0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views9 pagesThevenin's Theorem Lab Report
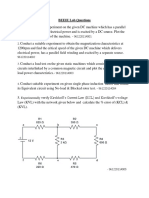
The document describes an electrical engineering lab experiment to verify Thevenin's Theorem. The experiment involved building a circuit with resistors and a power supply, calculating the theoretical Thevenin voltage and resistance, and measuring the actual voltage across a load resistor. The experimental results matched closely with theoretical calculations and circuit simulations, verifying Thevenin's Theorem. Students concluded that Thevenin's Theorem is a useful tool for simplifying complex circuits into an equivalent circuit of a single voltage source in series with a resistor.
Uploaded by
Zeeshan AmjadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views9 pagesThevenin's Theorem Lab Report
The document describes an electrical engineering lab experiment to verify Thevenin's Theorem. The experiment involved building a circuit with resistors and a power supply, calculating the theoretical Thevenin voltage and resistance, and measuring the actual voltage across a load resistor. The experimental results matched closely with theoretical calculations and circuit simulations, verifying Thevenin's Theorem. Students concluded that Thevenin's Theorem is a useful tool for simplifying complex circuits into an equivalent circuit of a single voltage source in series with a resistor.
Uploaded by
Zeeshan AmjadCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd