium hydroxide added
• Repeat several times
• Until at least three concordant results
© Exampro 2017 Page 16
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
You might also like
- Chemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableDocument15 pagesChemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableRenee DisaNo ratings yet
- Lower - Secondary - Science - 8 - End-Of-Year TestDocument9 pagesLower - Secondary - Science - 8 - End-Of-Year TestShahana Ahth100% (2)
- CBLM Implementing Plant Nutrition ProgramDocument64 pagesCBLM Implementing Plant Nutrition Programmarlene a. dinlayanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate Chemical ChangesDocument16 pagesChemistry Separate Chemical ChangesTahmid SiraziNo ratings yet
- Changes in Chemical Reactions Prac Report Sheet - 2023Document6 pagesChanges in Chemical Reactions Prac Report Sheet - 2023mxq88557No ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate and Trilogy Rate and Extent Chemical Change-2Document13 pagesChemistry Separate and Trilogy Rate and Extent Chemical Change-2wolfergemerioNo ratings yet
- Sep 2013Document28 pagesSep 2013Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- $titrationDocument6 pages$titrationMaryam ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableDocument17 pagesChemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableVictor WuNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument9 pagesYear 10 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- RateDocument29 pagesRateapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Chemistry Questions 2Document44 pagesChemistry Questions 2Yasmine CaparNo ratings yet
- c6 The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change HTDocument73 pagesc6 The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change HTewfjehwjfNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Mcse PiiDocument6 pagesChemistry Mcse PiiMoses SamalaniNo ratings yet
- Assesment For ChemistryDocument5 pagesAssesment For ChemistrymiraNo ratings yet
- Test 2-P2Document8 pagesTest 2-P2Salman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- 4.6 Rate of Reaction HDocument14 pages4.6 Rate of Reaction HAysha NaseerNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-05-21 at 22.25.04Document28 pagesScreenshot 2023-05-21 at 22.25.04aneyarajaNo ratings yet
- 6031 Q 2 SpecimenDocument16 pages6031 Q 2 Specimenmarume944No ratings yet
- Amali Wajib Kimia Tingkatan 4Document18 pagesAmali Wajib Kimia Tingkatan 4NUR FARRAH NAJIHAH BINTI AMIR KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Paper 2Document28 pagesChemistry Practice Paper 2Nimisha RejiNo ratings yet
- F5 Chemistry CHP 1Document12 pagesF5 Chemistry CHP 1muraliMuNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 (Pract Paper)Document19 pagesPaper 2 (Pract Paper)ephixNo ratings yet
- Pastyear Chemistry F4C3Document11 pagesPastyear Chemistry F4C3amie1312100% (1)
- 10ae Calculations 28TH FebDocument7 pages10ae Calculations 28TH FebFiefNo ratings yet
- c4 Titrations Chem OnlyDocument31 pagesc4 Titrations Chem OnlyMadhavi OchaniNo ratings yet
- Set 1 (Questions)Document35 pagesSet 1 (Questions)Thung LingNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate and Trilogy The AtmosphereDocument13 pagesChemistry Separate and Trilogy The AtmosphereseekingNo ratings yet
- C Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023Document12 pagesC Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Quantititive Chemistry - Paper 1 TES - 4Document37 pagesQuantititive Chemistry - Paper 1 TES - 4KshitijNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate Chemical AnalysisDocument15 pagesChemistry Separate Chemical Analysissallyamoah07No ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction FactorsDocument8 pagesRate of Reaction FactorsAmirah Noor AffandiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Time Allowed: 1 Hour Paper 2 Theory Total Marks: /45Document10 pagesChemistry Time Allowed: 1 Hour Paper 2 Theory Total Marks: /45Salman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- CSEC® Chemistry Past Papers EbookDocument2 pagesCSEC® Chemistry Past Papers EbookVivek BachuNo ratings yet
- S9 - End-Of-Unit 5 TestDocument2 pagesS9 - End-Of-Unit 5 TestMoganoni MogaNo ratings yet
- C8 Practice Paper 2Document10 pagesC8 Practice Paper 2jordan2trapzNo ratings yet
- Topic Test 4 MoleDocument8 pagesTopic Test 4 MoleJaspar GlagovsNo ratings yet
- Phy Mid Year ExamDocument13 pagesPhy Mid Year ExamKendrickNo ratings yet
- The Rate and Extent of Chemical ChangeDocument11 pagesThe Rate and Extent of Chemical ChangeKirsten AntonioNo ratings yet
- Review Test 2Document8 pagesReview Test 2Sameeh MuhammedNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry January 2011 P2Document18 pagesCSEC Chemistry January 2011 P2AshleyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Mcse PiDocument10 pagesChemistry Mcse PiMoses SamalaniNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry January 2012 P032Document7 pagesCSEC Chemistry January 2012 P032AshleyNo ratings yet
- May 2015Document52 pagesMay 2015Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- 2019f5s9ex7chemistry 2Document10 pages2019f5s9ex7chemistry 2AlyciaLeeNo ratings yet
- c9 Chemistry of The Atmosphere HTDocument66 pagesc9 Chemistry of The Atmosphere HTMadhavi OchaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Mais Nov 2020 10 IgcseDocument13 pagesChemistry: Mais Nov 2020 10 IgcseKrishvardhan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument11 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- 2022 Chemistry Paper I (Theory) MJ CLUSTERDocument11 pages2022 Chemistry Paper I (Theory) MJ CLUSTERishmaeljonas681No ratings yet
- Sep 2014Document28 pagesSep 2014Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 4 October 2004Document11 pagesChemistry Paper 4 October 2004Dean DambazaNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Analysis Lab ReportDocument5 pagesVolumetric Analysis Lab ReportcrissaniaNo ratings yet
- Rates Practice Exam QuestionsDocument18 pagesRates Practice Exam QuestionsisheanesuNo ratings yet
- 8.-Chamical-Analysis---Paper-2-TESDocument27 pages8.-Chamical-Analysis---Paper-2-TESYotos XdNo ratings yet
- 2017 Unit 3 Chemistry KTT 2 Combustion Question BookDocument10 pages2017 Unit 3 Chemistry KTT 2 Combustion Question Bookmichael scottNo ratings yet
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang Trial SPM 2019 Chemistry Form 5 Paper 3 Time: One Hour and Thirty Minutes Name: - School No: - ClassDocument6 pagesSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang Trial SPM 2019 Chemistry Form 5 Paper 3 Time: One Hour and Thirty Minutes Name: - School No: - ClassNicholson NicholsonNo ratings yet
- Form TP 2014154Document10 pagesForm TP 2014154Daniella SalandyNo ratings yet
- Y12 April Assessment 2019Document10 pagesY12 April Assessment 2019Anela XVIINo ratings yet
- Cover Booklet KS4 Chemistry 1Document61 pagesCover Booklet KS4 Chemistry 1Peter HoskinsNo ratings yet
- Nexus PMR Science Form 1 - 2 - 3 Page 123 (Extra Practice)Document4 pagesNexus PMR Science Form 1 - 2 - 3 Page 123 (Extra Practice)Ms_SyazanaNo ratings yet
- Tank FailuresDocument65 pagesTank FailuresAnonymous GfPSYi4n100% (1)
- Technology Scouting Carbon Capture From Todays To Novel TechnologiesDocument11 pagesTechnology Scouting Carbon Capture From Todays To Novel TechnologiesTarek Ahmed AbdelhadyNo ratings yet
- Prevent From Flower and Fruit DroppingDocument2 pagesPrevent From Flower and Fruit DroppingRachel BiostimulantsNo ratings yet
- Masterseal TC 257 D GREY Part ADocument10 pagesMasterseal TC 257 D GREY Part ADhiwagar MJNo ratings yet
- Immuno FluorescenceDocument2 pagesImmuno FluorescenceEstiak RonyNo ratings yet
- PE Health 11 Ist Semester Module 2 Energy System Version 3Document21 pagesPE Health 11 Ist Semester Module 2 Energy System Version 3Leary John TambagahanNo ratings yet
- Comparative Performance Analysis of Different Twisted Tape Inserts in The Absorber Tube of Parabolic Trough CollectorDocument14 pagesComparative Performance Analysis of Different Twisted Tape Inserts in The Absorber Tube of Parabolic Trough CollectorTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- فصل فينولات وقلويدات PDFDocument17 pagesفصل فينولات وقلويدات PDFThegoldenTigerNo ratings yet
- Role of Chemical EngineerDocument5 pagesRole of Chemical EngineerRichard MamoneNo ratings yet
- Tabla 8.1 Soldadura de Acero InoxidableDocument1 pageTabla 8.1 Soldadura de Acero InoxidableJuan Alberto Lopez SanchezNo ratings yet
- Nayak and Bhuschan, 2019 WastesDocument19 pagesNayak and Bhuschan, 2019 WastesdjfhdjNo ratings yet
- CP BIO: Ch. 7 The Cell MembraneDocument31 pagesCP BIO: Ch. 7 The Cell MembraneJohn Lester BerdinNo ratings yet
- Plasma-And Laser-Cutting ToolDocument17 pagesPlasma-And Laser-Cutting ToolRiyan EsapermanaNo ratings yet
- Nonferrous Metals and Alloys: Production, General Properties, and ApplicationsDocument13 pagesNonferrous Metals and Alloys: Production, General Properties, and Applicationsvicki20julyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Stress-Strain and True Stress-Strain Analysis in Uniaxial Tension TestingDocument33 pagesEngineering Stress-Strain and True Stress-Strain Analysis in Uniaxial Tension TestingZANTHERNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution Report TemplateDocument4 pagesExperiment 2 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution Report Templatemhonk479No ratings yet
- Class Programme: Type ApprovalDocument18 pagesClass Programme: Type ApprovalGoran VNo ratings yet
- Astm G 145 - 96Document10 pagesAstm G 145 - 96AL DOMANo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument82 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Data 2Document1 pageData 2Radha NandhiniNo ratings yet
- Sizing CostingDocument39 pagesSizing CostingMarilynYunLingNo ratings yet
- Judy Chemistry FinalDocument4 pagesJudy Chemistry FinalJudy IntervencionNo ratings yet
- Wittig LabDocument5 pagesWittig Labthrowaway_accountNo ratings yet
- 9 JEE Chemistry General Organic Chemistry Reaction IntermediatesDocument20 pages9 JEE Chemistry General Organic Chemistry Reaction IntermediatesA MesihaNo ratings yet
- VinnapasDocument2 pagesVinnapasNguyễn Quốc TiếnNo ratings yet
- MSS SP53Document9 pagesMSS SP53nile_asterNo ratings yet
- Huntsmann EU ELECTRONICS-Selector-GuideDocument24 pagesHuntsmann EU ELECTRONICS-Selector-GuideXavierNo ratings yet
- Principles of Steady-state Heat Transfer in RadiationDocument47 pagesPrinciples of Steady-state Heat Transfer in RadiationKamal JamaliNo ratings yet
- Using HSC Allows Longer Spans and Shallower BridgesDocument21 pagesUsing HSC Allows Longer Spans and Shallower BridgesMahbub AlamNo ratings yet