Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kiểm tra que thử và phân tích)
Uploaded by
Hà ChâuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kiểm tra que thử và phân tích)
Uploaded by
Hà ChâuCopyright:
Available Formats
SL31: PHYSIOLOGICAL TERMINOLOGY
SL32
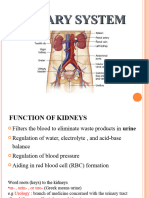
. Filter (lọc) /fil-ter/
The kidneys help filter the blood, removing some wastes from the blood.
.Filtrate (dịch lọc) /fil-treyt/
Product of body fluids after passing through the glomerular filtration membrane.
.Glomerular filtration rate (mức lọc tiểu cầu thận) : glomerular filtration rate.
The amount of glomerular filtrate per minute in both kidneys. This term is abbreviated as GFR .
.Reabsorption (tái hấp thu)
Tubular reabsorption , also known as tubular reabsorption , is the process by which nephrons
take up water and electrolytes from the renal tubular fluid and return them to the circulatory
system.
SL33
.secretion /si-kree-shuhn/ bài tiết
Is the process of taking substances from the capillaries around the kidney into the lumen of the
kidney tubule. This process is the opposite of reabsorption.
.Excretion /ik-shree-shuhn/ The process of eliminating or removing a substance from the body. This
process is the opposite of reabsorption.
Excretion = Filtration - Reabsorption - Secretion.
. homeostasis /hoh-mee-uh-stey-sis/ Cân bằng nội môi
Is a state of balance in physiological and chemical factors in the body.
- Kidneys help maintain homeostasis by maintaining body fluid and salt levels and thus blood
pressure.
SL42: LABORATORY TESTS
SL43: Includes 6 ways:
SL44:
Dipstick tesitng and Urinalysis (Kiểm tra que thử và phân tích)
Assess kidney function through urinalysis
-Color, sensory, odor, pH, Protein, specific gravity, glucose, hemoglobin, nitrite, leukocyte
esterase,...
Renal Angiography (Chụp động mạch thận)
After a physical examination, if the doctor suspects that the patient has a problem in the
blood vessels of the kidney, the doctor will prescribe the patient to perform a renal
angiogram.
SL45: Ultrasonography (siêu âm): Kidney ultrasound is one of the imaging diagnostic
methods.
This ultrasound method helps determine whether the kidney position is normal or not,
evaluate the size and structure of the kidney, and the relationship of the kidney to
surrounding organs.
Cystoscopy (Nội soi bàng quang) :Cystoscopy is a technique to examine the inside of the
bladder and urinary system by guiding a hollow tube with a camera at the end (endoscope)
through the urethra.
Operating principle: All image data from the tip of the endoscope will be magnified many
times and then transmitted to an external TV screen, helping doctors observe the inside of
the bladder lining and the human urinary system. disease in the most obvious way.
SL46: Pyelogram (đồ thị)
The patient is injected intravenously with a radioactive isotope, dynamic images and
graphs of radioactivity over time of each kidney are recorded, graphs and images are
analyzed, thereby assessing the function of each individual kidney. kidney.
SL47: Urographie intra veineuse (Chụp tĩnh mạch tiết niệu)
This means that after injecting contrast dye intravenously, the drug will reach the
kidneys, ureters, bladder... helping to evaluate diseases of the kidney and urinary system.
-Nowadays, the technique of intravenous urography is gradually being replaced by CT
scanning (CT Urography)of the urinary system with contrast injection.
CT Urography (CT tiết niệu)
imaging tests. Used to evaluate the urinary tract including the kidneys, bladder, and the
tubes (ureters) that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- A CT scanner of the urinary system will use X-rays to create multiple images (of one slice).
SL48: END
SL49:( VIDEO) We have a song of urinary system. Let’s watch and listen <3.
You might also like
- Glomerular Disease: Nephrotic vs. NephriticDocument26 pagesGlomerular Disease: Nephrotic vs. NephriticMarcel DocNo ratings yet
- Medical Pathology Ii. Pathology of Urinary System Lectuer NotesDocument26 pagesMedical Pathology Ii. Pathology of Urinary System Lectuer Noteseric epahNo ratings yet
- Urinary System PDFDocument27 pagesUrinary System PDFfiona100% (3)
- Lecture Notes On Renal Physiology For MBBSDocument129 pagesLecture Notes On Renal Physiology For MBBSNayyer Khan83% (6)
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument111 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisRico Ian Matondo Mercado100% (2)
- Aubf Review UermDocument18 pagesAubf Review UermZhiddah Japzon0% (1)
- Vijendra Kumar: Compiled byDocument15 pagesVijendra Kumar: Compiled byvijendrakumarsahuNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Genito-Urinary SystemDocument61 pagesCare of Clients With Genito-Urinary SystemAngelica Kaye BuanNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Wilms TumorDocument25 pagesCase Presentation On Wilms TumorDeepika100% (1)
- Case StudyDocument37 pagesCase StudyAnonymous t78m8ku100% (1)
- All Quiz QuestionsDocument60 pagesAll Quiz QuestionsMorgan ChristNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary SystemDocument23 pagesGenitourinary SystemRisma ZulfianiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management A. Nursing Care PlanDocument12 pagesNursing Management A. Nursing Care Planmabzbutterfly69% (13)
- Case Study Nephrotic SyndromeDocument26 pagesCase Study Nephrotic SyndromeDimpal Choudhary0% (2)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis Case StudyDocument12 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis Case Study19lyon92100% (6)
- Excretion: Excretion. Elimination of Drugs and Its Metabolites FromDocument18 pagesExcretion: Excretion. Elimination of Drugs and Its Metabolites FromAlphahin 17100% (1)
- Urinary SystemDocument25 pagesUrinary Systembessan alfqeatNo ratings yet
- Renal System AssessmentDocument124 pagesRenal System AssessmentAyman MohamedNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument1 pageUrinary SystemChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Investigation JF The Urinary TractDocument139 pagesInvestigation JF The Urinary TractВладимир КурпаянидиNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 PCDocument29 pagesChapter 7 PCJasminM.JimenezNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument27 pagesUrinary Systemtareqhaddad123No ratings yet
- Kidney UltrasoundDocument3 pagesKidney UltrasoundAfina Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemghghDocument23 pagesThe Urinary SystemghghJennibeb AmilNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument5 pagesUrinalysisKreshnik HAJDARINo ratings yet
- Diagnostic TestsDocument5 pagesDiagnostic TestsDUEÑAS, MARIELNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Urinary System: Chelsye Marviyouna Dearianto 1814201018Document19 pagesAssessment of The Urinary System: Chelsye Marviyouna Dearianto 1814201018Sinta WuLandariNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Kidney As A Filtration SystemDocument7 pages3.2 Kidney As A Filtration SystemSantosh hiremathNo ratings yet
- Radiological Investigations of Urinary TractDocument78 pagesRadiological Investigations of Urinary Tractzoher al naeemeNo ratings yet
- Urology Notes 1Document43 pagesUrology Notes 1Shazaan NadeemNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Renal or Urinary Tract DisorderDocument2 pagesNursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Renal or Urinary Tract DisorderJhasseryne Orias SanchezNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Urinary TractDocument34 pagesImaging of Urinary TractLiliaNo ratings yet
- Investigations of The Urinary System: Group 4Document53 pagesInvestigations of The Urinary System: Group 4YvonneNo ratings yet
- Special Investigation in RadiographyDocument4 pagesSpecial Investigation in RadiographyYamah PrincewillNo ratings yet
- X-Ray Neck Carotids Heart Aorta Chest Pulmonary Kidneys Gastrointestinal LimbsDocument8 pagesX-Ray Neck Carotids Heart Aorta Chest Pulmonary Kidneys Gastrointestinal Limbsfanofchips_noodles1No ratings yet
- Urinary System TerminologyDocument15 pagesUrinary System TerminologyRhahima SyafrilNo ratings yet
- Study of Human Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesStudy of Human Urinary SystemKʀɩsʜʌŋ ĸʀ ƦoƴNo ratings yet
- Scans: Dr. Padmesh. VDocument40 pagesScans: Dr. Padmesh. Vakheel ahammedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: The Urinary SystemSheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 57 Introduction To The Urinary SystemDocument24 pagesChapter 57 Introduction To The Urinary SystemtikkimarshallNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: TH RDDocument13 pagesUrinary System: TH RDdlneisha61No ratings yet
- Two Kidneys: Extract Waste From The Blood and Balance Body FluidDocument5 pagesTwo Kidneys: Extract Waste From The Blood and Balance Body FluidDani PhilipNo ratings yet
- Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek Faculty of Medicine Osijek Undergraduate Study of Medical Laboratory DiagnosticsDocument4 pagesJosip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek Faculty of Medicine Osijek Undergraduate Study of Medical Laboratory DiagnosticsKarla BorovečkiNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesUrinary SystemCurex QANo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology 1 170407164141Document76 pagesRenal Physiology 1 170407164141Vhutshilo MasithembiNo ratings yet
- 3 Obat Sedasi Dan Analgesia-Prof Munar - LubisDocument93 pages3 Obat Sedasi Dan Analgesia-Prof Munar - LubisFahmi NurNo ratings yet
- PyelonephrolithotomyDocument2 pagesPyelonephrolithotomyJohn Bryan TuganoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Radiographic Procedures of The Urinary SystemDocument32 pagesReviewer Radiographic Procedures of The Urinary SystemLyht TVNo ratings yet
- Uroradiology For Medical Students: Lesson 5 Nuclear Renography - 1 American Urological AssociationDocument49 pagesUroradiology For Medical Students: Lesson 5 Nuclear Renography - 1 American Urological AssociationlisarahmaasrilNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic ProceduresDocument3 pagesDiagnostic ProceduresMa Cheryll DueñasNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument21 pagesRenal Anatomy and PhysiologyAbisegan ZeuSNo ratings yet
- Imaging of The Genitourinary Tract: Mashuri, DR.,SP - Rad.,M.KesDocument90 pagesImaging of The Genitourinary Tract: Mashuri, DR.,SP - Rad.,M.KesmirzasullivanNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions: Chapter 45: Nursing Assessment: Urinary SystemDocument18 pagesStructures and Functions: Chapter 45: Nursing Assessment: Urinary SystemKennette LimNo ratings yet
- Radiology of Urinary System I-II - III 2024Document61 pagesRadiology of Urinary System I-II - III 2024mhmtrgnn67No ratings yet
- Aubf Prelim 1Document59 pagesAubf Prelim 1Kat JornadalNo ratings yet
- VET343 Urinary Lecture Notes 2014Document35 pagesVET343 Urinary Lecture Notes 2014walczakcNo ratings yet
- YR 4 Lecture Urogenital ImagingDocument59 pagesYR 4 Lecture Urogenital ImagingMUBIRU SAMUEL EDWARDNo ratings yet
- 17: Kidney and Nephronal Physiology: Key Terms Nephron Anatomy and FunctionDocument1 page17: Kidney and Nephronal Physiology: Key Terms Nephron Anatomy and FunctionElisa SalakayNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument53 pagesUrinary SystemKatherineVoNo ratings yet
- General Anatomu UrologyDocument60 pagesGeneral Anatomu UrologyAllan ManiNo ratings yet
- Prof Tirtayasa: Kuliah Fisiologi: Sistem PerkemihanDocument69 pagesProf Tirtayasa: Kuliah Fisiologi: Sistem Perkemihandidin FtNo ratings yet
- Imaging of The Genitourinary TractDocument86 pagesImaging of The Genitourinary TractNor AinaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of G I SystemDocument78 pagesDisorders of G I SystemAMAN KUMAR JHANo ratings yet
- Rayan Ali - Animal ScienceDocument19 pagesRayan Ali - Animal ScienceRayan AliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Urinary System (Renal System)Document27 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Urinary System (Renal System)dima_FlaviaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersDocument16 pagesAssessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersJhosita Flora LarocoNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Sistem Pernafasan, Ginjal & DarahDocument149 pagesFarmakoterapi Sistem Pernafasan, Ginjal & DarahVhandy GultomNo ratings yet
- Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewDocument5 pagesAnatomic and Physiologic OverviewShannen Alija M. LaoNo ratings yet
- Renal Reflections: Exploring the Marvels of Nephrology: The Intricate Ballet of Kidney Functions UnveiledFrom EverandRenal Reflections: Exploring the Marvels of Nephrology: The Intricate Ballet of Kidney Functions UnveiledNo ratings yet
- Trư NGDocument2 pagesTrư NGHà ChâuNo ratings yet
- MINHDocument1 pageMINHHà ChâuNo ratings yet
- Picschoup 2Document10 pagesPicschoup 2Hà ChâuNo ratings yet
- Q&ADocument3 pagesQ&AHà ChâuNo ratings yet
- Urinary System LecDocument7 pagesUrinary System LecMax DelvalleNo ratings yet
- Drosophila Tools and Assays For The Study of Human Diseases: at A GlanceDocument10 pagesDrosophila Tools and Assays For The Study of Human Diseases: at A Glancejonatas Cassiano da silvaNo ratings yet
- ACOG Practice Bulletin No 202 Gestational.49Document25 pagesACOG Practice Bulletin No 202 Gestational.49Diana Enco MurillosNo ratings yet
- 'Block E With Keys and Hints ' With YouDocument36 pages'Block E With Keys and Hints ' With YouAbdullah TanoliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 The Urinary SystemDocument18 pagesChapter 15 The Urinary SystemYeshia InocencioNo ratings yet
- Renal Anatomy EmbryologyDocument31 pagesRenal Anatomy EmbryologySnehal JayaramNo ratings yet
- RENAL WORKSHEET Anatomy AnswerDocument10 pagesRENAL WORKSHEET Anatomy AnswerJohnny eawNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System The HeartDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System The Heartmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury: Mark BevanDocument42 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: Mark BevannasimhsNo ratings yet
- Module 7 ProjectDocument30 pagesModule 7 ProjectLeena KamranNo ratings yet
- AKI (Pre Renal - Intra Renal - Post Renal)Document14 pagesAKI (Pre Renal - Intra Renal - Post Renal)Ashraf QotmoshNo ratings yet
- Ultrafiltration and Selective ReabsorptionDocument22 pagesUltrafiltration and Selective ReabsorptionKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- BCC, Laboratory Specimens and Microscopy, MLT 1040, Combo QuestionsDocument26 pagesBCC, Laboratory Specimens and Microscopy, MLT 1040, Combo QuestionsalphacetaNo ratings yet
- Bke1 - ch01 - Sug Ans - eDocument4 pagesBke1 - ch01 - Sug Ans - e蔡子100% (1)
- Acute Post Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument14 pagesAcute Post Streptococcal GlomerulonephritisDanica Alyssa CruzNo ratings yet
- 6 Acute Kidney InjuryDocument36 pages6 Acute Kidney InjuryyaminmuhNo ratings yet
- Urinary System and AdaptationDocument5 pagesUrinary System and AdaptationRashri SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pathological Changes of DM - 2023Document53 pagesPathological Changes of DM - 2023Visura PrabodNo ratings yet
- 2 UrinarySystemDocument83 pages2 UrinarySystemLemuel Lagasca Razalan IVNo ratings yet
- List of AnticoagulantsDocument9 pagesList of Anticoagulantschristianz39100% (1)