Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bpe Micro Project
Uploaded by
Ishwari Jadhav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views9 pagesHalf-wave rectifiers use a single diode to allow only the positive half of the AC voltage waveform to pass, blocking the negative half. This converts the AC to a pulsing DC voltage. The firing angle of an SCR can be controlled to change the starting point of load current in a controlled half-wave rectifier. A half-wave rectifier circuit consists of a transformer, SCR, load resistor, and connecting wires. It is a simple design but has low output voltage and high ripple. Applications include electrochemical processes and magnet power supplies.
Original Description:
Original Title
BPE MICRO PROJECT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHalf-wave rectifiers use a single diode to allow only the positive half of the AC voltage waveform to pass, blocking the negative half. This converts the AC to a pulsing DC voltage. The firing angle of an SCR can be controlled to change the starting point of load current in a controlled half-wave rectifier. A half-wave rectifier circuit consists of a transformer, SCR, load resistor, and connecting wires. It is a simple design but has low output voltage and high ripple. Applications include electrochemical processes and magnet power supplies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views9 pagesBpe Micro Project
Uploaded by
Ishwari JadhavHalf-wave rectifiers use a single diode to allow only the positive half of the AC voltage waveform to pass, blocking the negative half. This converts the AC to a pulsing DC voltage. The firing angle of an SCR can be controlled to change the starting point of load current in a controlled half-wave rectifier. A half-wave rectifier circuit consists of a transformer, SCR, load resistor, and connecting wires. It is a simple design but has low output voltage and high ripple. Applications include electrochemical processes and magnet power supplies.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
1.
INTRODUCTION
Half-wave rectifiers transform AC voltage to DC voltage. A half wave
rectifier circuit uses only one diode for the transformation. A half wave
rectifier is defined as a type of rectifier that allows only one-half cycle of
an AC voltage waveform to pass while blocking the other half cycle. At
the most basic level, load resistance is the cumulative resistance of a
circuit, as seen by the voltage, current, or power source driving that
circuit. This includes the resistance of the wires and the resistance of any
devices connected to those wires. The word “controlled” means that, we
can change the starting point of load current by controlling the firing
angle of SCR. These words might seem a lot technical. But firing
of SCR simply means, the SCR turn ON at certain point of time when it
is forward biased.
SANJAY GHODAWAT POLYTECHINC Page 1
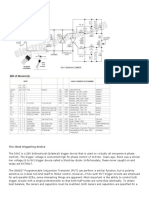
2. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
SANJAY GHODAWAT POLYTECHINC Page 2
3. Working
A half-wave rectifier converts an AC signal to DC by passing either the
negative or positive half-cycle of the waveform and blocking the other.
The half wave rectifier passes one half cycle of the alternating current
and blocks the other half cycle. Thus in one complete cycle of the AC
waveform, the half-cycle is passed. In a half wave rectifier, the circuit
operation depends on the state of the AC source and the firing angle α of
the 2-pulse generator. Single Phase Half Wave Controlled Rectifier, as
the name suggests, is a rectifier circuit which converts AC input into DC
output only for positive half cycle of the AC input supply. The word
“controlled” means that, we can change the starting point of load current
by controlling the firing angle of SCR. These words might seem a lot
technical. But firing of SCR simply means, the SCR turn ON at certain
point of time when it is forward biased.
SANJAY GHODAWAT POLYTECHINC Page 3
3. CIRCUIT IMAGE
SANJAY GHODAWAT POLYTECHINC Page 4
4. LIST OF COMPONENTS
Sr.no Component Name Quantity
1. Centre tapped transformer 1
2. SCR 1
3. Load Resistor 1
4. PCB Board 1
5. Connecting wire 3
SANJAY GHODAWAT POLYTECHINC Page 5
5. ADVANTAGES
1. Half wave rectifier is a simple circuit.
2. It has a low cost.
3. We can easy to use it.
4. We can easily construct.
6. DISADVANTAGE
1. Low output voltage.
2. The output contains a lot of ripples.
3. transformer utilization factor is low.
4. They produce a low output voltage.
5. Ripple factor is high and elaborate filtering is, therefore required to give
steady dc output.
6. They only allow a half cycle through per sinewave, and the other half
cycle is wasted. This leads to power loss.
SANJAY GHODAWAT POLYTECHINC Page 6
7. APPLICATIONS
1. electro-metallurgical and Electrochemical processes.
2. Reactor controls.
3. Magnet power supplies.
4. Portable hand instrument drives.
SANJAY GHODAWAT POLYTECHINC Page 7
8. CONCLUSION
A half-wave rectifier transforms an AC signal to DC by allowing one
half-cycle of the waveform to pass while blocking the other. Half-wave
rectifiers are simple to build using only one diode, but they are
inefficient compared to full-wave rectifiers. A half-wave rectifier is
used to demodulate the amplitude of a modulated signal. IN half-wave
rectification removes just the negative voltage component using a single
diode before converting to DC.
SANJAY GHODAWAT POLYTECHINC Page 8
9. REFERENCE
1. https://www.electronics-tutorial.net/
2.https://www.daenotes.com/electronics/industrial
3.https://electricalbaba.com/
4.https://www.eeeguide.com/
5.https://electricalvoice.com/
SANJAY GHODAWAT POLYTECHINC Page 9
You might also like
- Repair Manual Polaroid Land Camera Model 360 Revision I - September 1970Document87 pagesRepair Manual Polaroid Land Camera Model 360 Revision I - September 1970Elizabeth Perry Muderick100% (5)
- DC To Ac Converter by Using 555 Timer ICDocument6 pagesDC To Ac Converter by Using 555 Timer ICAlfred Adukobirre AdukobillaNo ratings yet
- Errori Engine FPTDocument70 pagesErrori Engine FPTAziez MonzhaNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors Drives Vol 4Document112 pagesElectric Motors Drives Vol 4matealoredana8015100% (5)
- Power Electronics NotesDocument44 pagesPower Electronics Notessameekshaa75% (4)
- 24V Battery Charger With SCRDocument8 pages24V Battery Charger With SCRluisNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Direction Control Using Power TriacDocument7 pagesDC Motor Direction Control Using Power TriacAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Ee2301 - Power Electronics: Om SathiDocument15 pagesEe2301 - Power Electronics: Om SathiNavneeth50% (6)
- 132kv SwitchyardDocument72 pages132kv Switchyardjogiyajee0% (1)
- Presentation UPPTCL 400KV Substation Motiram Adda, GorakhpurDocument23 pagesPresentation UPPTCL 400KV Substation Motiram Adda, GorakhpurAnik Goyal50% (6)
- Analog Circuits and Simulation LabDocument77 pagesAnalog Circuits and Simulation LableevasusanNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual1Document72 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual1Harish SvNo ratings yet
- Advance Power ElectronicsDocument20 pagesAdvance Power ElectronicsSudip MondalNo ratings yet
- SCRDocument9 pagesSCRCarlos GFNo ratings yet
- Bpe MicroprojectDocument8 pagesBpe MicroprojectIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- Team Sigma - Controlled Halfwave RectifierDocument15 pagesTeam Sigma - Controlled Halfwave Rectifiersababjamil66No ratings yet
- Uppcl 132kv SubstationDocument36 pagesUppcl 132kv SubstationRitvik DhanjaaniNo ratings yet
- Isolated Bidirectional Full-Bridge DC-DC Converter With A Flyback SnubberDocument62 pagesIsolated Bidirectional Full-Bridge DC-DC Converter With A Flyback SnubberqwertyuiopNo ratings yet
- EdcccDocument18 pagesEdccckauyaNo ratings yet
- Low Power Inverter For Domestic ApplicationsDocument39 pagesLow Power Inverter For Domestic ApplicationsNarendhar MudavathNo ratings yet
- 19MO504-IE 2 MarksDocument40 pages19MO504-IE 2 MarksSaranya. M SNSNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks and 3 MarksDocument14 pages2 Marks and 3 Marksnani2012No ratings yet
- Snubber Circuits Suppress Voltage Transient Spikes in Multiple Output DC-DC Flyback Converter Power SuppliesDocument11 pagesSnubber Circuits Suppress Voltage Transient Spikes in Multiple Output DC-DC Flyback Converter Power SuppliesPlatin1976No ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics - 1 Marks - ECE-Polytechnic PDFDocument14 pagesIndustrial Electronics - 1 Marks - ECE-Polytechnic PDFSukesh RNo ratings yet
- 200 - EE8552, EE6503 Power Electronics - Question Bank 3Document119 pages200 - EE8552, EE6503 Power Electronics - Question Bank 3NiteshNarukaNo ratings yet
- Battery Charger Circuit Using SCRDocument5 pagesBattery Charger Circuit Using SCRlokesh100% (2)
- RACTIFIERDocument19 pagesRACTIFIERDhananjay Aghara100% (1)
- Double Freq TransientDocument22 pagesDouble Freq TransientMelissa Miller100% (1)
- Meena P EDocument32 pagesMeena P EKani mozhiNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument3 pagesHalf Wave RectifierAadhil .A. KareemNo ratings yet
- Light Dimmer Circuit: The Ideal Triggering DeviceDocument4 pagesLight Dimmer Circuit: The Ideal Triggering DeviceEmmanuel MiguelNo ratings yet
- Final ActivityDocument8 pagesFinal Activityodrhey hernandezNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Kapil Sahani 10EGIEE029 Presented To: Mr. Shakti Singh Shekhawat Head of The Department Electrical EngineeringDocument28 pagesPresented By: Kapil Sahani 10EGIEE029 Presented To: Mr. Shakti Singh Shekhawat Head of The Department Electrical Engineeringkapil97827No ratings yet
- EE51POWER ELECTORNICS EzDocument20 pagesEE51POWER ELECTORNICS EzAnonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- Verification Methods of Snubber Circuits in Flyback ConvertersDocument37 pagesVerification Methods of Snubber Circuits in Flyback ConvertersAydcon SccNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Simulation Project ReportDocument5 pagesPower Electronics Lab Simulation Project ReportMaha RaufNo ratings yet
- Single PhasingDocument41 pagesSingle PhasingdiljithNo ratings yet
- Elec 2 Report FinalDocument17 pagesElec 2 Report FinalMamoon KhanNo ratings yet
- Comparision of Voltage Stress Across The MOSFET Switch of A Flyback Converter With Various SnubbersDocument5 pagesComparision of Voltage Stress Across The MOSFET Switch of A Flyback Converter With Various SnubbersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesHalf Wave RectifierRishav PrasadNo ratings yet
- A High-Gain Nanosecond Pulse Generator Based On Inductor Energy Storage andDocument4 pagesA High-Gain Nanosecond Pulse Generator Based On Inductor Energy Storage andAhmadreza GhanaatianNo ratings yet
- Power Electronic Lab 4Document17 pagesPower Electronic Lab 4Muhammed Rafay LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 4 Half Wave Rectifier Pre - Lab QuestionsDocument8 pagesExperiment - 4 Half Wave Rectifier Pre - Lab Questionsgautam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For SCR and UJT: (Electronics: PHYS4008)Document24 pagesLecture Notes For SCR and UJT: (Electronics: PHYS4008)Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Inverter FT Correction 1Document33 pagesPower Inverter FT Correction 1Yusuf KehindeNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics-2 MarksDocument12 pagesPower Electronics-2 Marks20EUEE053- MADHUBALAN.SNo ratings yet
- Electronics IndustrialDocument6 pagesElectronics IndustrialhongNo ratings yet
- ECE 51 - Lab Activity 1 PDFDocument5 pagesECE 51 - Lab Activity 1 PDFJules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Power and Drive Elecrtonics MR - Hussien Muhsin Ms - Nabaa Issa Fdhelullah Abdulkarim Abdulmuhsin Fourth Stage (A)Document10 pagesPower and Drive Elecrtonics MR - Hussien Muhsin Ms - Nabaa Issa Fdhelullah Abdulkarim Abdulmuhsin Fourth Stage (A)فضل الله عبد الكريم عبد المحسنNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Group FiveDocument3 pagesPower Electronics Group FiveAgaba SamuelNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Group Five PDFDocument3 pagesPower Electronics Group Five PDFAgaba SamuelNo ratings yet
- Inverters and Applications Requirements of The Final ReportDocument5 pagesInverters and Applications Requirements of The Final ReportHuỳnh BảoNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Full Wavecontrolled RectifierDocument2 pagesSingle Phase Full Wavecontrolled Rectifierjosebijo17No ratings yet
- SCR Based Single Phase CycloconverterDocument6 pagesSCR Based Single Phase Cycloconverterchandra sekhar sahuNo ratings yet
- EE6503-Power ElectronicsDocument41 pagesEE6503-Power Electronicscwizard60No ratings yet
- Mendoza FinalActivityPTEDDocument8 pagesMendoza FinalActivityPTEDCARLIN JOSH MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument2 pagesPower ElectronicsnomNo ratings yet
- QB NewDocument13 pagesQB NewNarasimman DonNo ratings yet
- Group1 Battery ChargerDocument18 pagesGroup1 Battery ChargerNguyễn Nam AnhNo ratings yet
- Load Power Control by Using SCRDocument40 pagesLoad Power Control by Using SCRalthaf hussainNo ratings yet
- Project PDFDocument50 pagesProject PDFPiyali PalNo ratings yet
- Special Devices or Breakdown DevicesDocument13 pagesSpecial Devices or Breakdown DevicesMuhammad Arif Rattar100% (1)
- AEE311L Experiment 7 8Document8 pagesAEE311L Experiment 7 8Fe BaltazarNo ratings yet
- SUMMER TRAINING REPORT - Astha - FinalDocument35 pagesSUMMER TRAINING REPORT - Astha - FinalAstha AroraNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Last 2Document30 pagesElectronic Circuits Last 2AimanNo ratings yet
- OTDRDocument2 pagesOTDRIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument12 pagesQuestion BankIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Dse Round 1 Cutoff 2021 For VjtiDocument3 pagesMaharashtra Dse Round 1 Cutoff 2021 For VjtiIshwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- Free Education To Girl-Students Upto 12th STD (1994-95)Document9 pagesFree Education To Girl-Students Upto 12th STD (1994-95)Ishwari JadhavNo ratings yet
- A Three Phase Induction Motor Is Basically A Constant Speed Motor So ItDocument39 pagesA Three Phase Induction Motor Is Basically A Constant Speed Motor So ItManish MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Micro Project Report: Title:Characterstics of TRIACDocument14 pagesMicro Project Report: Title:Characterstics of TRIACgaikwad vijayNo ratings yet
- EMT 369 Wk2 Power Semiconductor Devices (GC)Document53 pagesEMT 369 Wk2 Power Semiconductor Devices (GC)Ashraf YusofNo ratings yet
- For Quadrant DC Motor ControlDocument43 pagesFor Quadrant DC Motor ControlDarshanRupani100% (1)
- Cr3-A 2 035 P: CR-series SCR Operation ManualDocument4 pagesCr3-A 2 035 P: CR-series SCR Operation ManualBENJAMIN COLELLNo ratings yet
- Application of High Power Thyristors in HVDC and FACTS SystemsDocument8 pagesApplication of High Power Thyristors in HVDC and FACTS SystemsNusrat Mary ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- What Is The Scope of Electrical EngineeringDocument9 pagesWhat Is The Scope of Electrical EngineeringMahesh NidumoluNo ratings yet
- 2B +RC+Triggering+CircuitDocument3 pages2B +RC+Triggering+CircuitklascoolNo ratings yet
- Types of Static SwitchesDocument55 pagesTypes of Static SwitchesSubhash MurkuteNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument26 pagesRectifierhemnphysic91No ratings yet
- Thyristor and Diode Modules2013Document19 pagesThyristor and Diode Modules2013jagadeesh.bammidiNo ratings yet
- SCR CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesSCR CharacteristicsFaizan MalikNo ratings yet
- Thyristors PDFDocument53 pagesThyristors PDFKashyap ChintuNo ratings yet
- Macro Electronic Lager ListaDocument55 pagesMacro Electronic Lager ListaDragoNo ratings yet
- Sdc-Labmanual by Prabhu Kumar SurarapuDocument62 pagesSdc-Labmanual by Prabhu Kumar Surarapuprabhu4scribdNo ratings yet
- Triac Lamp Dimmer Circuit.: DiacsDocument7 pagesTriac Lamp Dimmer Circuit.: DiacsBaquiran John Paul BaquiranNo ratings yet
- 04 Power SCD 2Document82 pages04 Power SCD 2riajulNo ratings yet
- GATE EE 2007 With SolutionsDocument62 pagesGATE EE 2007 With SolutionsAbhishek MohanNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Power ElectronicsDocument14 pagesThyristor Power ElectronicssayedtafseerNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Prof. Shete Omkar M. SRCOE, Pune Department of Electrical Engineering University of PuneDocument84 pagesPower Electronics: Prof. Shete Omkar M. SRCOE, Pune Department of Electrical Engineering University of PuneOmkar SheteNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument66 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manualm_javaidkhanNo ratings yet
- Static TransferDocument13 pagesStatic TransferCristian BandilaNo ratings yet
- Cours RedresseursDocument40 pagesCours RedresseursMoez YoussefNo ratings yet
- PEC-Diodes and SCRs PDFDocument12 pagesPEC-Diodes and SCRs PDFrizwanNo ratings yet