Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCC7 Bildiri Örneği (Ek-1)
NCC7 Bildiri Örneği (Ek-1)
Uploaded by
yalcintaha12Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCC7 Bildiri Örneği (Ek-1)
NCC7 Bildiri Örneği (Ek-1)
Uploaded by
yalcintaha12Copyright:
Available Formats
Preparation of Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Supported Cu and Pd
Nanoparticles Using Supercritical CO2 Deposition Method
Fatma Ulusala
a
Chemistry Departmant, University of Cukurova, 01330 Adana, TURKEY,
example@gmail.com
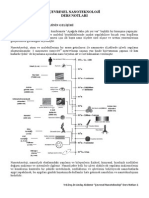
Metal nanoparticles supported on high surface area carbon substrates are used extensively as
catalysts for a wide variety of reactions. Among these catalysts, multiwall carbon nano tube
(MW-CNT) supported Pd and Cu catalysts are commonly used for hydrogenation and
oxydation reactions in organic synthesis. MW-CNT supported metal nanoparticles are
prepared by a variety of methods including microemulsion method, impregnation,
sonochemical method, modified polyol reduction and deposition-precipitation method. The
supercritical fluid (SCF) deposition technique has recently been receiving increased attention
for the preparation of carbonsupported catalysts. This process involves the dissolution of a
metallic precursor (MP) in a supercritical fluid and the exposure of the carbon support to the
solution. After adsorption of the precursor onto the support, the metallic precursor is
converted to its metal form by chemical or thermal reduction. This technique has been used to
prepare nanoparticles of a wide variety of metals including Pt, Pd, Ru and Rh supported on
various types of carbon substrates as well as other substrates[1].
In this work the scCO2 deposition method is used for the preparation of solid supported
heterogeneous catalysts using by vic-dioxime derivative new precursors bis(3-
perfluorophenylglyoximato)Cu(II) and Pd(II). The complexes were prepared with
perfluorodiphenylglyoxime and copper(II) acetate mono hydrate and palladium (II) chloride.
The ligands and their complexes were characterized by elemental analyses, FT-IR, 1H, and
elemental analysis The prepared catalysts were characterized using Xray diffraction (XRD)
and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Cu particles were found to be homogeneously
distributed with small particle sizes between 7 and 22 nm on MWCNT.
Key Words: Catalyst, Deposition, scCO2
Reference
[1] S. Eriksson, Applied Catalysis A: General 265 (2004) 207-219.
You might also like
- Deniz Taşımacılığında Yakıt Tüketimi ve Graf Teorisi UygulamalarıFrom EverandDeniz Taşımacılığında Yakıt Tüketimi ve Graf Teorisi UygulamalarıNo ratings yet
- 9.ukmk 3-176Document25 pages9.ukmk 3-176Özge Kerkez KuyumcuNo ratings yet
- Doğal Kaynaktan Gelen Karbon Kuantum NoktalarıDocument16 pagesDoğal Kaynaktan Gelen Karbon Kuantum NoktalarıAyşe KuplayNo ratings yet
- Demir2 TRDocument18 pagesDemir2 TRmertNo ratings yet
- Merve Makale 26.08.2021 Son Revi̇zyonDocument22 pagesMerve Makale 26.08.2021 Son Revi̇zyonH Merve Çetin AnnagürNo ratings yet
- 2b Sozlu Sunum1Document9 pages2b Sozlu Sunum1sonficyusNo ratings yet
- Yeralti Jeolojik Rezervuarlarinda Karbondioksitin DepolanmasiDocument10 pagesYeralti Jeolojik Rezervuarlarinda Karbondioksitin DepolanmasiMaria De La HozNo ratings yet
- 3Document138 pages3Ahmet KarakışNo ratings yet
- Çevre Nanoteknolojisi PDFDocument21 pagesÇevre Nanoteknolojisi PDFhardemNo ratings yet
- 9 Bolum 6A Grubu ElementleriDocument37 pages9 Bolum 6A Grubu ElementleriDilek AdakNo ratings yet
- Elektroliz KapalamcılıkDocument23 pagesElektroliz Kapalamcılıkma8119459No ratings yet
- Örnek Proje DefteriDocument22 pagesÖrnek Proje DefteriMuhittinNo ratings yet
- Elementer Bor ÜretimiDocument7 pagesElementer Bor ÜretimiMesut ArıkoğluNo ratings yet
- D9e5a1f1b4da308 EkDocument6 pagesD9e5a1f1b4da308 EkHalil Burak KaybalNo ratings yet
- Atik Pi̇llerden Metal Üreti̇mi̇Document32 pagesAtik Pi̇llerden Metal Üreti̇mi̇Yalçın DorukNo ratings yet
- NanogönderilenDocument31 pagesNanogönderilenBatuhan KöseNo ratings yet
- Nanoenerji SunumDocument45 pagesNanoenerji SunumOnur Ardalı67% (3)
- KarbürlemeDocument7 pagesKarbürlemeOzan Pekel100% (1)
- KYM 446 Enerji Teknolojisi Ders Notları (Kömür) - ÖğrenciDocument50 pagesKYM 446 Enerji Teknolojisi Ders Notları (Kömür) - Öğrencittugce29No ratings yet
- Biyosensorler Icin ElektrotDocument8 pagesBiyosensorler Icin ElektrotmiaryoonNo ratings yet
- Altının HidrometalurjisiDocument56 pagesAltının HidrometalurjisiaasdcdcNo ratings yet
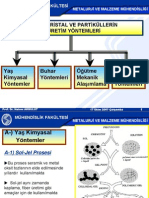
- Nano Kristal Ve Partikullerin Uretim YontDocument23 pagesNano Kristal Ve Partikullerin Uretim YontBerkan AkınNo ratings yet
- TiO2 Tez 4Document116 pagesTiO2 Tez 4scorpion seasonsNo ratings yet
- Sementasyon DeneyiDocument10 pagesSementasyon Deneyidelgado6044No ratings yet
- Damla SahinDocument98 pagesDamla SahinRıdvan SürmeliNo ratings yet
- Refrakter MalzemelerDocument33 pagesRefrakter Malzemeleraslanalpi0% (1)
- Noranda ProsesiDocument35 pagesNoranda Prosesiferidun09No ratings yet
- Kireç Söndürme Şartlarının Söndürülmüş Kireç Kalitesine EtkisiDocument8 pagesKireç Söndürme Şartlarının Söndürülmüş Kireç Kalitesine EtkisimelikederNo ratings yet
- Yesil Hidrojen Ekonomisi Icin Yol Ayriminin Esiginde Turkiyenin Attigi Umut Verici AdimlarDocument13 pagesYesil Hidrojen Ekonomisi Icin Yol Ayriminin Esiginde Turkiyenin Attigi Umut Verici Adimlarfhasanzade1995No ratings yet
- Karbon Nanotüpler Araştırma RaporuDocument7 pagesKarbon Nanotüpler Araştırma Raporuselguc123No ratings yet
- Yeni̇lenebi̇li̇r Enerji̇ Kaynaklari Ve Teknoloji̇leri̇ 14Document57 pagesYeni̇lenebi̇li̇r Enerji̇ Kaynaklari Ve Teknoloji̇leri̇ 14AhmetNo ratings yet
- Doğalgaz Ve Petrol Boru Hatlarinda Hi̇drojeni̇n Neden Olduğu ÇatlamalarDocument10 pagesDoğalgaz Ve Petrol Boru Hatlarinda Hi̇drojeni̇n Neden Olduğu ÇatlamalarozcanNo ratings yet
- 3-Çam Kozalakları KarbonizasyonuDocument8 pages3-Çam Kozalakları KarbonizasyonuBayram BostancıNo ratings yet
- Sonuç Raporu FYL-2013-4498Document69 pagesSonuç Raporu FYL-2013-4498Onur KopanNo ratings yet
- A3 Grubu-PVD TeknolijisiDocument26 pagesA3 Grubu-PVD TeknolijisiDeniz KarakayaNo ratings yet
- PEM1Document20 pagesPEM1tuwien08No ratings yet
- Elementler Ki̇myasiDocument163 pagesElementler Ki̇myasielif eda bulutNo ratings yet
- Temi̇z Kömür Yakma Teknoloji̇leri̇ Ve Süperkri̇ti̇k Buhar SantrallariDocument7 pagesTemi̇z Kömür Yakma Teknoloji̇leri̇ Ve Süperkri̇ti̇k Buhar SantrallaricanakkaleicindeNo ratings yet
- Kömür Kökenli Doğal GazDocument5 pagesKömür Kökenli Doğal GazÖzkan KocaoğluNo ratings yet
- Bi̇lal Can Tek-820220801-Alternati̇f YakitlarDocument24 pagesBi̇lal Can Tek-820220801-Alternati̇f YakitlarBilal Can TekNo ratings yet
- Metaller Kimyası 1Document28 pagesMetaller Kimyası 1Faruk ÇAKIRNo ratings yet
- T.C. Tokat Gazġosmanpaġa Ünġversġtesġ Lġsansüstü Eğġtġm Enstġtüsü Kġmya Anabġlġm DaliDocument151 pagesT.C. Tokat Gazġosmanpaġa Ünġversġtesġ Lġsansüstü Eğġtġm Enstġtüsü Kġmya Anabġlġm Daliömer faruk nasipNo ratings yet
- Mekanik Alaşimlama Yöntemi İle Demir Bor Alaşimlarinin Üretimi Ve KarakterizasyonuDocument74 pagesMekanik Alaşimlama Yöntemi İle Demir Bor Alaşimlarinin Üretimi Ve KarakterizasyonuHalil KocNo ratings yet
- 9 HaftaDocument9 pages9 Haftaeda.cagla12344No ratings yet
- Altn2 TRDocument11 pagesAltn2 TRmertNo ratings yet
- Kimtek 7Document56 pagesKimtek 7abdiqani egeNo ratings yet
- 2013erdogan NRecyclingofWasteMagnesitePowdersEkolojiDocument10 pages2013erdogan NRecyclingofWasteMagnesitePowdersEkolojiwb9269xkzkNo ratings yet
- Pota MetalurjisiDocument16 pagesPota MetalurjisicuneytcNo ratings yet
- C - Ruf - e - Tler - Ve Kullanim Alanlari (#398010) - 501675Document16 pagesC - Ruf - e - Tler - Ve Kullanim Alanlari (#398010) - 501675wefewfwefNo ratings yet
- Çinko ProsesiDocument17 pagesÇinko Prosesi418475No ratings yet
- 2 Uretim MetalurjisiDocument76 pages2 Uretim MetalurjisiElif ArancıNo ratings yet
- Neval Bozer Tez PDFDocument65 pagesNeval Bozer Tez PDFMurat AslanNo ratings yet
- Application of Diagnostic Leaching Technique For Refractory Gold OresDocument11 pagesApplication of Diagnostic Leaching Technique For Refractory Gold OrespilanichisekoNo ratings yet
- KÜTLE TRANSFERİ PROJE ÖDEVİiiiDocument31 pagesKÜTLE TRANSFERİ PROJE ÖDEVİiiiilknurdurmus09No ratings yet
- Clean Energy Sources and Maritime Applications Temiz Enerji Kaynaklari Ve Denizcilik UygulamalariDocument20 pagesClean Energy Sources and Maritime Applications Temiz Enerji Kaynaklari Ve Denizcilik UygulamalariFırat AydınNo ratings yet
- Endustriyel Kimya Ders NotlariDocument38 pagesEndustriyel Kimya Ders NotlariEsra ÖztürkNo ratings yet