Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formulas 2
Uploaded by
udumariomCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas 2
Uploaded by
udumariomCopyright:
Available Formats
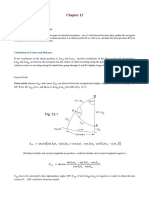
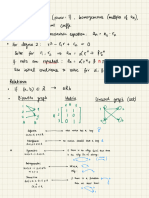
14.
Computed Altitude (He)
• Sin He = [(sin L x sin d) + (cos L x cos d x cos LHA)]
Note. Affix name of the direction Note. Affix name of direction Sin A SmB Sin C
: i f > 180 (-) it to 360 B 15. Intercept Method
then affix name of Long 1 c=hyp jS
Ho or T / A l t
2. Plane Sailing s^ a=opp
- lie
a. Sin Co = Dep /Dist
Intercept
• b. Cos Co = Dlat /Dist A^g_ C
GOAT (Greater Observe Altitude Towards)
• c. Tan co = Dep/ Dlat b=adj
d Polar to Rect ( P -» R) C. Natural Functions 16. Azimuth Angle
Sin 0 - -r Cos Z =
(Altitude Known) (cos L x cos He)
adj Relationship of 30" and 45 1 triangle
e Rectangular to Polar (R -» P) Cos 0 = . (Sin LHA)
hyp ^ Tan Z =
ID Lat |1NV| R - » P |DEP| = i Dist I * /&'< (cos L x tan d) - (sin L x cos LHA)
HNV||X~Y||Co| Tan9 = -SEE. S 1 (Altitude Unknown)
adj ^r
•3. Parallel Sailing STVt' 901
17. Hull Speed In knots
CscO = J*L /y
opp • S = 1 34 /waterlme length (in feet)
• a Dist = Dlo x cos Lat
• b. Dep = Dlo x cos Lat
c. Dist = D l a t ( i f c o N o r S )
sece '* *A 18. Distance to the visible horizon
C
d Spd = 900 kts x cos lat D = 1.144 /tLE'infeet
Note : Dlo in mins. Co,0 = ^L Z^J
OPP 1
D = 2.07 /H E in meter
<
4. Mercator Sailing
'<•
c2= a2 + b2 19. Dip of the visible horizon
• a. Finding Meridional Parts (MP)
Lat/ 2 + 45 = Tan Log x 791 5. 7 -Lat Sin c=/a 2 + b2
Dip = 0 97 /H E in feet
X23.2 = MP
Dip = 1 76 /H.E in meter
' b T a n C °=DTvTp-
c Di-t - D'at
20. Distance of the Radar horizon
COS CO
Note Dlat and Dlo in mins S m O = 7—T Csce = TT-T D = l . 2 2 /H E. in feet
Csc9 Sm0
. D = 2.21 /H.E. in meter
5. Great Circle Sailing CosO= ^— Sece =-?-
SecO CosQ
21. ConvertingThermometer Scales
a. Cos GCD = (Cos Lat 1 x Cos Lat 2 x Cos Dlo) +/ - Tan9 = 7^ CotQ -=7-5
CotO Tan 9
(Sin Latl x Sin Lat 2) - °C = 5 ( F° - 32°)
Note: (+) When not crossing Equator • E Degree to Versine
( - ) when crossing Equator 1 - cos 0 °F = 9_C°__.±32
„- ,«• , Cosl,at2 x Sin Dlo • F. Deg to Haversme 5
Sin Dist (in deg) 1 - cos 9 °K = C + 273.15°
Note Make Lat2 Negative when crossing Equator 2
• G Arc to Time 22. Maximum length of sea waves
• InitialcourscangleislabeledsameasaLatl and same as Dlo 00° 00' 00" M 5
W = 1.5 -/ Fetch in nautical miles
• H Time to Arc
CjnFC An j
Cos Latl x Sin Dlo OOH OOM OOS x 1 5
Sin Dist (in deg) 23. Wave Height = 0.026 S1
Note. Make Latl Negative when crossing the equator 9 Course to Steer / Intercept a Vessel
24. Wave speed in knots
• Final course angle is labeled contrary name to Lat2 and • Z.A = Bearing of Own Ship from target - Target Course
same as Dlo c ._ ^ Target Speed x Sin .^.A = 1.34 i wavelength (infect)
• d. Cos Lat Vertex = Cos Latl x Sin I C Own Ship Speed = 3 03 x wave period (in sec)
Note: - Use Initial course angle not the course
• True course to Steer = Target BRG +/ --- C 25. Geographical Position (GP)
• Name the Latitude vertex according to the name of Latl • B = 180-( A + C)
• e. Sin Dlo Vertex = Cos 1 C Target Range x Sin Z.A Rules: If GHA < ISO , GHA = Long (W)
Sin Lat V Sui^-B x Own Ship Speed
Note. Dlov is the Dlo from Departure to vertex If GHA > 180° = 360 - GHA = Long(E)
10. Bow and Beam Bearing
6. Amplitude: • a. Bearing at Any Angle 26. Time Diagram
Sin Ampl = Sin Dec B C = A B S m Z.A/Sin(ZB - Z A )
GHA & GHA Y' GHA V' LHA Y'
Cos Lat CD = BCSin Z'B + +
+E +E
Note. Rismg(E) Setting (W) and Copy Dec. BD = BCcos /.B l.ong-W Long - W SHA * SHA *
To get true (+/- ) 270 or (+/-) 90 LHA © LHA Y" GHA * LHA *
• b. Doubling the Angle
7. Napier's Rule AB = BC (Gel + / Leg -)
Rule I = the sine of any middle part is equal to the CD = BC Sin __B
GHA * LHA * GHA * LHA *
product of the cosine of the opposite parts. BD = B C C o s Z B -SNA * -SHA * - LHAY"
-GHA V
Sine Middle part = cosine opposite x cosine opposite GHAY" LHAv" SHA * SHA *
• c. Special Case
Rule 2 = The sine of any middle part is equal to the AB = BD = CD \-»(2&.5°/45 0 ) Note If GHA * and LHA * are Less + 360
product of the tangent of the adjacent parts. BC=1.4AB J
Sin Middle Part - tan adjacent x tan adjacent CD = 2.33 AB -» (22.5° / 26.5°) • If LHA = 0 - 1 8 0 . ' . L H A = ( t ) W
BC = 2AB-*(635°/90°) L H A = 1 8 0 - 3 6 0 .'. 360 - LHA = (t) E
Cos Z = Sin Dec ./Cos Lat BC = 2 4AB-* (67.5/90)
26. Zone Time
Cos P = Tan Lat x Tan Dec BC = 3 AB-> (71 5°/90>
AB = CD i
n * B o = Cot
r , a - 1i .0r, J} Nat - Cot Rule LMT =
• b. Body at equinoctial Cot Long In Time = E -
Cos Z =• Tan Alt x Tan Lat
Cos P = Sin Alt / Cos Lat 1L Correcting / L'ncorrecting 12. Lat by Polaris GMT
C T Ho ZD E+
Sin Dec = cos Alt x Cos Z D E+ V E- Ao W-
Tan P = S m Z / T a n A l t M M W+ Al +
V W- D A2
• d. Body on the Prime Vertical T C -! Note: Applicable for sunrise /sunset; moon rise/set,
Sin Dec = Sin Lat x Sin Alt Obs Latitude twilight and meridian transit
CosAlt = S i n P x C o s D e c 13. Correction of Altitudes
Sextant Alt 9 N 0 S 27. Equation of Time
e Body on the PN - PS Line I.E. = on the arc (-) Off (+)
Cot Z - cos Lat x Tan Dec AppAlt - If mean sun is ahead of the apparent sun the equation of
Sin Alt = Sin Dec x Sin Lat Dip always (-) time is added to LAN 12-00
App Alt (+ lower transit)
8. Oblique Plane Tiangle M.C. (- upper transit)
• A Cosine Law TrueAltO N9 S
-90"
a — b + c - 2 b c x Cos A Zx OS ON (Lat/Decsame+)
b2 = a2 + c2 - 2ac x Cos B Dec O N 9N (Lat/Dec diff -) Arranged by.
c -a+b -2abxCosC Obs lat CAPT ANTOINE B. DELA TORRE
You might also like
- Other Navigational Formulas: Calculation of Course and DistanceDocument4 pagesOther Navigational Formulas: Calculation of Course and DistanceYasser Metawea100% (1)
- The Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64From EverandThe Equidistribution Theory of Holomorphic Curves. (AM-64), Volume 64No ratings yet
- Gear TopicDocument7 pagesGear Topicch0k3 iiiNo ratings yet
- Formula 2Document6 pagesFormula 2Juven LuzorataNo ratings yet
- Appendix C - Calculation of Face BoltDocument20 pagesAppendix C - Calculation of Face BoltDEBASIS BARMAN100% (1)
- Sight Distance For Horizontal CurvesDocument89 pagesSight Distance For Horizontal CurvesFirdaus MangawingNo ratings yet
- 14 Linear Combination of Atomic OrbitalsDocument8 pages14 Linear Combination of Atomic OrbitalsVandana AdiwasiNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 - MATH 222Document82 pagesMidterm 1 - MATH 222alexbstp10No ratings yet
- Unit 5 SDDocument64 pagesUnit 5 SDGanapati Girish KamatNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas PDFsakuNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas PDFTriyananda Diva100% (1)
- Geometry FormulasDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulaskau0017No ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas PDFJohn Carlo de Leon100% (1)
- Geometry Formulas PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas PDFCher Jay-ar Doronio100% (1)
- Geometry FormulasDocument2 pagesGeometry FormulasShaik AakheelNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas PDFSuleman Nagoor100% (4)
- Nda Math Mind MapDocument19 pagesNda Math Mind MapSAURAV MODINo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia and TorqueDocument12 pagesMoment of Inertia and TorqueMary Rhose VidalloNo ratings yet
- H & V Alignment ODocument11 pagesH & V Alignment Odisasa abebeNo ratings yet
- Week 9 - Planar KinematicsDocument10 pagesWeek 9 - Planar KinematicsTaoTao at NYCNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: - Complex Problems Trigonometry - Elevation and DepressionDocument1 pageTrigonometry: - Complex Problems Trigonometry - Elevation and DepressionTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- G (R) DK: RayleighDocument8 pagesG (R) DK: RayleighTitu RajputNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument12 pagesPhysics NotesMary Rhose VidalloNo ratings yet
- 09 VectorsDocument10 pages09 VectorsCrystal x365No ratings yet
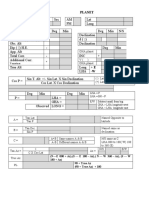
- Longitude by Chronometer PlanetDocument1 pageLongitude by Chronometer PlanetBandar AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet (Regular Font, No Margins)Document2 pagesCheat Sheet (Regular Font, No Margins)Arun ChandranNo ratings yet
- Final CheatsheetDocument4 pagesFinal CheatsheetmehulbasuNo ratings yet
- COLTRANE Heath Soprano SoloDocument4 pagesCOLTRANE Heath Soprano SoloDawid NowakNo ratings yet
- Rafaqat Ali NotesDocument2 pagesRafaqat Ali Noteskalpesh100% (1)
- Module3 Worksheet TrigDocument9 pagesModule3 Worksheet TrigjyotibabaniNo ratings yet
- CFA+2020+ +Level+1+Schweser's+QuicksheetDocument6 pagesCFA+2020+ +Level+1+Schweser's+Quicksheetvxm9pctmrrNo ratings yet
- SurveysDocument1 pageSurveysFrancis Jem ReyesNo ratings yet
- Rotation Equations Cheat SheetDocument1 pageRotation Equations Cheat SheetRoberto MartinezNo ratings yet
- 133 FormulasDocument1 page133 FormulasAubrey QuilanetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter11 The Navigational TriangleDocument4 pagesChapter11 The Navigational TriangleYasser MetaweaNo ratings yet
- Name of Figure Perimeter AreaDocument7 pagesName of Figure Perimeter AreaDarwin ManoNo ratings yet
- Problem 2.73: Given: Find: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 2.73: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoNo ratings yet
- Solutions JEEAdvanced2014 Paper2 Code-5Document35 pagesSolutions JEEAdvanced2014 Paper2 Code-5Vagarth AgrwalNo ratings yet
- Solutions & Colligative PropertiesDocument14 pagesSolutions & Colligative PropertiesPoonam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Flight Performance-Part 1 (Steady Level Flight) Min and Max SpeedDocument5 pagesFlight Performance-Part 1 (Steady Level Flight) Min and Max SpeedGCVishnuKumarNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis Cheat Sheet PDFDocument5 pagesStructural Analysis Cheat Sheet PDFCarl Justin AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Formulae: Laws of IndicesDocument2 pagesMathematics Formulae: Laws of IndicesyasirNo ratings yet
- Membranska Teorija Rotacionih Ljuski Pri Rotaciono Simetričnom OpterećenjeDocument5 pagesMembranska Teorija Rotacionih Ljuski Pri Rotaciono Simetričnom OpterećenjeLazić MilošNo ratings yet
- Physics 401 Assignment # Retarded Potentials Solutions:: Wed. 15 Mar. 2006 - Finish by Wed. 22 MarDocument3 pagesPhysics 401 Assignment # Retarded Potentials Solutions:: Wed. 15 Mar. 2006 - Finish by Wed. 22 MarSruti SatyasmitaNo ratings yet
- Are Structures Cheat Sheet 1Document5 pagesAre Structures Cheat Sheet 1priodeep chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 15.3: Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates: Learning ObjectivesDocument14 pages15.3: Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates: Learning Objectivesيا ابا صالح المهديNo ratings yet
- OMN 201612 110645 1 Course - Notes v1Document59 pagesOMN 201612 110645 1 Course - Notes v1cjmauraNo ratings yet
- 363-Formula SheetDocument2 pages363-Formula SheetOrhan KarakayaNo ratings yet
- "Just The Maths" Unit Number 11.3 Differentiation Applications 3 (Curvature) by A.J.HobsonDocument7 pages"Just The Maths" Unit Number 11.3 Differentiation Applications 3 (Curvature) by A.J.Hobsonelias pappasNo ratings yet
- 4160 Lecture 28Document7 pages4160 Lecture 28jjwfishNo ratings yet
- CE Module 20 - Relative Equilibrium (Principles)Document1 pageCE Module 20 - Relative Equilibrium (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- 3.1 2D TransformationsDocument6 pages3.1 2D TransformationsMuhammedNo ratings yet
- Mathematical ToolsDocument80 pagesMathematical ToolsVarshiniNo ratings yet
- Ifsvdociiy: Motion in 1-DDocument1 pageIfsvdociiy: Motion in 1-DHems MadaviNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion &projectileDocument5 pagesCircular Motion &projectileLazar BeamNo ratings yet
- שדות אלקטרומגנטיים - אופרטורים בקוארדינטות שונות - 356159Document2 pagesשדות אלקטרומגנטיים - אופרטורים בקוארדינטות שונות - 356159Faruz DanielNo ratings yet
- Spark GravitationDocument29 pagesSpark GravitationShrihari MancharkarNo ratings yet
- Intercept PlanetDocument6 pagesIntercept Planetbandar almalkiNo ratings yet
- QR Decomposition ExampleDocument4 pagesQR Decomposition ExamplejhonnyNo ratings yet
- Met 1Document6 pagesMet 1udumariomNo ratings yet
- Ugly or Not You Still Have The Power To LiveDocument1 pageUgly or Not You Still Have The Power To LiveudumariomNo ratings yet
- Met 2Document8 pagesMet 2udumariomNo ratings yet
- Canteen Policy PDFDocument4 pagesCanteen Policy PDFudumariom0% (1)
- Resume FranciscoDocument2 pagesResume FranciscoudumariomNo ratings yet
- Buys Ballot NoteDocument3 pagesBuys Ballot NoteudumariomNo ratings yet
- Deck Cadet Manager Interview Questions FDocument1 pageDeck Cadet Manager Interview Questions FFatin Raniahthifal AdiwijayaNo ratings yet
- Rao (2022) - A Course in Time Series AnalysisDocument527 pagesRao (2022) - A Course in Time Series AnalysisEduardo Schirmer FinnNo ratings yet
- OTIS ExcerptsDocument257 pagesOTIS ExcerptsTanmayNo ratings yet
- Fourth PERIODIC TEST Math 9 - 2022 2023Document5 pagesFourth PERIODIC TEST Math 9 - 2022 2023Jonathan OlegarioNo ratings yet
- First Push Grade 12 March 2024Document10 pagesFirst Push Grade 12 March 2024monkbons15No ratings yet
- (Template) 9702 Student Learner Guide (Paper Specific Checklist)Document9 pages(Template) 9702 Student Learner Guide (Paper Specific Checklist)shahzodbekaliyev07No ratings yet
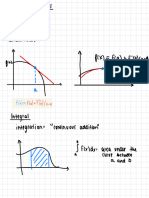
- Basic Cal Quarter 4 Week 1 2 Antiderivative of FunctionsDocument8 pagesBasic Cal Quarter 4 Week 1 2 Antiderivative of FunctionsVega, Charles Gabriel G.No ratings yet
- 2850-361 Sample Formulae Sheet v1-0 PDFDocument3 pages2850-361 Sample Formulae Sheet v1-0 PDFMatthew SimeonNo ratings yet
- Yts 08 Xi Maths Sample Papers O.P. GuptaDocument5 pagesYts 08 Xi Maths Sample Papers O.P. GuptashrutiNo ratings yet
- Important Question MacDocument3 pagesImportant Question Macashwithkumar2779No ratings yet
- 3.5 The Hyperbolic Functions: C Pearson Education LTD 2000Document2 pages3.5 The Hyperbolic Functions: C Pearson Education LTD 2000Lance ShahNo ratings yet
- 7 4C in Class Practice ExamDocument4 pages7 4C in Class Practice ExamkchhangNo ratings yet
- 2021 Sec 4 A Math Prelim P1 AnsDocument20 pages2021 Sec 4 A Math Prelim P1 AnsAdwin JY LowNo ratings yet
- Smackslidecom Powerpoint Pres 5f99a5107c4a1Document61 pagesSmackslidecom Powerpoint Pres 5f99a5107c4a1Mamo JimmaNo ratings yet
- Maths XII OIG SolutionDocument182 pagesMaths XII OIG SolutionArun BaralNo ratings yet
- Physics IA 3Document10 pagesPhysics IA 3rayirthr2010No ratings yet
- Q1 W7 Sine Law and Cosine LawDocument4 pagesQ1 W7 Sine Law and Cosine LawAvriane Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Super Grads QT Trigonometry Formulas Copy 0262d8ea8417fDocument2 pagesSuper Grads QT Trigonometry Formulas Copy 0262d8ea8417fLIFE QUOTESNo ratings yet
- Ps Tricks PPTDocument28 pagesPs Tricks PPTMihir MehraNo ratings yet
- 1617 Maths Paper2 (E)Document15 pages1617 Maths Paper2 (E)Kai Cheong CHIUNo ratings yet
- EST2 Rules..Document17 pagesEST2 Rules..khadijakarimestNo ratings yet
- Q4 - WEEK1 - WW For G9Document3 pagesQ4 - WEEK1 - WW For G9RC FerrerNo ratings yet
- Module 3A (Missing Data,)Document5 pagesModule 3A (Missing Data,)molina.markelord123No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 POWER FLOW THROUGHT INTERCONNECTORSDocument19 pagesChapter 8 POWER FLOW THROUGHT INTERCONNECTORSSampi LuminaNo ratings yet
- QB BMS-311302 - Sem-I Ut-2 111223Document3 pagesQB BMS-311302 - Sem-I Ut-2 111223pagareaaryan.2007No ratings yet
- Myp Curriculum OverviewDocument15 pagesMyp Curriculum OverviewYusifbay PadarovNo ratings yet
- 정역학 13판 11장Document63 pages정역학 13판 11장leejingpNo ratings yet
- P2 Chp9 DifferentiationDocument52 pagesP2 Chp9 DifferentiationmudabaraffanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Additional Mathematics 4037/11Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: Additional Mathematics 4037/11Alameen JamanNo ratings yet
- Basic Trig Skills PDFDocument3 pagesBasic Trig Skills PDFndjwndnnd sjwjhsbdbdbdNo ratings yet
- SkillsTest1 SAMPLEDocument1 pageSkillsTest1 SAMPLEkatethekat2.0No ratings yet